-
Adding sensors: Air Quality
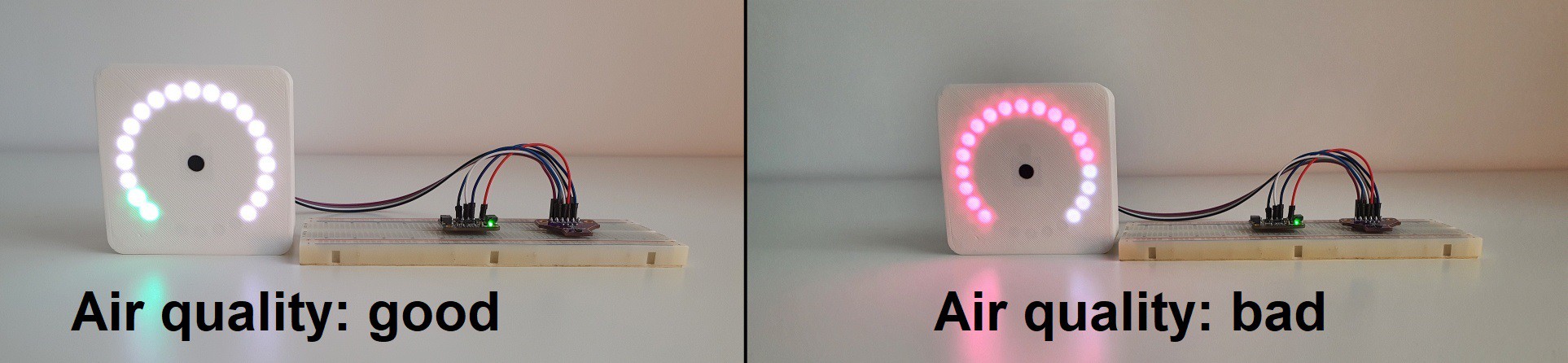
10/23/2021 at 13:47 • 0 commentsAdding a CCS811 sensor, in addition to the SHT31 MakeTime can indicate equivalent total VOC (eTVOC) levels.
Sensor readings are transformed to ug/m^3 and the full scale displayed reads from 0 to 1000 ug/m^3. The higher the reading, the more the display color shifts from green to red.
![]()
Arduino sketch
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h> #include <Wire.h> #include "Adafruit_CCS811.h" #include "Adafruit_SHT31.h" #define LED_PIN 9 #define LED_COUNT 24 Adafruit_NeoPixel strip(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800); Adafruit_CCS811 ccs; Adafruit_SHT31 sht31 = Adafruit_SHT31(); void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); strip.begin(); strip.show(); if (! sht31.begin(0x44)) // Set to 0x45 for alternate i2c addr { strip.setPixelColor(12, 0x00800000); strip.show(); while (1) delay(1); } if(!ccs.begin()) { strip.setPixelColor(12, 0x00008000); strip.show(); while(1); } while(!ccs.available()); } // https://help.atmotube.com/technical/13-atmotube-ppm-ug/ // https://myhealthyhome.info/assets/pdfs/TB531rev2TVOCInterpretation.pdf void loop() { float t = sht31.readTemperature(); float h = sht31.readHumidity(); float voc; uint32_t color, displayColor; uint8_t vocLevel, i; voc = 0; if(ccs.available()) { if(!ccs.readData()) { ccs.setEnvironmentalData(h, t); voc = ccs.getTVOC() * 100 * 0.0409; // [ug/m^3] Serial.print("TVOC [ug/m^3]: "); Serial.println(voc); vocLevel = round(voc / (1000.0/19)); strip.clear(); for (i = 0; i < 19; i++) { if (voc < 200) displayColor = 0x00003000; else if (voc < 300) displayColor = 0x00082800; else if (voc < 400) displayColor = 0x00102000; else if (voc < 500) displayColor = 0x00181800; else if (voc < 600) displayColor = 0x00201000; else if (voc < 700) displayColor = 0x00280800; else displayColor = 0x00300000; color = 0x00101010; if (vocLevel > i) color += displayColor; strip.setPixelColor((i + 15) % 24, color); } strip.show(); } } delay(0.5); } -
MakeTime with friends!
