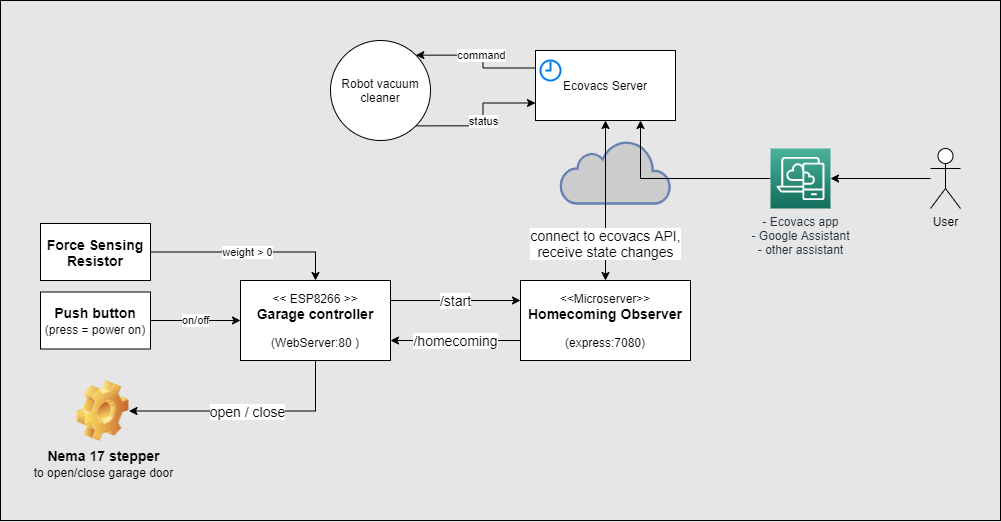
The ESP8266 operates a nema 17 stepper motor that lifts the kitchen skirting board up and down. As long as the robot is in parking postion, one of the robot's wheels stand on an inverted push button so the ESP is powered off. The power is turned on when the robot starts leaving the docking station. On startup the controller executes the following startup routine:
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
// stepper pins
pinMode(enablePin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(stepPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(dirPin, OUTPUT);
// force resistance pin
pinMode(frsPin, INPUT);
openDoorWaitAndClose(); // function waits 30 sec before closing the door again
// connect to home WiFi
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.print("Attempting to connect to WPA ");
Serial.println(ssid);
if (WiFi.waitForConnectResult() != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.println("WiFi failed!");
return;
}
Serial.println("connected");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
// register API endpoints on ESP8266WebServer
server.on("/open", handleOpenDoor); // for test usage
server.on("/close", handleCloseDoor); // for test usage
server.on("/homecoming", handleHomecoming); // for use by nodejs server
server.onNotFound(handleNotFound);
server.begin();
Serial.println("HTTP server started");
// send signal to nodejs server
wakeupBackendService();
}
The nodejs server opens a connection to the Ecovacs REST API and starts to listens for inbound status notification events. If the "returning" event is received, the program forwards the event via http to the ESP8266WebServer
const observe = async () => {
if (vacbot !== undefined) {
console.log('Already observing')
return
}
console.log('Start observing')
const connectStatus = await api.connect(username, passwordHash)
const devices = await api.devices()
let vacuum = devices[0];
vacbot = api.getVacBot(api.uid, EcoVacsAPI.REALM, api.resource, api.user_access_token, vacuum, continent)
vacbot.on('ready', async (event) => {
console.log('Vacbot ready')
vacbot.on('CleanReport', async (state) => {
console.log('CleanReport: ' + state)
if (state === 'returning') {
disconnect()
vacbot = undefined
console.log('Try open garage door')
var response = await openGarage()
console.log('Garage door opens...')
let i = 0
while (response !== 200 && i < 5) {
i++;
console.log(`Error ${response}, retry open garage door #${i}`)
response = await openGarage()
await sleep(500)
}
}
})
})
process.on('SIGINT', function () {
console.log("\nGracefully shutting down from SIGINT (Ctrl+C)")
disconnect()
process.exit()
});
function disconnect() {
try {
vacbot.disconnect();
} catch (e) {
console.log('Failure disconnecting: ', e.message)
}
}
}
The ESP is now set into homecoming mode. The homecoming function waits for the robot to run over the force sensing resistor, that is placed right in front of charging station, and closes the door in the final moment before the system is powered off again.
void homecoming(){
openDoor();
do {
frsValue = analogRead(frsPin);
delay(500);
} while (frsValue == 0); // wait for force resistance sensor signal, the quickly close the door before the power is turned off
closeDoor();
}
 MiKa
MiKa
Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.