Overview
The body of this robot is built using recycled cardboard boxes, paper sheets and polystyrene foam pieces.
A few recycled plastic parts are added (e.g. for the eyes).
The main goal of this project, apart from enjoying time with my nephews, is to enable people to replicate something similar using only recycled objects and, of course, some electronics.
See the robot in action in this video: https://1drv.ms/v/s!AptRC3vrl3Svg9k3Y7uQPuJKLkSglg?e=Ba90eq
Body
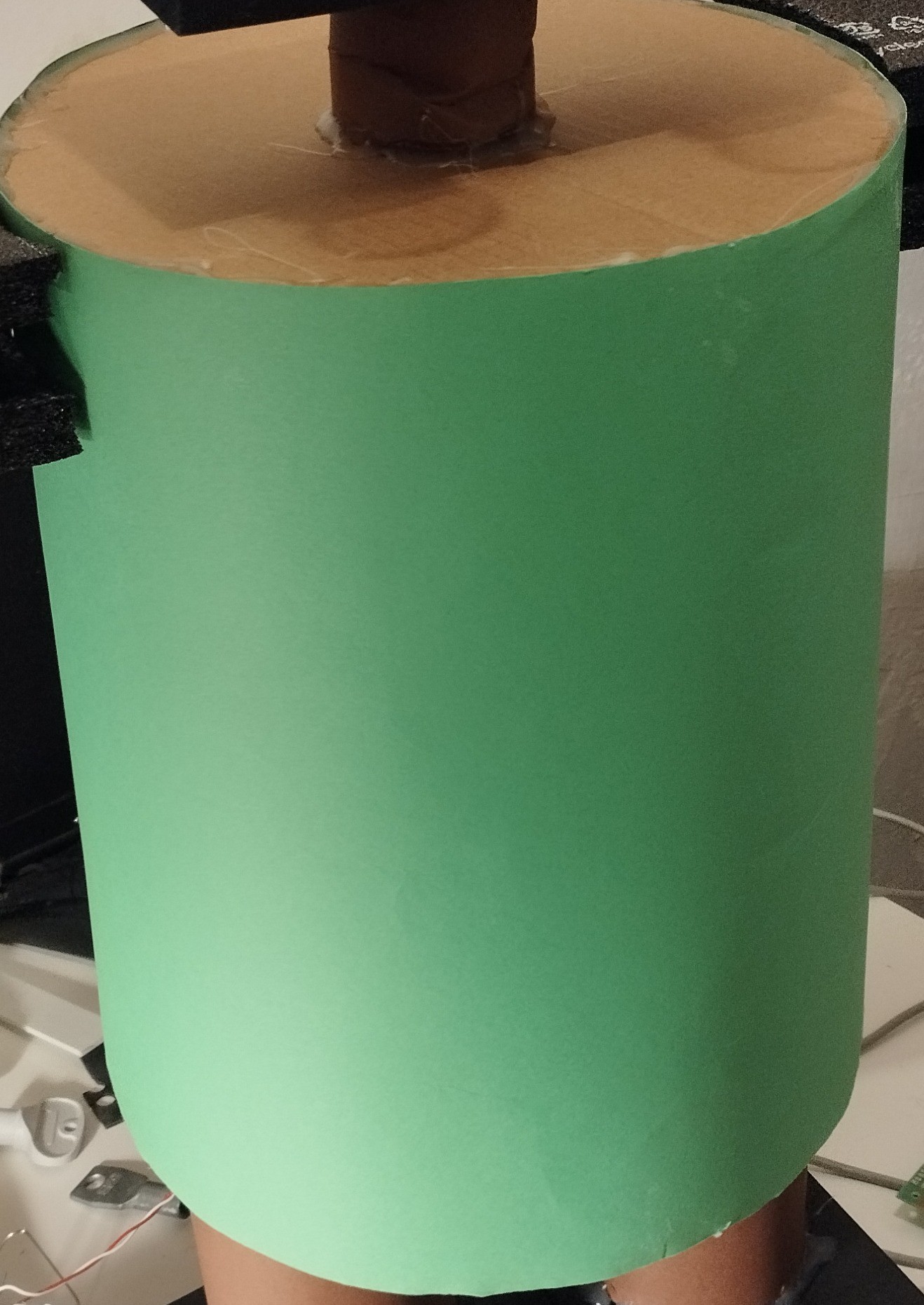
- Two (top and bottom) 3 mm cardboard disks (in light brown)
- one cylinder made with a green paper sheet
hot glued together.

