Intro
One of the top environmental problems is food and water Insecurity.
Rising temperatures and unsustainable farming practices has resulted in the increasing threat of water and food insecurity.
Globally, more than 68 billion tons of top-soil is eroded every year at a rate 100 times faster than it can naturally be replenished. Laden with biocides and fertilizer, the soil ends up in waterways where it contaminates drinking water and protected areas downstream.
Furthermore, exposed and lifeless soil is more vulnerable to wind and water erosion due to lack of root and mycelium systems that hold it together.
With the global population expected to reach 9 billion people by mid-century, the FAO projects that global food demand may increase by 70% by 2050.
If we also include industry needed to support current food production, including farming, packaging, transport, storage etc. all of these elements contribute to the list of the top environmental problems, including:
- Food waste
- Plastic pollution
- Air pollution
Vertical farming
Vertical farming is the practice of growing crops in vertically stacked layers.
It often incorporates controlled-environment agriculture, which aims to optimize plant growth, and soilless farming techniques such as hydroponics, aquaponics, and aeroponics.
Current applications of vertical farming coupled with other technologies, have resulted in over 10 times the crop yield than would receive through traditional farming methods.
The main advantage of utilizing vertical farming technologies is the increased crop yield that comes with a smaller unit area of land requirement. The increased ability to cultivate a larger variety of plants at once because plants do not share the same soil. Additionally, plants are resistant to weather disruptions because of their indoor placement.
The main disadvantage is cost of setting up a vertical farm, application and space specific implementations, system rigidity, and no modularity. Vertical farms also face large energy demands due to the use of supplementary light like LEDs.
