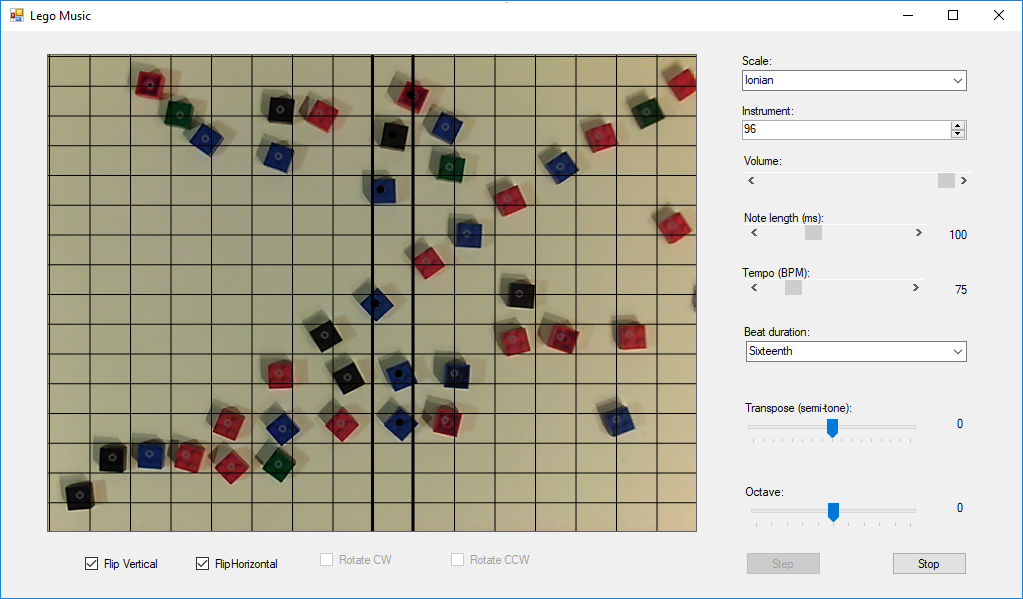
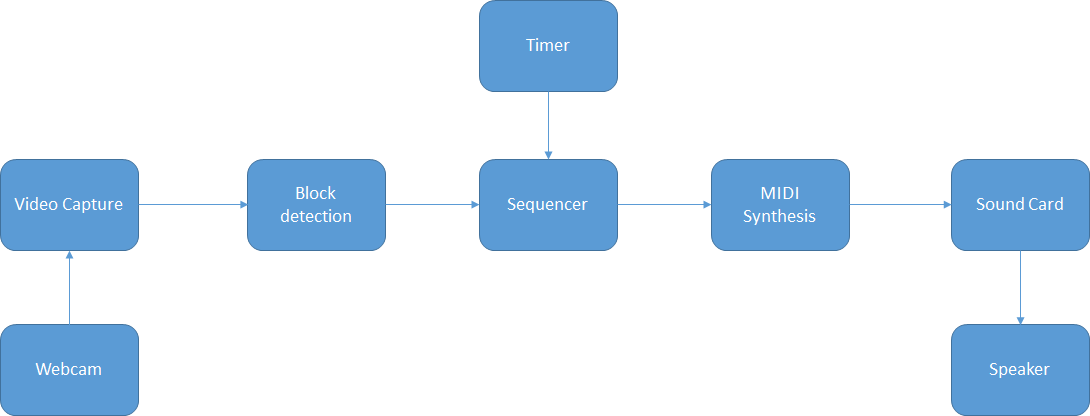
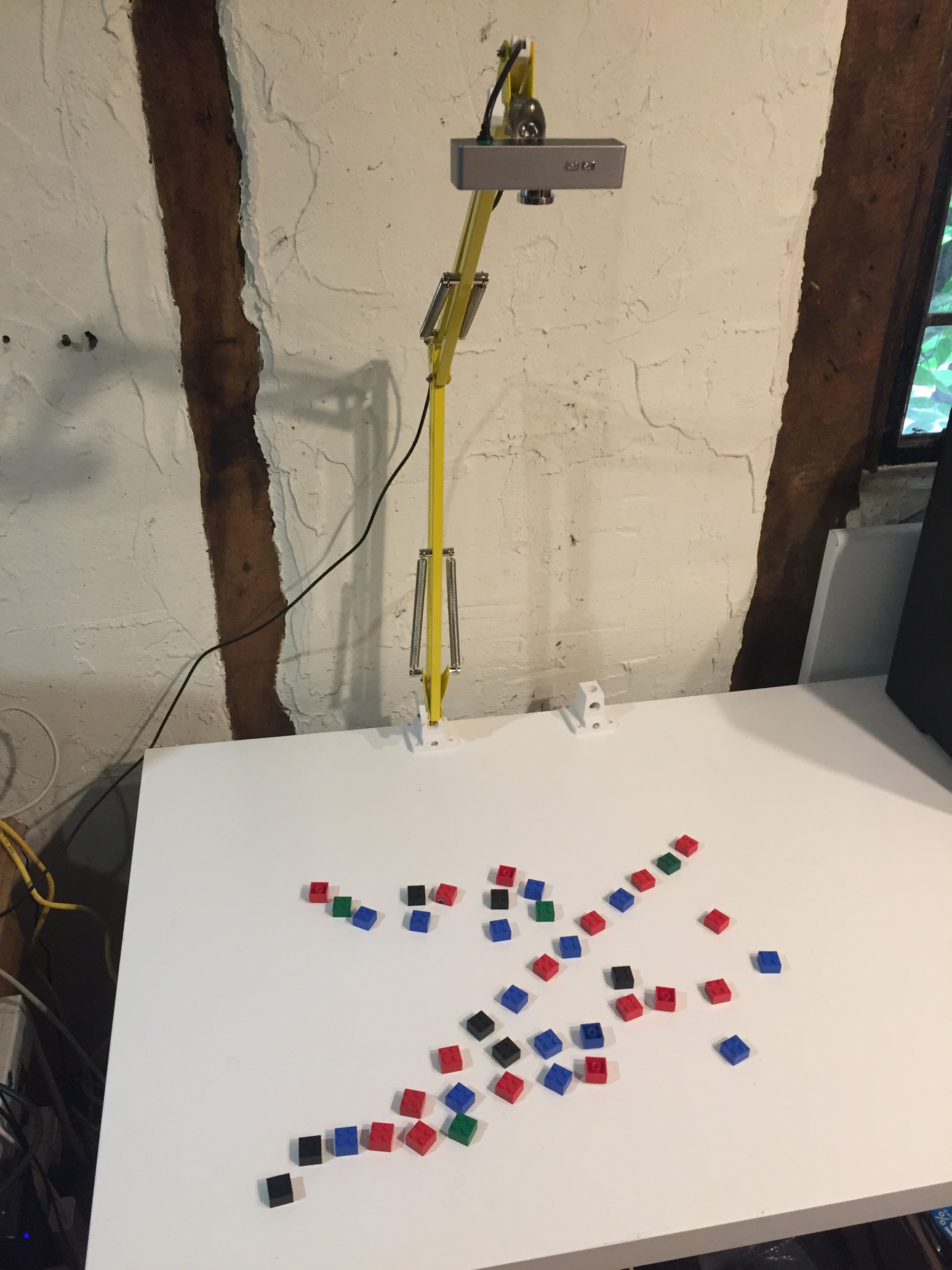
Lego blocks (other plastic blocks are available) are arranged on a virtual 16 by 16 grid layout and a virtual cursor repeatedly scans the grid from left to right. As the cursor reaches each grid column, the blocks in that column trigger a note to be played, the pitch of which is determined by the vertical position of the block. Multiple blocks in a column result in multiple notes being played simultaneously.
