SPACE key on PS/2 keyboard return scancode of 0x29 (41 in decimal). In Zeddies the SPACE is at line 0 (KB0) of row 7 (A15)
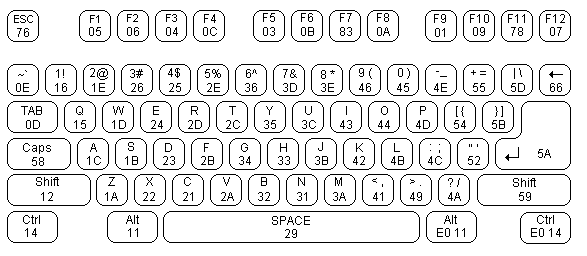
Then the 41th positon in vector PS2Keymap[ ] contains the value 0x07
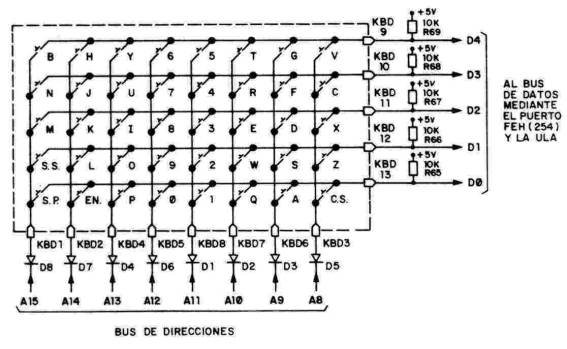
Backspace has a PS/2 scancode of 0x66 (102) and is a good example of the use of the modifier. On the Zeddies the corresponding key is SHIFT + '0' (ROBOUT). Key 0 itself is at line 0 of row 4. Then the 102th entry in vector PS2Keymap[ ] has the value of 04 for the '0' key plus 128 that is the 7th bit for the encoded value.
Arrow keys are extended PS/2 codes but are also mapped as SHIFT plus the values for keys 5 to 8.
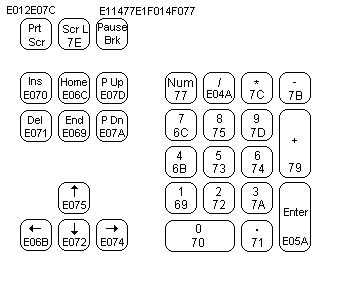
...
if (EXT==true) { // extended set
EXT=false;
switch (code) {
case _PS2_UP: m=0x80 | _7; break; // Caps Shift bit + map code for ZX key 7
case _PS2_DOWN: m=0x80 | _6; break;
case _PS2_LEFT: m=0x80 | _5; break;
case _PS2_RIGHT: m=0x80 | _8; break;
case _PS2_KPENT: m=_ENT ; break; // Enter key
case _PS2_LCONTROL: m=_SYMB ; break; // Enter key
...
...The function Update_matrix( ) uses this value to SET or RESET a bit on the keyboard matrix depending upon the reception of a 'break' code previously.
void Update_matrix( char m){
uint8_t line= m & 0x07;
uint8_t row= (m>>3) & 0x07;
if (BRK==true) {
BRK=false;
Keymap[line]|=(1<<row); // set bits to break
if (m & 0x80) Keymap[0]|=(1<<0); // if bit 7 is set then set Caps Shift bit at row=0, line=0
if (m & 0x40) Keymap[7]|=(1<<1); // if bit 6 is set then set Symbol Shift bit at row=1, line=7
} else {
Keymap[line]&=~(1<<row); // reset bits to make
if (m & 0x80) Keymap[0]&=~(1<<0); // if bit 7 is set then reset Caps Shift bit at row=0, line=0
if (m & 0x40) Keymap[7]&=~(1<<1); // if bit 6 is set then reset Symbol Shift bit at row=1, line=7
}
 danjovic
danjovic
Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.