Of course the first thing that comes to the average makers mind when they want to add smart connectivity to something is the venerable Raspberry PI. These boards are great, but almost impossible to find in quantity and definitely impossible to buy at the advertised price if you live outside USA. The only Raspberry I could consider for size and availability is the CM version, but I'd have to add WiFi and Ethernet to the already high price of the board. Finally, they're way overpowered for my purpose. What I'm looking for is the sweet spot between a Raspberry PI and an ESP32 in terms of size, price and features.
So I started looking around for Linux SBCs. There's plenty of choice around, let's look at the best options I tested:
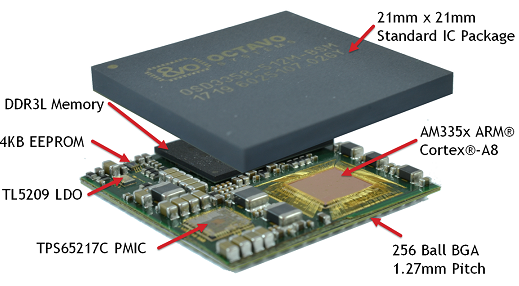
- the Beaglebone is ultra-reliable , and there are awesome SIPs with CPU, RAM and FLASH integrated in a single BGA IC. Octavo Systems really made miracles, but prices are still high and you still have to add WiFi
- Olimex boards are really nice, but while cheaper they have the same drawbacks of the other SBCs based on TI chips.
- OrangePI boards are incredibly cheap and have multiple connectivity options! I spent *a lot* of time testing and debugging their Allwinner H3 based boards, and while they work great for your average mediacenter or weekend project, they're definitely not reliable enough for long-term, 24/24 use. Too bad - they had the perfect price point, great features and power, maybe even too much...
