Summary
The Vinduino project saved 25% , or 430,000 gallons, irrigation water.
Cost saving on water and labor was $1,925.
Project component cost was $635.
Irrigation Cost Before Vinduino
In 2014, and the years before that, we had irrigation managed by our vineyard management company. They decided when and how long to irrigate. This was done manually. Someone drove up to the vineyard, opened the valves, and returned later that day to close them again. Apart from the labor cost, my concern was that I had no control, and no way to tightly manage water in another year of severe drought.
| Cost | Irrigation QTY | |
| Irrigation water (2014) | $ 3,200 | 2,325 HCF |
| Irrigation management (2014) | $ 1,125 | |
| Total cost for irrigation | $ 4,325 |
Savings
| Cost | Irrigation QTY | |
| Irrigation water (potential) | $ 2,400 | 1,750 HCF** |
| Irrigation management (2015) | $ 0 | |
| Total estimated annual savings for irrigation | $ 1,925 | 575 HCF (25%) (430,000 gallons) |
** this is the goal for 2015, actual is a bit higher due to equipment failure and overestimated water requirement directly after installation. Subtracting these, we would have met the target saving of 25%, and have repeatable results next seasons.
Cost summary
| Installed sensors cost (1 x Watermark, 10 x gypsum) | $50 |
| 2 x DC latching valves + timers | $450 |
| Vinduino handheld reader + Vinduino remote node | $135 |
| Total project components cost | $635 |
Including one time cost for new irrigation valves and irrigation timers, the payback period for this project is less than one year.
The financial savings are an additional bonus for saving water!
Developing Countries Configuration
A minimum cost Vinduino setup for developing includes: a handheld reader, multiple gypsum sensors, and a salinity probe.
The total estimated component cost for this is $60. High volume purchasing can bring cost down significantly.
While not as convenient as a remote reading station, taking daily measurements in the field is considered sufficient for keeping track of soil moisture and estimating irrigation time.
The salinity probe allows salinity measurement of soil, and checking of irrigation- and drinking water quality.
Soil sample measurements should be taken a few times per year, avoiding crop loss due to soil salinity.
Vinduino Component Cost
The handheld reader has evolved into a multi-purpose agricultural meter. It can be used to measure :
- soil moisture (using DIY gypsum sensors, or commercial Watermark sensors)
- Soil and water salinity
- Water pressure
Low volume component cost estimate is $51.50
(excl. VAT and component shipping cost)

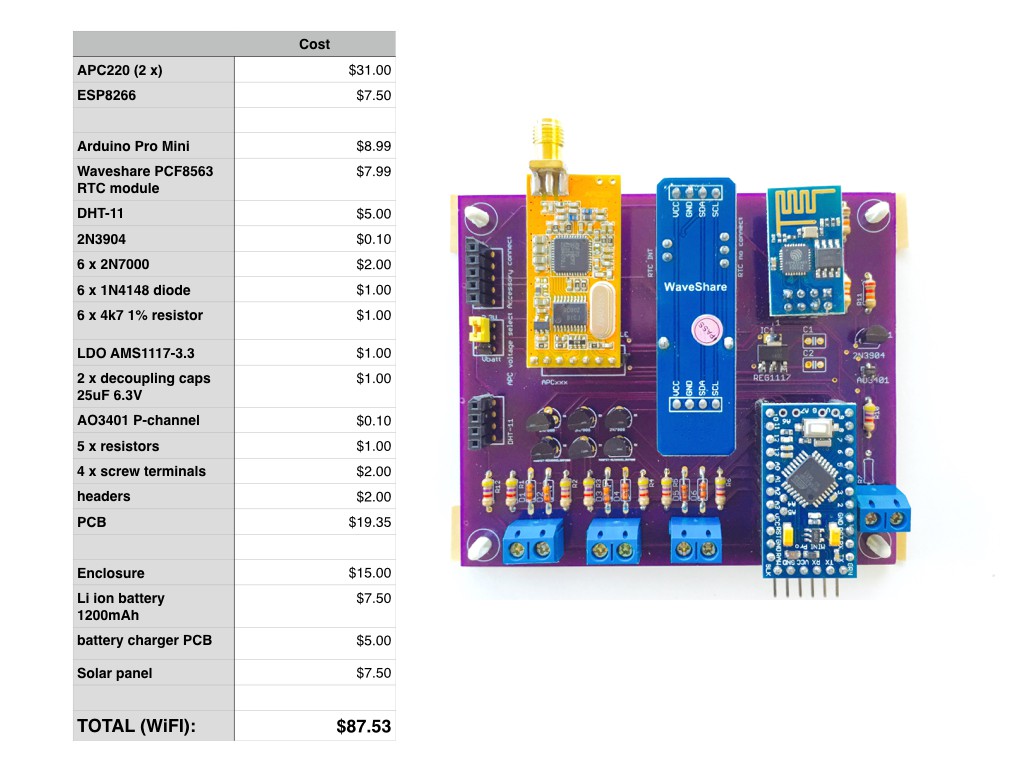
The remote reader station (picture below) can measure :
- 3 x soil moisture sensors
- Inside enclosure temperature and relative humidity
- Battery voltage
Connectivity options include log range RF modules or WiFi (ESP8266)
The board can be configured to control DC latching irrigation valves and measure water pressure (as feedback that valves work properly). This will require an additional motor driver board and DC/DC boost converters.
