-
1Print a Christmas tree
Search the internet for a nice looking Christmas tree and print it at the desired size (I used 2 pieces of A4 paper).
![]()
-
2Cut out the Christmas tree
Cut the image of the Christmas tree around the outline.
![]()
-
3Draw the Christmas tree on to the wood
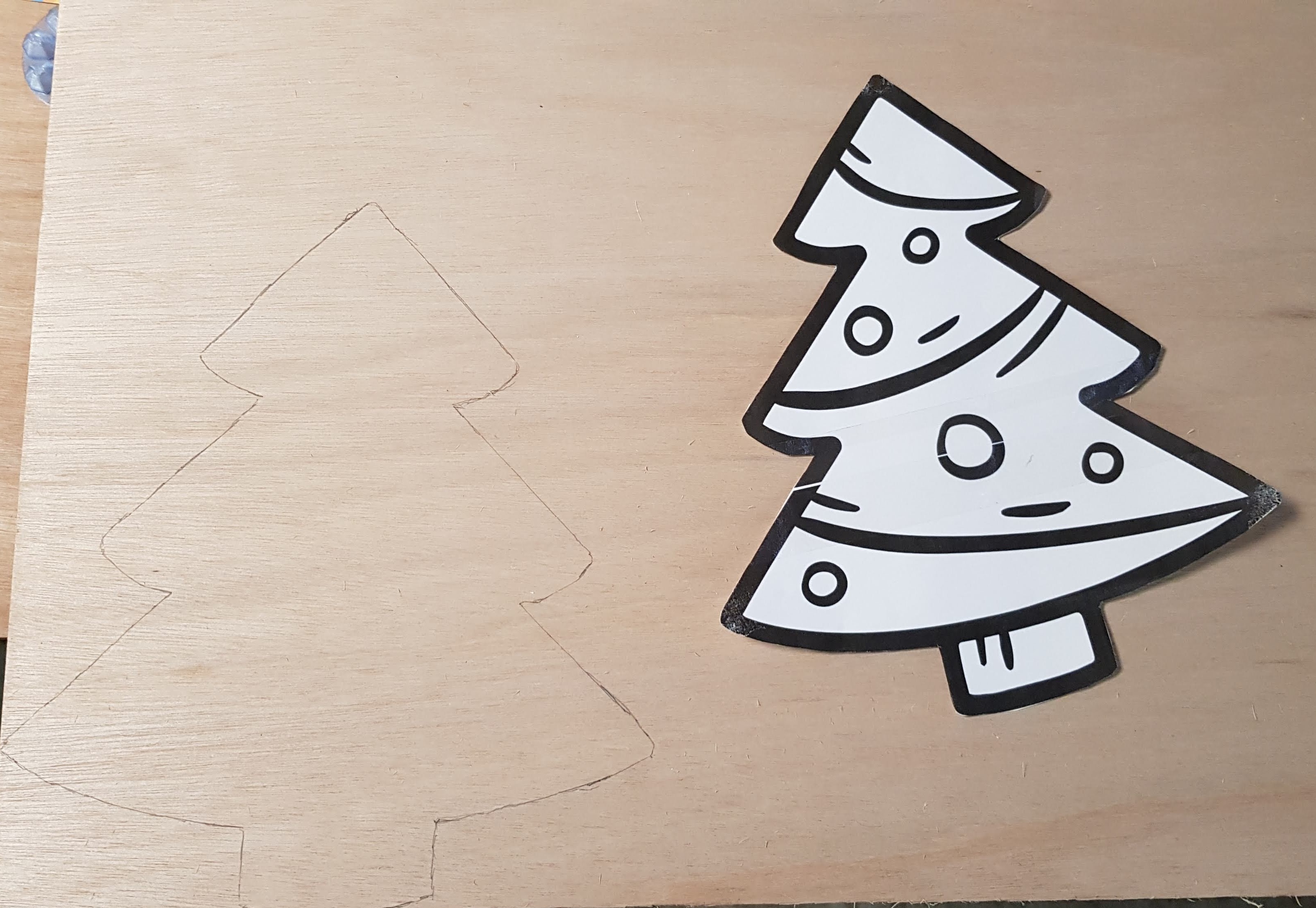
Tape the Christmas tree to the wood and than trace the outline of the Christmas tree with a pencil on to the wood.
![]()
![]()
-
4Cut out the Christmas tree
Remove the paper christmastree from the wood and cut out the shape with a jigsaw.