Here's a diagram to show the principle more clearly. Time is on the horizontal axis and pitch on the vertical axis. (For simplicity this shows an 8 by 8 grid)
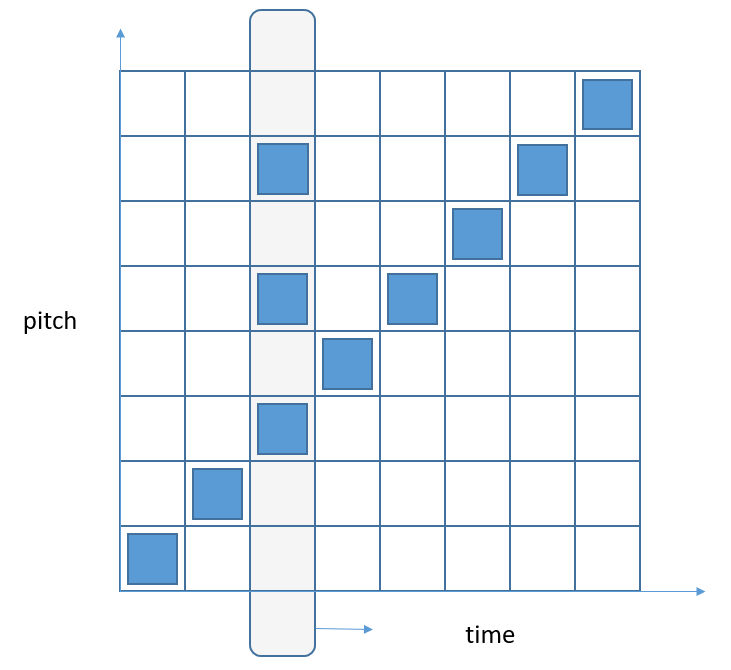
This arrangement of blocks would play an ascending scale. When the cursor is at the position shown a three note chord would be played.
The final pitch of a note is not only determined by the position on the grid, but also by the user-selectable scale. There are nine scales in the software which map position to pitch. The pitch can also be globally transposed in semitone or octave increments.