The cylinder is windowed in the back, to easily place the RC receiver (see the small Velcro on the bottom disk) and the wires going to the head (5 wires) and to the feet (4 wires).
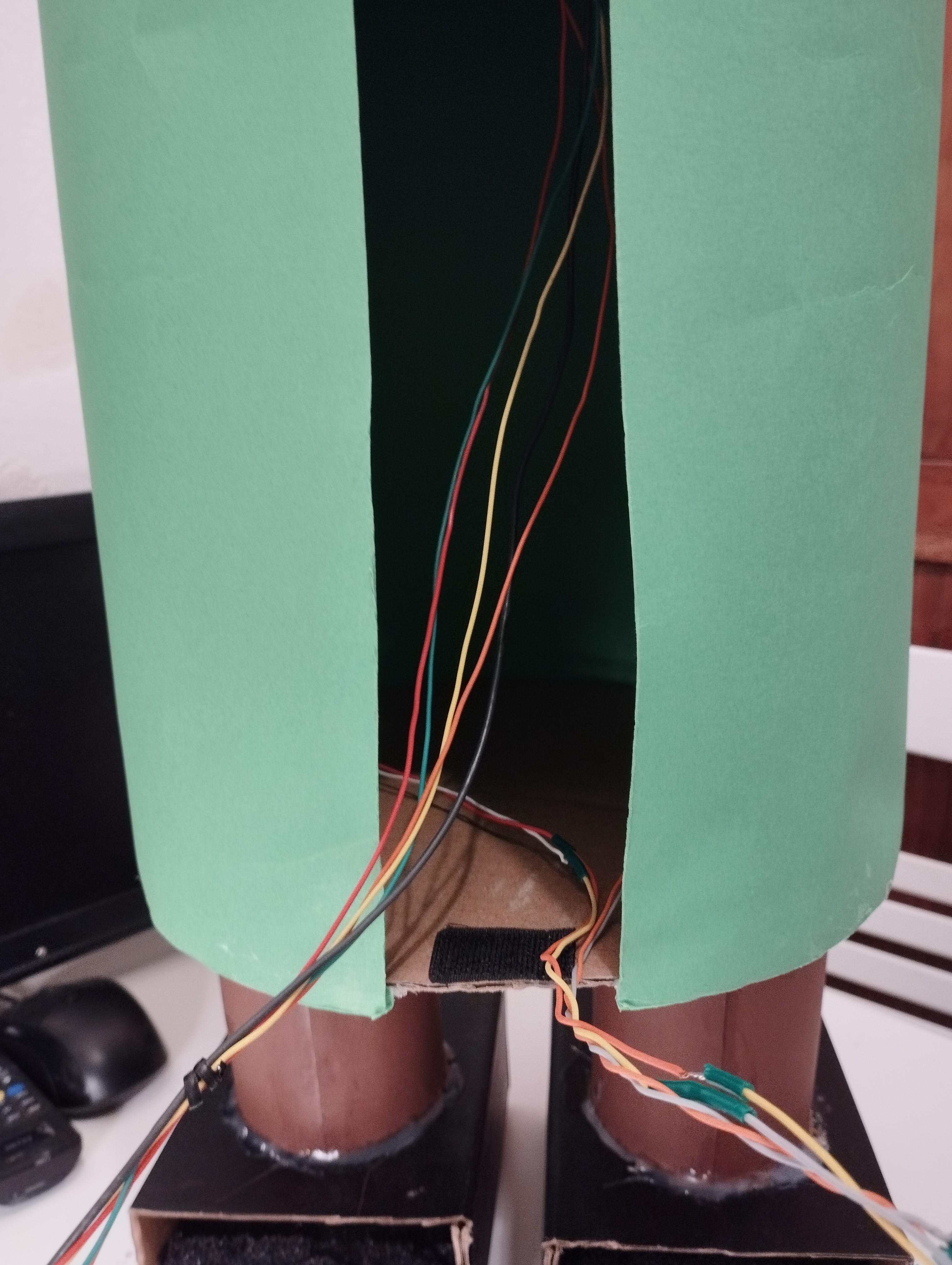
Legs
With the same technique used for the body, two small brown paper sheets build the legs.