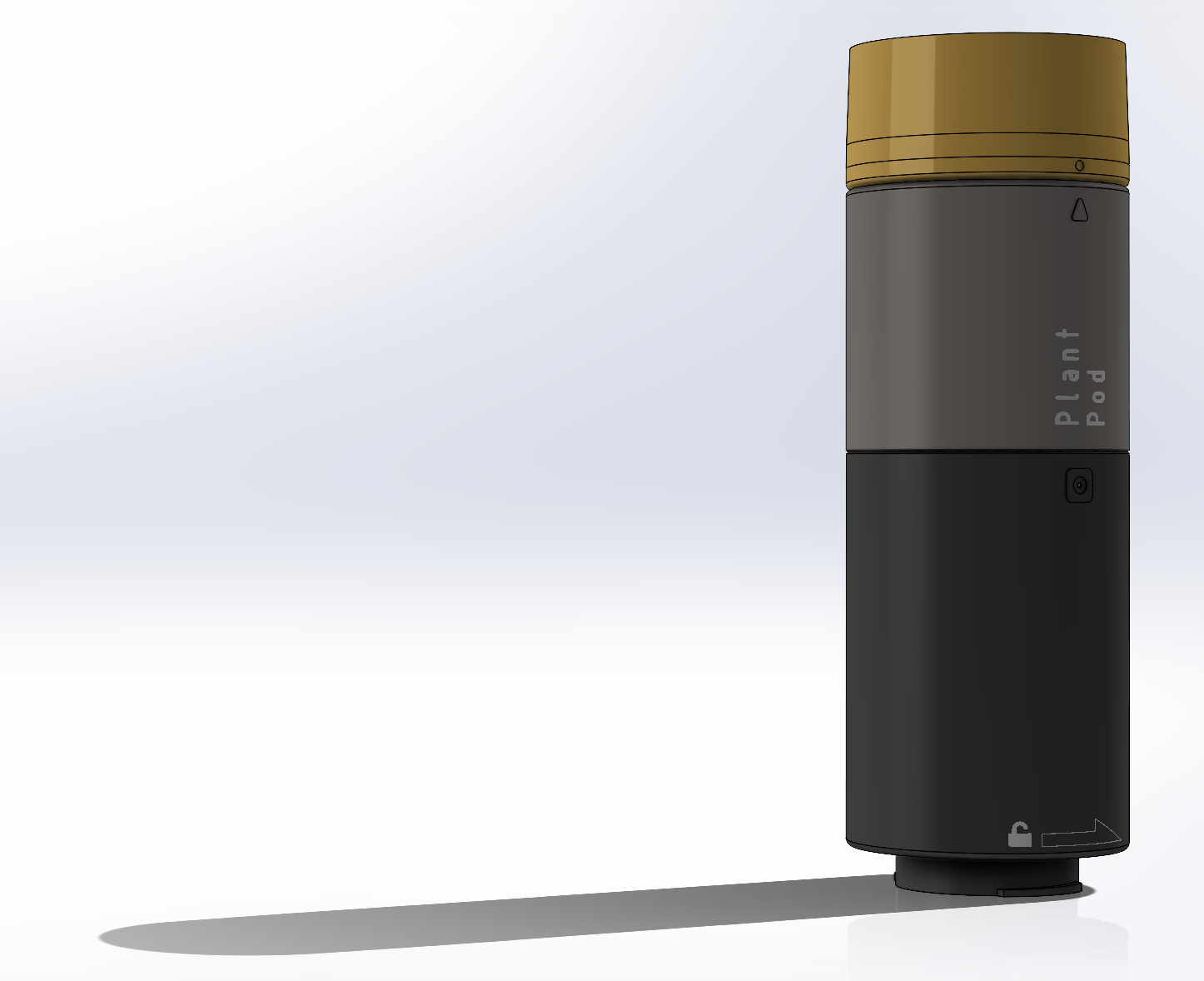
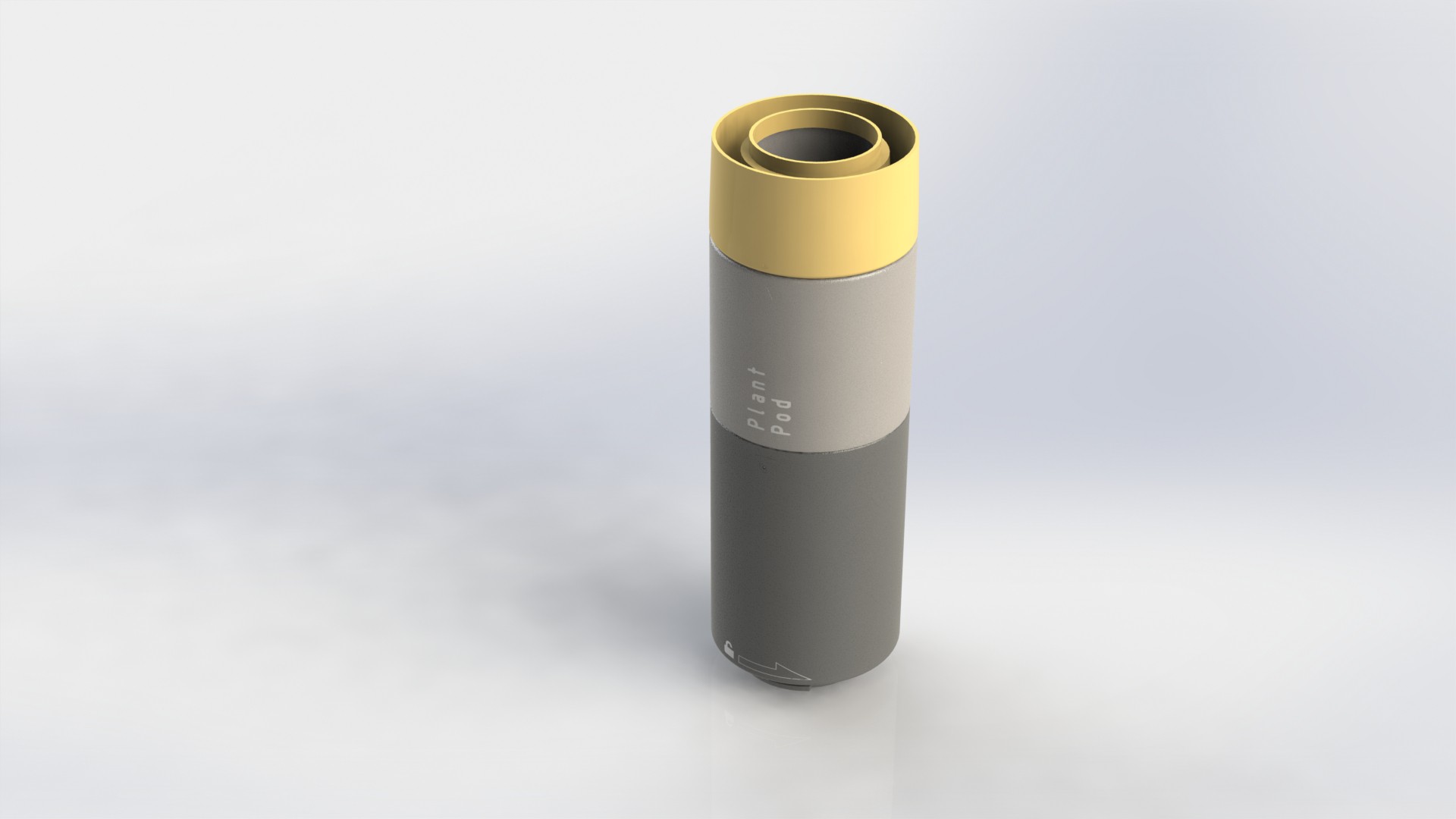
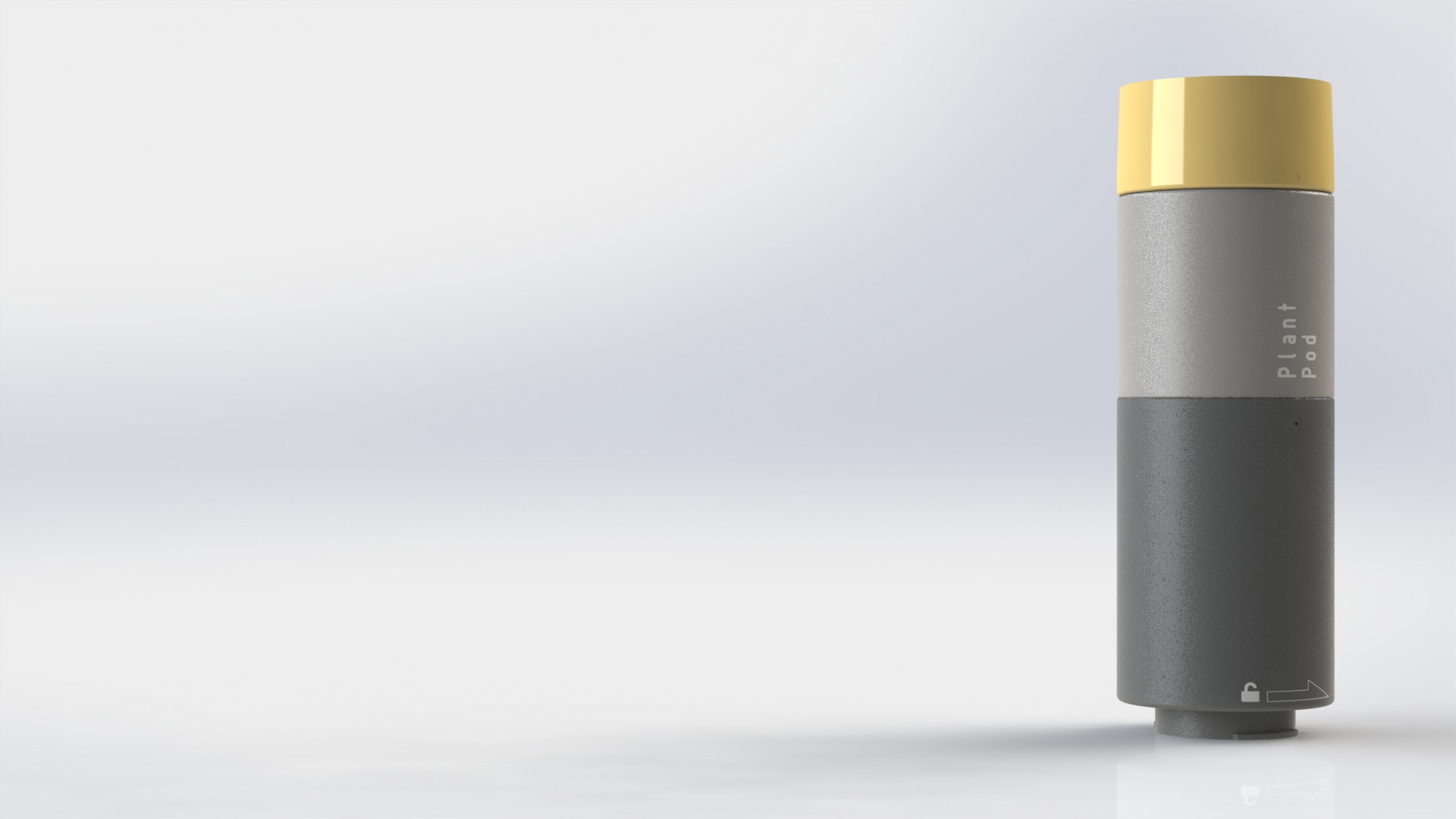
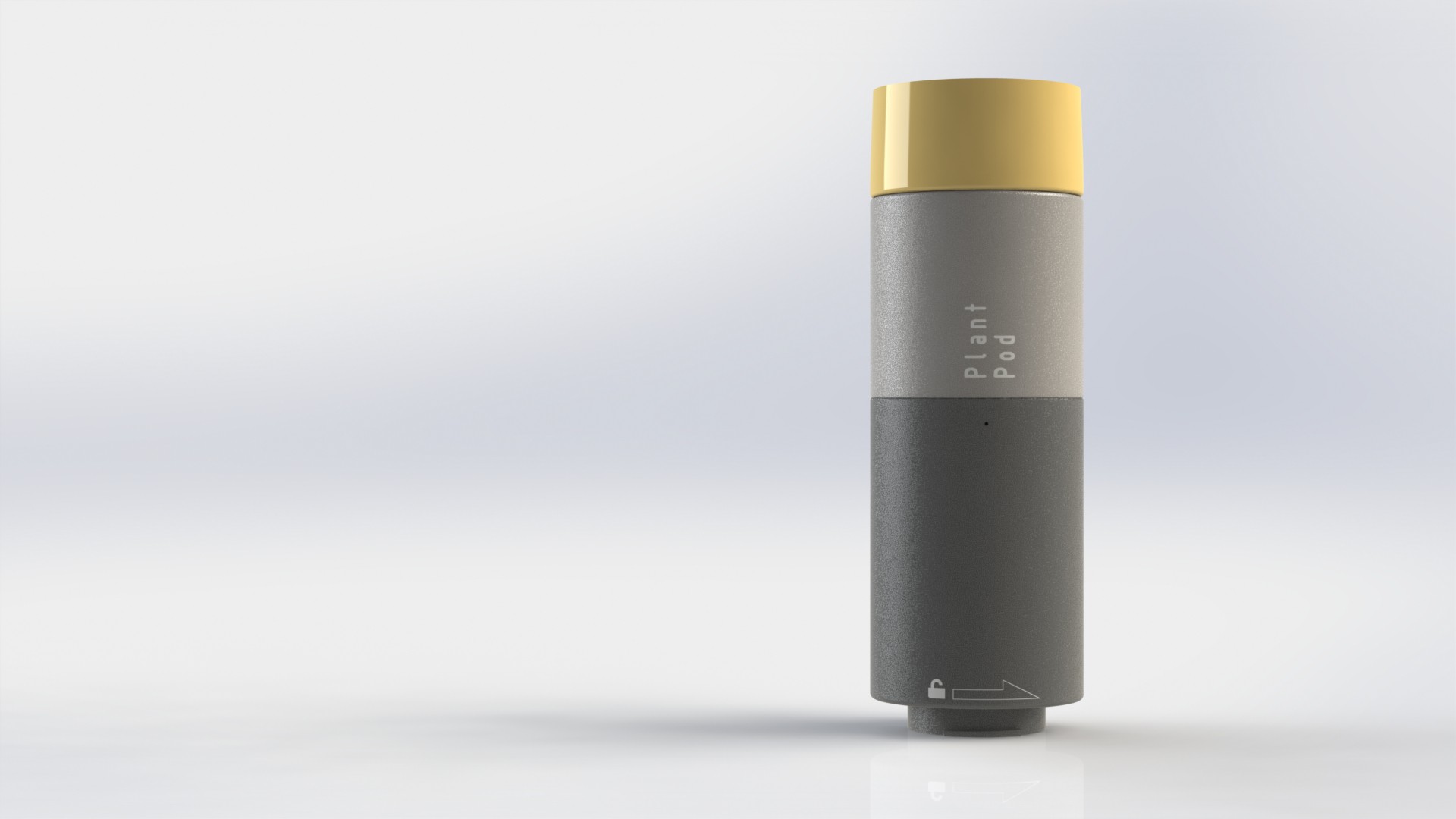
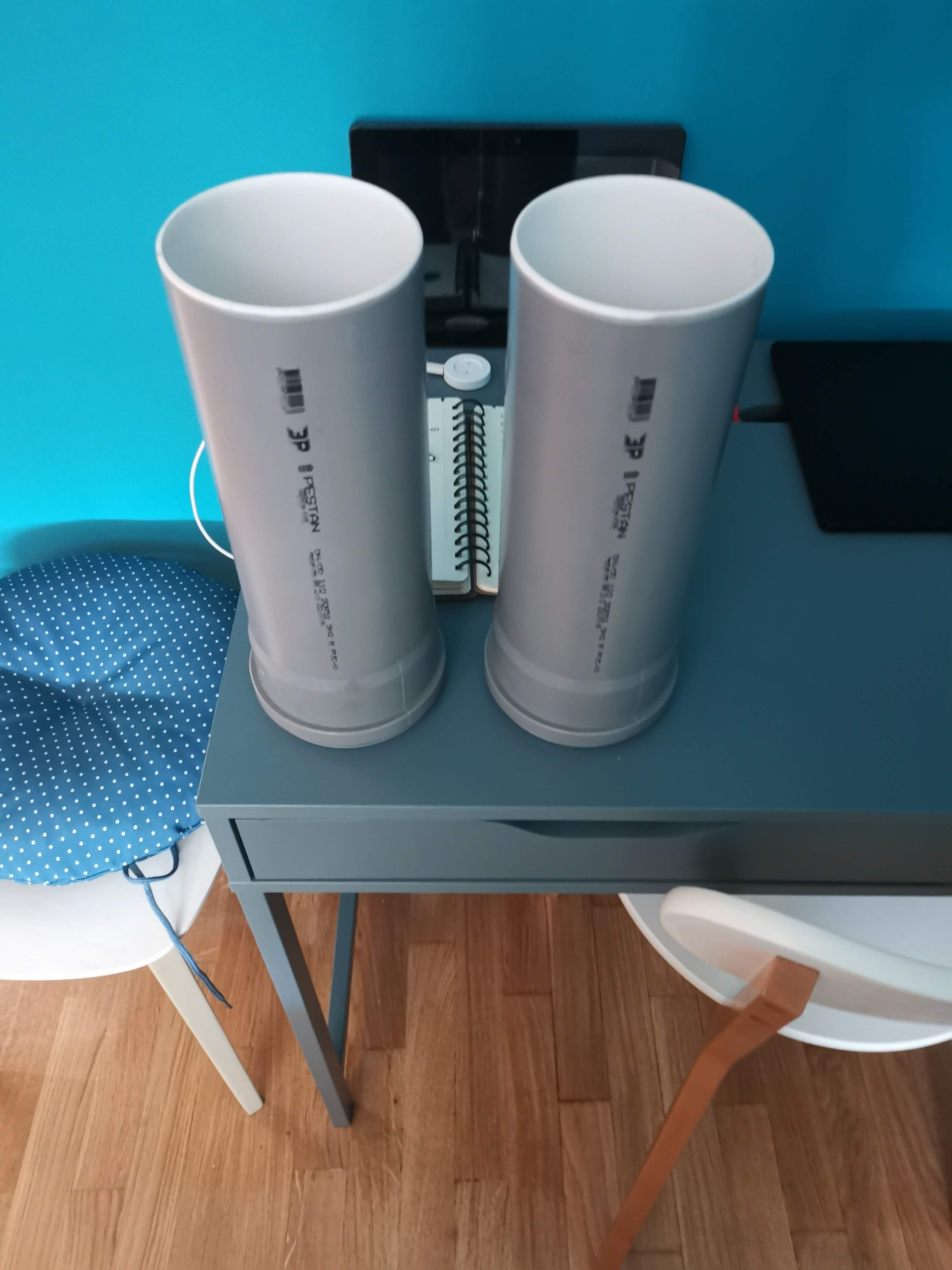
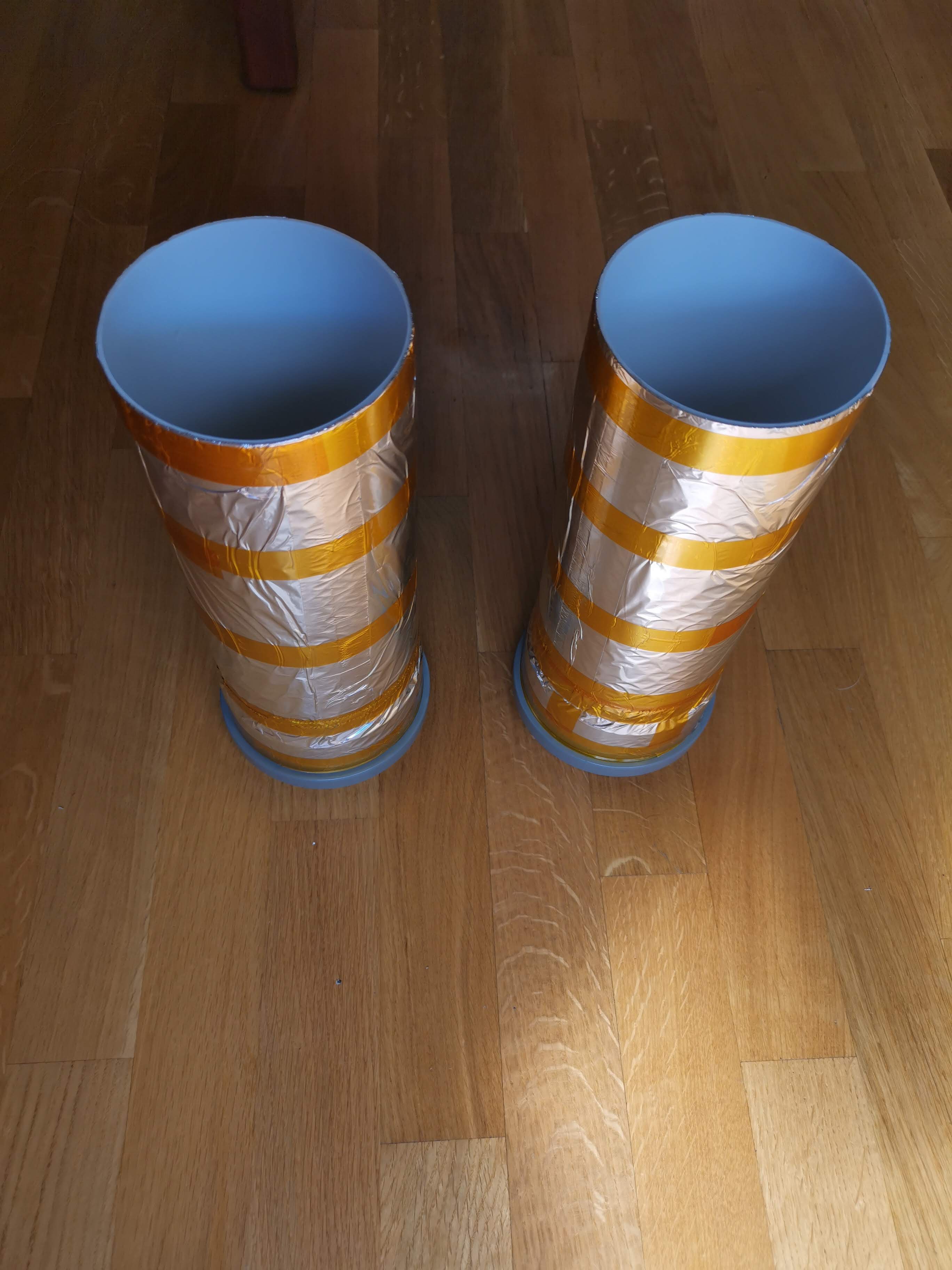
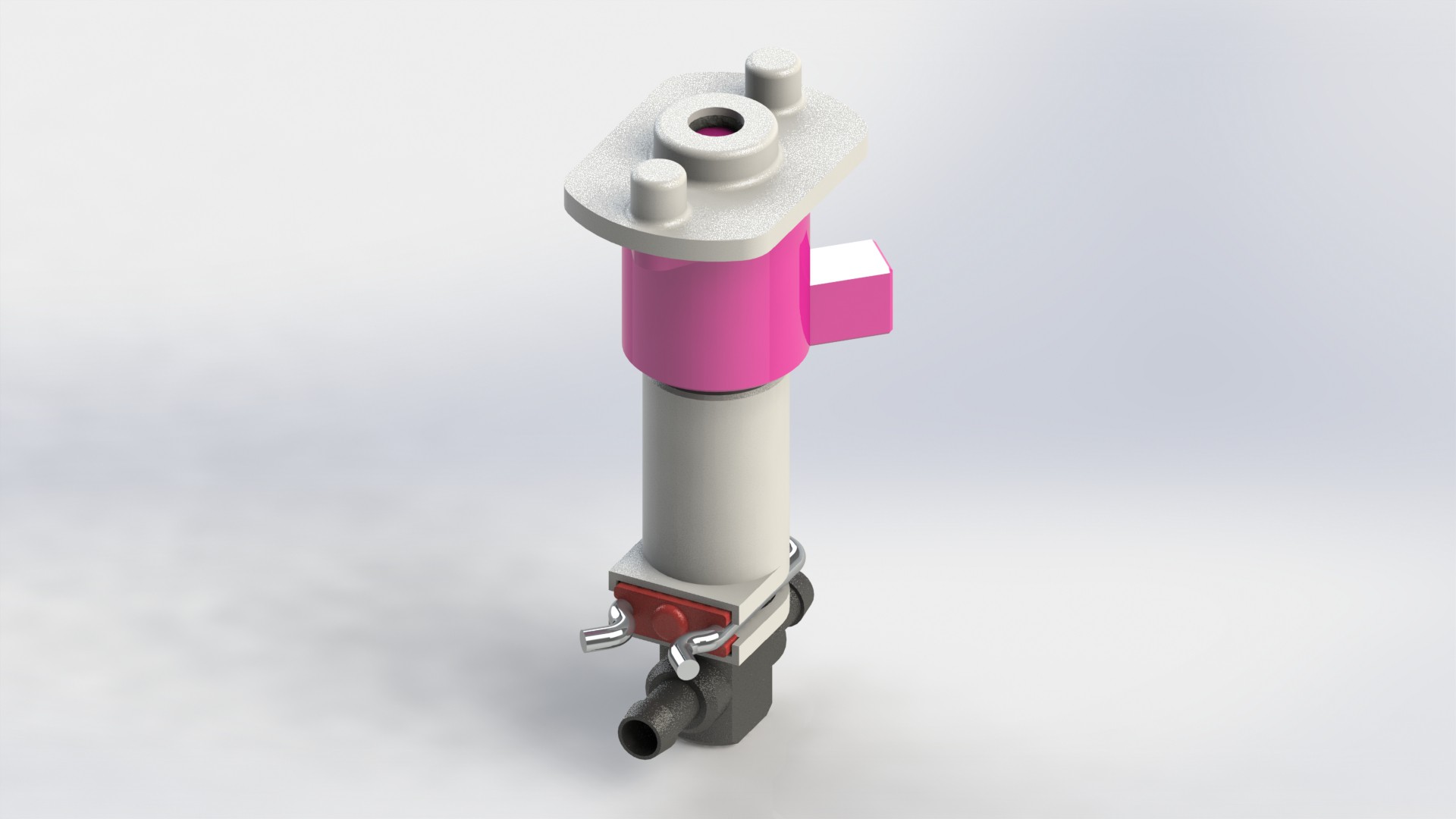
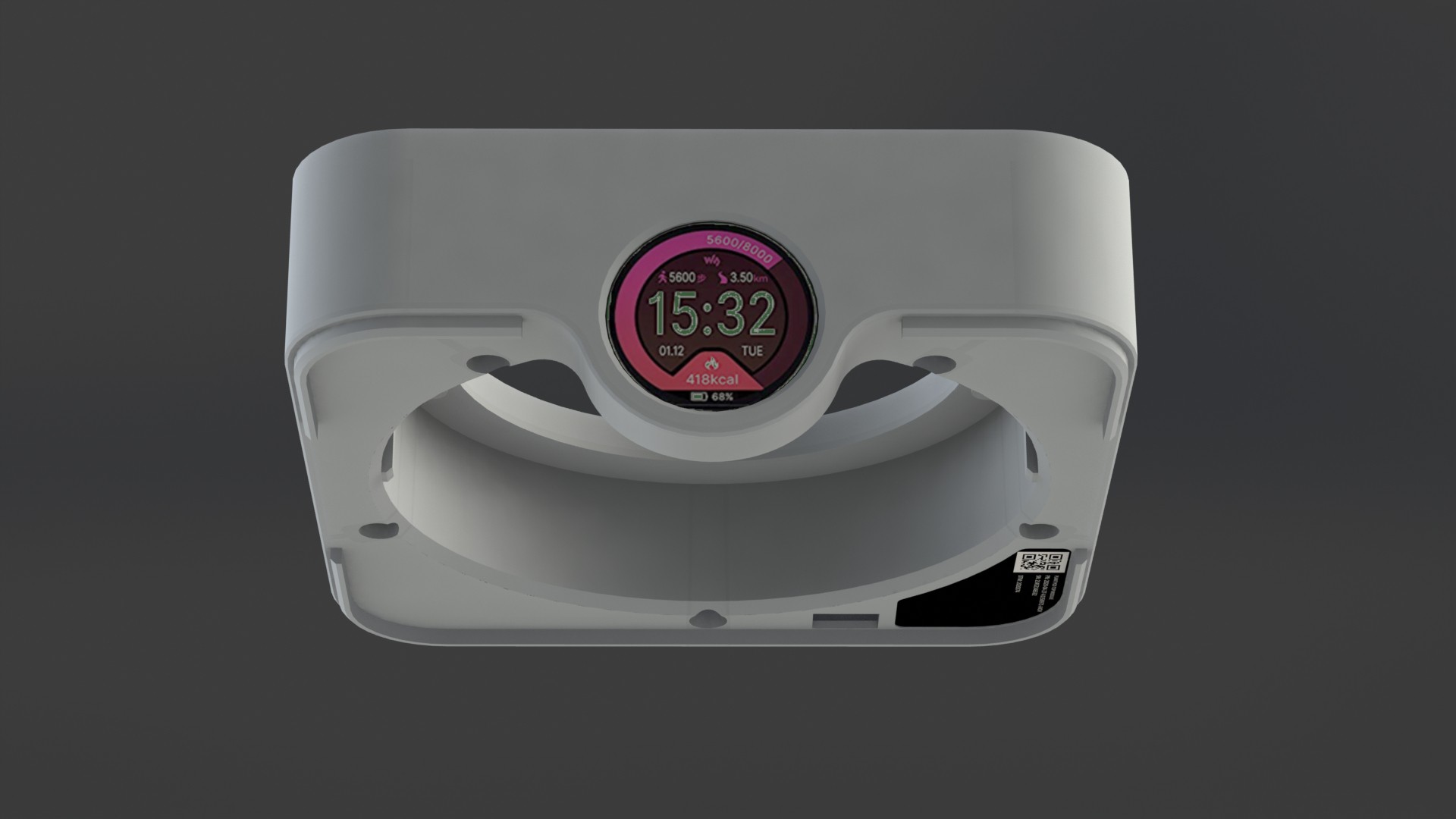
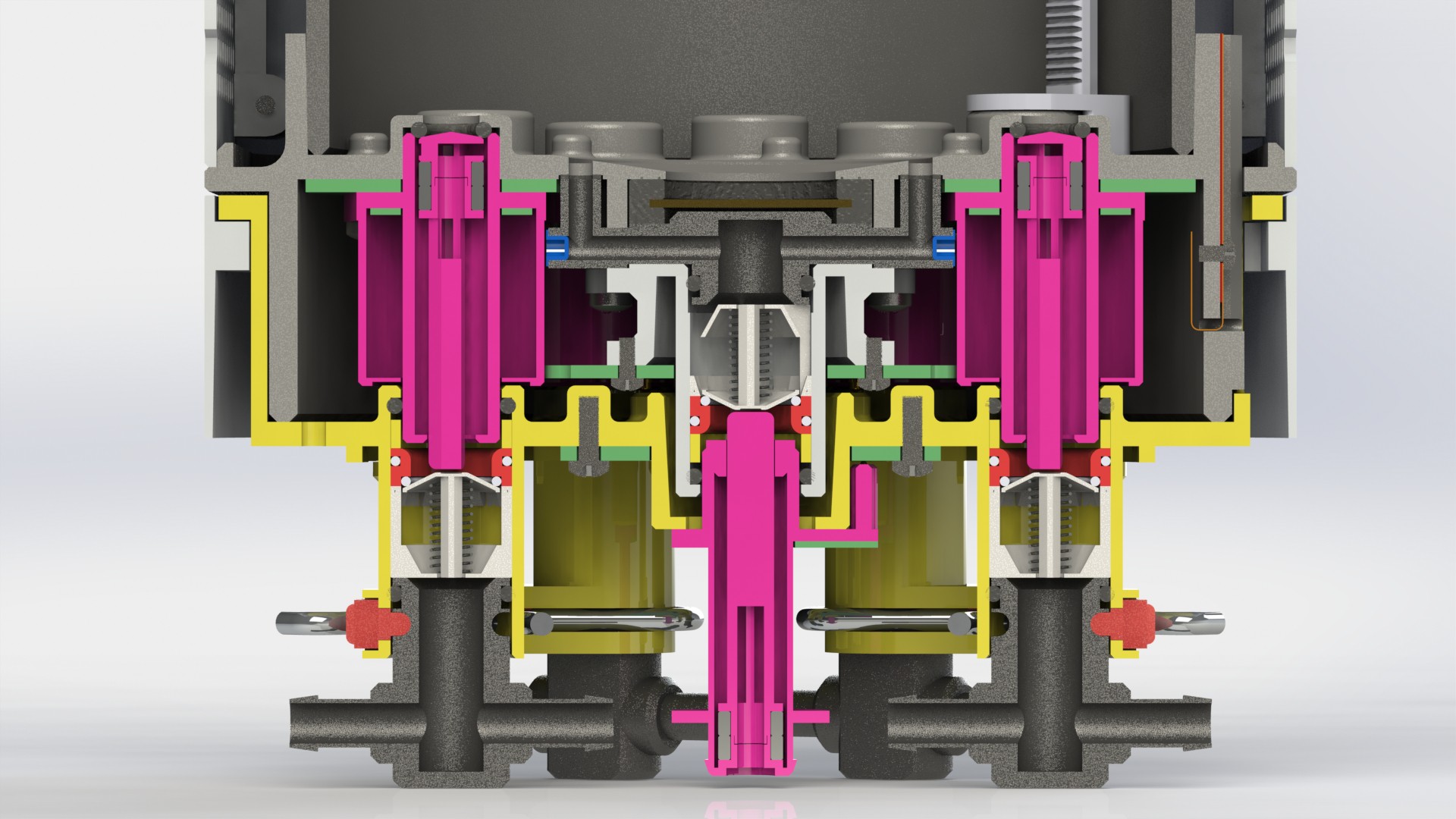
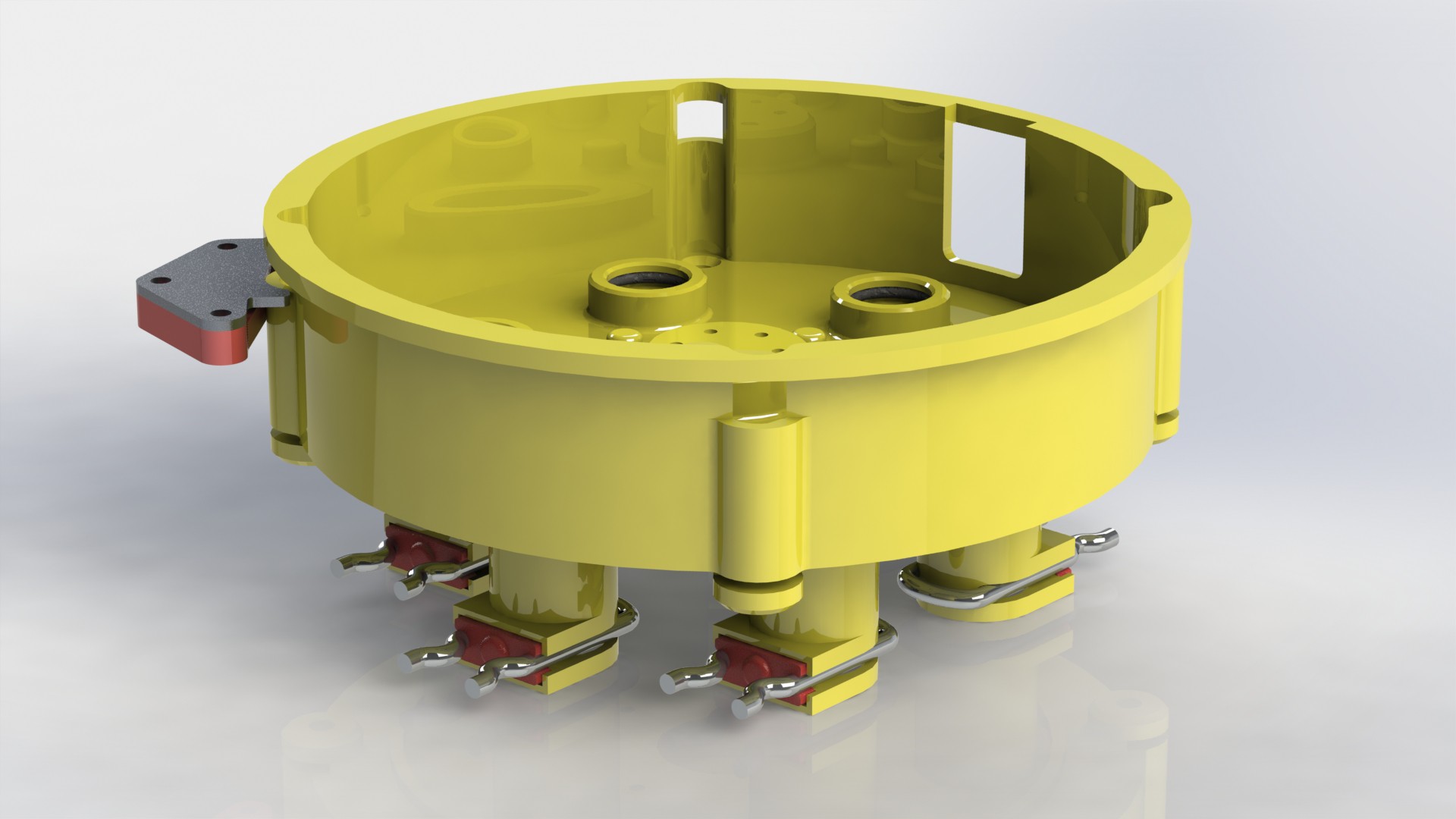
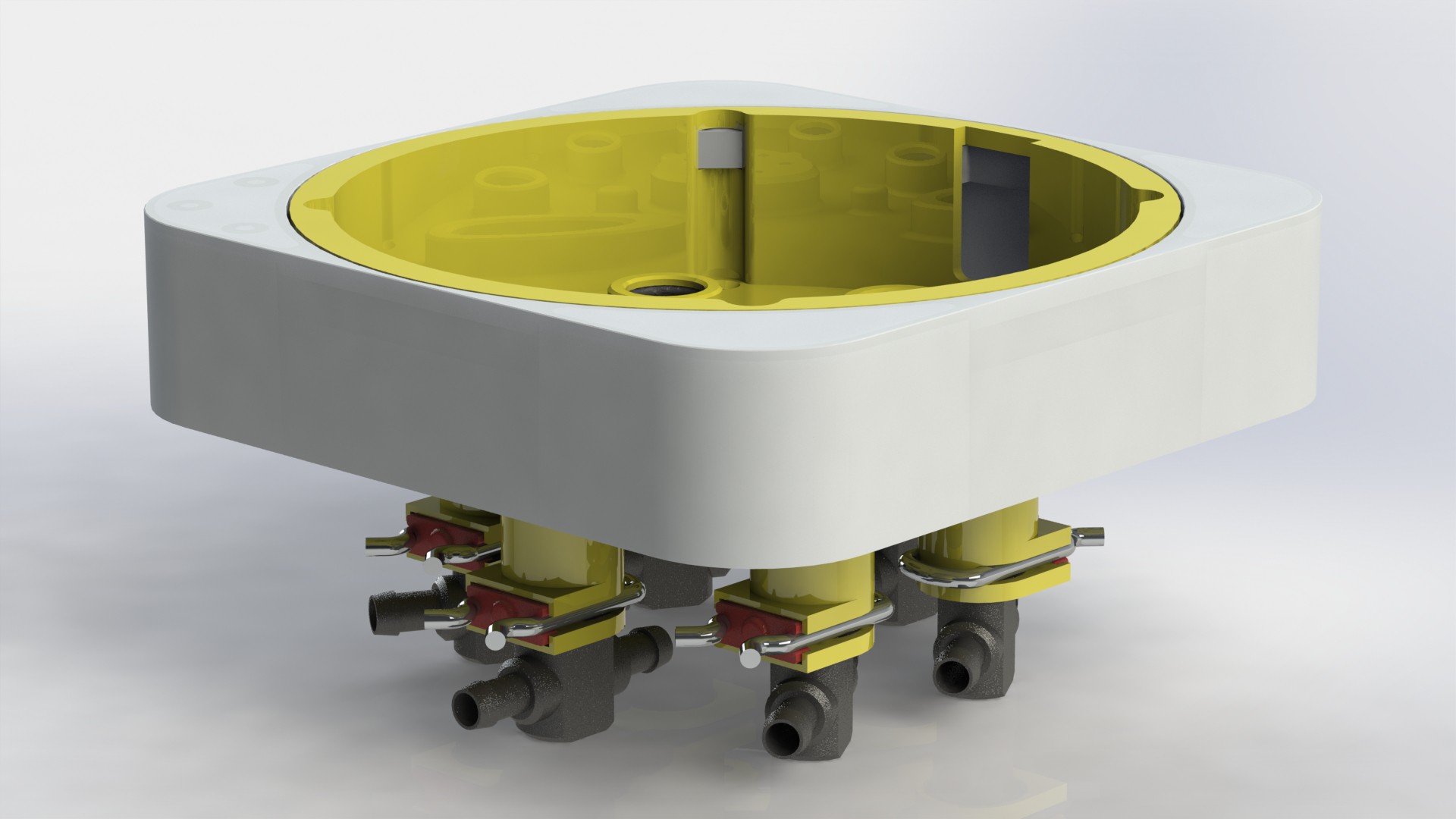
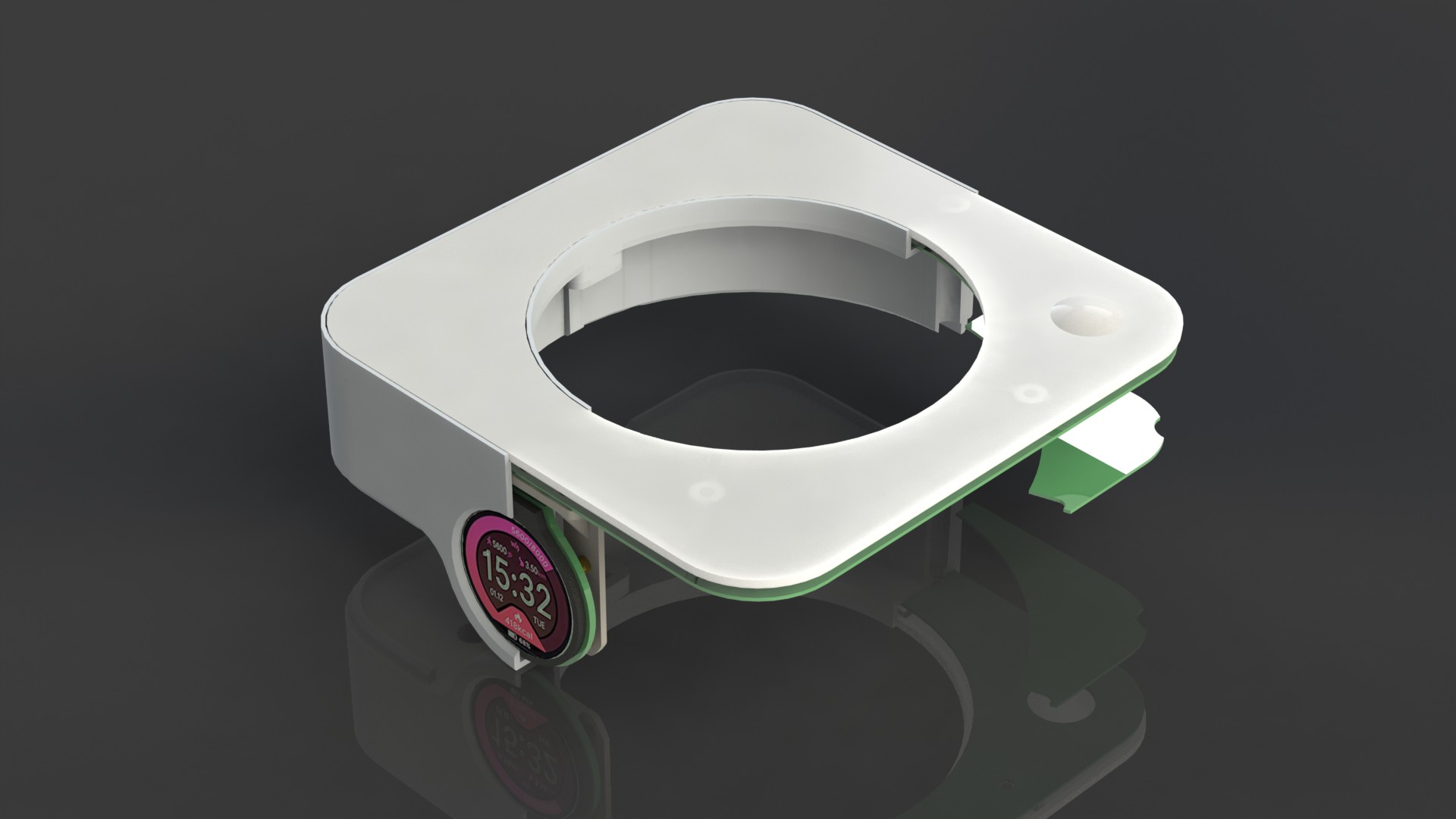
Plant pod
Main goal of the Plant pod is to provide low cost, scalable, modular and flexible solution for vertical farming. Plant pod device is designed to be plant per module system, capable of fast and flexible implementation, independent of chosen soilless farming techniques, and even allow mixing of these, depending on the specific plant, or rather group of plants.
