The Problem
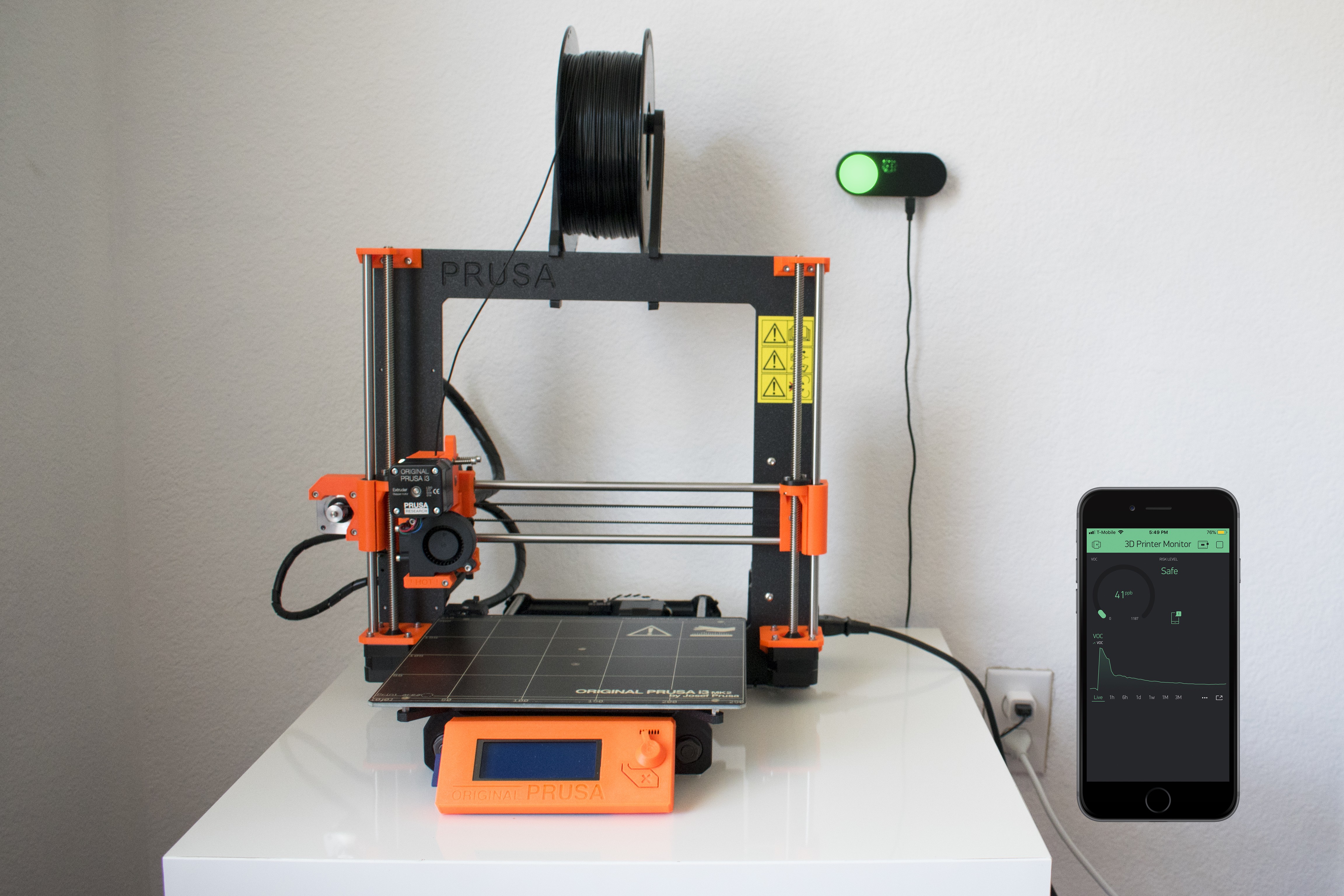

3D printing has become increasingly popular and accessible. As they become more desktop-friendly and affordable, they are now making their way into residential homes and classrooms.
But is 3D printing really safe in a home environment? 3D printing is a relatively new technology, and its danger is often overlooked. The research on the toxicity of 3D printing is few and far between, but one thing is certain: harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are emitted during 3D Printing.
One of the most toxic VOCs released during 3D printing is formaldehyde - a known human carcinogen. It's released during the melting of ABS plastic, which just happens to be one of the most popular 3D printing materials.