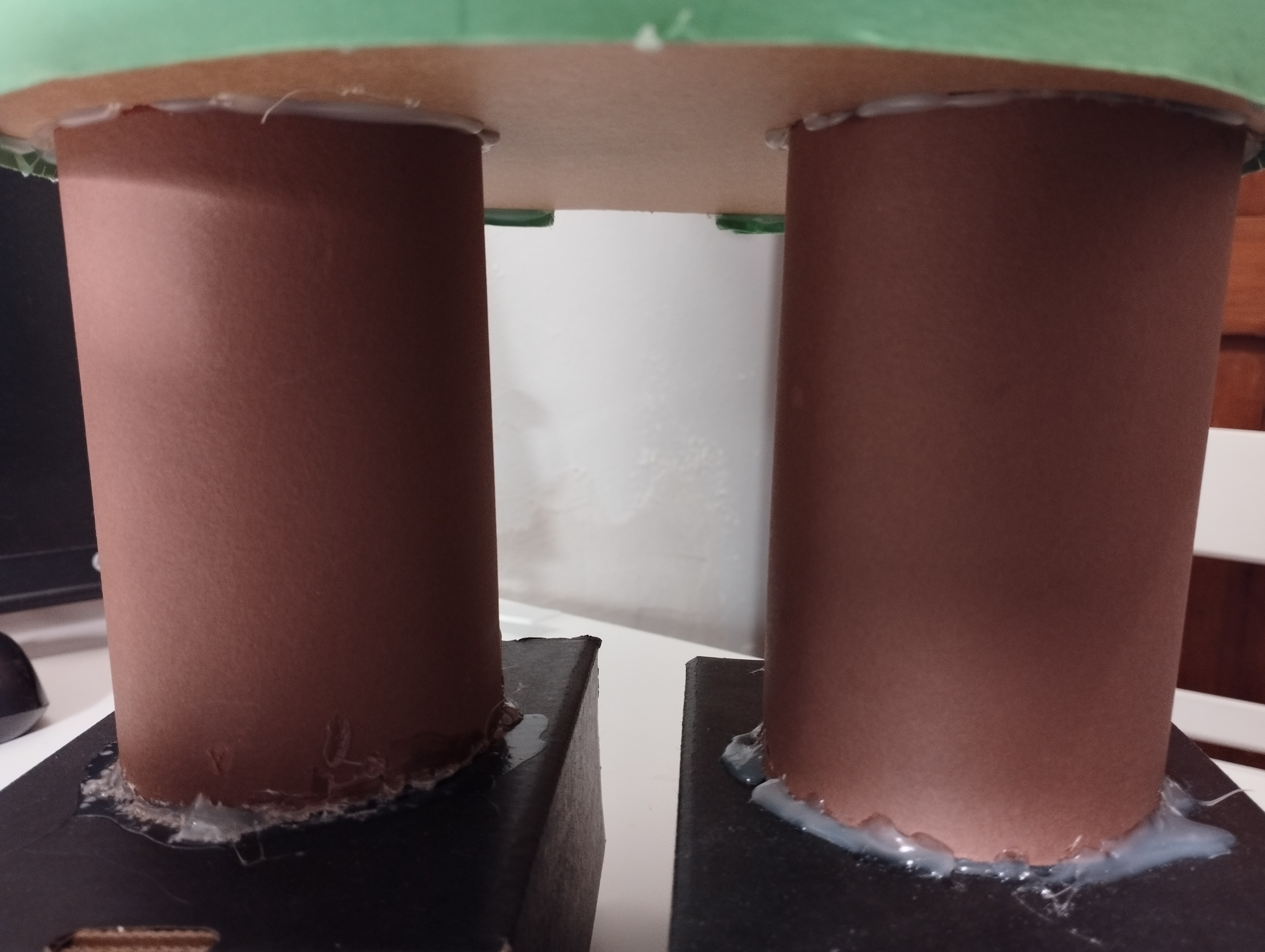

Note that my nephews glued the legs. The result could be better 😀
Feet
A black cardboard box, cut in two, is used for the feet.