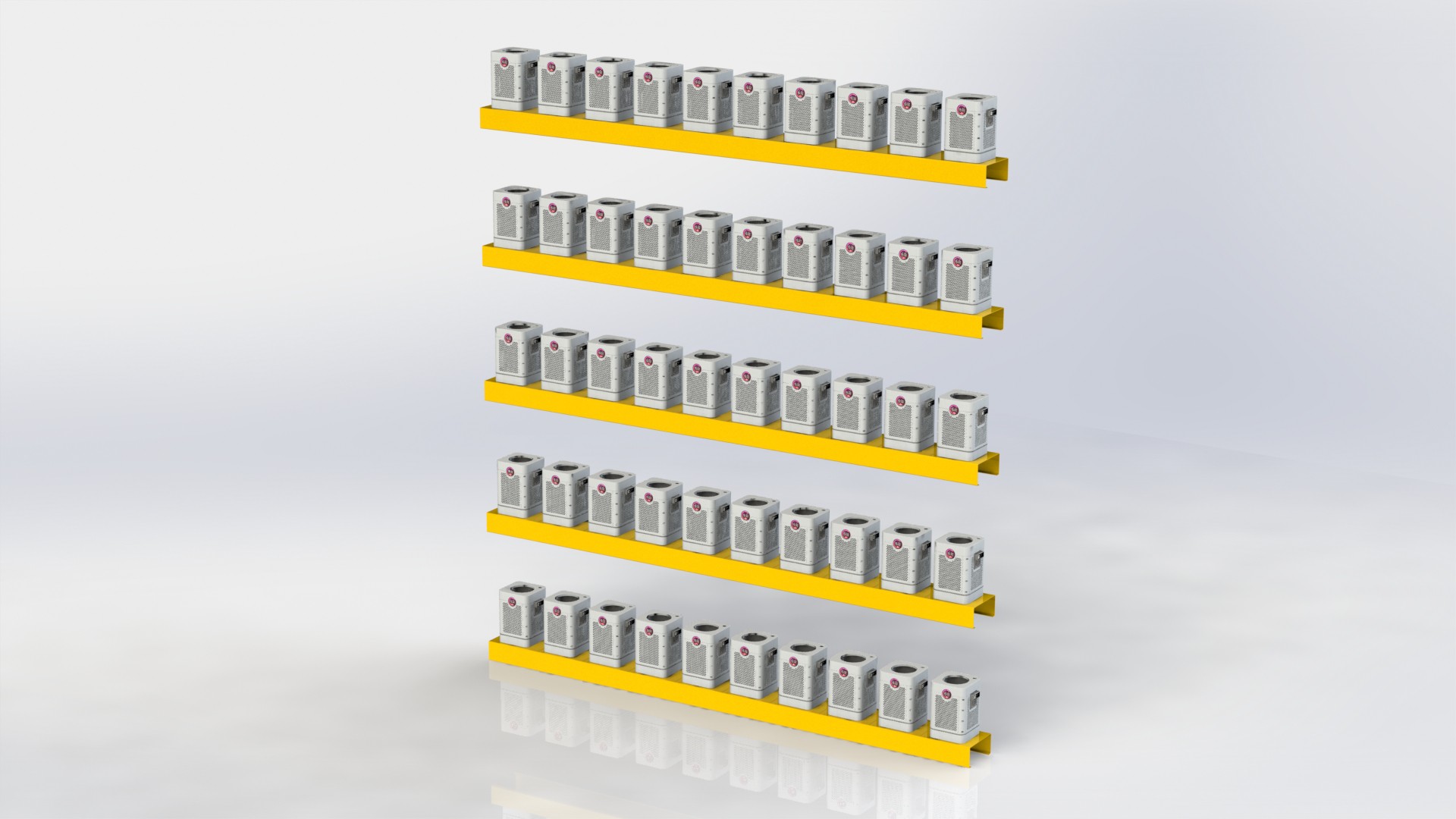
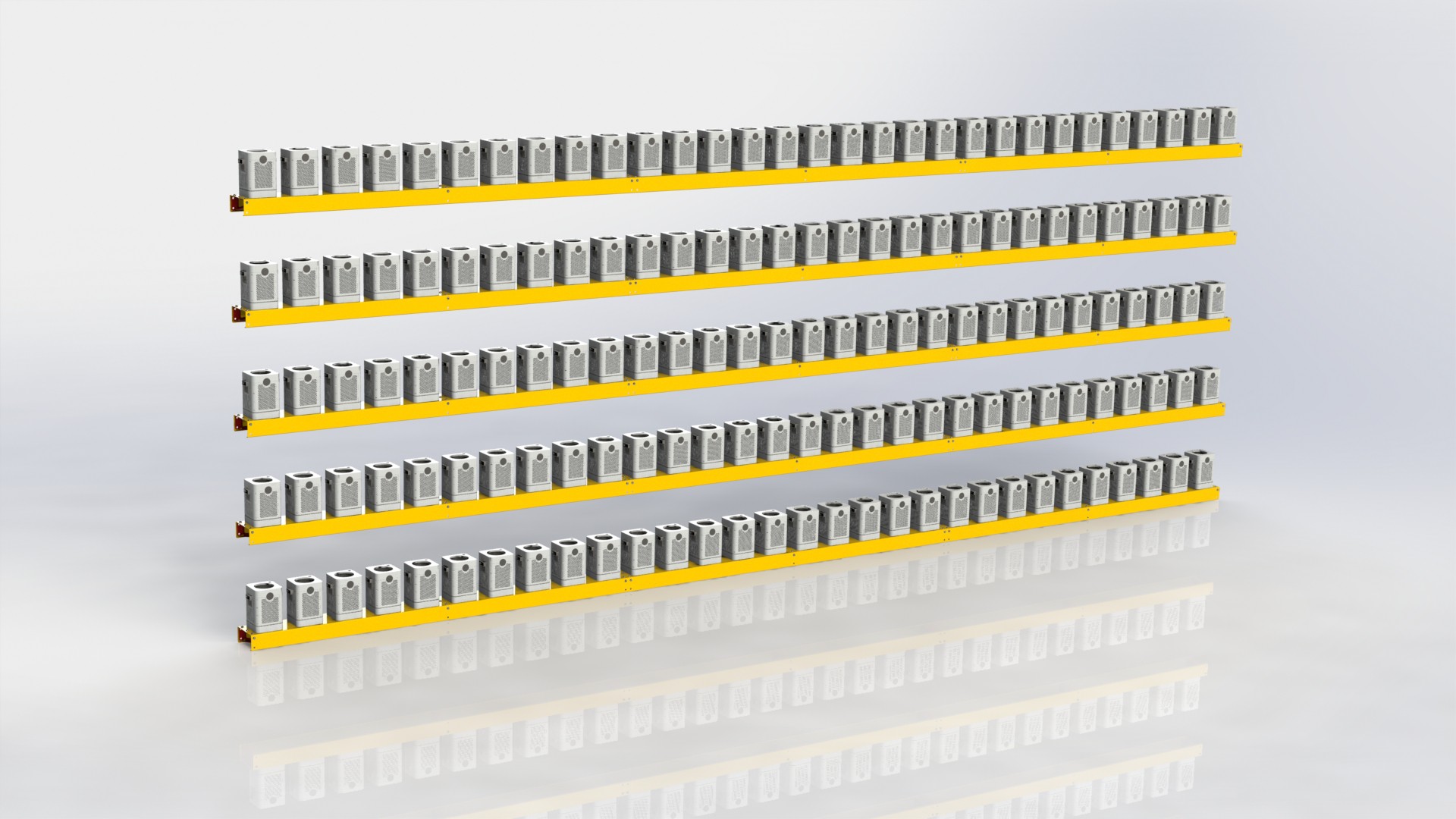
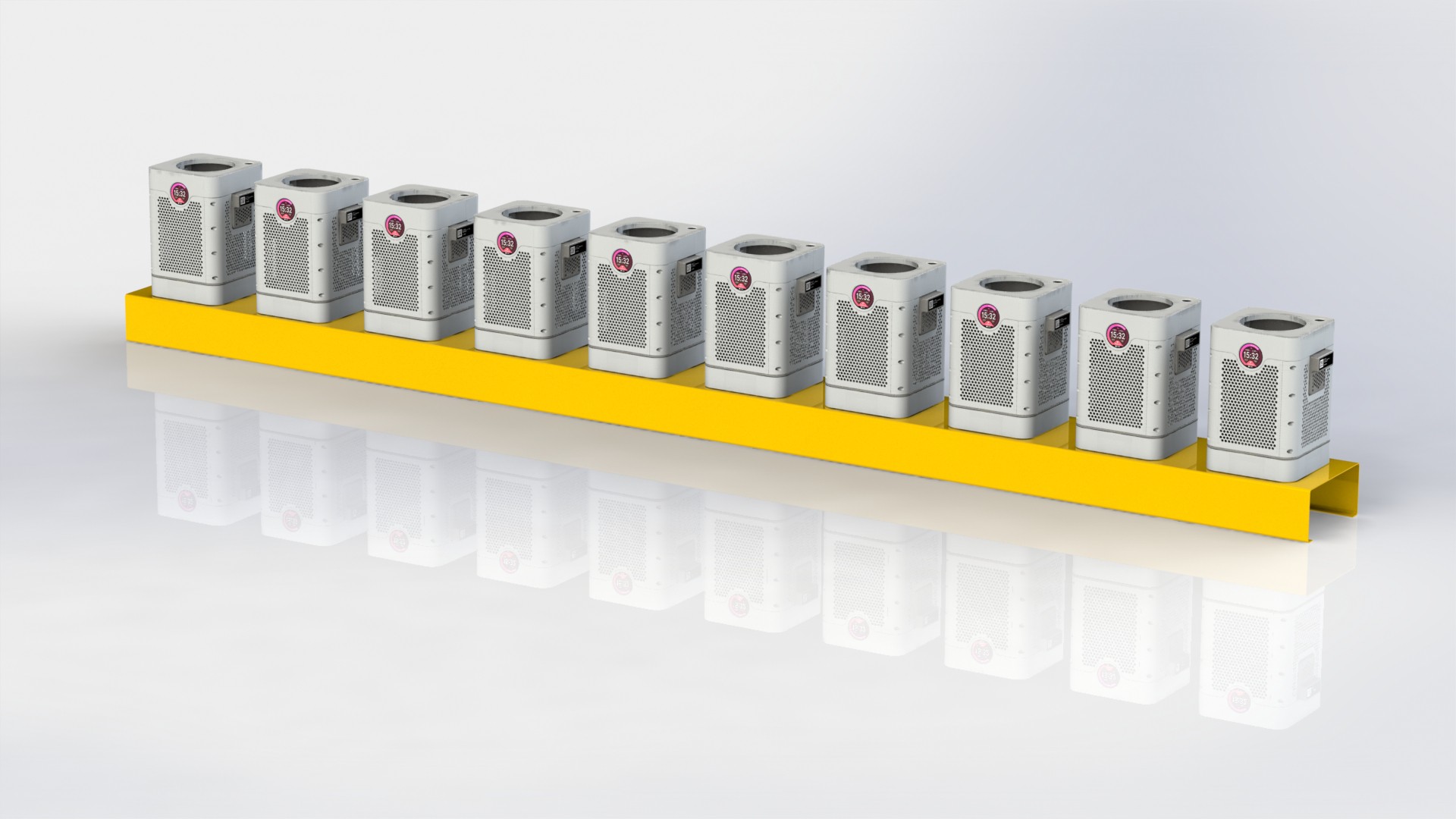
This kind of solution can provide fast farming setups, that are flexible both in the sense of ability to physically move, and Indoor space positioning, like layers, plant orientation etc.
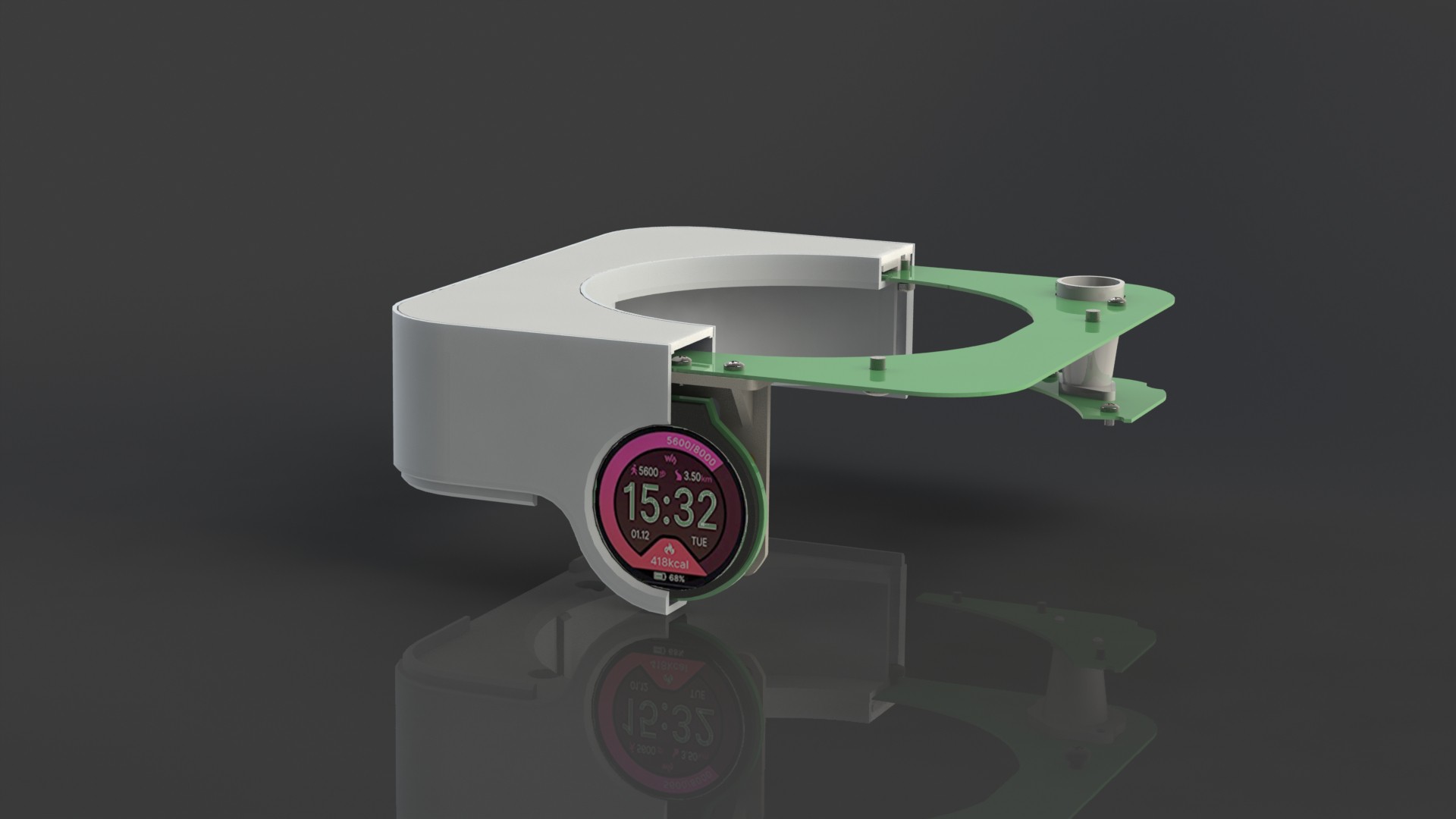
Each Plant pod device is modular and can be customized for specific type of plant, like height of the device, number of active liquid inlets/outlets, air flow, size, shape and type of the net cup.
System needs to scale well, depending on the food demand, it can be configured like a small to medium in store solution, or per building solution, micro hub etc. Or it can be a large scale operation, that might replace farmers market in the city center.