- The gorgeous ARIETTA-G25-V is Made in Italy with high quality and reliable components. I used it for a project in the past, and I really liked it. Unfortunately, its price is still a bit over my budget, especially after adding WiFi and Ethernet.
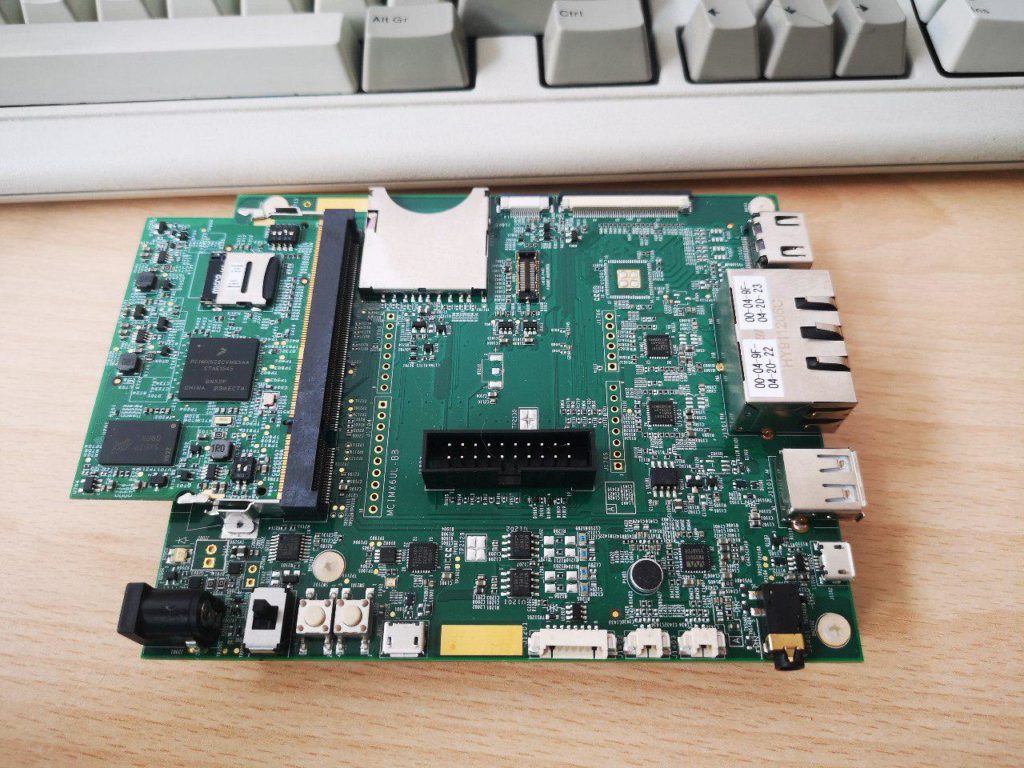
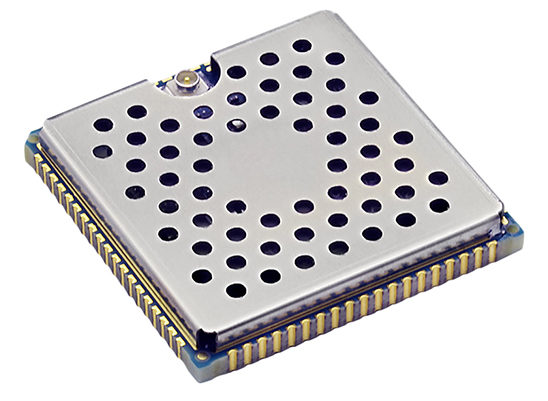
- Freescale/NXP chips are very cool and the choice I'd make if I had more budget or the time to layout an debug complex multi-layer boards. My favorite one for this project was the i.MX6 UL chip: plenty of peripherals, great Yocto support, plenty of third party modules. Unfortunately modules are still quite expensive, but I was really impressed by the power/performance/price/size ratio of the Digi parts:
![]()
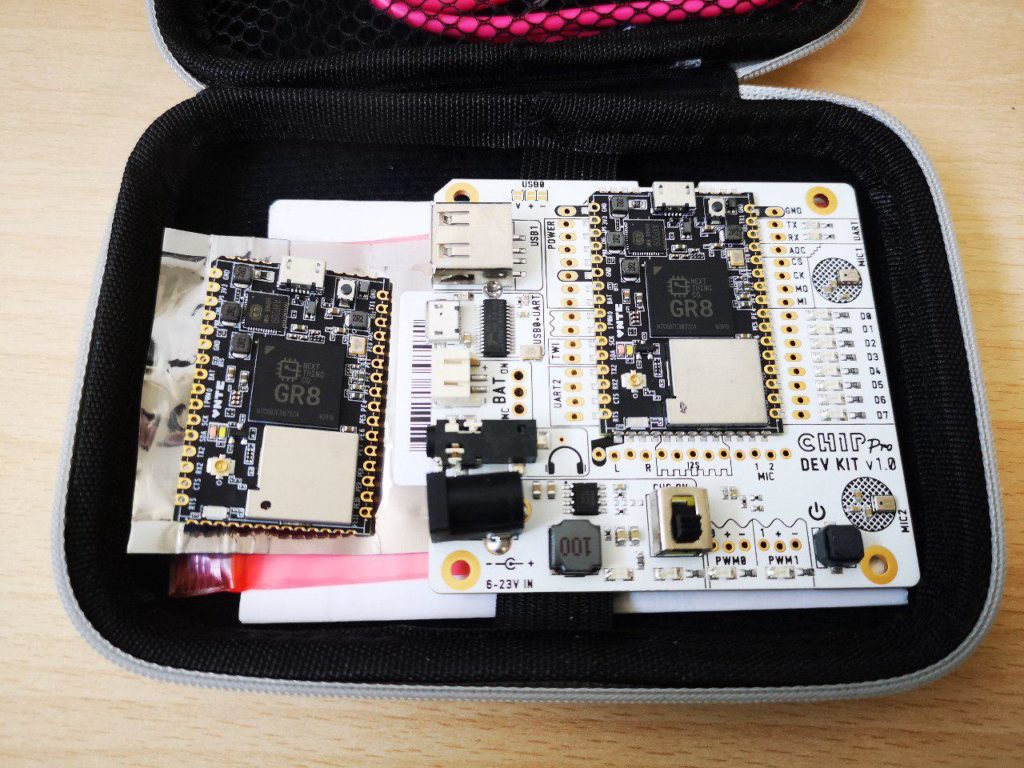
- The GR8 C.H.I.P. was a great choice, but unfortunately the project died. I'll treasure my board as a memento mori.
![]()
What these boards have in common is that they're way overpowered for the task, and priced accordingly. Trying to find a better option, I missed the most obvious one that was hanging under my nose and I was already using daily:
Routers!
I already had a lot of experience with the amazing OpenWRT project. I flashed every single router I've ever owned, built NASes, battery powered drop-boxes to crack WiFi passwords with Reaver, network bridges and more... Routers are great, are very powerful for any application not requiring graphics, are cheap, efficient and very well connected by definition. It's weird I don't see many projects using them around HackADay, kids these days only use those pesky Raspberries... Long gone are the glorious days of the WRT54GL!
