The fourth version is alive. Hopefully it will be dummy-proof enough to be programmed without headaches or the need for expensive diagnostic equipment. The following features are being evaluated in this iteration.
- Through-hole USB connector – Previous surface mount seemed pretty fragile. Through-hole attachment should be more resilient.
- Temperature compensated oscillator – Use of TXCO with +-2ppm stability instead of the +-10ppm crystal oscillator.
- RS485 – Development of new interface based on feedback. With it,
the device can be used as wireless extension of RS485 bus further
improving integration into sensor network.
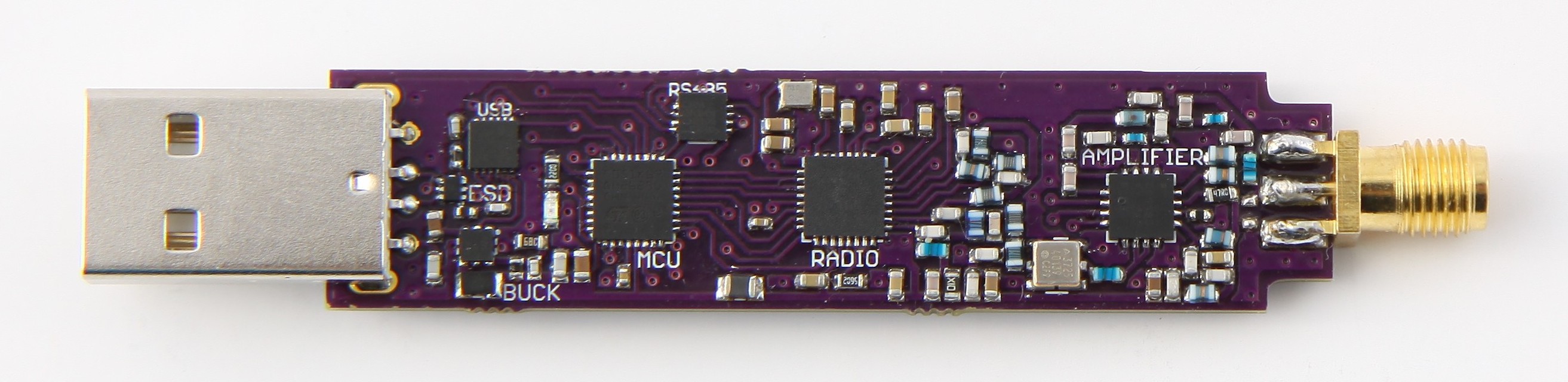
Version 4 has undergone crowdfunding campaign at CrowdSupply. Unsuccessfully. You can check its old page. Device may be eventually found on Tindie. This day has yet to come.
Wondering why to use sub-GHz radio instead of wifi? Main reason is range. Sub-GHz radio trades speed for range, which means you can easily have triple range of wifi, but with only few kilo bits per second. As mentioned in other logs this device is tested to reach 500meters at 4,8kbps with wire antenna 8cm long. Range can be further improved by lowering bitrate or improving antenna.
Let’s take a look on few example applications you could use this device for :
- Wireless COM port – Pair two devices together and use them as point-to-point datalink allowing you slow, but long range link to remote devices. ( Like solar powered Raspberry Pi inside your greenhouse? )
- Radio-to-RS485 bridge – Because maybe your greenhouse have sensor network of its own. Can also be used to replace long coax wires going from rooftop antennas to your radio. You can put this device in a box right by the antenna and route it’s data on RS485 bus avoiding radio signal losses.
- Instant messaging broadcast – Simple chat. Useful in places with poor internet connection or as back-up communication.
- Platform for proprietary protocol or encryption – Define custom protocol or embed encryption into the lowest level of transmission. This reduces chances of your algorithm being cracked.
- Spectrum analyzer – Device can be configured to give feedback about strength of received signal. This can be send to attached computer which could visualize the data. You can use this to form poor man’s radio spectrum analyzer or to estimate distance of the transmitter.
- Wireless sensor network – And of course you can attach sensors over RS485 and control them from the device. ( Example of a network in image below ) Being open allows you to define custom routing, data formatting, compression and pre-proccessing.
