I have knocked up some code on my Linux Mint machine to communicate with the my WICE interface. So far all look good.
But sorry folks, I did not use C code not even Assembly.
I did it in factor, I have been using this language for 5 years now, I like its forthy-ness, interactive interface and the library of functions.
First I need open serial, this took some time work, how to do this on linux environment. I use library "io.serial" use "termios" and "streams" libraries. I had some issue on read operation, transmission was the easiest, only thing to remember is use the "flush" function to send the data out after "write" function.
: wice-start ( -- )
"/dev/ttyUSB0" 115200 <serial-port>
[
break
wice-ack drop
wice-status drop
wice-reset drop
wice-read-memory drop
wice-read-minc drop
wice-read-saddress drop
wice-close drop
0 wice-open drop
wice-reset drop
0 wice-write-memory drop
wice-reset drop
0x55 wice-write-minc drop
wice-read-u30 drop
wice-read-u4 drop
wice-read-u5 drop
wice-read-u6 drop
wice-reset drop
16 wice-dump drop
] with-serial-port-fix ;
wice-start basically sets up a serial port tuple. The with-serial-port-fix opens the serial port into a stream namespace and then executes all function in the quotation [ ] .
: with-serial-port-fix ( serial-port quot -- )
break
[ open-serial ] dip
[ [ serial-modify ] keep ] dip
[ [ stream>> 10 seconds over set-timeout drop ] keep ] dip
! [ [ stream>> dup in>> buffer>> 1 >>size drop drop ] keep ] dip
! [ [ dup serial-fd F_SETFL 0 fcntl drop drop ] keep ] dip
[ stream>> ] dip
with-stream ; inline
So in the quotation I run some function like wice-ack. Which sends out $00 on the serial port and read 1 byte back, does a test to see if it is zero.
! acknowlge the device : wice-ack ( -- ? ) 0 1byte-array write flush 1 read-partial ?first 0 = ;
I test each command and then I do a memory read function of 16 bytes x 16 lines.
! read memory addressed by address counter and increment
: wice-read-minc ( -- d )
4 1byte-array write flush
1 read-partial ;
! dump one inline
: wice-read-marray ( n -- array )
<byte-array>
[
drop
wice-read-minc first
] map ;
: wice-dump ( n -- array )
f <array>
[
drop
16 wice-read-marray
] map ;
The result in an array of 16 byte arrays read from the WICE all values are in decimal, next I will do print that out as hex dump. Then I will try to do write array to memory.
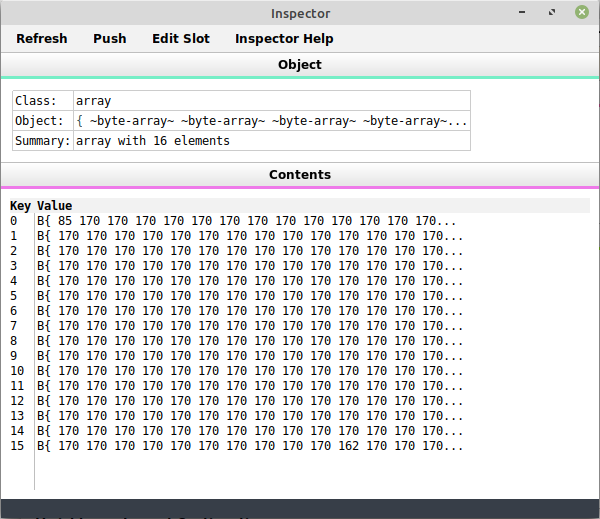
So far factor has made testing very easy.
 forthnutter
forthnutter
Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.