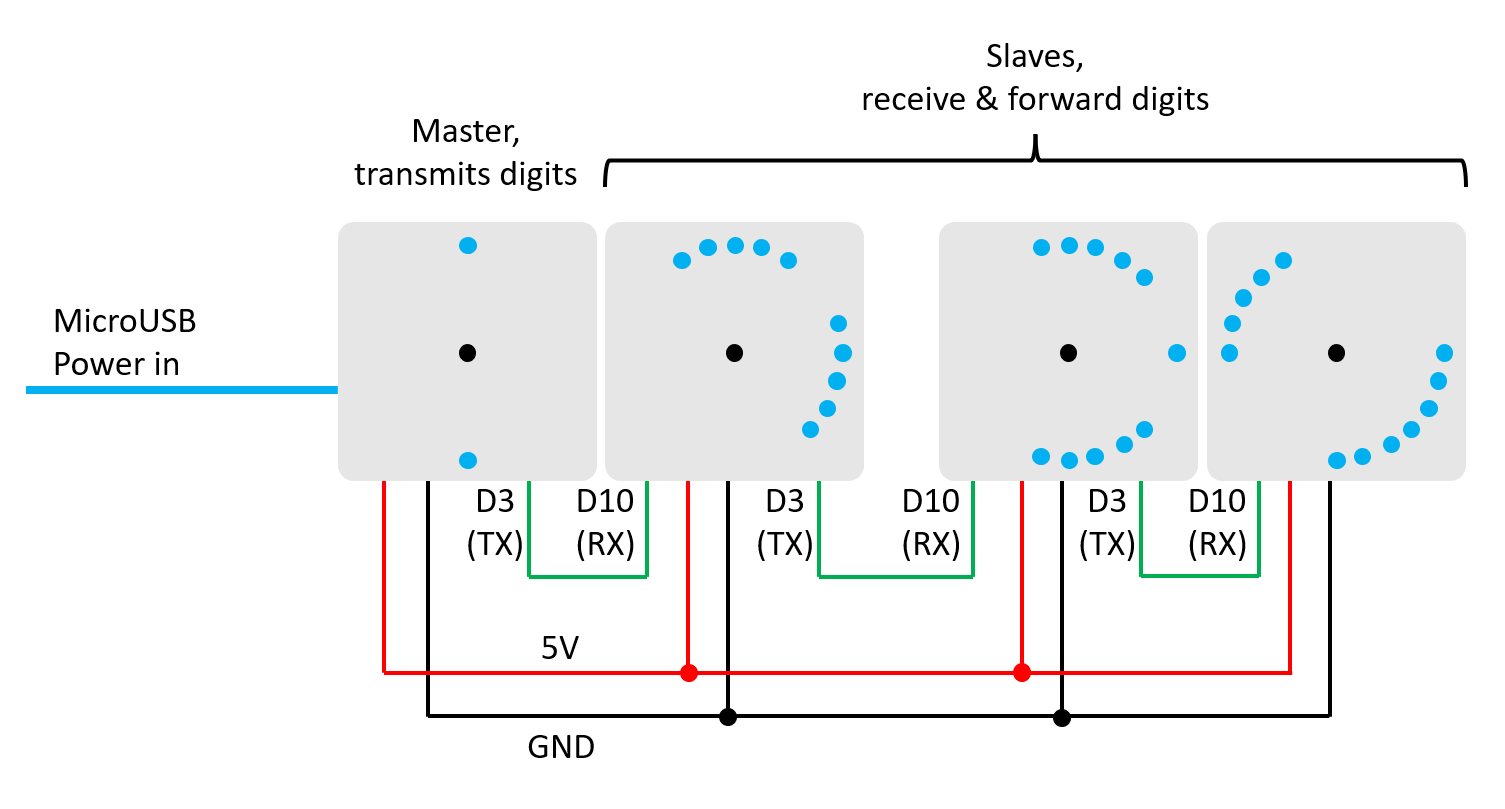
10/18/2021 at 19:07 • 0 commentsHow about using multiple MakeTime units into a single display? Let's show the clock on 4 units, where each displays a single digit. This will require one of the units to act as a master, holding the time and displaying one of the digits, and the other three will be slaves and receive what they should display. Unfortunately having all LEDs on a circle makes for some very approximate fonts. Here's a timelapse running from 09:00 to 10:00.