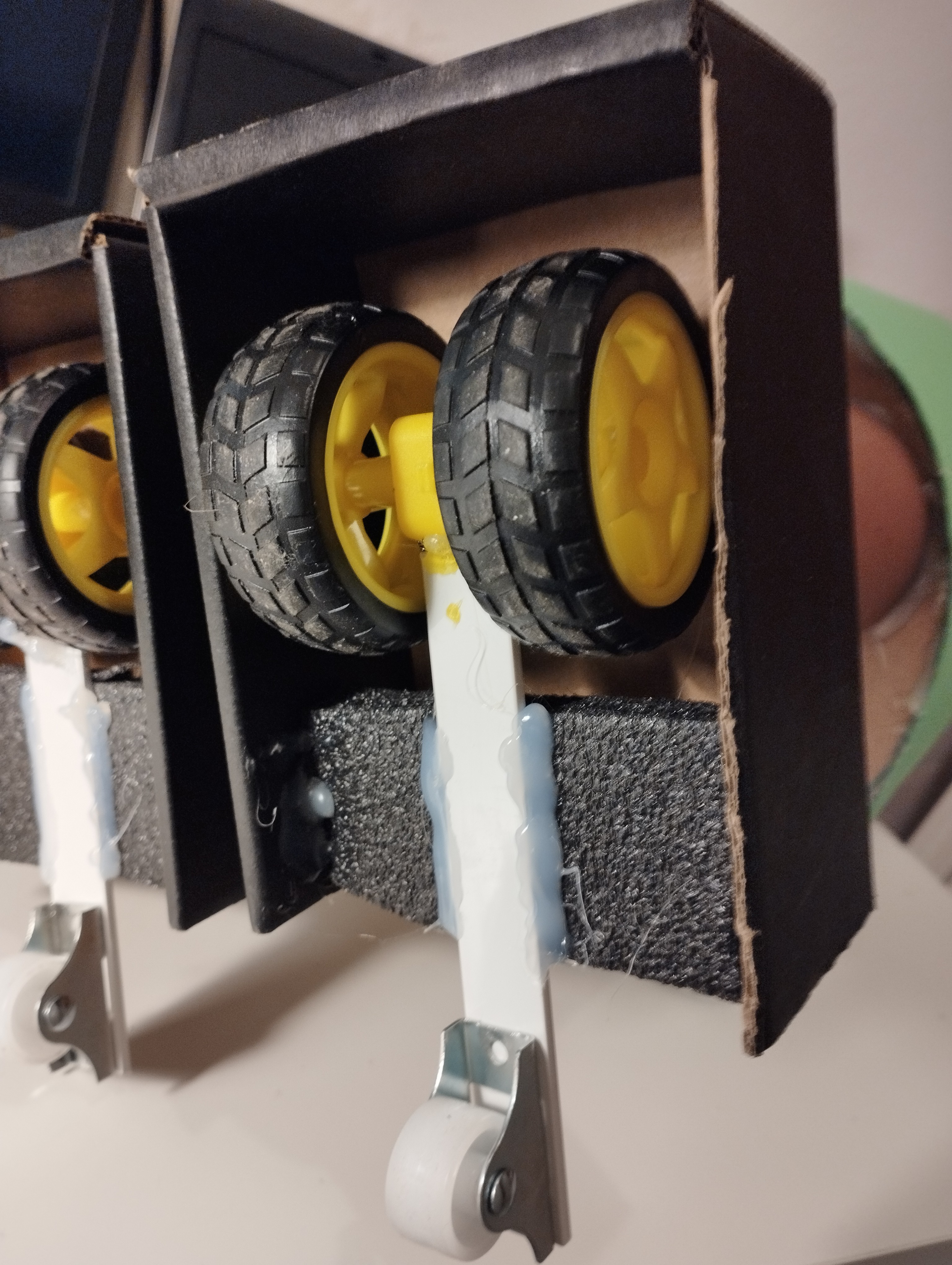

An extra free wheel (white) enlarge the base to give some more stability (the center of gravity of my robot is probably too high.
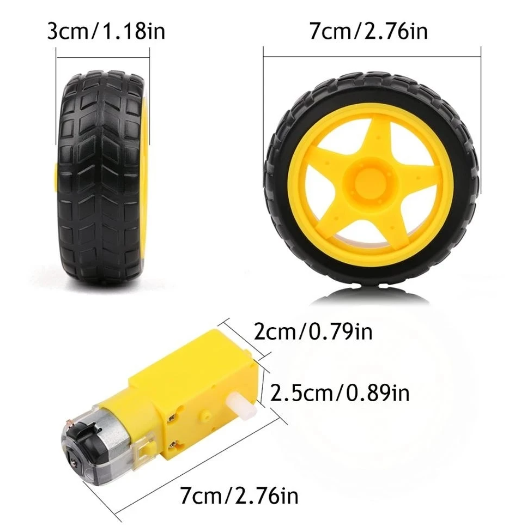
The cheapest motors and wheels I found on AliExpress (or Amazon or Ebay) are used. The motor is inserted into a hole in the cardboard.