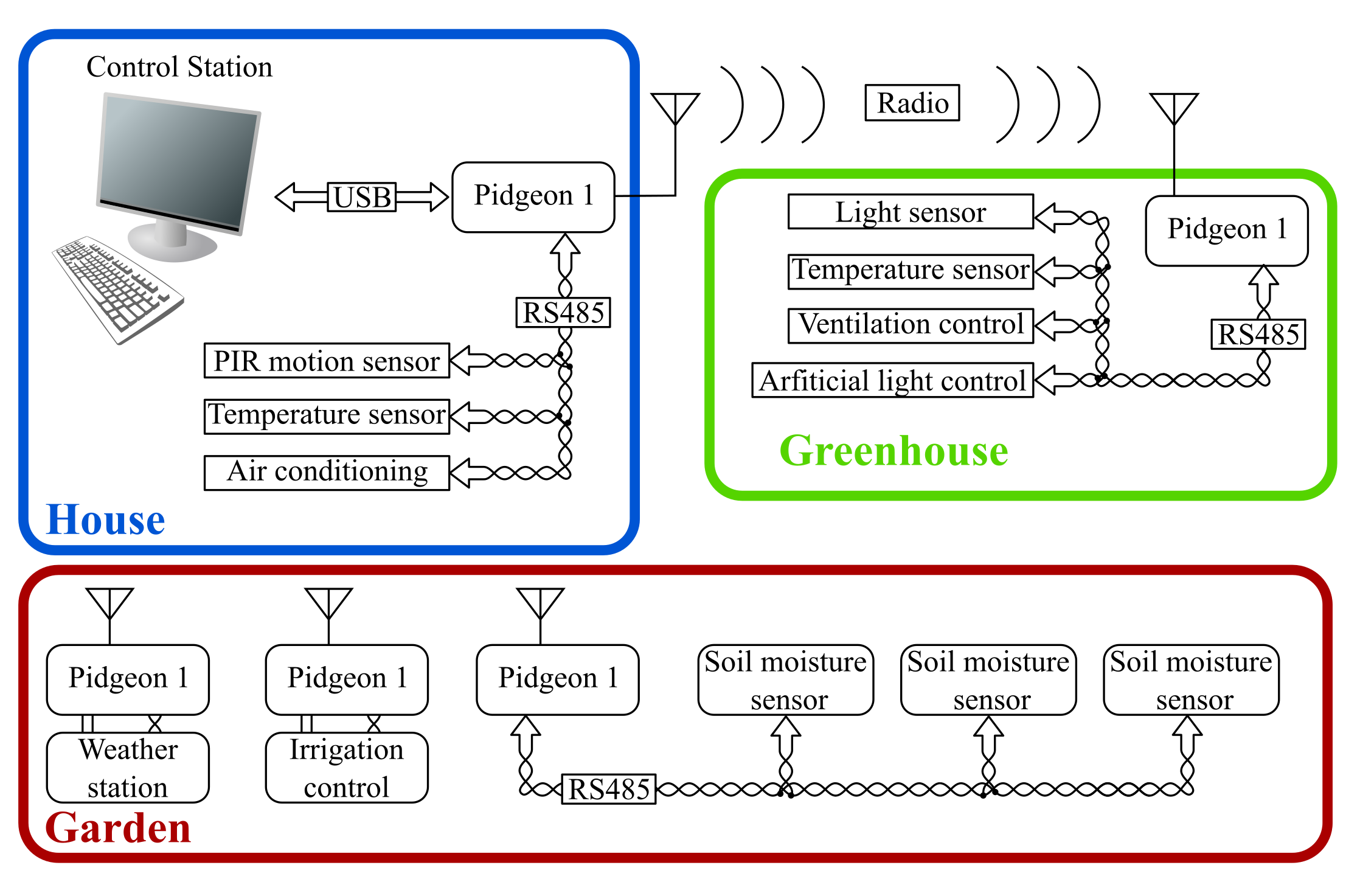
Can you think of other use of this device?
Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.
Great project! We're excited to see your Crowd Supply campaing luanch
Are you sure? yes | no