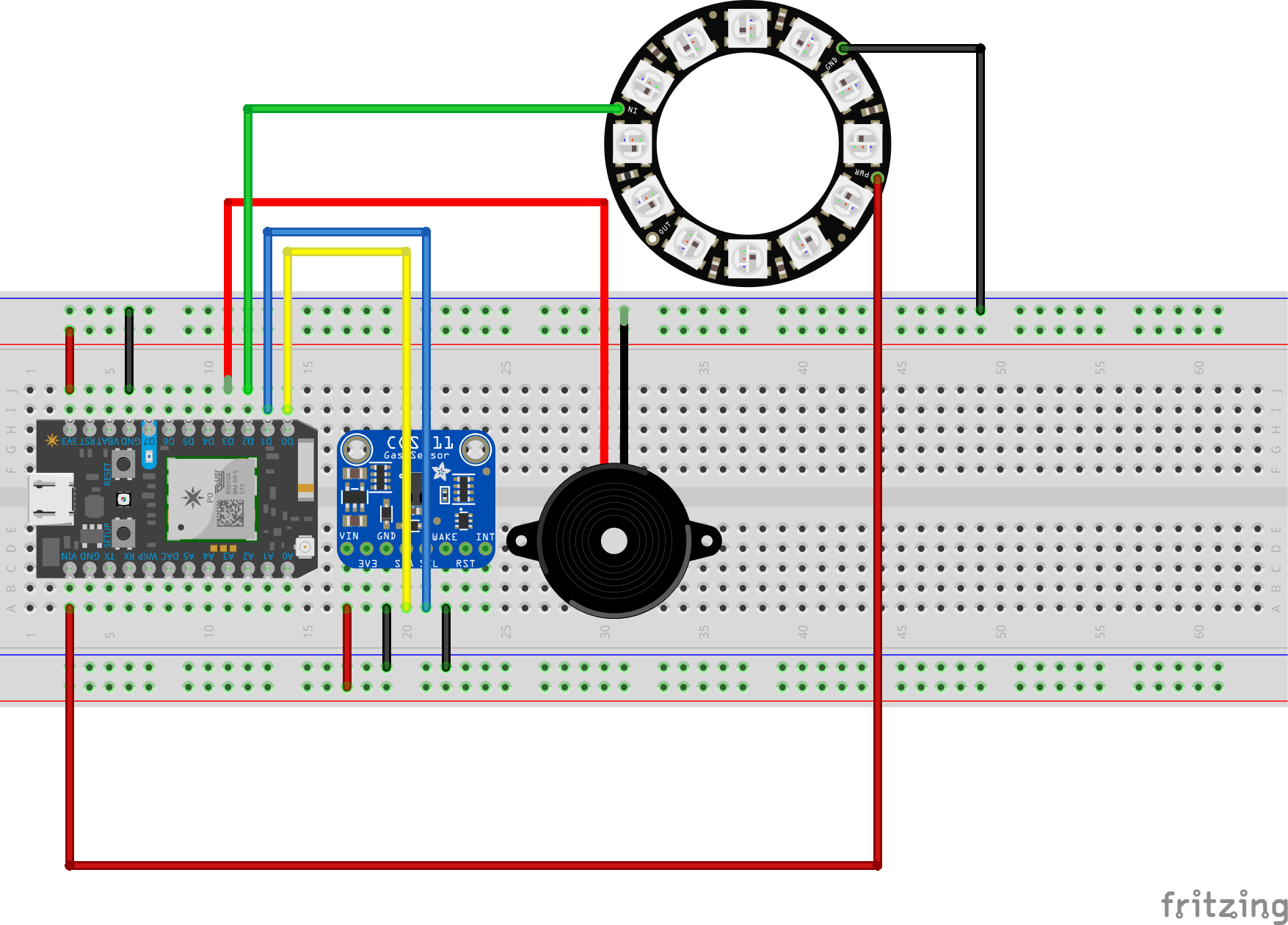
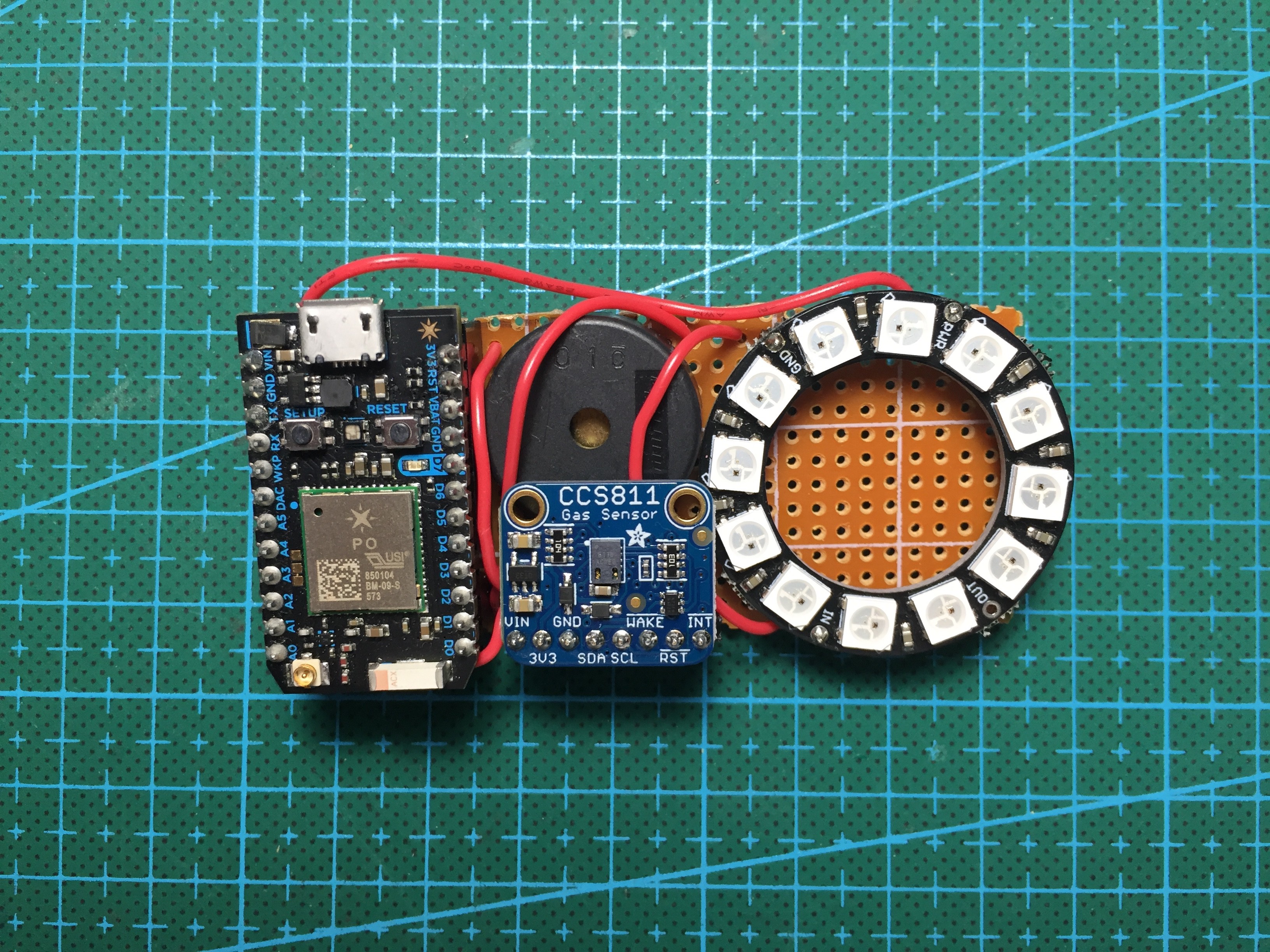
This monitor serves two purposes: to alarm the user when the workspace environment becomes toxic and collect VOC emission data.
To collect emission data, the sensor of choice is CCS811, a hot-plate MOX sensor capable of detecting a wide range of VOCs, including formaldehyde. The detected concentration is transmitted via Wi-Fi to a smartphone app, which displays and plots the data.
To inform the user of the toxicity, I used this guideline to create 3 risk levels based on the concentration of VOCs: low, moderate, and high. When the risk level becomes moderate, the light indicator will change from green to yellow. This is also accompanied by a notification to your phone, which tells you to open a window and ventilate. When the risk level becomes high, the indicator will turn red. This time, in addition to the phone notification, the onboard buzzer will start buzzing to alarm the user to leave the area.
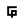 Gary Peng
Gary Peng









 Gianlu Owen
Gianlu Owen
 robert
robert
 Jordan French
Jordan French
I have a difficulties to put that program in Arduino IDE. Could you advise me please?