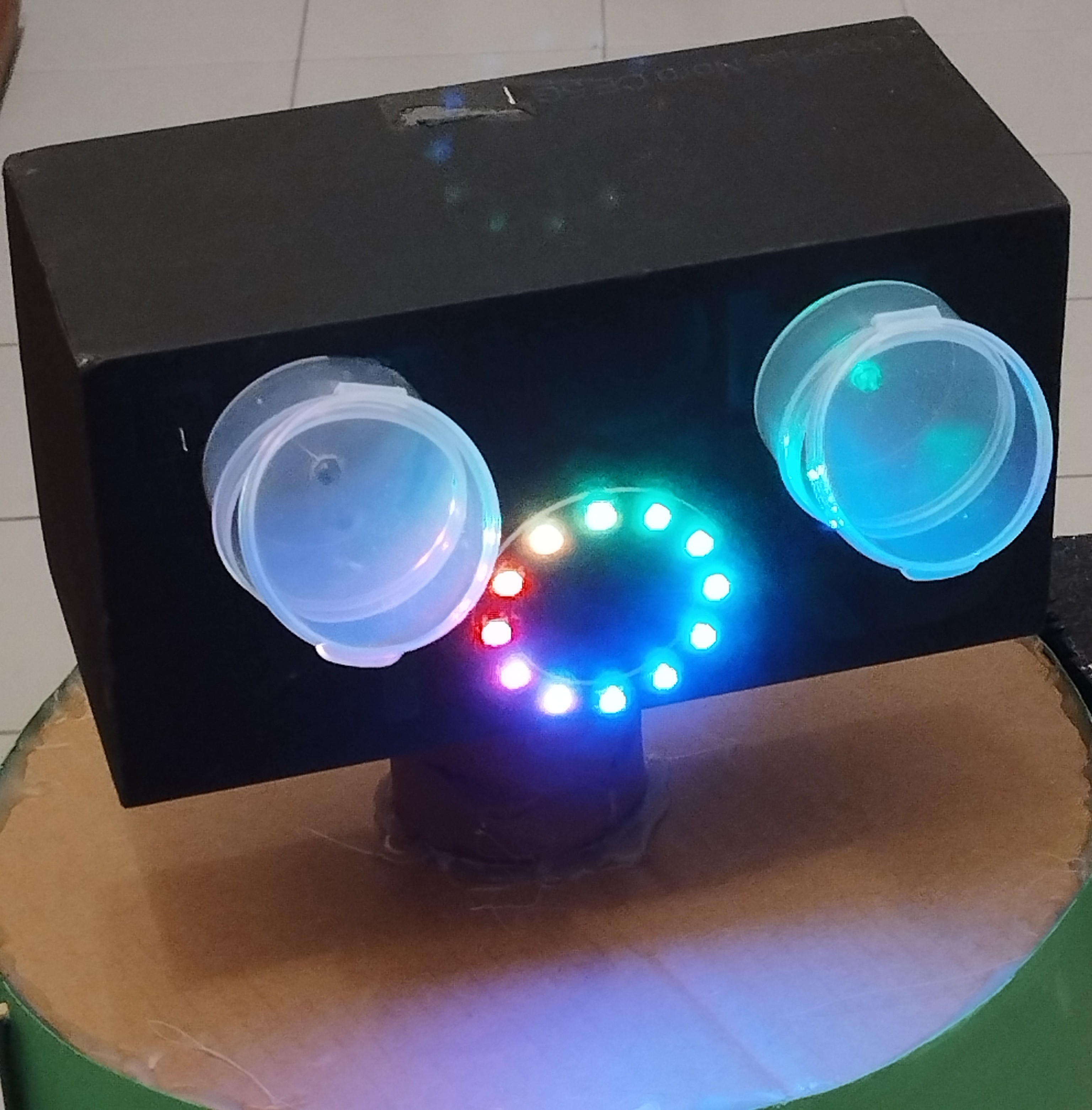
Head
Two plastic pills containers with a 5 mm LED in the middle try to resemble eyes and eyelashes.