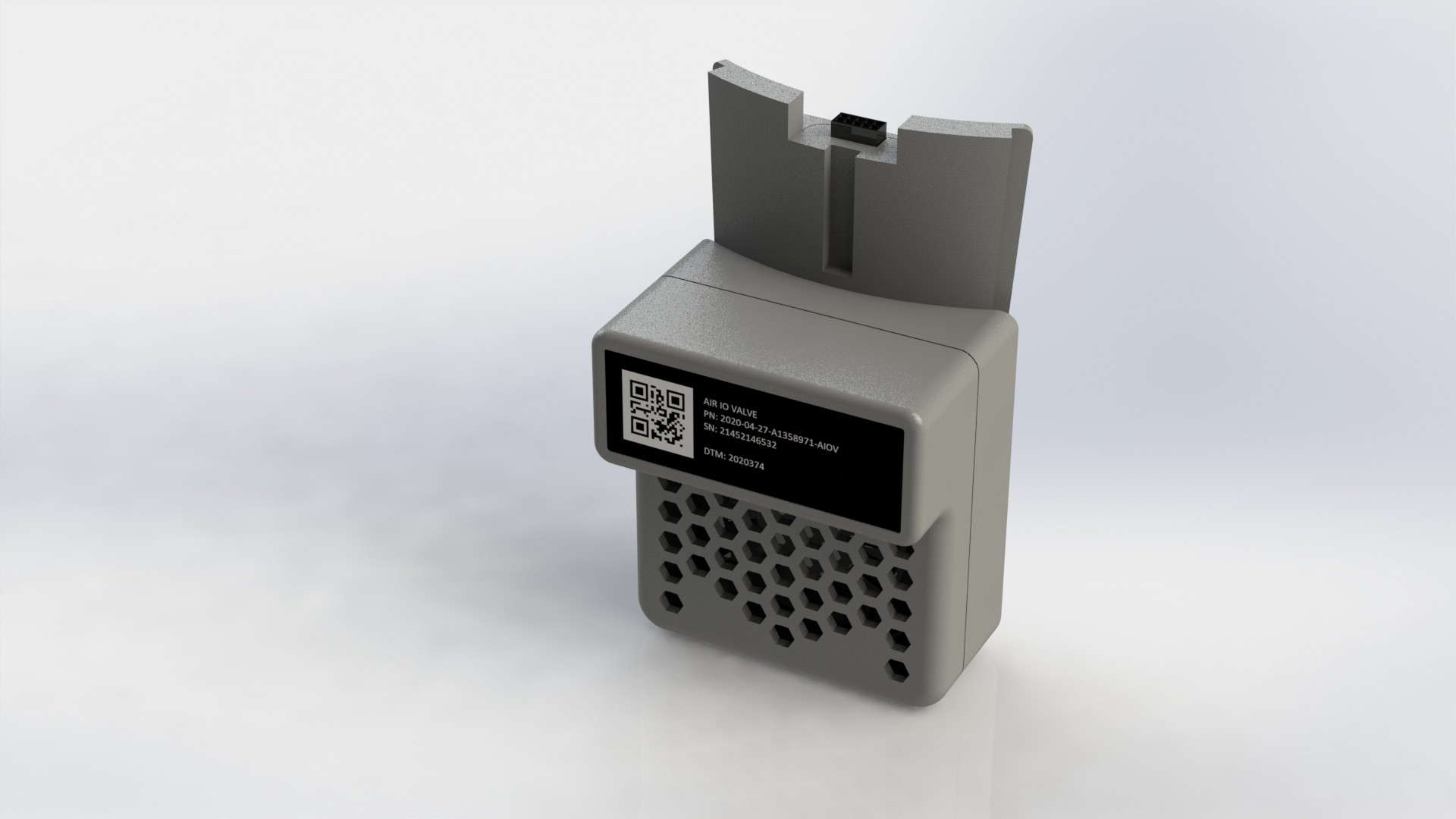
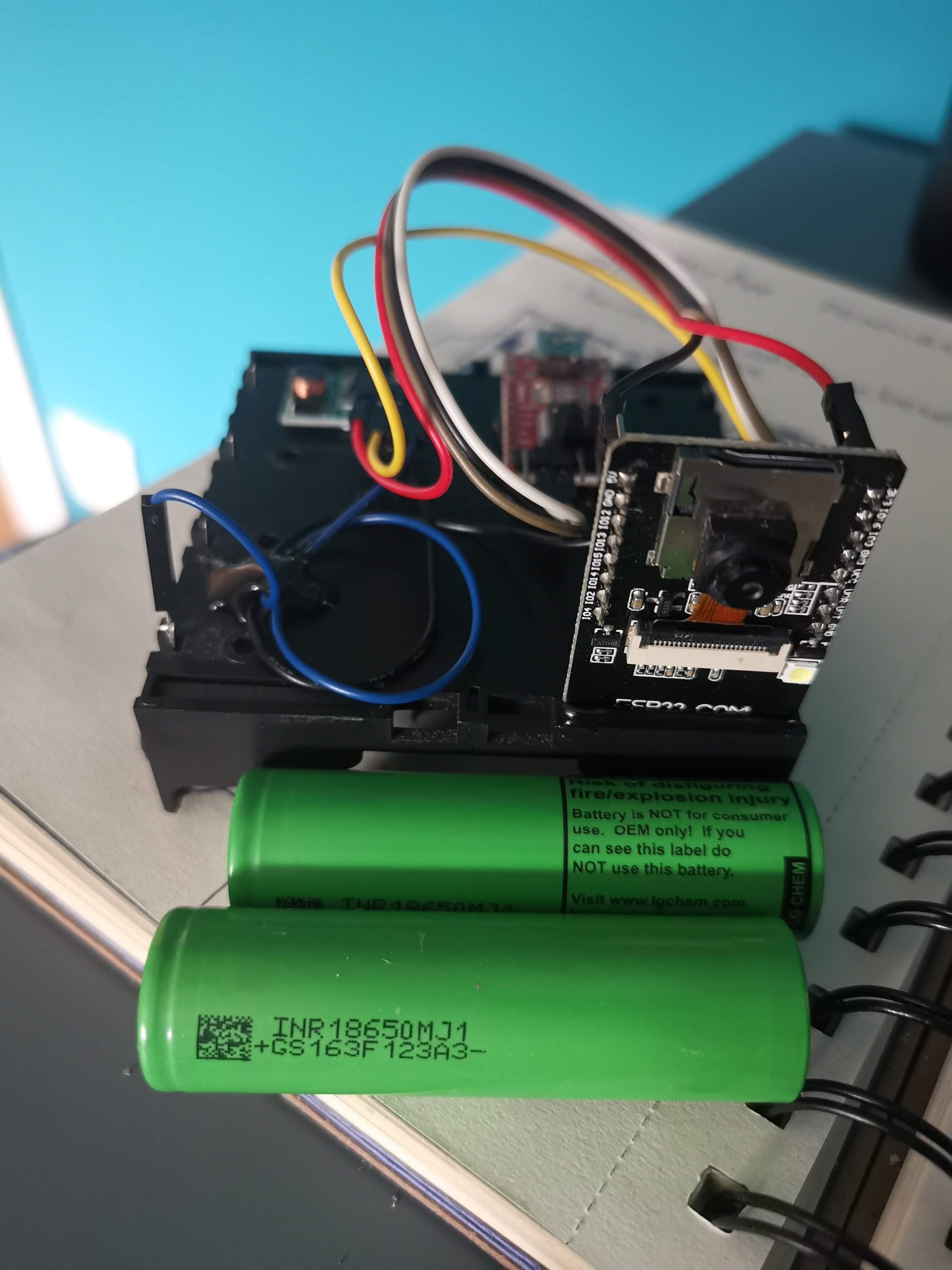
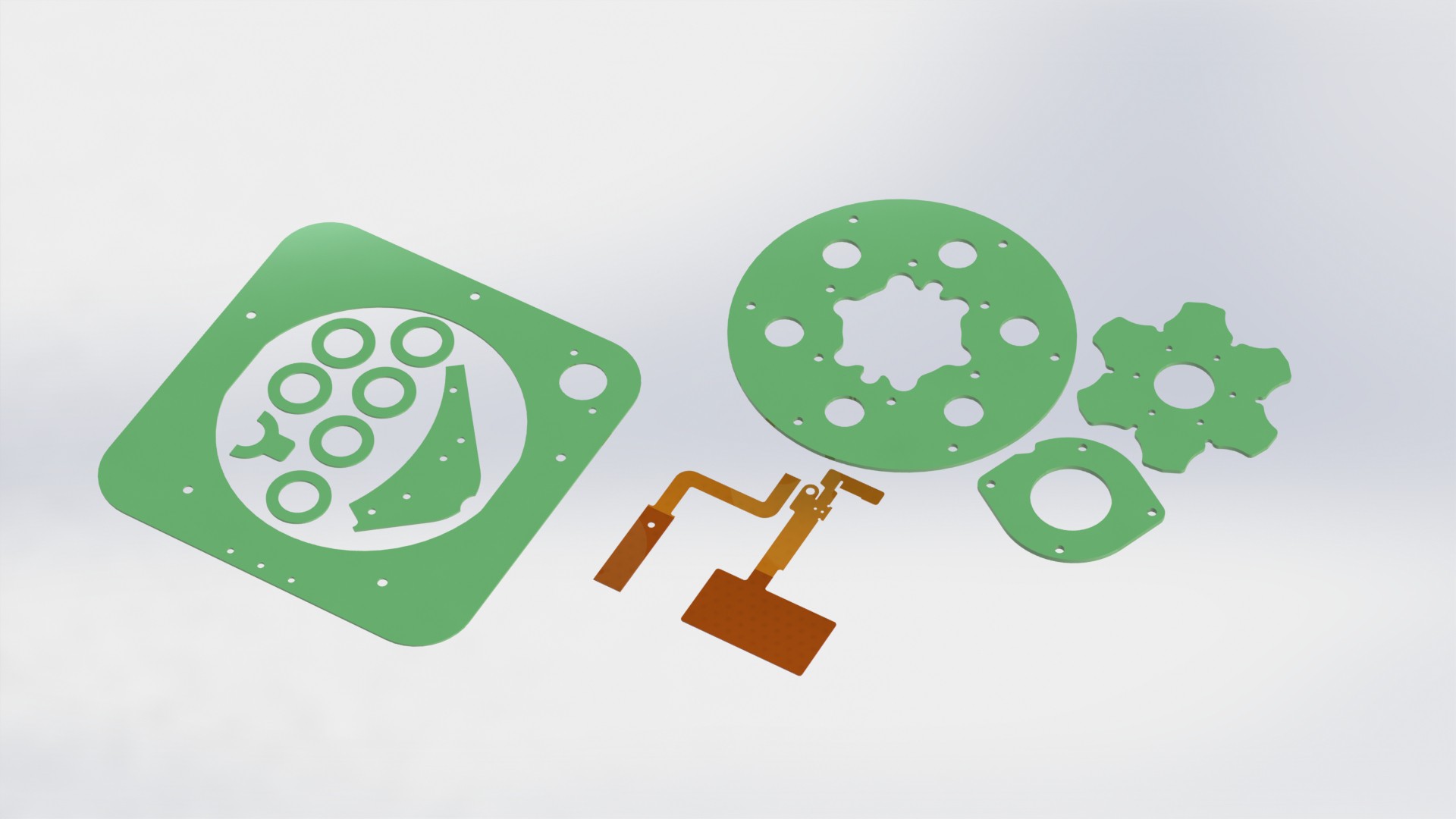
Plant pod is designed to be as simple a possible, and use as many of the shelf components, to maintain low production cost. Materials used for the main body are mostly plastic, so all other components are designed in such a way that it can be replaced, and by so, prolongate the devices life cycle. 3D printing main body is also an option.