Low volume component cost estimate is $87.50
(excl. VAT and component shipping cost)
Plumbing Cost
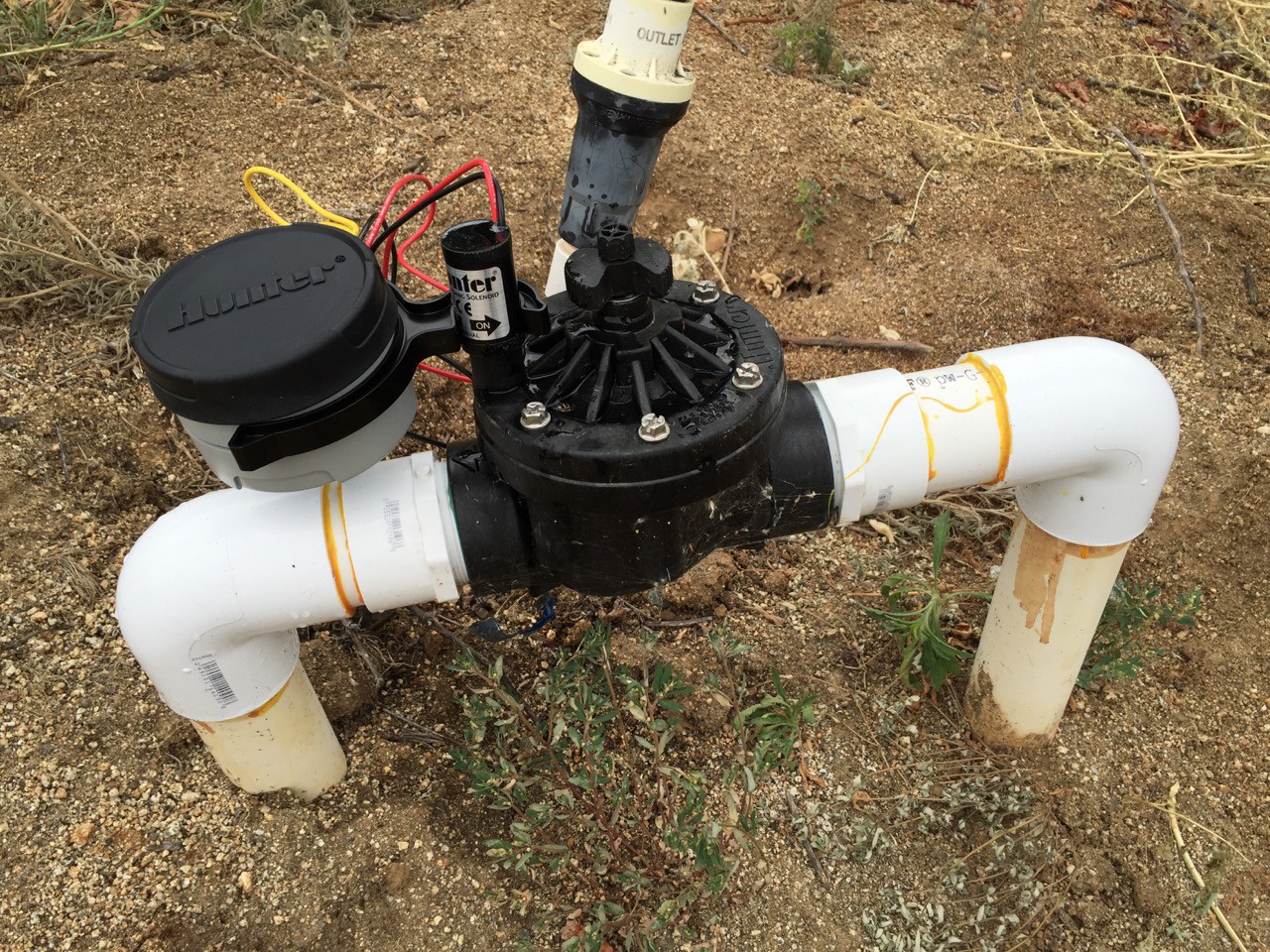
I installed 2 x DC latching 2" irrigation valves ($125 each) and control them with battery operated timers ($100 each). The timers are set for daily irrigation, and the irrigation time is adjusted weekly. For next season, the goal is to replace the timers with Arduino-based irrigation control.
 Reinier van der Lee
Reinier van der Lee
Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.