A 12 LEDs ring is similar to the mouth.

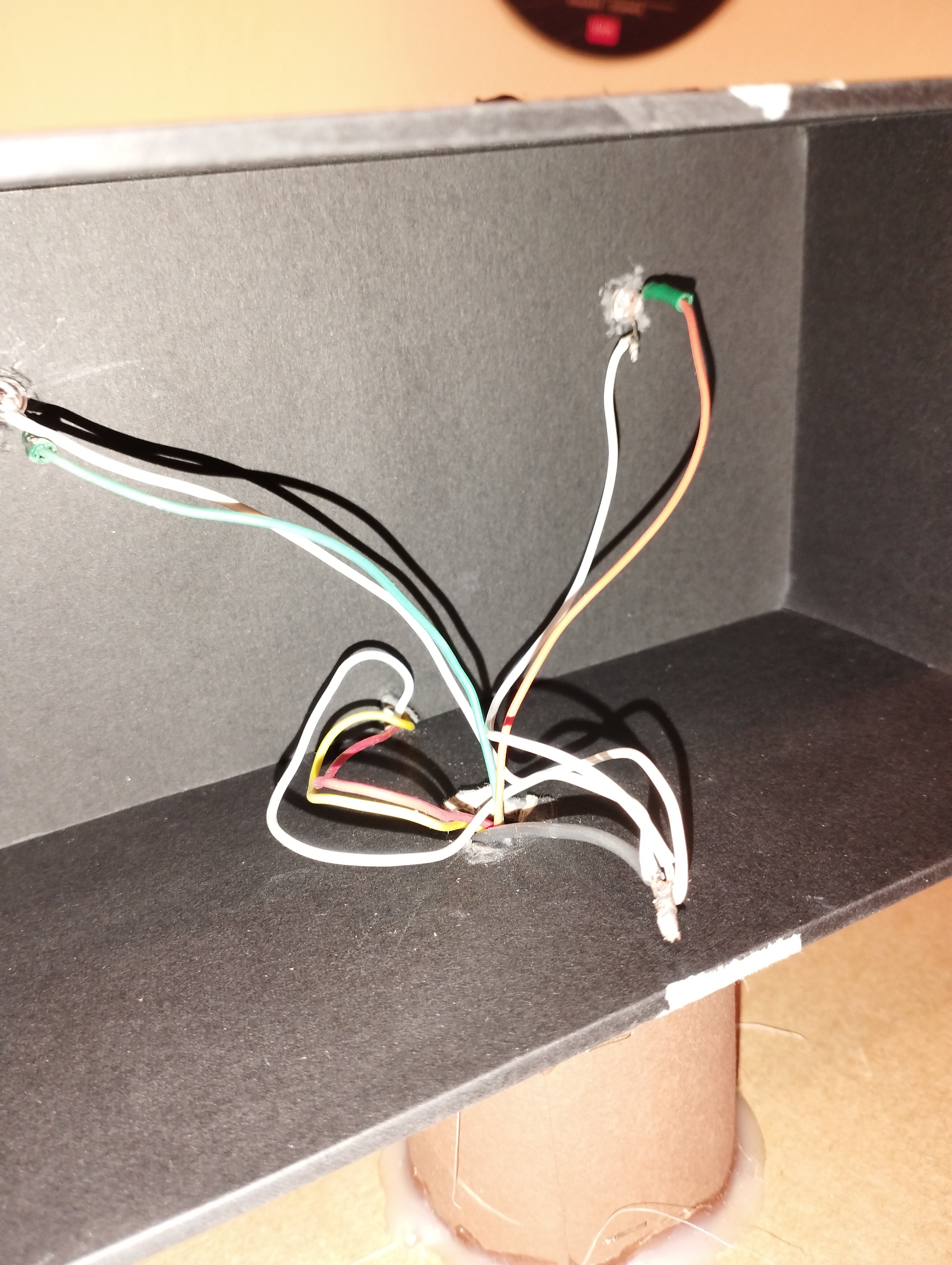
- A single wire connects the ground for the two LEDs and for the 12 LEDs ring.
