-
References and Links about Small Computers which I find Fascinating
10/04/2021 at 13:13 • 0 commentsHere's my stash of unforgettable links to prior art in the realm of small computers
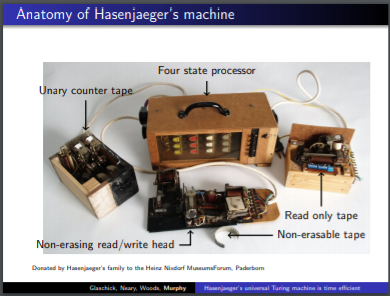
Gisbert Hasenjaeger's Machine![]()
The most tantalising small relay computer of all time?
- Hasenjaeger’s electromechanical small universal Turing machine is time efficient http://www.frontiersinai.com/turingfiles/October/slides_murphy.pdf
- Wang’s B machines are efficiently universal, as is Hasenjaeger’s small universal electromechanical toy. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0885064X14000181#fn000010 https://reader.elsevier.com/reader/sd/pii/S0885064X14000181?token=CEB846849710AAB7F8165B97A511661A76C464520A354AB0139545D0235A7598716AC4D10181143529690D27D3EFD92A
One Bit Computers
- agp.cooper One Bit CPUs
https://hackaday.io/project/26338-one-bit-cpus - Jeff Laughton - all these are fascinating to read.
- Motorola MC14500B http://tinymicros.com/mediawiki/images/e/ec/MC14500B_Handbook.pdf
- WDR -1 http://wdr-1-bit-computer.talentraspel.de/documents/wdr_1-40.pdf
OISC One Instruction Set Computers
- justin davis Move TTL https://hackaday.io/project/21298-one-instruction-ttl-computer
- esolangs https://esolangs.org/wiki/OISC
- DUO Compact 2 http://ostracodfiles.com/compact2/main.html
- DUO COMPACT DESCRIPTION http://www.ostracodfiles.com/compactpage/description.html
- subleq
- davidr https://github.com/davidar/subleq
- sublec mazonka http://mazonka.com/subleq/
- A Simple Multi-Processor Computer Based on Subleq http://mazonka.com/st/lcss.pdf
- Subtract and Branch if Negative http://bitstuff.blogspot.com/2007/02/subtract-and-branch-if-negative.html
- http://homepage.cs.uiowa.edu/~jones/arch/risc/
- >span class="name">NOR and fork conditionally
PHYWE - this one is a legend!
- 1966 four students of the Freiherr vom Stein School in Frankfurt a. M. won the first prize in the group assessment of the German contest "Jugend forscht" with their project " Function Model of a Computer". After many requests came from different schools the company for teaching materials Phywe in Goettingen from 1967 on built only about 35 copies of a Relais Demonstrationcomputer, whose concept of the students was taken over by Phywe with slight modifications. The result was a one-address machine consistently built in accordance with the von-Neumann principle, working purely sequentially, memory programmable, with 6-bit per word, capacitors as storage elements and electromechanical relays as switching devices. The program could run with variable speed down to all processing steps one at a time, so that each processing step could be explained separately. After some short introduction the talk touches the Boolean algebra which is underlying the technical execution of the machine and the physical implementation in simple electromechanically controlled electronic circuits. After that, the Phywe model computer is presented and for some representative programs the flowcharts are shown together with the memory layout for commands and data. This examples have been documented in video sequences before the talk, because the real existing, fully-functional device, owned by the authors former school is no longer transportable because of its age. The Presentation will be completed by some didactic considerations in the proceedings of the conference.
