In this project, you will learn how to build your own GPS and Arduino vehicle position recorder system. Now we will teach you the building process step by step for you to assemble yours.
To construct this project you'll need of this following components presented below.
- PCBWay Custom PCB
- NEO-GM GPS Arduino Module - UTSOURCE
- Arduino UNO - UTSOURCE
- LED 5mm - UTSOURCE
- Switch Button - UTSOURCE
- Breadboard - UTSOURCE
- SD Card Module for Arduino - UTSOURCE
Now, I'll present the full project for you.
The Project
First, we will use some modules to create this project. As provided in the bill of materials, we will use GPS to collect position data and the Memory Card Module to store GPS read positions.
Arduino Nano will be used in this project to perform all control of programming logic.
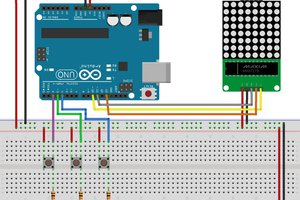
According to this principle of operation, the electronic circuit diagram is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1 - Electronic Schematic of the GPS Register System.
As is possible to see in this project, there are two buttons. Each button is responsible to start and stop the register processing of GPS positions in the SD Card.
The Red LED will be used to signalize when the data positions are being stored in the SD Card.
According to this circuit at protoboard, the electronic scheme was built. The electronic scheme is presented in Figure 2.
Figure 2 - Schematic circuit of thie GPS Register Position.
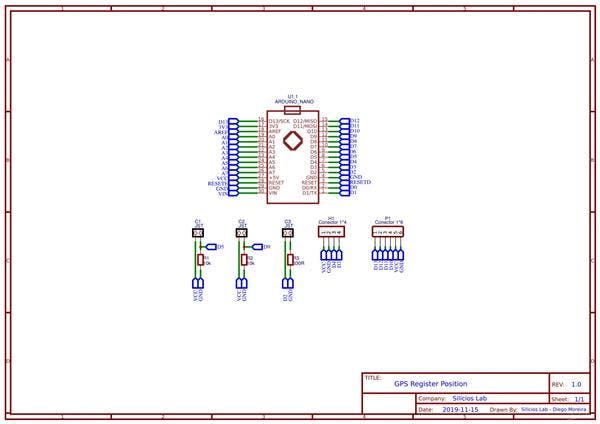
Hereafter, was designed the Printed Circuit Board is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 - Printed Circuit Board of the GPS Register Position with Arduino.
According to this project, was created the code presented below.
The code is used to communicate Arduino Nano with SD Card Module and GPS Module.
javascriptCopy
#include <SD.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h> #include <TinyGPS.h>
SoftwareSerial SerialGPS(4,3); //Pino 4 - TX do Modulo e Pino 3 - RX do Modulo GPS
TinyGPS GPS; File myFile;
bool controle = 0;
float lat, lon;
byte pinoCS = 10; //Pin 10 para Nano/UNO #define INICIA 9
#define TERMINA 5
#define LEDVERMELHO 2 void setup() { SerialGPS.begin(9600); Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(pinoCS, OUTPUT); //Define o pinoSS como saida pinMode(LEDVERMELHO, OUTPUT); if (SD.begin())//Inicializa o SD Card { Serial.println("SD Card pronto para uso."); //Imprime na tela } else { Serial.println("Falha na inicializa??o do SD Card."); return; }
} void loop() { bool BotaoInicia = digitalRead(INICIA); bool BotaoTermina = digitalRead(TERMINA); if(BotaoInicia == 1 && controle == 0) { controle = 1; myFile = SD.open("GPS.txt", FILE_WRITE); //Cria e abre o arquivo delay(1000); myFile.print("Latitude"); myFile.println(" Longitude"); }
if(controle == 1) { while (SerialGPS.available()) { if (GPS.encode(SerialGPS.read())) { digitalWrite(LEDVERMELHO, HIGH); //latitude e longitude GPS.f_get_position(&lat, &lon); myFile.print(lat , 6); myFile.println(lon, 6); delay(1000); } } } if(BotaoTermina == 1 && controle == 1) { controle = 0; myFile.close(); digitalWrite(LEDVERMELHO, LOW); }
}
In the first lines, it will be declared the libraries of the modules and the variables used to manipulate the data in the project, as is shown in the following code.
javascriptCopy
#include <SD.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h> #include <TinyGPS.h>
SoftwareSerial SerialGPS(4,3); //Pino 4 - TX do Modulo e Pino 3 - RX do Modulo GPS
TinyGPS GPS; File myFile;
bool controle = 0;
float lat, lon;
byte pinoCS = 10; //Pin 10 para Nano/UNO #define INICIA 9
#define TERMINA 5
#define LEDVERMELHO 2
After this, the system will execute the void setup function. In this function, the system will configure the pins used to connect the LED, button and others like a digital input or output.
Posteriorly, will test the initialization process of the SD Card through the code presented below
javascriptCopy
if (SD.begin())//Inicializa o SD Card { Serial.println("SD Card ready for use"); //Imprime na tela } else { Serial.println("SD Card initialization failed");...
Read more »
 Silícios Lab
Silícios Lab



 peter ward
peter ward