- One wire for the left LED
- One wire for the right LED
- One wire for the LEDs ring +5V
- One wire for the LEDs ring data

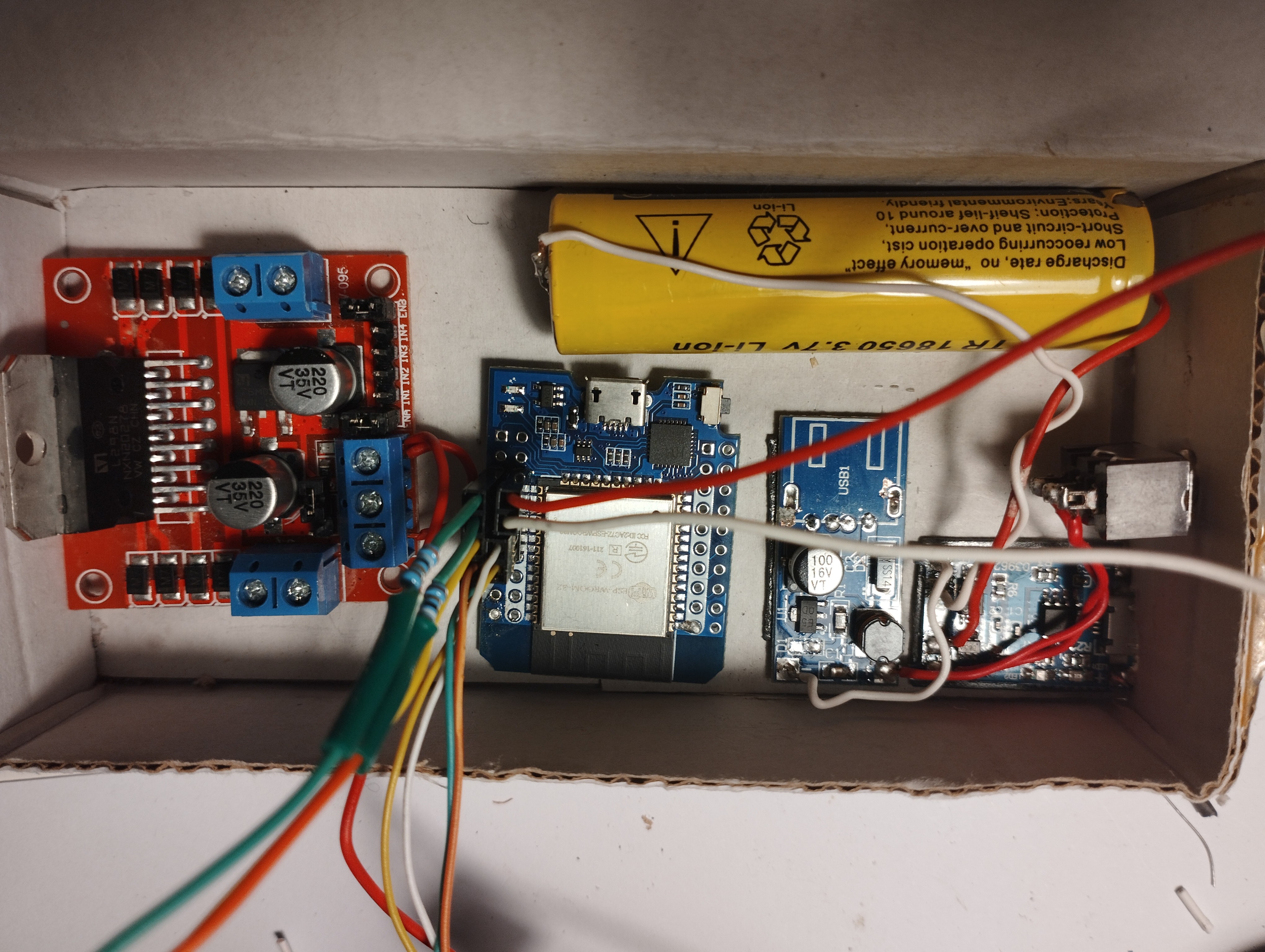
Electronics
It is located in a cardboard box. The boards and the battery are fixed with some two faces scotch tape.