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280831869_A_Look_at_the_Roots_Der_Relais-Demonstrationrechner_von_PHYWE_Prasentation_mit_Textnotizen_und_Videoclips_21_MB
- http://www.uranmaschine.de/86978.Phywe_Programmgesteuerter_Rechner_06978_00/06978_00_Phywe_Programmgesteuerter_Rechner_Copyright_Phywe_Orig_DS.pdf
- https://www.facebook.com/computerarchaeologie/
- https://benpinslabenchri.ga/phywe-relais-computer.html
- http://www.osjbuf.co/phywe-gottingen/
- https://data.collectienederland.nl/detail/foldout/void_edmrecord/dcn_nationaal-register-historische-computers_0025
- http://www.vaxman.de/my_machines/phywe/pgr/pgr.html
- http://www.vaxman.de/my_machines/phywe/pgr/phywe.mpg
- http://www.uranmaschine.de/86978.Phywe_Programmgesteuerter_Rechner_06978_00/06978_00_Phywe_Programmgesteuerter_Rechner_Copyright_Phywe_Orig_DS.pdf
- http://www.uranmaschine.de/86978.Phywe_Programmgesteuerter_Rechner_06978_00/Phywe_Programmgesteuerter_Rechner_PDR01_geoeffnete_Rueckseite_hires.jpg
- Programmgesteuerter Rechner Phywe PDR01 06978.00 - http://www.uranmaschine.de/86978.Phywe_Programmgesteuerter_Rechner_06978_00/
