See the demo here:
Most educational robots available today run on small computers which include raspberry pi, Jetson, and arduino which are amongst the most popular.
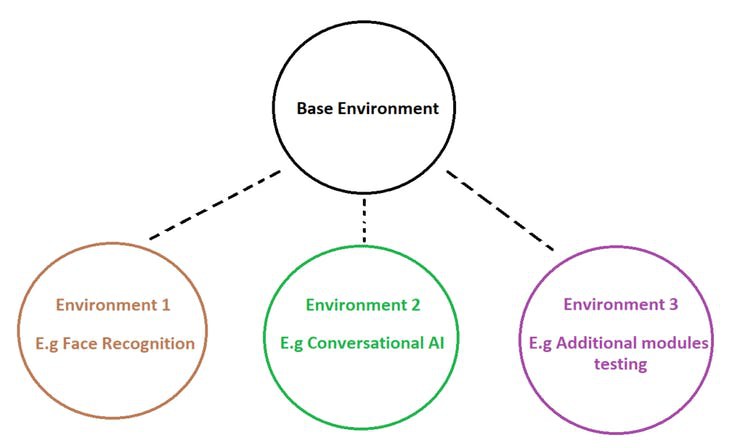
Some of the added functionalities we are going to look at are face recognition and conversational AI.
Install Virtualenvwrapper on Raspberry Pi Model 3, 4
Before we start any AI/ML projects on our raspberry pi, we have to setup the environments first.
It is best practice to always create virtual environments so that we leave our base environment untouched and use it for administrative purposes only.
Another reason is to avoid conflicts between the different applications. It is very common that applications use different versions of the same module, so to avoid these conflicts we use different environments.
We will be using virtualenvwrapper:
https://virtualenvwrapper.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
We will call Environment 1 – facrec (short for face recognition)
and
Environment 2 – cbot (short for chatbot)
virtualenvwrapper 5.0.1.dev2
First, some initialization steps. Most of this only needs to be done one time. You will want to add the command to source /usr/local/bin/virtualenvwrapper.sh to your shell startup file, changing the path to virtualenvwrapper.sh depending on where it was installed by pip or your package manager.
$ pip install virtualenvwrapper... $ export WORKON_HOME=~/Envs $ mkdir -p $WORKON_HOME $ source /usr/local/bin/virtualenvwrapper.sh $ mkvirtualenv facrec Installing setuptools.................................................................................................................................................................................done. virtualenvwrapper.user_scripts Creating /Users/dhellmann/Envs/facrec/bin/predeactivate virtualenvwrapper.user_scripts Creating /Users/dhellmann/Envs/facrec/bin/postdeactivate virtualenvwrapper.user_scripts Creating /Users/dhellmann/Envs/facrec/bin/preactivate virtualenvwrapper.user_scripts Creating /Users/dhellmann/Envs/facrec/bin/postactivate New python executable in facrec/bin/python (facrec)$ ls $WORKON_HOME facrec hook.log
Create another environment call it cbot
(facrec)$ ls $WORKON_HOME
facrec hook.log
(facrec)$ mkvirtualenv cbot
Installing setuptools...............................
....................................................
....................................................
........... ...............................done.
virtualenvwrapper.user_scripts Creating /Users/dhellmann/Envs/cbot/bin/predeactivate
virtualenvwrapper.user_scripts Creating /Users/dhellmann/Envs/cbot/bin/postdeactivate
virtualenvwrapper.user_scripts Creating /Users/dhellmann/Envs/cbot/bin/preactivate
virtualenvwrapper.user_scripts Creating /Users/dhellmann/Envs/cbot/bin/postactivate New python executable in cbot/bin/python
(env2)$ ls $WORKON_HOME
facrec cbot hook.log
Switch between environments with workon:
(cbot)$ workon facrec
(facrec)$ echo $VIRTUAL_ENV
/Users/dhellmann/Envs/facrec
(facrec)$
List all of the environments:
lsvirtualenv [-b] [-l] [-h]
Show the details for a single virtualenv:
showvirtualenv [env]
Remove an environment, in the WORKON_HOME:
rmvirtualenv ENVNAME
You must use deactivate before removing the current environment.
(mynewenv)$ deactivate
$ rmvirtualenv mynewenv
$ workon
$
Switch from a virtual environment to the system-installed version of Python:
deactivate
The environments are located in :
cd ~/.virualenvs
Now we can start installing inside the environments :))
 Wajid Ahmad
Wajid Ahmad
 Dmitry
Dmitry
 Chengwei
Chengwei

 Stefan
Stefan