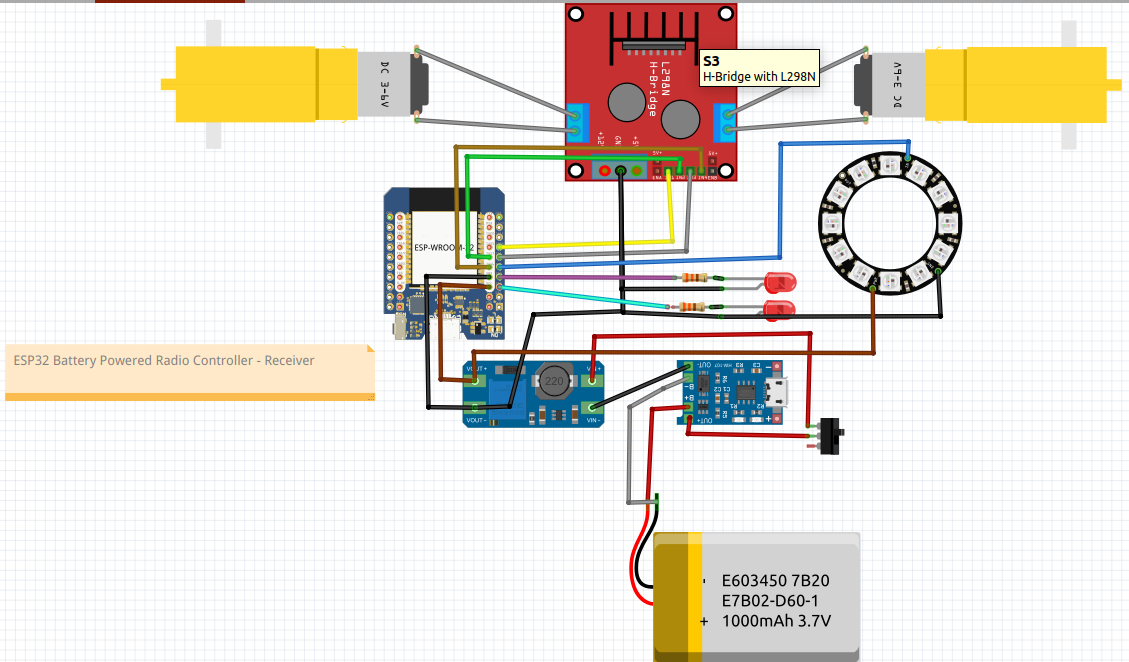
This is the Fritzing schematic for the Receiver. The fritzing file is in the Github repository.
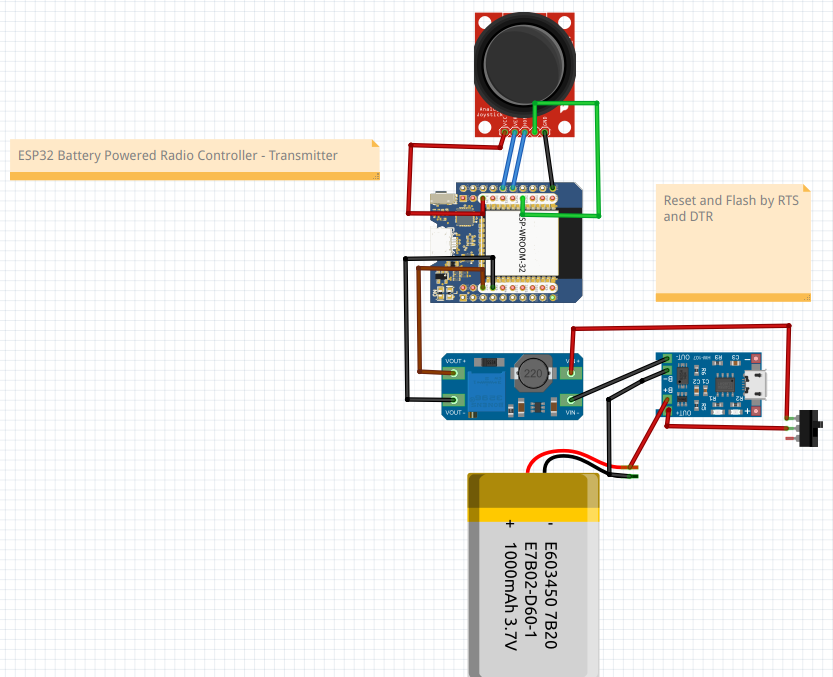
This is the Fritzing schematic for the Transmitter.
I used this cheap joystick, bought on Amazon.

it is not very precise but it's enough for the purpose to change the direction and speed of the robot.
Note the two variable resistors for X and Y axis.
 Guido
Guido