First things first - since everyone is mainly here for specs and moving robots I guess :)
The Robot Specs:
- 6 Degrees of Freedom
- BLDC Servo driven
- absolute encoders on all axis
- all structual parts are made from Aluminium
- belt drives on first four axis, wave gears on axis 5 and 6
- total weight of the arm about 5 kg
- max power 1,5 kW (all axis max)
- max. payload in all poses: 3 kg
- G1 and G2: 40 Nm max
- G3: 25 Nm max
- G4 to G6: 18 Nm max
- tested maximum Speed G1 at max radius (500 mm): 2 m/s
- repeatability (20 min continuously testing): 0.02 mm
Moving robot arm - sneak peek
Motivation
The motivation for the construction of this robot has developed along the project step by step.
At the beginning of my studies (mechatronics and robotics), I had set myself the goal of developing a robot on which I can practically apply the theory I have learned and thus create knowledge. Using the equipment that I built over the last years (CNC mill, lathe, 3D-printer, ...).
The more I engaged myself with the topic, the more I got an insight. An insight that allows me to better assess the current market of robotics, with fulfilled needs, wishes or visions, and thus the potential of an individual robot - like this one.
For now this robot is intended to serve as a teaching and research platform for further robot development and control schemes, mainly as interactive robot since those most likely have significant impact in our future. I'd like to make this platform available for everyone by further improving it, to be simpler and less expensive to build, but keeping the performance thats needed to allow for direct interaction of the robot and its environment.
Status Quo
The hardware development of the robot, control box and control device (HMI) is completed. This also includes the development of the base software, which allows low-level control, safety and simple motion tasks (point-to-point). The robot has been tested extensively for repeatability/positioning accuracy, maximum torque/force, speed and acceleration, and long-term thermal stability. These tests have resulted in the specifications listed below.
Additionally I developed a joint test bench, which allows me to bring the performance of the robot on hardware and espacially software side to the next level - an interactive one.
Vision
My overall vision is to make robots available/attainable for many purposes - lowering cost and increasing performance. So that "the robot" can become part of "the everyday life", what goes far beyond mechanics, electronics and software.
Robot Hardware