Hardware
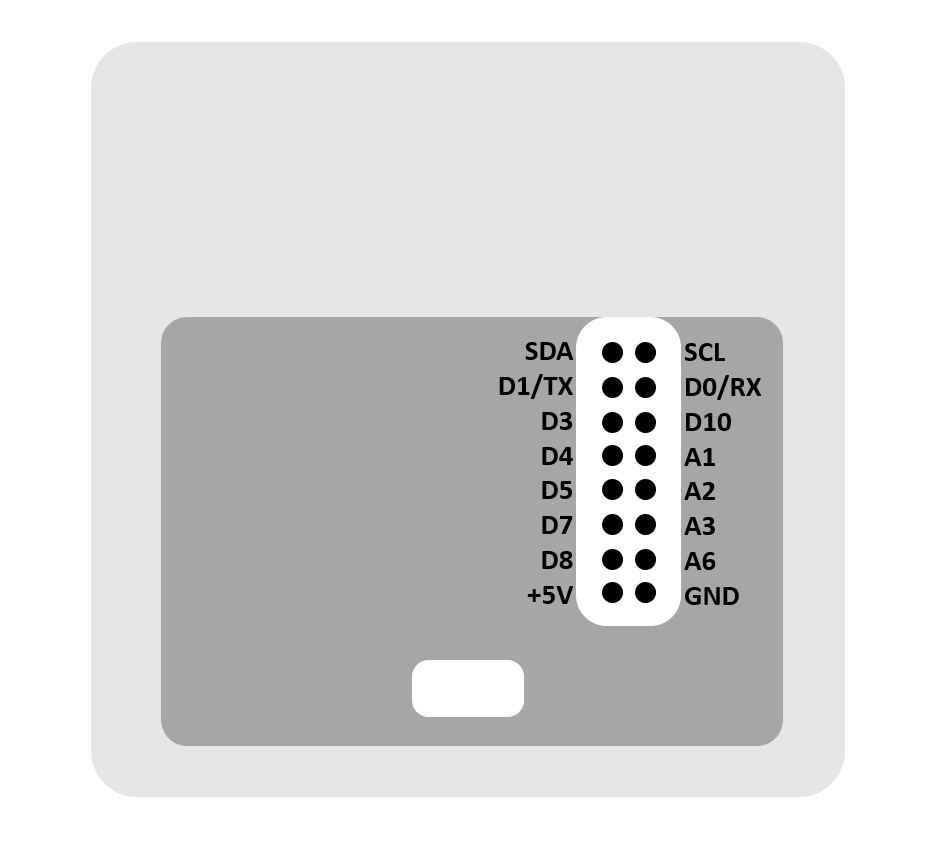
MakeTime has the expansion header on the back, giving access to some of the Arduino pins. +5V and GND are also present on this header, so we can steal power from the master unit to deliver to the other three. For the protocol I used a software UART (using the Arduino SoftwareSerial library) that I daisy-chained the software serial ports, using pin D3 for TX and D10 for RX. Below is a diagram of which pins are easily accessible on the back for extension. On GitHub there is an alternate back piece for the case that provides access to these pins.
![]()
The whole 4-digit clock with the connecting wires is represented in the following schematic.![]()
The time shown in this example is 17:34
Protocol
The master transmits a zero to signal that data is coming and then the character corresponding to each of the 3 digits the slaves should display. Each slave displays the first character it receives after one or more zeroes have been received. It then forwards all bytes, but changes the byte it displayed into a zero. Thus, to display 17:34 the master displays '1' and transmits:
0x00, 0x37, 0x33, 0x34
The first slave receives this, displays the first char after 0x00 which is 0x37 ('7') and retransmits:
0x00, 0x00, 0x33, 0x34
The second slave displays '3' and retransmits:
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x34.
