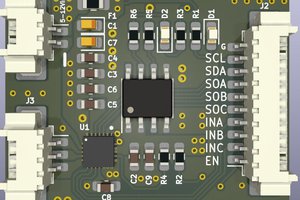
About Project
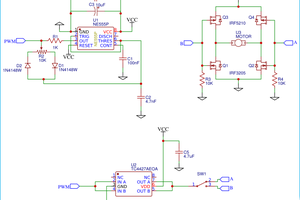
Transistor
Here transistors are utilized to direct current from Vin pin of Arduino to relay which is managed utilized a push-button connected from digital pin to the base terminal of the transistor.
Arduino Purpose
It offers the amount of current required to turn on the relay also the transistor.
MOSFET
It is needed to handle the speed of the motor. The PWM value of voltage determines the speed of the motor.
Current Calculations:
The resistance of the relay coil is estimated utilizing relay which turns out to be = 400 ohms
Vin pin of Arduino gives = 12v
So current require to turn on the relay = 12/400 Amps = 30 mA
Working of the bidirectional motor
When no pushbutton is pressed:
In this case, no current flows to the base of the transistor, hence the transistor remains off behaves as an open switch.
When one push button is pressed:
Some current runs to the base of the transistor via a pressed push button which turns it on. Instantly current simply flows to the relay coil from Vin pin via this transistor which turns this relay (RELAY A) on and the switch of this relay is thrown to NO position. This is the clockwise motion of the motor.
When another push button is pressed:
Here other relay turns on. Now current simply flows to the relay coil from Vin pin through the transistor which turns this relay (RELAY B) on and the switch of this relay is driven to NO position. This is the anticlockwise rotation of the motor.
.When both pushbuttons are pressed:
Here current moves to the base of both transistors because of which both transistors turn on (acts like a closed switch). And thus both relay is now in NO position.
Controlling the Speed of DC Motor:
MOSFET is switched on and off at high PWM frequency voltage and since the motor is attached in series with the drain of MOSFET, the PWM value of voltage defines the speed of the motor.
 hIOTron
hIOTron

 Jithin Sanal
Jithin Sanal