In this section I will explain the structure and design of the mechanics and electronics of the robot in more detail. You can find detailed pictures of the actual prototype build process in "build logs".
System Structure
In the following picture the overall system structure of the robot, the control box and the HMI is illustrated.
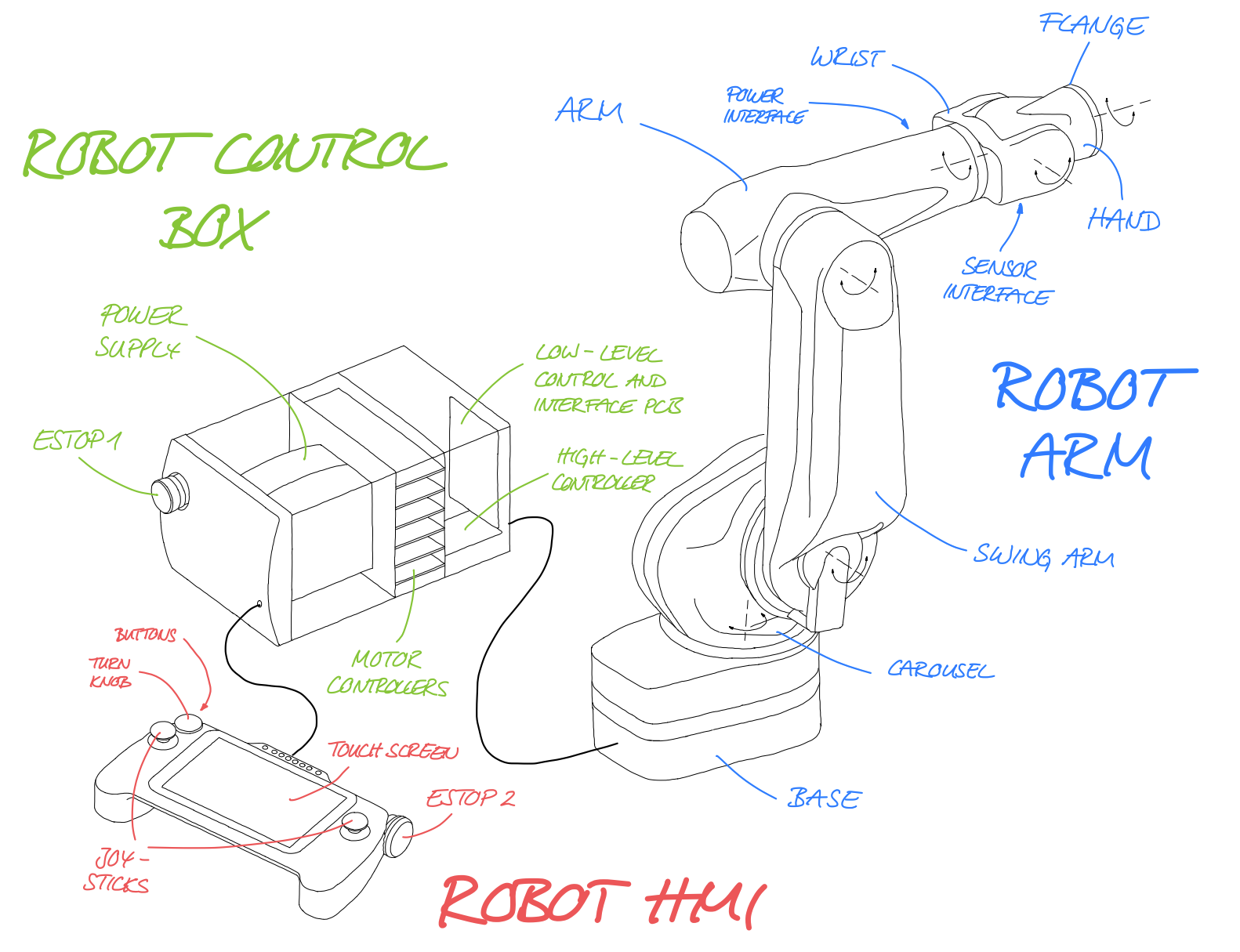
The robot arm is composed of: the base, the carousel, the swing arm, the wrist, the hand and the flange (6 axis). The base frame is fixed in the reference workspace and is not movable. The connection to the carousel is formed by the first rotation axis. The carousel is connected to the swing arm by means of the second rotation axis. The rotation of the arm , relative to the swing arm, is achieved by means of the the third axis. In this configuration, the first three rotational axes are essentially for the positioning of the tool center point (TCP - intersection point of the last three axes) in the reference workspace. The last three rotational axes are controlled by the connections of arm/wrist, wrist/hand and hand/flange. These axes all meet at one point. Therefore, they are essentially responsible for the orientation of the TCP in the reference workspace. The flange enables the mechanical connection of tools or gripper systems. In addition, a sensor interface and a power connection in the hand or the arm, respectively, is provided.
The robot control box is used for power provision, motor control and motion control. All sensor data acquired in the robot are transmitted via a communication bus to a central low-level control unit in the robot controller, which is responsible for motion control and sequence control. The low-level control unit regulates the movement of the motors via six individual motor controllers located in the robot controller, which are interconnected via a communication bus. An additional high-level control unit is used for communication with external devices and peripherals, and enables extended functions for motion and sequence control.
The robot HMI is used for displaying data during the operation of the robot system as well as the direct input of commands from the user without an additional device (e.g. PC). It is connected to the low-level control unit in the robot controller by means of a further communication bus. In addition to a display, it has further input elements: two joysticks, an E-stop switch, a rotary encoder and two buttons.
Build video
The following video shows the construction and manufacturing of the first three robot axis.
 Adrian Prinz
Adrian Prinz