The CPU is a full 8-bit harvard architecture CPU. Instructions, data and addresses are all 8 bits wide. Program and data memory are separate, and each 256 bytes in size.
Program memory can be programmed using DIP switches, but the program itself cannot write to it (by design, there are no program memory writing instructions in the instruction set).
A stack can be used, by using a dedicated stack pointer register. It shares space in data memory with global data. The stack is pre-decrement push, post-increment pop, so it grows down from the top of data memory.
The instruction set includes:
DATA - move immediate data into a register
MOV - copy data from one register to another
JMP - transfer control to another address in program memory. Address can be immediate, or another register.
JZ - conditional jump (if zero)
JC - conditional jump (if carry)
JN - conditional jump (if negative)
JO - conditional jump (if signed overflow)
LOD - load data from program or data memory to a register. Address can be immediate, or another register.
STO - store data (immediate or from a register) to data memory. Address can be immediate or another register
PUSH - store data (immediate or from a register) onto stack. Automatically adjusts stack pointer
POP - retrieve data from stack into a register. Automatically adjusts stack pointer
CALL - push return address onto stack, and jump to subroutine
RET - return from subroutine
INC - increment data register contents
DEC - decrement data register contents
ADD - 8-bit add of 2 data registers
ADC - 8-bit add with carry of 2 data registers
SUB - 8-bit subtract of 2 data registers
SBC - 8-bit subtract with carry of 2 data registers
CMP - compare 2 data registers
TST - compare data register with 0
AND - bitwise and of 2 data registers
OR - bitwise or of 2 data registers
XOR - bitwise xor of 2 data registers
NOT - bitwise not of data register
 James Bates
James Bates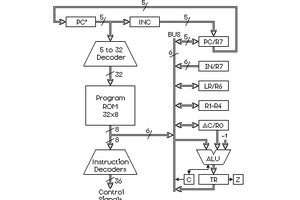

 Justin R.
Justin R.
 Meksim
Meksim
 Szoftveres
Szoftveres