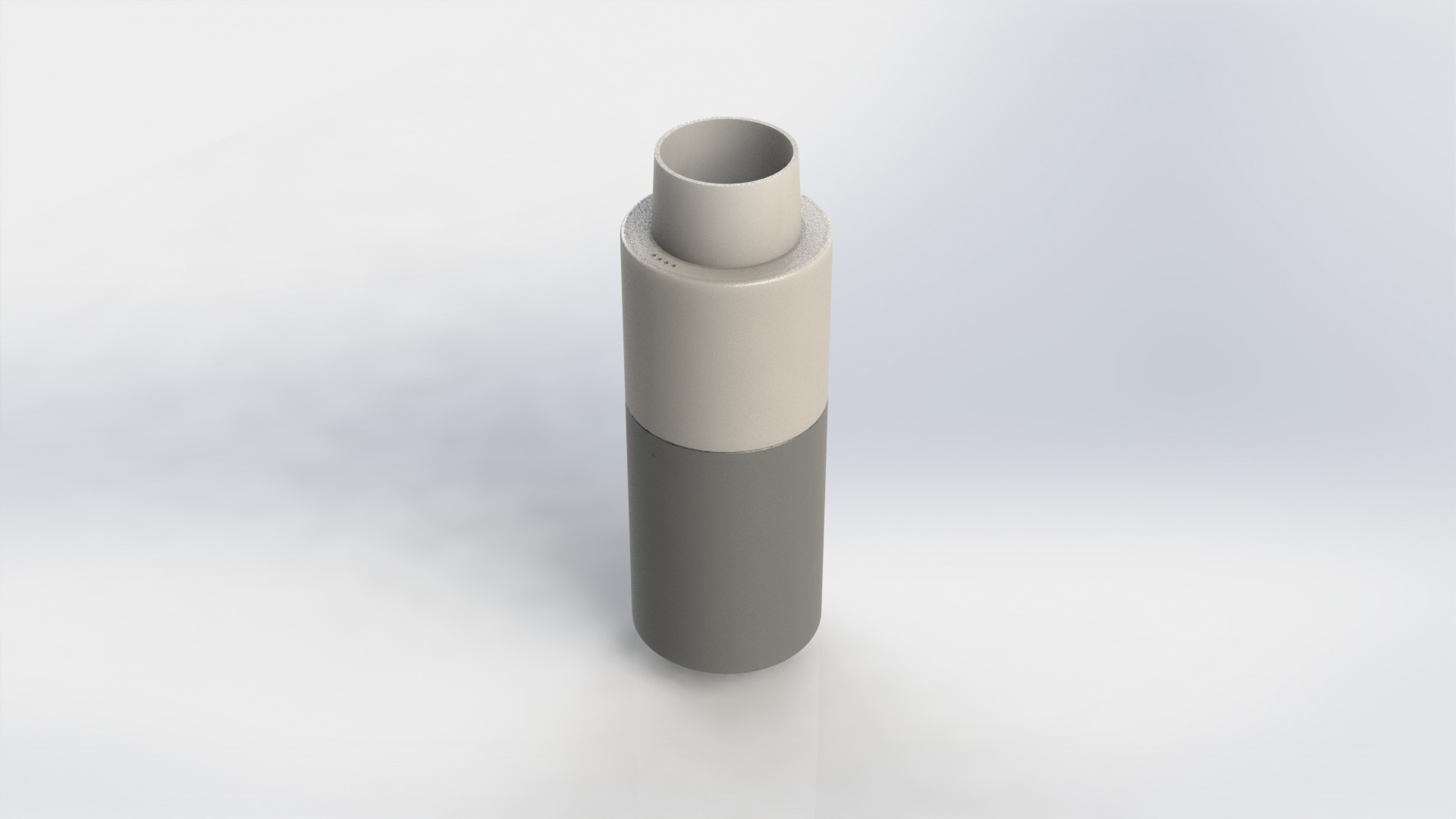
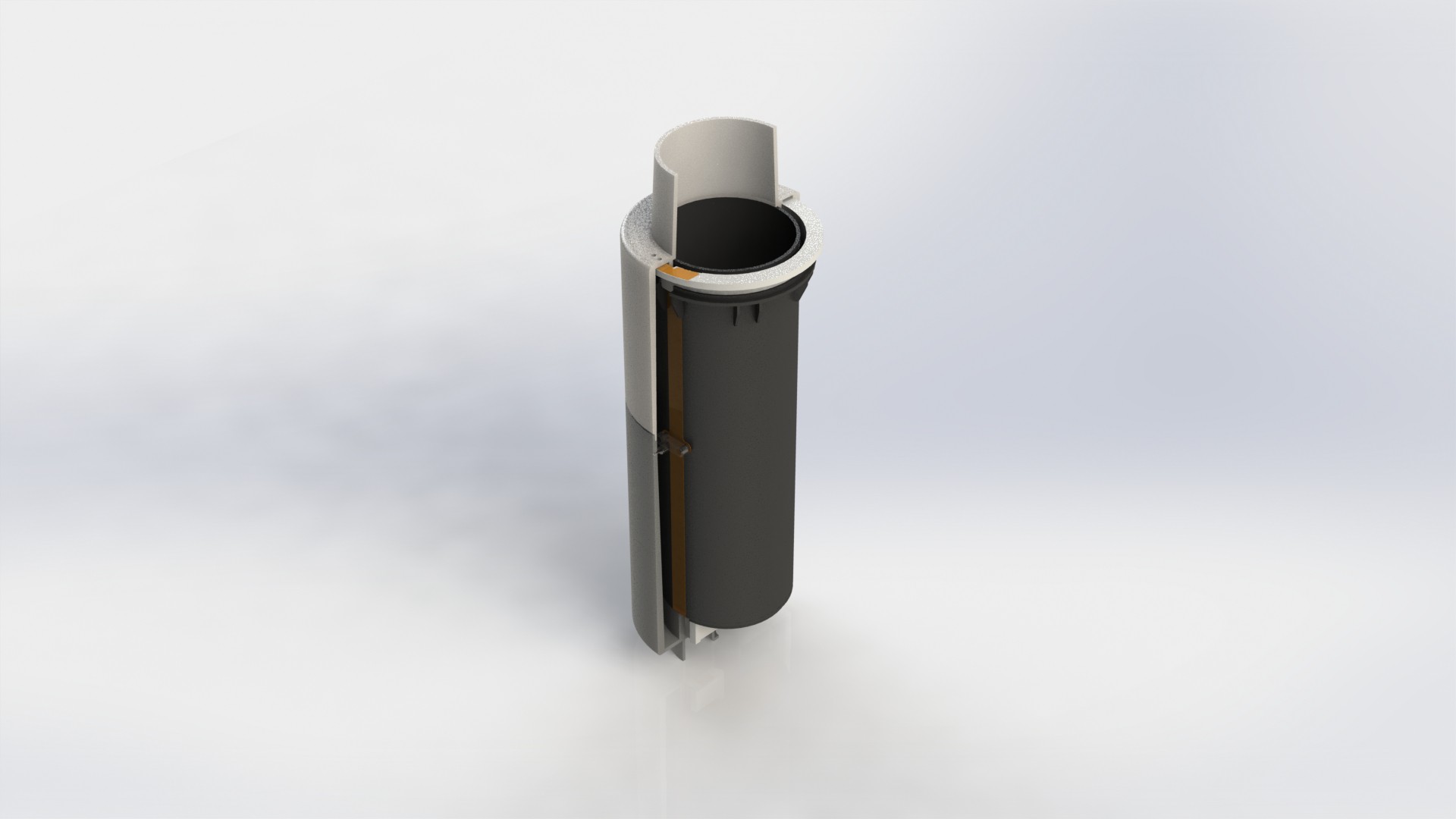
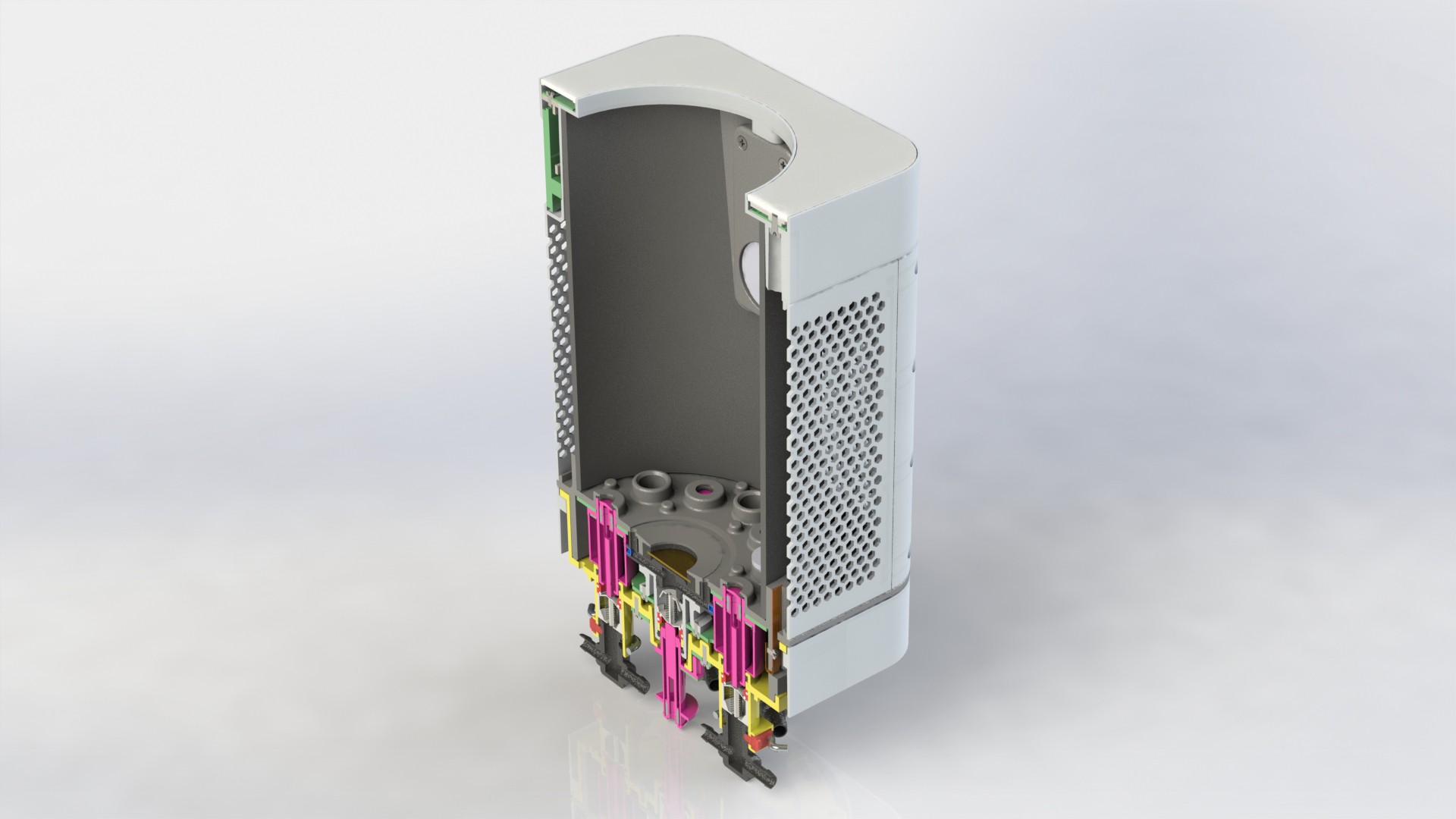
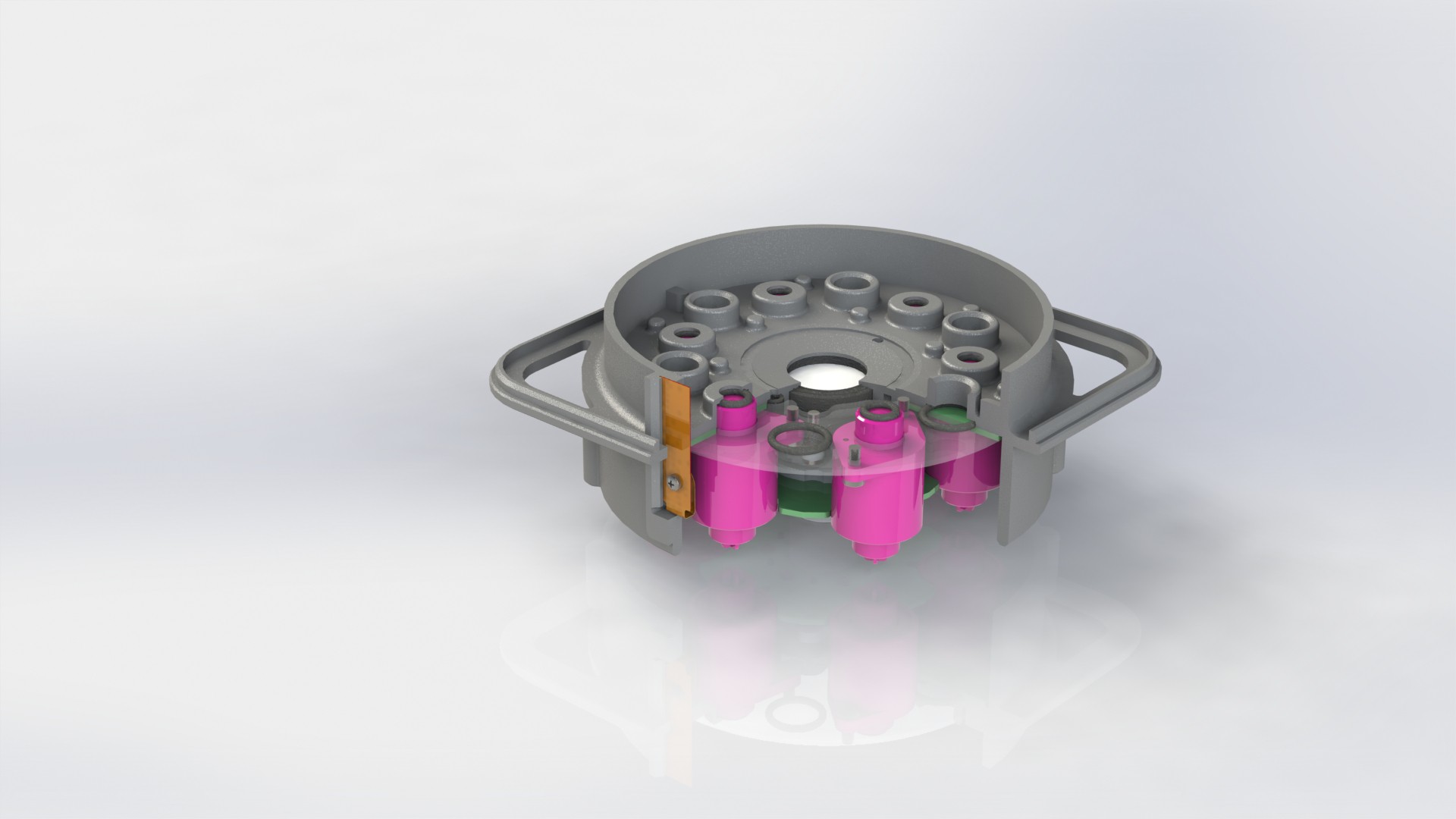
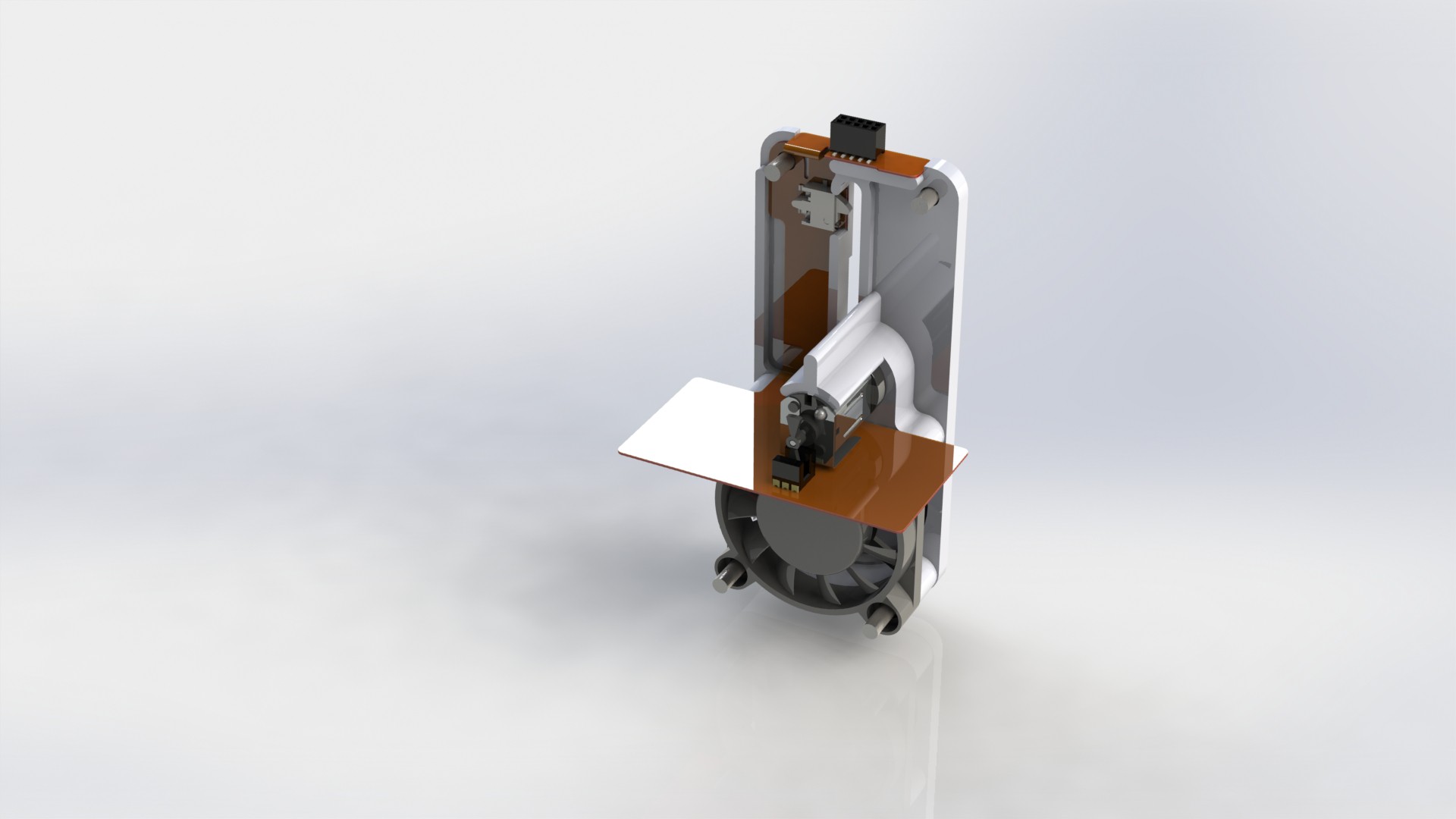
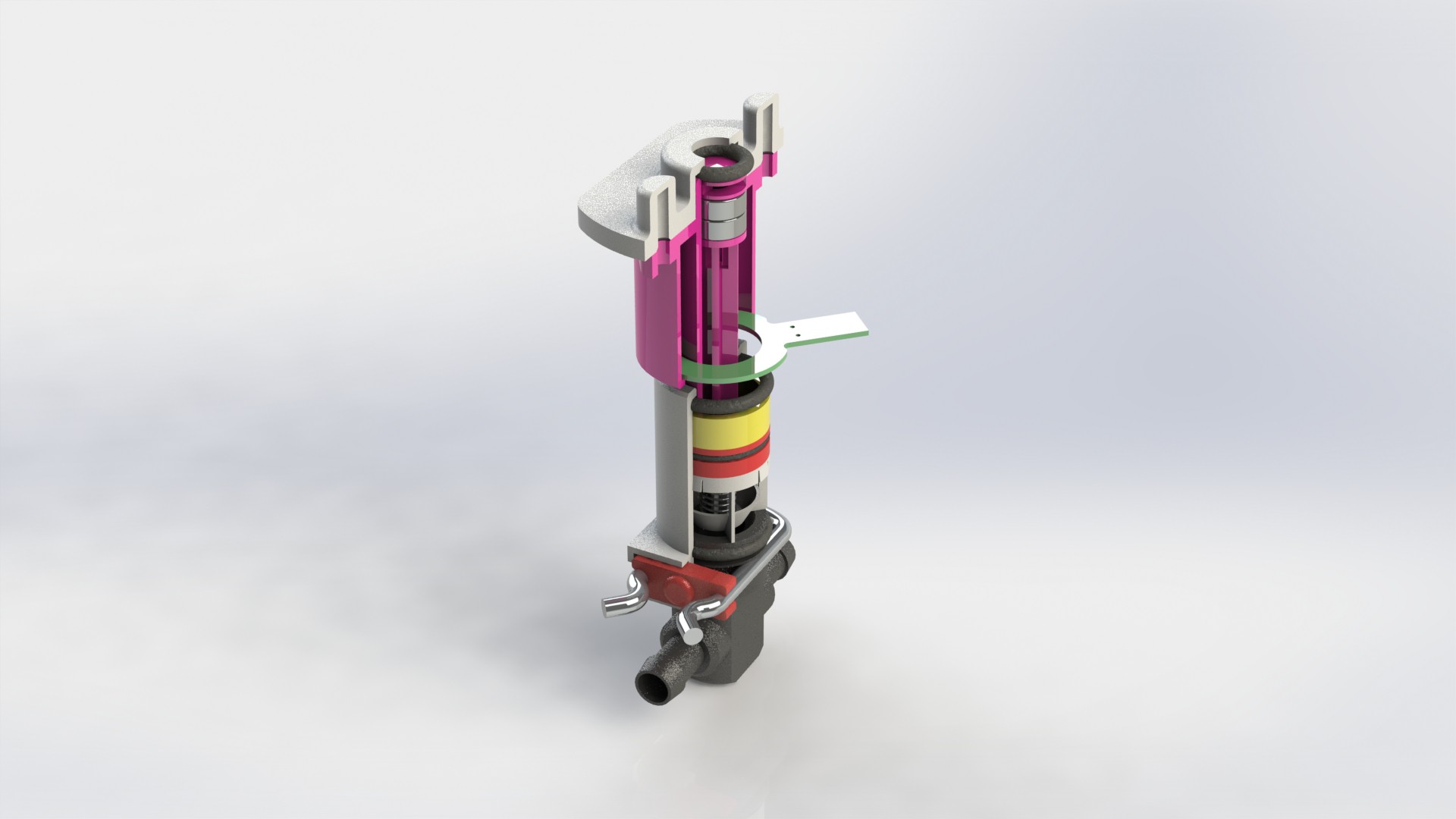
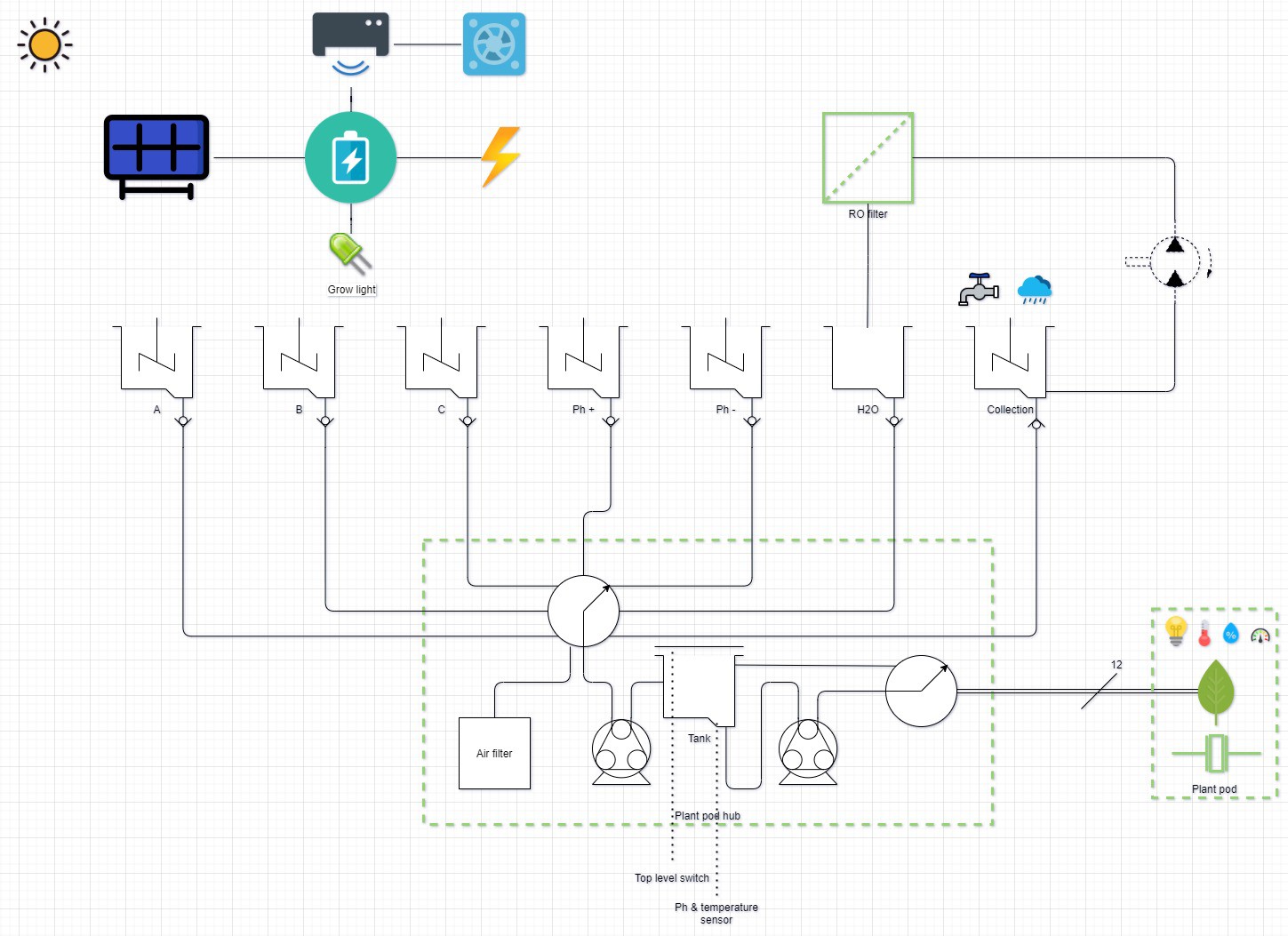
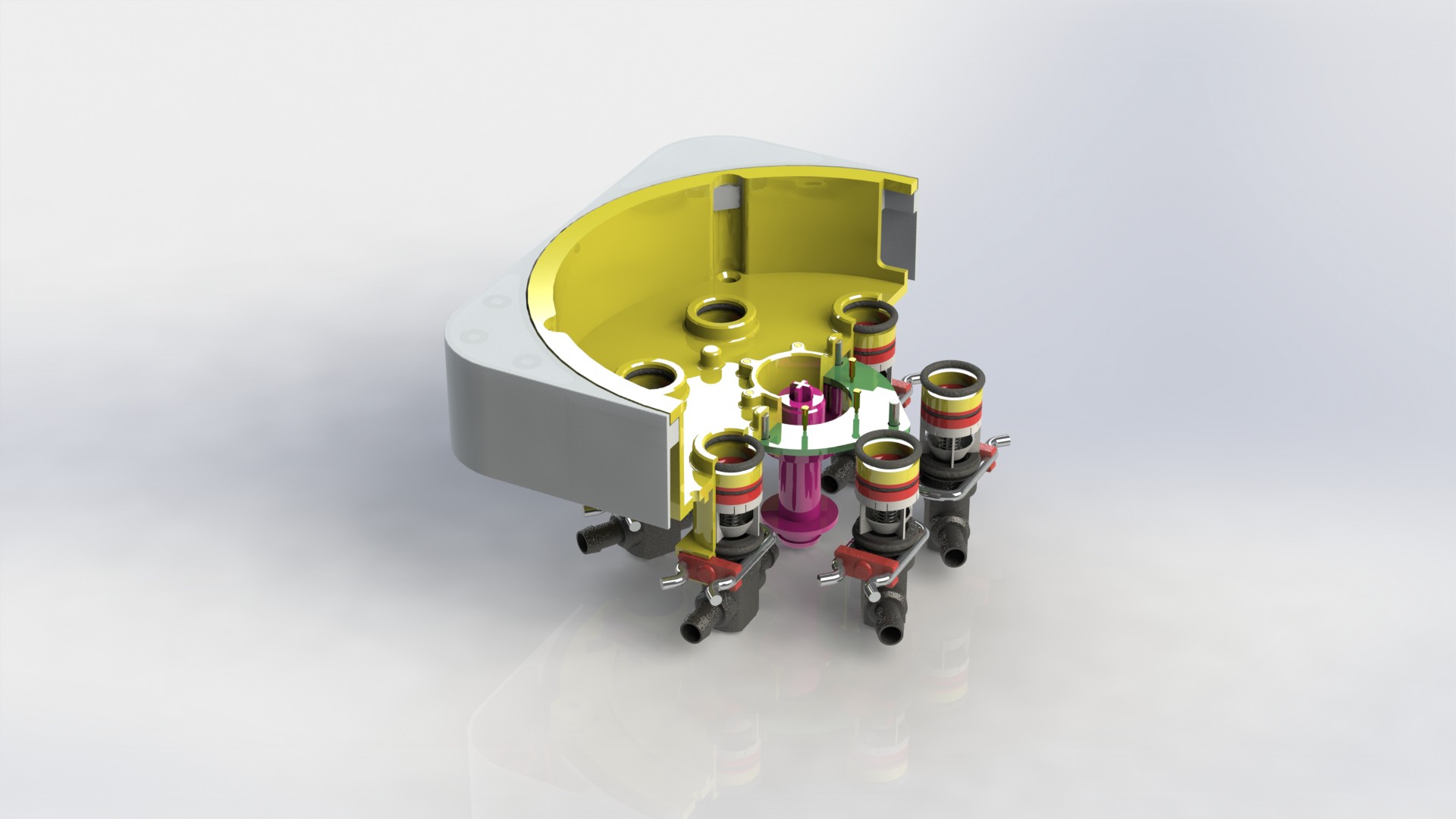
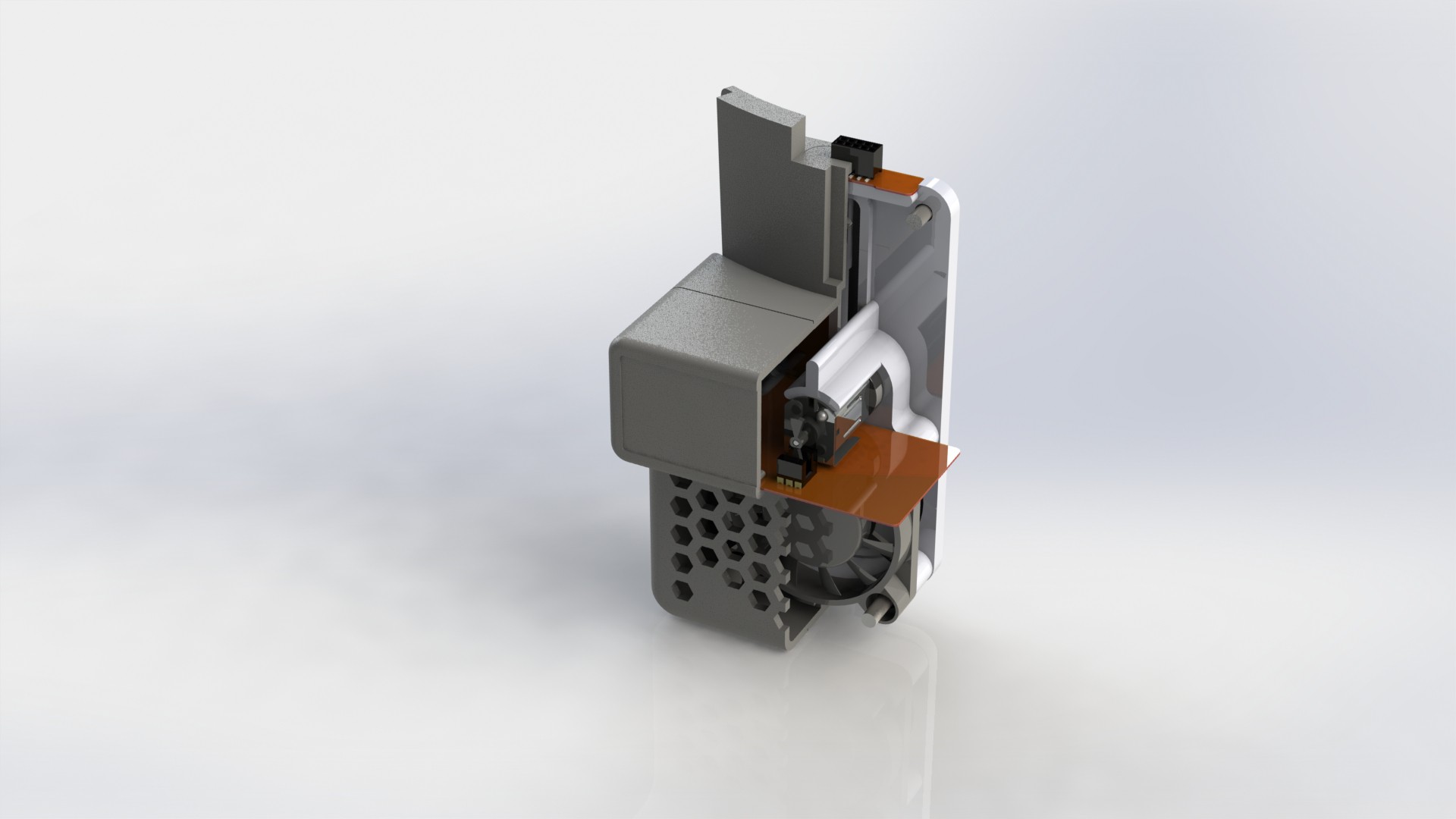
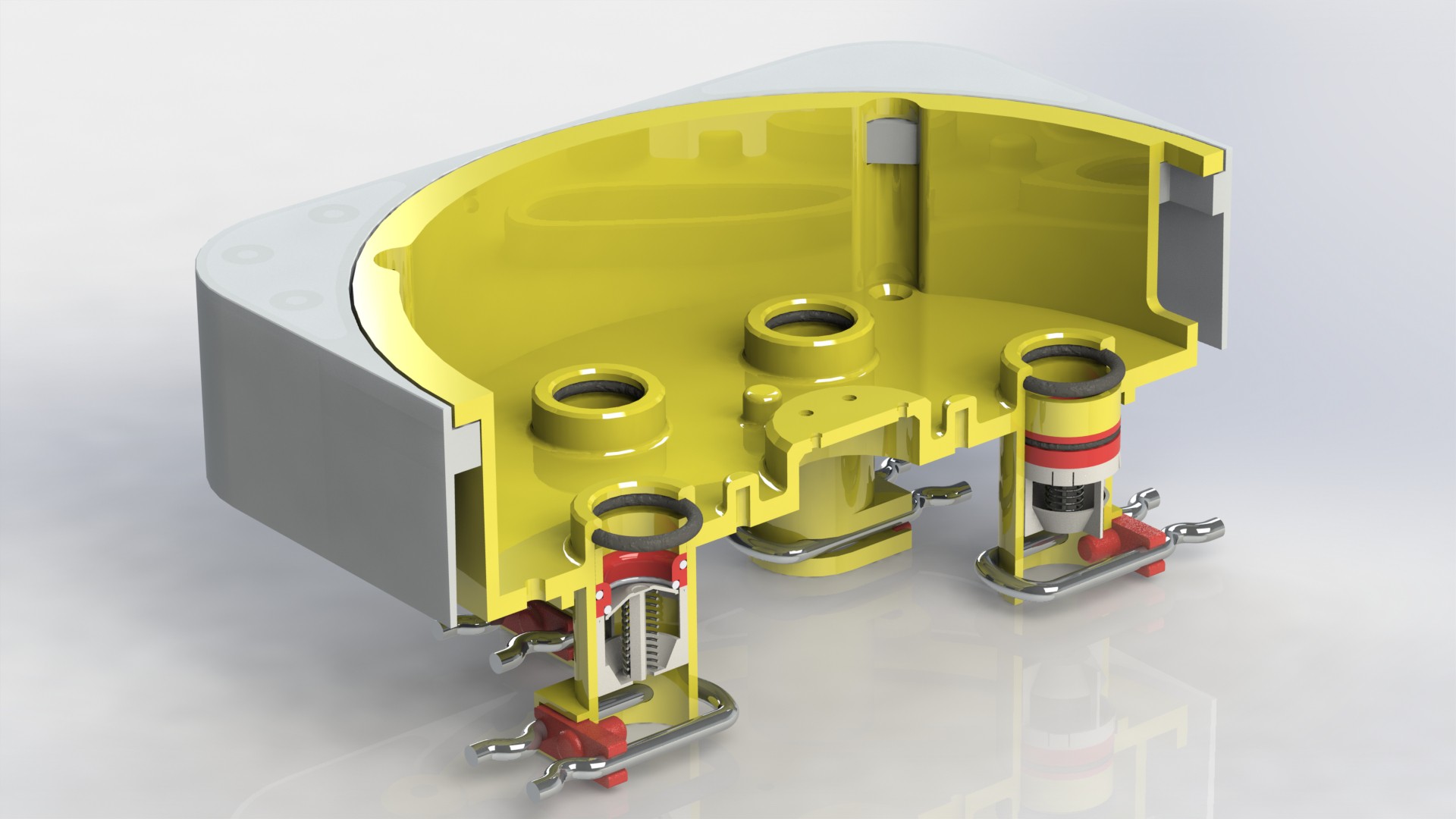
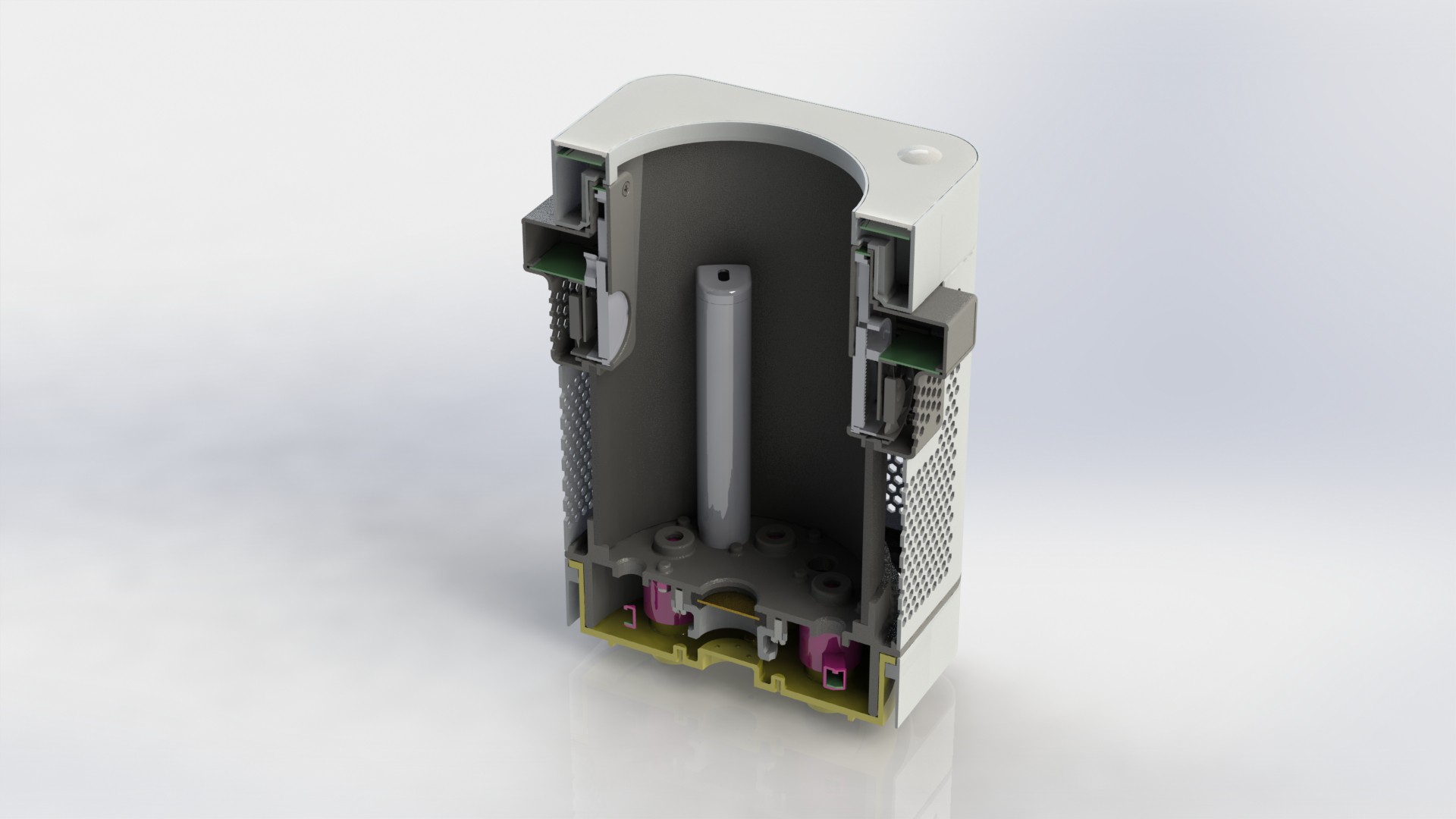