One of the best platform I played with was the GL-MT300N-V2, very reliable and with plenty of CPU power (MIPS24KEc @580MHz), flash (16MB) and RAM (128MB), WiFi, Ethernet, USB host, UARTs, a nice enclosure and certification, for a very low price! It's very well supported by the tiny, rock-solid and security focused OpenWRT Linux distro.
It's based on Mediatek MT7628, a brother of the MT7688AN. You may have never heard of them, but they're the chips powering a lot of maker platforms, sometimes combined with a microcontroller, like the Arduino Yun, the ingenious WRTnode2R with an STM32F103, the LinkIt Smart7688 with an optional Atmega32u4, the VoCore2, the Onion Omega2, the WiDora Neo and the ReSpeaker. Here's some stuff I tested:
What I love even more of this platform is that after prototyping your design with one of the aforementioned boards, there are many cheap module options that you can easily drop in your design and just work as long as you provide a stable 3.3V supply. At the time, the two best options available were the HLK-7688A and the SKW92B. I tested both, and decided for the HiLink module as it's smaller and shielded. Recently Onion introduced the Omega2S+ in a similar form factor; if it were available at the time, I would probably have chosen this part. I will definitely switch to them after the first batch that already went into production, they're slightly more expensive but it's important to reward who contributes to the community.
In the meantime, my experience with the HLK-7688A has definitely been positive. Everything worked on first try, except for a big problem: I got the 32MB flash version with a Macronix MX25L25635E that has some issues with 3bytes addressing. Basically, the system sets the flash addressing to 4bytes to use the whole 32MB flash, but the MTK7688 is configured for 3b booting. This is a problem because after a soft reboot the flash would stay in 4b mode and not switch back to 3b, so you have to do a hard reset to reboot correctly. There are a few workarounds for this:
- leave everything at 3b, and only use 16MB of flash. But I paid for 32MB!
- run a script to reset the flash to 3b just before rebooting, but that works only if we do a "controlled" reboot - neither practical nor safe
![]()
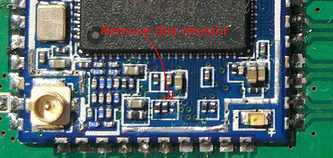
- remove the shield and a tiny pull-down resistor inside the module and add an external pull-up to configure the MTK to always use 4b mode. Impractical to do in production at scale.
- add a stronger pull-up resistor at the relevant pin. This kinda worked within a particular range of resistor values, but sometimes it randomly didn't work at all. Too risky for production.
- add an external watchdog that controls the enable pin of the 3.3V regulator, performing a power cycle when necessary
Implementing the last option made a lot of sense for other reasons too, so I went with it. At the same time I tried contacting the manufacturer. I didn't even expect an answer, but incredibly they followed up and quickly fixed their module by replacing the flash with a Winbond part with a different command set that fixed the problem. I ordered a bunch of these news modules to test and they worked! I left the power enable workaround in place anyway, because you never know. Transistors are cheap.
OpenWRT
Using a router firmware has a lot of advantages. First of all, it's extremely compact and efficient: the base system is only 4MB. It's also very well maintained, with constant releases and quick patches for any new vulnerability. After all, you want your router to be as secure as it gets!
And, of course, it's extremely focused on connectivity. This allowed me to easily implement an Access Point mode, that is very useful for EV owners with an underground garage. This way users can monitor the state of charge of their vehicles even if the cars GSM module has no signal.
OpenWRT has a great build system with a lot of very useful packages already ported to the platform. A nice feature is the the stm32flash and avrdude integration to program microcontrollers using the MTK GPIOs. Updates are easily deployed with the internal system; the user is safe from mistakes as the important parts are read-only, and the file system is overlaid to another partition to easily reverse any mistake . I developed scripts to check updates signatures and encrypt communication with the remote server.
We'll talk more about OpenWRT in a dedicated article, where I'll show you how to compile the firmware image, use UBUS for IPC, DTS files and a few tricks I learnt along the way. In the meantime, here's my fork of the distro with the custom files for my module.
 Mastro Gippo
Mastro Gippo







Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.
I have one tip for a OpenWRT project which is quite cheep, has exposed GPIO pins, USB3.0, wifi and ethernet: https://www.turris.cz/en/mox/overview/
Are you sure? yes | no
Wow again! I was just thinking I could press a router into a new role of EVSE since they have most of the pieces required and are well documented! The one company I worked for I created a solution that used flashed routers to setup a VPN and required port forwarding so that equipment installed at customers sites could be remotely monitored. Works really well and provides the end users with up to date information on their equipment.
Are you sure? yes | no