![]()
![]()
-
5Stick the LEDs to the wood
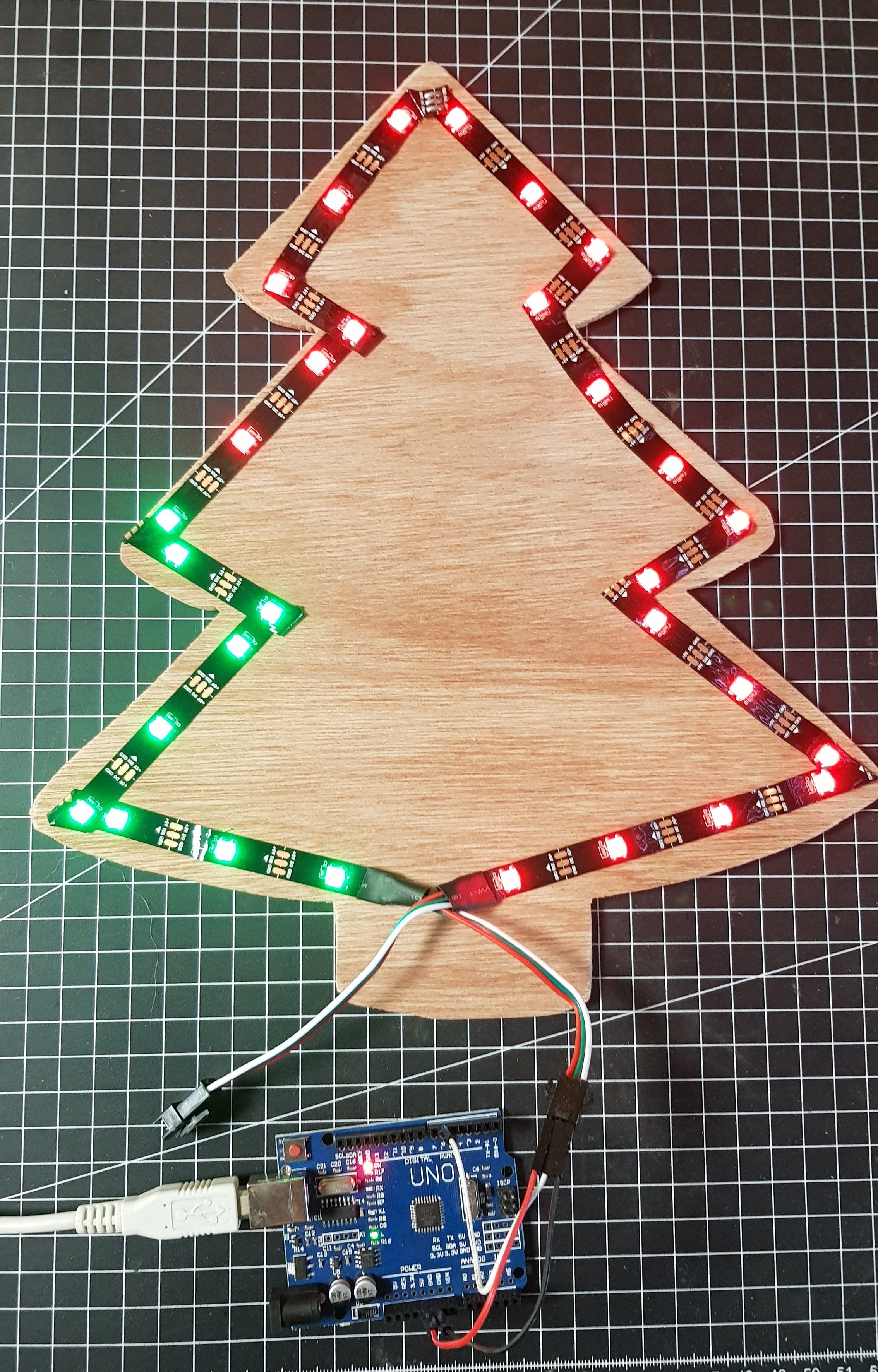
Use the adhesive on the back of the LED strip to stick it to the wood. Bent the strip to make turns.
![]()
-
6Paint the Christmas Tree
I painted the Christmas tree with my 3 year old niece but you can paint it any way you like. You could even leave it just as it is.
-
7Connect the Arduino
Connect the Arduino to the LED strip. I connected the red wire of the strip to 5V, the white wire to GND and the green wire to Pin 6.
![]()
-
8Upload the code to the Arduino
I used the strandtest example from Adafruit. My LED strip has 30 pixels so I used this value in the code. My code looks like this:
// A basic everyday NeoPixel strip test program. // NEOPIXEL BEST PRACTICES for most reliable operation: // - Add 1000 uF CAPACITOR between NeoPixel strip's + and - connections. // - MINIMIZE WIRING LENGTH between microcontroller board and first pixel. // - NeoPixel strip's DATA-IN should pass through a 300-500 OHM RESISTOR. // - AVOID connecting NeoPixels on a LIVE CIRCUIT. If you must, ALWAYS // connect GROUND (-) first, then +, then data. // - When using a 3.3V microcontroller with a 5V-powered NeoPixel strip, // a LOGIC-LEVEL CONVERTER on the data line is STRONGLY RECOMMENDED. // (Skipping these may work OK on your workbench but can fail in the field) #include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h> #ifdef __AVR__ #include <avr/power.h> // Required for 16 MHz Adafruit Trinket #endif // Which pin on the Arduino is connected to the NeoPixels? // On a Trinket or Gemma we suggest changing this to 1: #define LED_PIN 6 // How many NeoPixels are attached to the Arduino? #define LED_COUNT 30 // Declare our NeoPixel strip object: Adafruit_NeoPixel strip(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800); // Argument 1 = Number of pixels in NeoPixel strip // Argument 2 = Arduino pin number (most are valid) // Argument 3 = Pixel type flags, add together as needed: // NEO_KHZ800 800 KHz bitstream (most NeoPixel products w/WS2812 LEDs) // NEO_KHZ400 400 KHz (classic 'v1' (not v2) FLORA pixels, WS2811 drivers) // NEO_GRB Pixels are wired for GRB bitstream (most NeoPixel products) // NEO_RGB Pixels are wired for RGB bitstream (v1 FLORA pixels, not v2) // NEO_RGBW Pixels are wired for RGBW bitstream (NeoPixel RGBW products) // setup() function -- runs once at startup -------------------------------- void setup() { // These lines are specifically to support the Adafruit Trinket 5V 16 MHz. // Any other board, you can remove this part (but no harm leaving it): #if defined(__AVR_ATtiny85__) && (F_CPU == 16000000) clock_prescale_set(clock_div_1); #endif // END of Trinket-specific code. strip.begin(); // INITIALIZE NeoPixel strip object (REQUIRED) strip.show(); // Turn OFF all pixels ASAP strip.setBrightness(50); // Set BRIGHTNESS to about 1/5 (max = 255) } // loop() function -- runs repeatedly as long as board is on --------------- void loop() { // Fill along the length of the strip in various colors... colorWipe(strip.Color(255, 0, 0), 50); // Red colorWipe(strip.Color( 0, 255, 0), 50); // Green colorWipe(strip.Color( 0, 0, 255), 50); // Blue // Do a theater marquee effect in various colors... theaterChase(strip.Color(127, 127, 127), 50); // White, half brightness theaterChase(strip.Color(127, 0, 0), 50); // Red, half brightness theaterChase(strip.Color( 0, 0, 127), 50); // Blue, half brightness rainbow(10); // Flowing rainbow cycle along the whole strip theaterChaseRainbow(50); // Rainbow-enhanced theaterChase variant } // Some functions of our own for creating animated effects ----------------- // Fill strip pixels one after another with a color. Strip is NOT cleared // first; anything there will be covered pixel by pixel. Pass in color // (as a single 'packed' 32-bit value, which you can get by calling // strip.Color(red, green, blue) as shown in the loop() function above), // and a delay time (in milliseconds) between pixels. void colorWipe(uint32_t color, int wait) { for(int i=0; i<strip.numPixels(); i++) { // For each pixel in strip... strip.setPixelColor(i, color); // Set pixel's color (in RAM) strip.show(); // Update strip to match delay(wait); // Pause for a moment } } // Theater-marquee-style chasing lights. Pass in a color (32-bit value, // a la strip.Color(r,g,b) as mentioned above), and a delay time (in ms) // between frames. void theaterChase(uint32_t color, int wait) { for(int a=0; a<10; a++) { // Repeat 10 times... for(int b=0; b<3; b++) { // 'b' counts from 0 to 2... strip.clear(); // Set all pixels in RAM to 0 (off) // 'c' counts up from 'b' to end of strip in steps of 3... for(int c=b; c<strip.numPixels(); c += 3) { strip.setPixelColor(c, color); // Set pixel 'c' to value 'color' } strip.show(); // Update strip with new contents delay(wait); // Pause for a moment } } } // Rainbow cycle along whole strip. Pass delay time (in ms) between frames. void rainbow(int wait) { // Hue of first pixel runs 5 complete loops through the color wheel. // Color wheel has a range of 65536 but it's OK if we roll over, so // just count from 0 to 5*65536. Adding 256 to firstPixelHue each time // means we'll make 5*65536/256 = 1280 passes through this loop: for(long firstPixelHue = 0; firstPixelHue < 5*65536; firstPixelHue += 256) { // strip.rainbow() can take a single argument (first pixel hue) or // optionally a few extras: number of rainbow repetitions (default 1), // saturation and value (brightness) (both 0-255, similar to the // ColorHSV() function, default 255), and a true/false flag for whether // to apply gamma correction to provide 'truer' colors (default true). strip.rainbow(firstPixelHue); // Above line is equivalent to: // strip.rainbow(firstPixelHue, 1, 255, 255, true); strip.show(); // Update strip with new contents delay(wait); // Pause for a moment } } // Rainbow-enhanced theater marquee. