Project Overview
This DIY IoT alert system uses a Send SMS Alert using Seeed Studio XIAO ESP32 microcontroller and an HC-SR04 ultrasonic distance sensor to detect nearby movement and send SMS notifications over Wi-Fi via a cloud API. Instead of GSM hardware, the ESP32 sends HTTP requests to a free SMS service, keeping the design compact, cheap, and easy to replicate.

What You’ll Need
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Seeed Studio XIAO ESP32-S3 | Main microcontroller with Wi-Fi |
| HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor | Proximity/motion detection |
| Breadboard & jumper wires | Prototype wiring |
| Wi-Fi network | Internet connectivity |
| Free CircuitDigest Cloud API key | SMS delivery service |
You can swap the HC-SR04 with other digital sensors (e.g., PIR motion, temp sensors) without changing the core logic.
How It Works
-
Boot & Wi-Fi: On power-up, the XIAO ESP32 connects to your Wi-Fi network.
-
Distance Checking: The HC-SR04 repeatedly measures how far an object is.
-
Trigger Detection: If an object is within a defined threshold (e.g., <100 cm), the code triggers an SMS alert.
-
SMS API Request: An HTTP POST with your API key and message data is sent to the cloud SMS API.
-
Deliver Alert: The cloud service forwards the text to your phone via the mobile network.
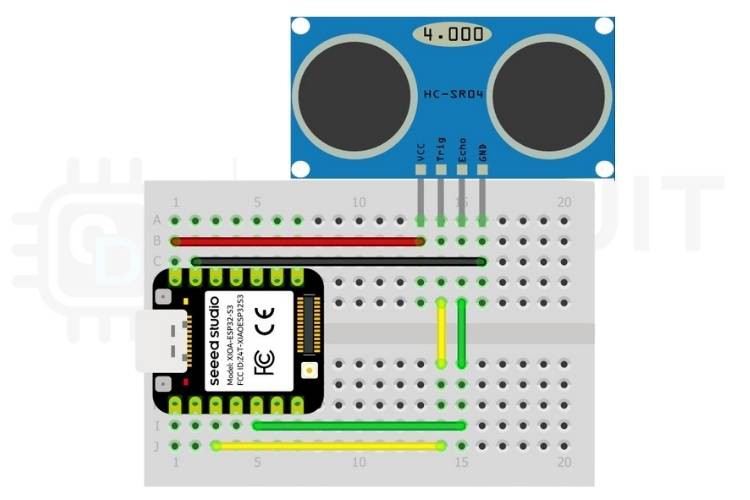
Wiring Guide
Keep the hardware simple with just four connections:
| HC-SR04 Pin | XIAO ESP32 Pin | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | 5V | Power |
| GND | GND | Ground |
| Trig | GPIO 5 | Trigger signal |
| Echo | GPIO 3 | Echo pulse input |
No level shifting is needed for basic operation with the HC-SR04, and the tiny XIAO form factor fits neatly on a breadboard.

Arduino Code Summary
Libraries & Credentials
#include <WiFi.h> // Pins #define TRIG_PIN 5 #define ECHO_PIN 3 // Wi-Fi const char* ssid = "YOUR_SSID"; const char* password = "YOUR_PASS"; // SMS API const char* apiKey = "YOUR_API_KEY"; const char* templateID = "103"; const char* mobileNum = "91XXXXXXXXXX"; // SMS text variables const char* var1 = "Sensor"; const char* var2 = "Object Detected"; bool alertSent = false;
Send SMS Function
This function sends an HTTP POST request with JSON containing the recipient and dynamic text variables:
void sendSMS() { if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECTED) { WiFiClient client; if (client.connect("www.circuitdigest.cloud", 80)) { String payload = "{\"mobiles\":\""+String(mobileNum)+"\"," "\"var1\":\""+String(var1)+"\"," "\"var2\":\""+String(var2)+"\"}"; client.println("POST /send_sms?ID="+String(templateID)+" HTTP/1.1"); client.println("Host: www.circuitdigest.cloud"); client.println("Authorization: "+String(apiKey)); client.println("Content-Type: application/json"); client.println("Content-Length: "+String(payload.length())); client.println(); client.println(payload); while (client.connected() || client.available()) { if (client.available()) Serial.println(client.readStringUntil('\n')); } client.stop(); } }
}
Distance Measurement
A simple function to read the distance from the ultrasonic sensor:
float readDistance() { digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, LOW); delayMicroseconds(2); digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, HIGH); delayMicroseconds(10); digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, LOW); long duration = pulseIn(ECHO_PIN, HIGH); return duration * 0.034 / 2; // cm
}
Main Loop
Measure and send SMS when the object comes closer than the threshold:
void loop() { float dist = readDistance(); Serial.println(String(dist) + " cm"); if (dist < 100 && !alertSent) { sendSMS(); alertSent = true; } if (dist >= 100) alertSent = false; delay(500);
}
Complete code builds the Wi-Fi connection, handles cloud API messaging, and ensures SMS is sent only once per “event.”
Testing & Troubleshooting
-
Wi-Fi: The Serial Monitor should print connection progress and IP address.
-
Sensor feedback: You’ll see continuous distance readings.
-
SMS status: The API response appears in Serial output.
Common issues include incorrect API keys, incorrect phone number format (include country code), or Wi-Fi disconnects. If Wi-Fi drops, the module keeps trying to reconnect...
Read more » ElectroScope Archive
ElectroScope Archive
 Augusto
Augusto
 Rodmg
Rodmg
 Hari Wiguna
Hari Wiguna
 Rohan Barnwal
Rohan Barnwal