Mars rovers encounter problems during dust storms in two main areas: Locomotion and Mission Operations. For this robot, one of the main requirements is to move without requiring primarily electrically driven propulsion. Bio-inspiration was referenced from tumbleweeds and maple seed pods, and design inspiration from Strandbeests and the NASA Zephyr landsail for Venus. The human exploration application is to perform on the ground prospecting of sites for nomadic style of establishment of habitats. Read more in the project overview.
We're building the Mars Wind Tumbler Robot for the Trans-Atlantic MDRS Mars analogue mission launching in December 2021.
Big thanks to the mission crew who will be helping immensely with our project.
Stay in the loop with the updates along the development journey by giving this project a like and a follow!
👾
Project Logs Table of Contents
Mars:
Prototype #001:
- https://hackaday.io/project/177305/log/198412-prototype-001-start
Project:
 EK
EK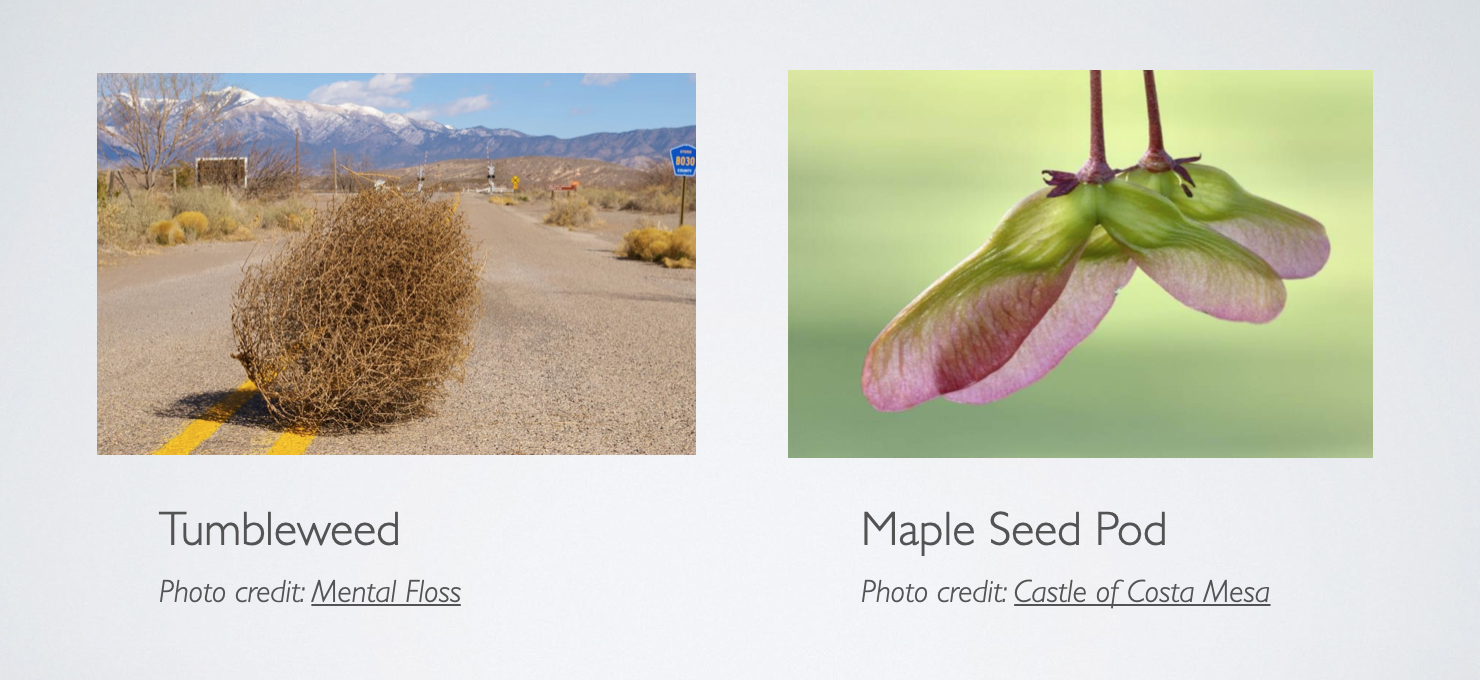


 Alex Bell
Alex Bell
 Kenji Larsen
Kenji Larsen
 Jordan Less'ard-Springett
Jordan Less'ard-Springett
 Tom Farnell
Tom Farnell