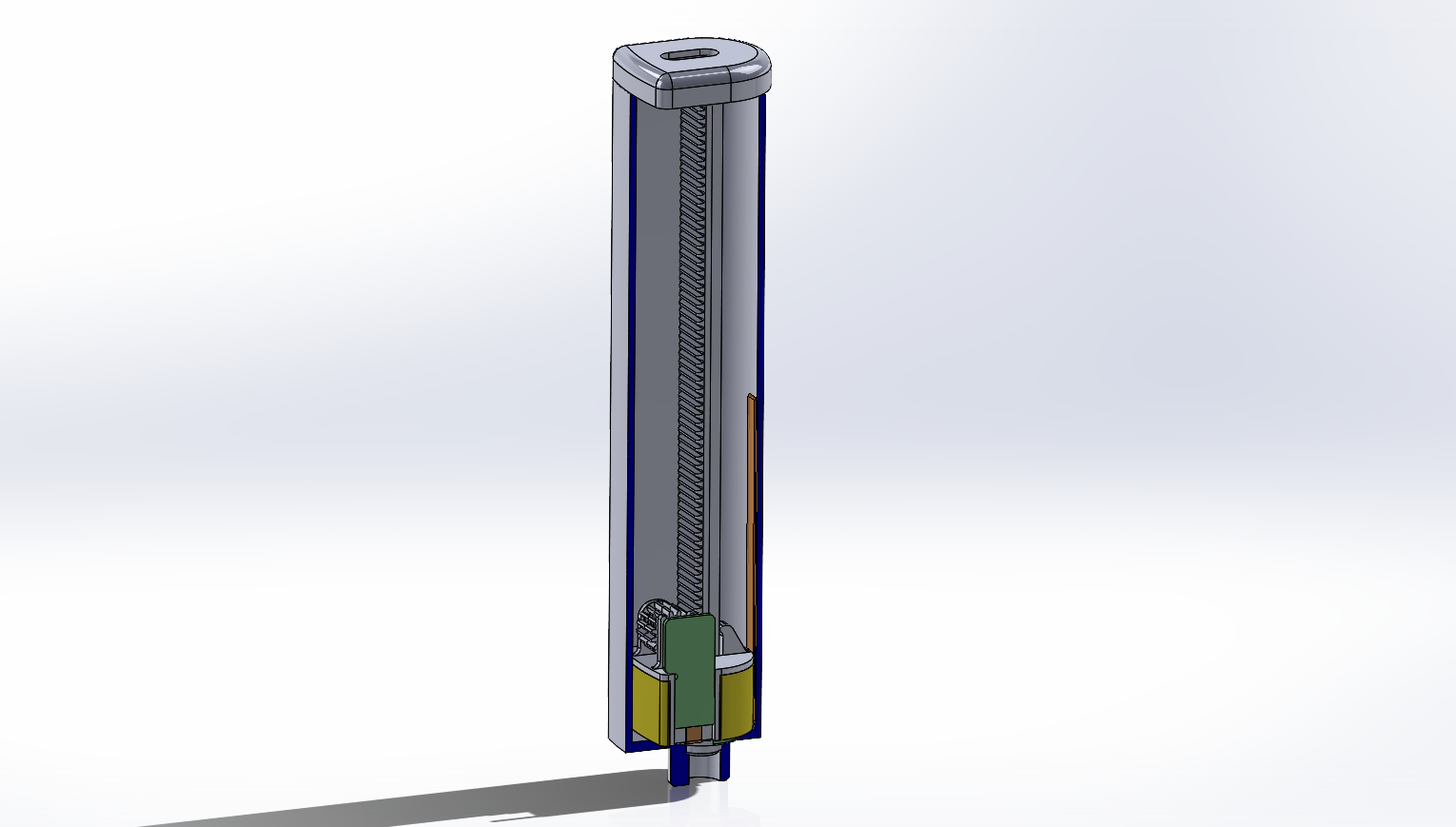
Device has three main parts, lower body, upper body and middle section.
Lower body houses main logic board, liquid and electrical connections.
There are total of six liquid connections, to enable the supply of:
- Water
- Ph+
- Ph-
- Nutrient A
- Nutrient B
- Nutrient C
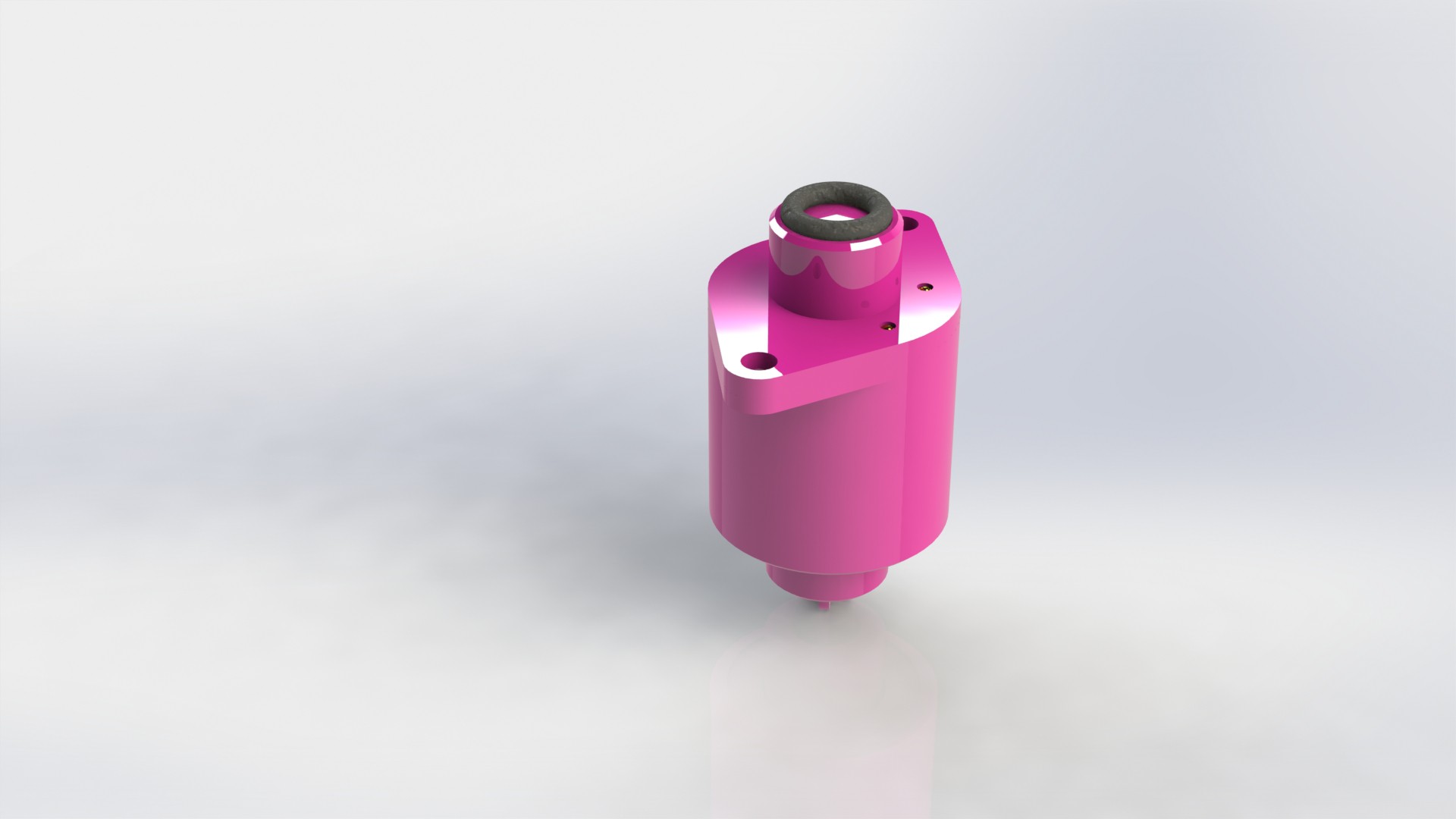
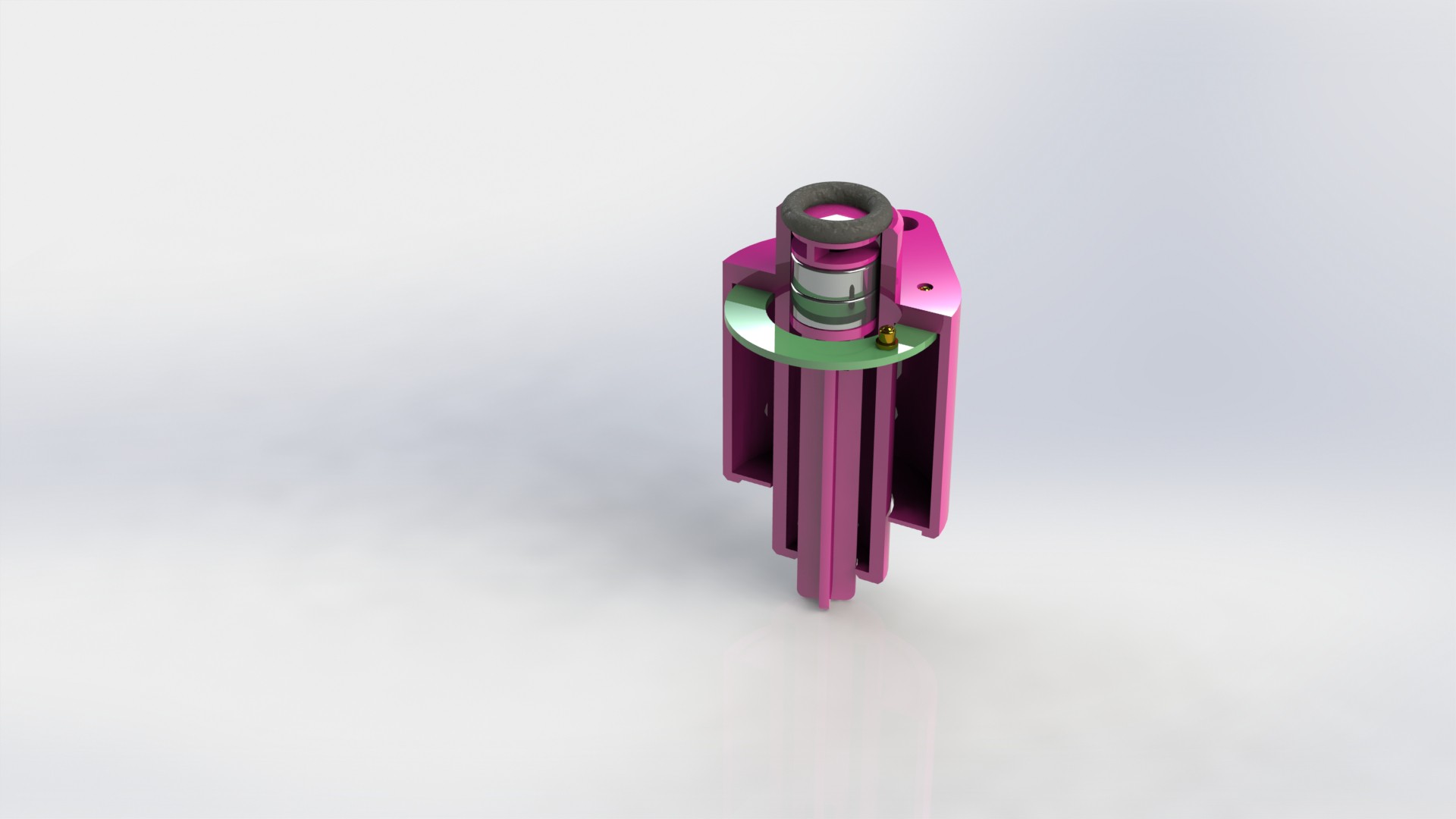
Depending on the chosen farming technique, device can be configured to use variable number of liquid connections. Flow of liquid components is controlled by using integrated solenoid pumps, fixed amount of liquid is taken...
Read more » Nikola Secerovski
Nikola Secerovski




























 Tim Taylor
Tim Taylor
 Michael Barton-Sweeney
Michael Barton-Sweeney
 Emma Barme
Emma Barme
 EK
EK
This is a very cool project and I really love the concept renderings. Looking forward to seeing how it progresses!