Arduino sketch - Master
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h> #include <Wire.h> #include <SoftwareSerial.h> #include <ds3231.h> #define LED_PIN 9 #define LED_COUNT 24 Adafruit_NeoPixel strip(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800); SoftwareSerial mySerial(10, 3); // RX, TX ts t; //ts is a struct findable in ds3231.h uint8_t hh, mm; #define DIGIT_DISPLAY_MS 750 #define DIGIT_GAP_MS 100 #define HM_GAP_MS 750 #define REPEAT_MS 2000 void setup() { pinMode(2, INPUT); digitalWrite(2, HIGH); strip.begin(); strip.show(); Wire.begin(); //start i2c (required for connection) DS3231_init(DS3231_INTCN); //register the ds3231 (DS3231_INTCN is the default address of ds3231, this is set by macro for no performance loss) Serial.begin(115200); while (!Serial) ; mySerial.begin(57600); } void loop() { if (digitalRead(2) == 0) { // I was in a rush. If you click the button it sets the hardcoded time, here 21:30 DS3231_get(&t); t.hour = 21; t.min = 30; DS3231_set(t); delay(1000); } runClock(); showClock(); } void showClock() { static unsigned long lastRefresh = 0; if ((millis() - lastRefresh) >= 500) { strip.clear(); displayDigit('0' + hh/10, 0x00060606); strip.show(); mySerial.write((uint8_t)0); delay(10); mySerial.write((uint8_t)('0' + (hh%10))); delay(10); mySerial.write((uint8_t)('0' + (mm/10))); delay(10); mySerial.write((uint8_t)('0' + (mm%10))); lastRefresh = millis(); } } void runClock() { static unsigned long lastRefresh = 0; if ((millis() - lastRefresh) >= 500) { lastRefresh = millis(); DS3231_get(&t); hh = t.hour; mm = t.min; } } void displayDigit(uint8_t d, uint32_t color) { uint8_t i; strip.clear(); switch(d) { case ' ': break; case '0': for (i = 0; i < 24; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; case '1': strip.setPixelColor(0, color); strip.setPixelColor(12, color); break; case '2': for (i = 3; i <= 9; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } for (i = 15; i <= 21; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; case '3': strip.setPixelColor(23, color); strip.setPixelColor(0, color); strip.setPixelColor(1, color); strip.setPixelColor(2, color); strip.setPixelColor(3, color); strip.setPixelColor(6, color); strip.setPixelColor(9, color); strip.setPixelColor(10, color); strip.setPixelColor(11, color); strip.setPixelColor(12, color); strip.setPixelColor(13, color); break; case '4': for (i = 18; i <= 22; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } for (i = 6; i <= 12; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; case '5': strip.setPixelColor(18, color); strip.setPixelColor(20, color); strip.setPixelColor(21, color); strip.setPixelColor(22, color); strip.setPixelColor(23, color); strip.setPixelColor(0, color); strip.setPixelColor(1, color); for (i = 6; i <= 12; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; case '6': strip.setPixelColor(0, color); for (i = 6; i <= 23; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; case '7': strip.setPixelColor(22, color); strip.setPixelColor(23, color); strip.setPixelColor(0, color); strip.setPixelColor(1, color); strip.setPixelColor(2, color); for (i = 5; i <= 9; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; case '8': strip.setPixelColor(21, color); strip.setPixelColor(22, color); strip.setPixelColor(23, color); strip.setPixelColor(0, color); strip.setPixelColor(1, color); strip.setPixelColor(2, color); strip.setPixelColor(3, color); for (i = 9; i <= 15; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; case '9': for (i = 18; i <= 23; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } for (i = 0; i <= 12; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; default: break; } strip.show(); }Arduino sketch - Slave
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h> #include <SoftwareSerial.h> #define LED_PIN 9 #define LED_COUNT 24 Adafruit_NeoPixel strip(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800); SoftwareSerial mySerial(10, 3); // RX, TX void setup() { pinMode(2, INPUT); digitalWrite(2, HIGH); strip.begin(); strip.show(); Serial.begin(115200); while (!Serial) ; mySerial.begin(57600); } void loop() { uint8_t incomingByte; static uint8_t used = 0; if (mySerial.available() > 0) { incomingByte = mySerial.read(); if (incomingByte == 0) { used = 0; } else { if (used == 0) { displayDigit(incomingByte, 0x00060606); used = 1; incomingByte = 0; } } mySerial.write(incomingByte); } } void displayDigit(uint8_t d, uint32_t color) { uint8_t i; strip.clear(); switch(d) { case ' ': break; case '0': for (i = 0; i < 24; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; case '1': strip.setPixelColor(0, color); strip.setPixelColor(12, color); break; case '2': for (i = 3; i <= 9; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } for (i = 15; i <= 21; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; case '3': strip.setPixelColor(23, color); strip.setPixelColor(0, color); strip.setPixelColor(1, color); strip.setPixelColor(2, color); strip.setPixelColor(3, color); strip.setPixelColor(6, color); strip.setPixelColor(9, color); strip.setPixelColor(10, color); strip.setPixelColor(11, color); strip.setPixelColor(12, color); strip.setPixelColor(13, color); break; case '4': for (i = 18; i <= 22; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } for (i = 6; i <= 12; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; case '5': strip.setPixelColor(18, color); strip.setPixelColor(20, color); strip.setPixelColor(21, color); strip.setPixelColor(22, color); strip.setPixelColor(23, color); strip.setPixelColor(0, color); strip.setPixelColor(1, color); for (i = 6; i <= 12; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; case '6': strip.setPixelColor(0, color); for (i = 6; i <= 23; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; case '7': strip.setPixelColor(22, color); strip.setPixelColor(23, color); strip.setPixelColor(0, color); strip.setPixelColor(1, color); strip.setPixelColor(2, color); for (i = 5; i <= 9; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; case '8': strip.setPixelColor(21, color); strip.setPixelColor(22, color); strip.setPixelColor(23, color); strip.setPixelColor(0, color); strip.setPixelColor(1, color); strip.setPixelColor(2, color); strip.setPixelColor(3, color); for (i = 9; i <= 15; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; case '9': for (i = 18; i <= 23; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } for (i = 0; i <= 12; i++) { strip.setPixelColor(i, color); } break; default: break; } strip.show(); } -
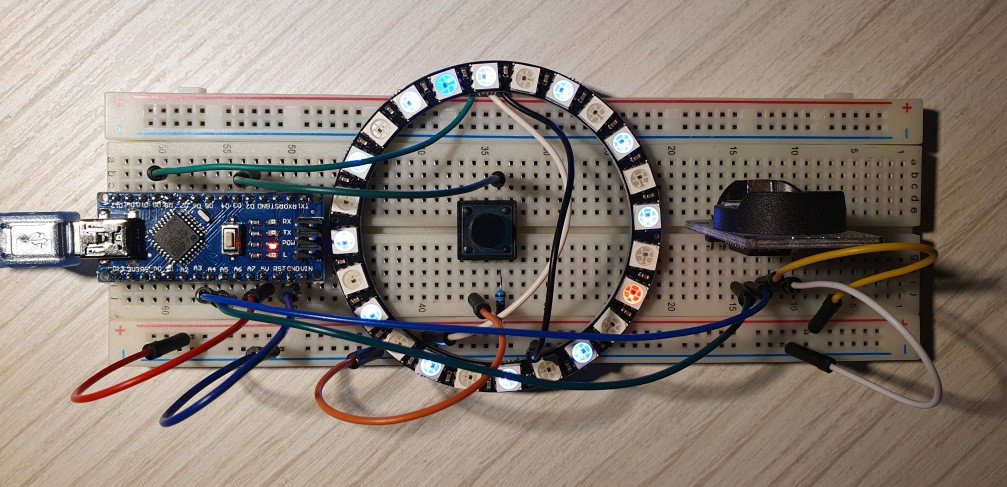
Breadboard prototype
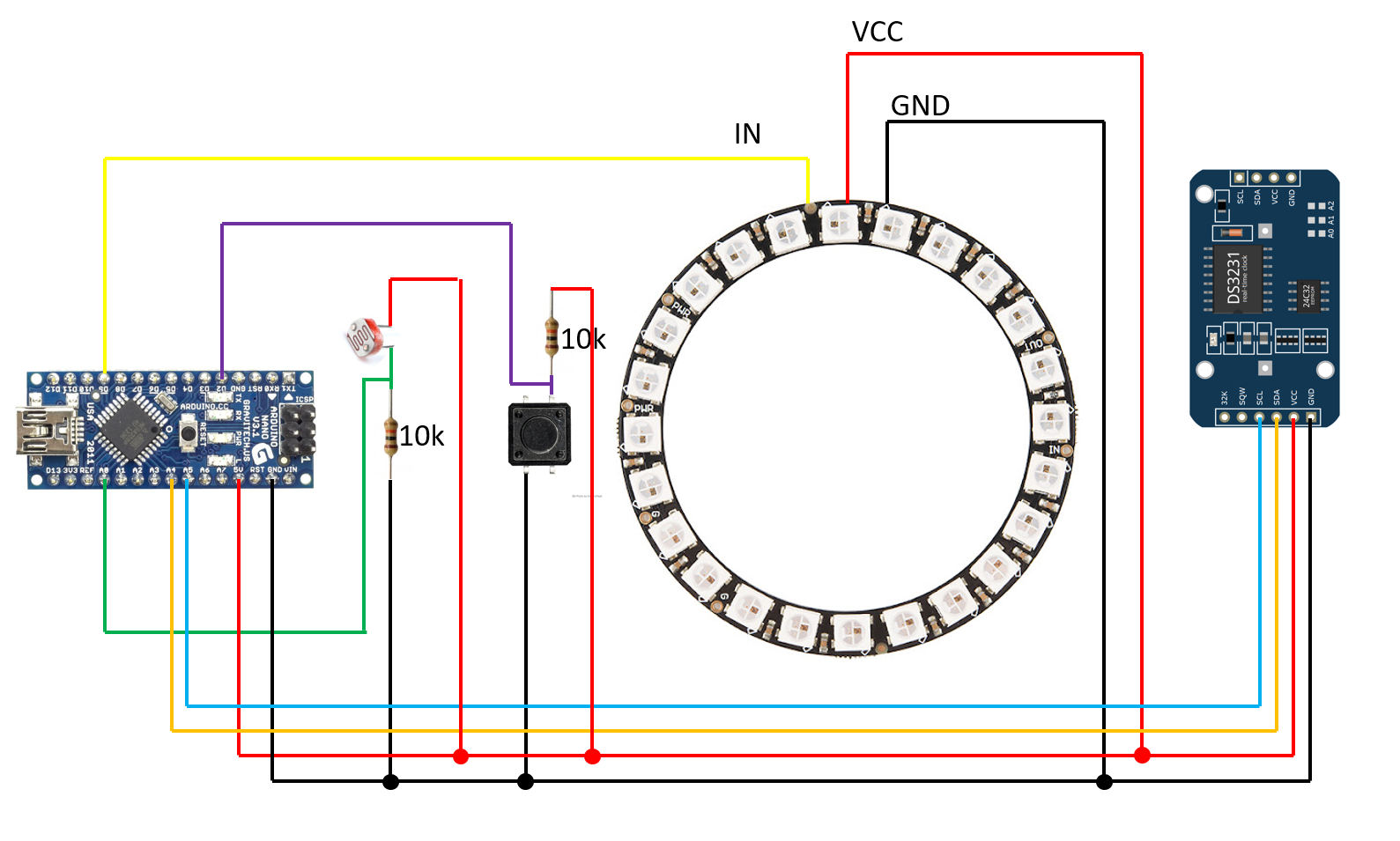
10/12/2021 at 18:37 • 0 commentsDon't feel like committing to getting PCBs made and then soldering a handful of SMD components? How about trying it out on a breadboard first? After all, this is how it all started.
You'll need:
- 1x Arduino Nano
- 1x DS3231 RTC module
- 1x Addressable LED ring with 24 LEDs
- 2x 10 kOhm resistors
- 1x Pushbutton
- 1x Light dependent resistor (LDR)
- Breadboard, wires, soldering iron (for the LED ring as it doesn't come with anything connected to the pads)
Use the firmware from GitHub
Wiring diagram and a picture of what you can expect to get:
![]()
![]()
-
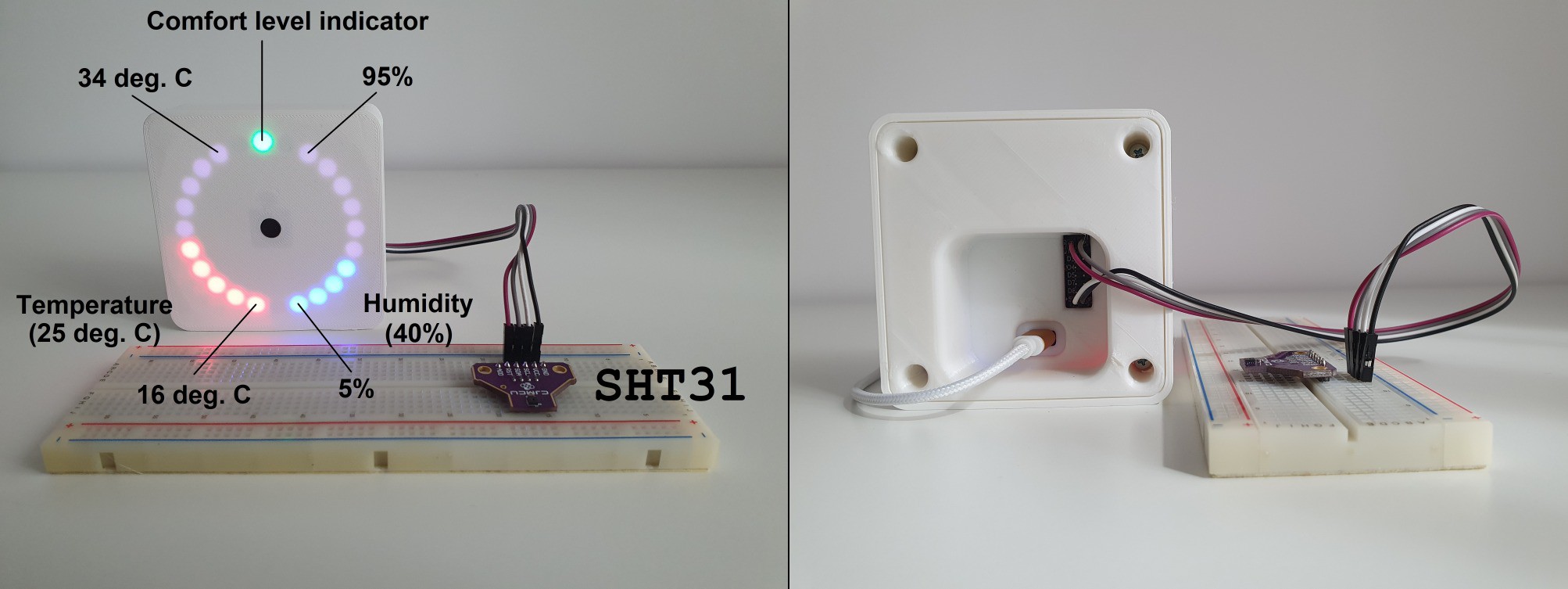
Adding sensors: Temperature and Humidity
10/10/2021 at 12:09 • 0 commentsOn the back of the PCB there is an expansion header that can be populated to add functionality. Adding an SHT31 allows MakeTime to measure temperature and humidity.
The display is divided into 3 sections.
- On the left, the temperature is shown on 10 LEDs. The first LED turns on above 16 degrees Celsius and the last one above 34 degrees Celsius.
- On the right, humidity is shown with 10% granularity.
- At the top a single LED turns Green/Yellow/Red to indicate comfort level, loosely based on the information in this article https://www.azosensors.com/Article.aspx?ArticleID=487
![]()
Arduino sketch#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h> #include <Wire.h> #include "Adafruit_SHT31.h" #define LED_PIN 9 #define LED_COUNT 24 Adafruit_NeoPixel strip(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800); Adafruit_SHT31 sht31 = Adafruit_SHT31(); void setup() { strip.begin(); strip.show(); if (! sht31.begin(0x44)) // Set to 0x45 for alternate i2c addr { strip.setPixelColor(12, 0x00800000); strip.show(); while (1) delay(1); } } void loop() { float t = sht31.readTemperature(); float h = sht31.readHumidity(); uint32_t color; uint8_t r, b, i; if (! isnan(t)) { r = round((t - 15) / 2); } else { r = 0; } if (! isnan(h)) { b = round(h / 10); } else { b = 0; } strip.clear(); // Draw temperature for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { color = 0x00040404; if (r > i) color += 0x00200000; strip.setPixelColor(i + 13, color); } // Draw humidity for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { color = 0x00040404; if (b > i) color += 0x00000020; strip.setPixelColor(11 - i, color); } // Comfort level: // https://www.azosensors.com/Article.aspx?ArticleID=487 // T in [20 - 26 deg] and RH in [30 - 70 %] - Green // T in [19 - 27 deg] and RH in [30 - 70 %] - Yellow // T in [20 - 26 deg] and RH in [20 - 80 %] - Yellow // else - Red color = 0; if (t >= 20 && t <= 26 && h >= 30 && h <= 70) color = 0x00002000; else if (t >= 19 && t <= 27 && h >= 30 && h <= 70) color = 0x00202000; else if (t >= 20 && t <= 26 && h >= 20 && h <= 80) color = 0x00202000; else color = 0x00200000; strip.setPixelColor(0, color); strip.show(); delay(0.5); } -
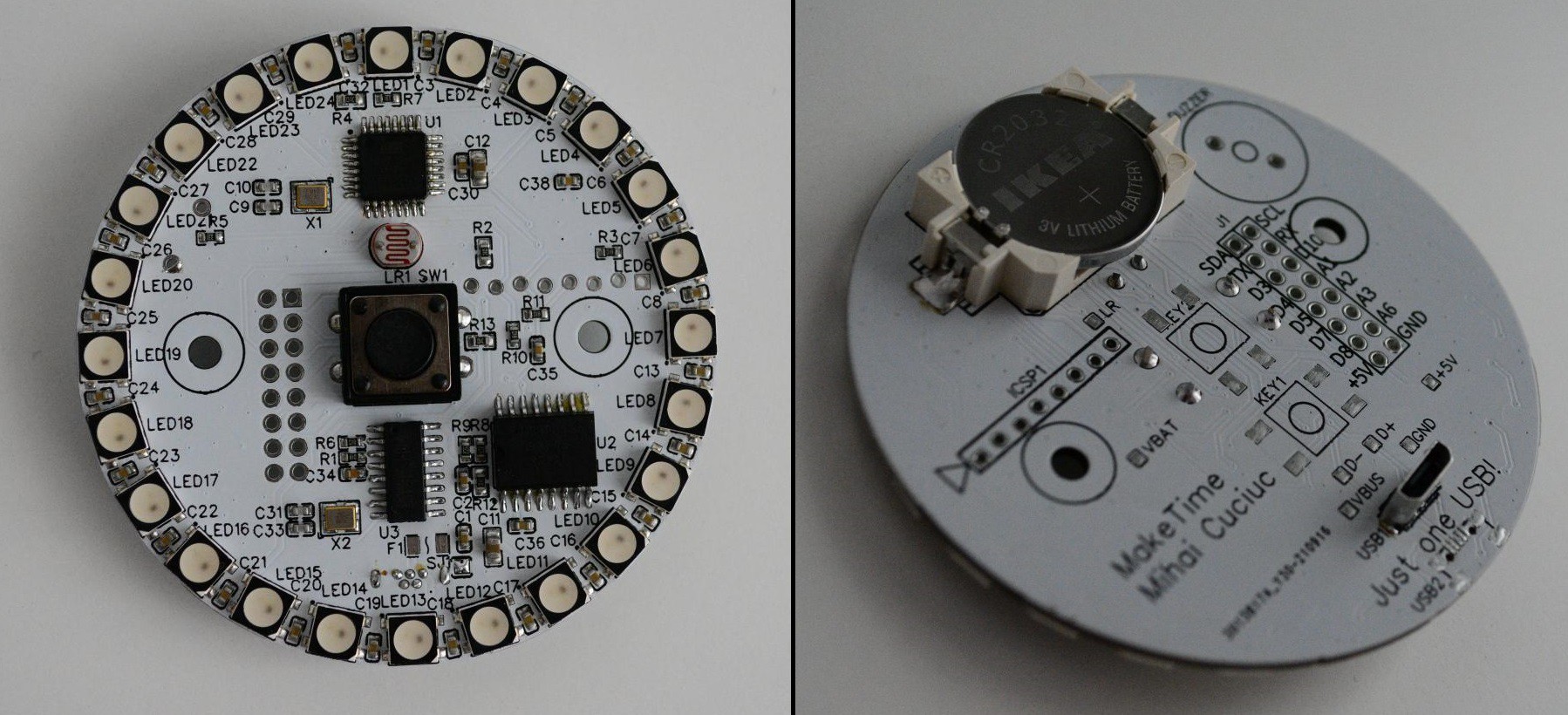
Updated PCBs
10/02/2021 at 11:54 • 0 commentsFixed missing 100nF cap on MCU reset line. This is needed for programming the chip from the Arduino IDE and was the reason there was an orange wire on the original PCBs.
Added footprints for 2 additional buttons on the back.
![]()
-
MakeTime as instrument display
09/25/2021 at 09:21 • 0 commentsYou can use MakeTime as an indicator for your PC's performance. Or for anything else, for that matter. Here's an example of it being used as a CPU load monitor
or you can use more than one to make an instrument cluster
![]()
MakeTime is simply listening on the serial port for what it should be displaying and a python script sends the stats.
Arduino sketch#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h> #define LED_PIN 9 #define LED_COUNT 24 Adafruit_NeoPixel strip(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800); void setup() { strip.begin(); strip.show(); Serial.begin(115200); Serial.setTimeout(100); } void loop() { String s; int r, g, b, i; uint32_t color; s = Serial.readString(); if (s != "") { sscanf(s.c_str(), "%d %d %d", &r, &g, &b); strip.clear(); for (i = 0; i < 19; i++) { color = 0x00101010; if (r > i) color += 0x600000; if (g > i) color += 0x006000; if (b > i) color += 0x000060; strip.setPixelColor((i + 15) % 24, color); } strip.show(); } }
Python script for CPU load monitorimport serial import psutil serialPort = serial.Serial("COM6", 115200, xonxoff=False, rtscts=False, dsrdtr=False) while (1): cpu_percent = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=0.2) str = "%d 0 0" % int(cpu_percent*19 / 100.0) bstr = bytearray(str) serialPort.write(bstr) print cpu_percent, bstr serialPort.close()
 mihai.cuciuc
mihai.cuciuc