- Video https://www.facebook.com/watch/?v=726539284058266
- https://unterrichten.zum.de/wiki/Johnny-Simulator
- https://informatik.bildung-rp.de/werkzeuge-und-software/digitaltechnik-rechnerarchitektur.html
- https://sourceforge.net/projects/johnnysimulator/
-
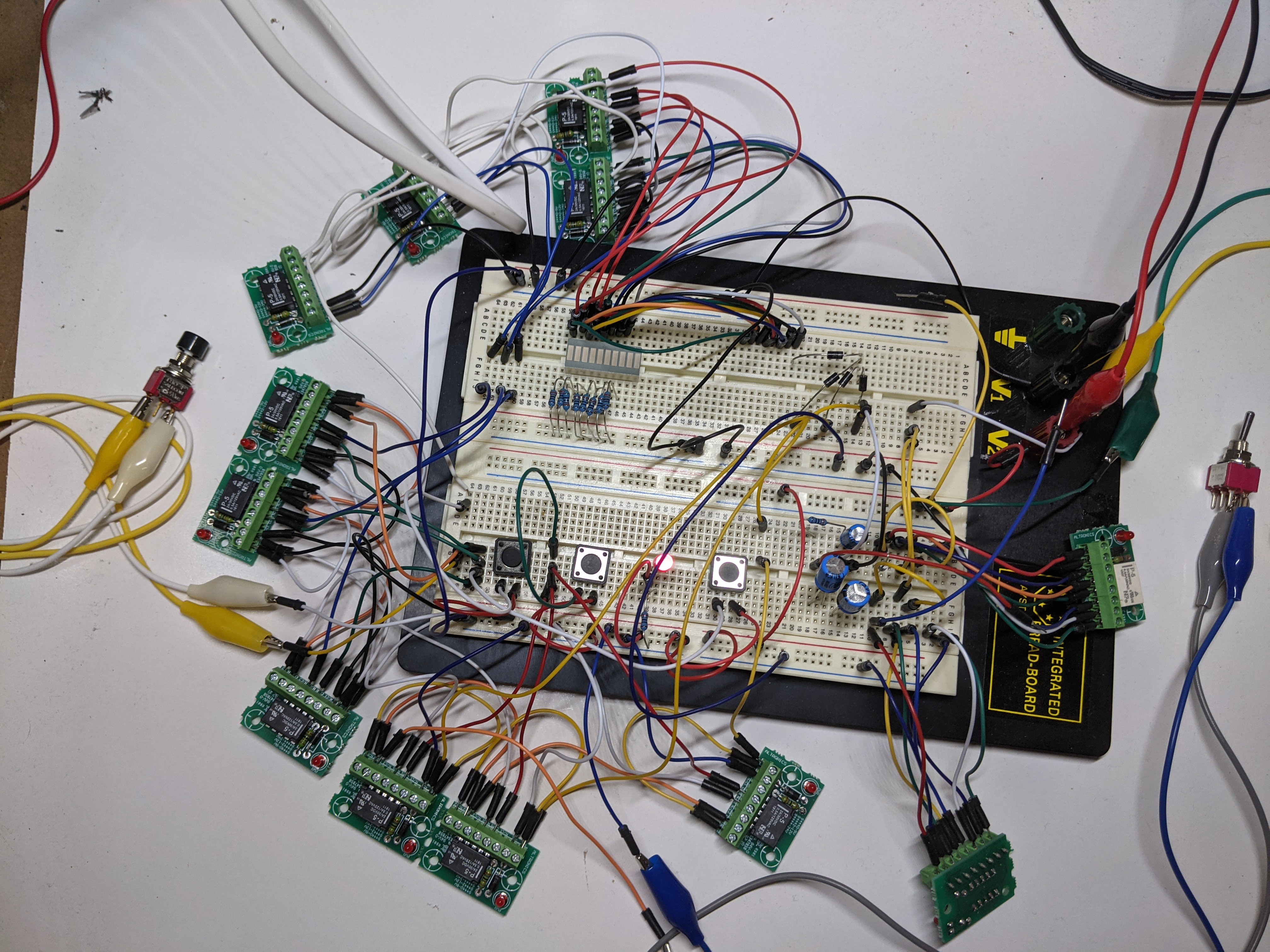
Breadboad Wolffia 21.9.2021
10/04/2021 at 12:21 • 0 commentsHere's the Wolffia breadboard at the moment.
![]()
-
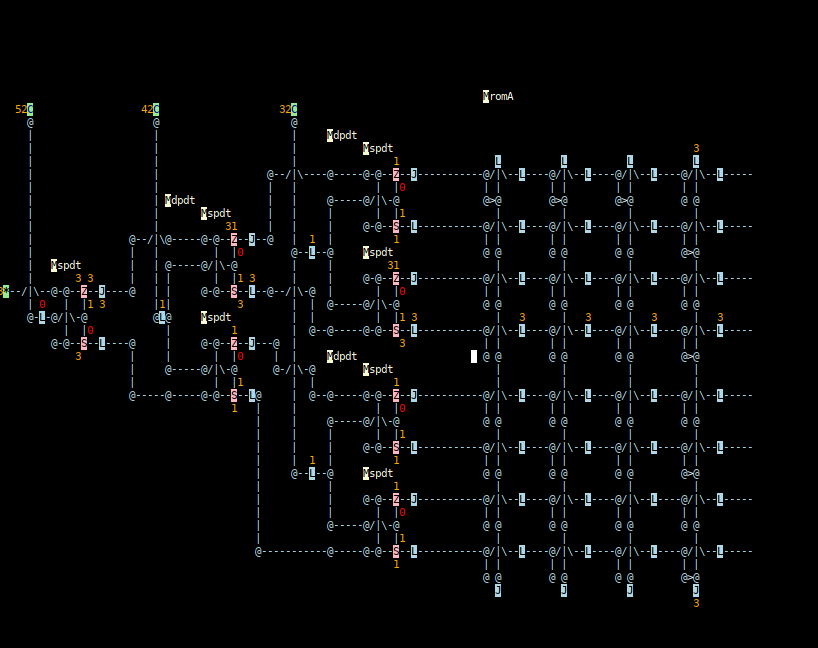
Betula simulation now catching up with the prototype.
10/04/2021 at 12:15 • 0 commentsOK so the hardware lacks a schematic. So I have started coding a logic simulator in Golang for this project which runs in ordinary terminals (it's a T.U.I) This first simulation is also the first schematic.
You can see a recording of the simulator here:
The Betula simulation of the decode and state transition ROM
Here's a snapshot:
![]()
There are three address lines which are decode by the 7 relay encoder on the left. The eight select lines are connected to an array of diodes on the right which are going to make up the program read-only-memory of the Wolffia computer.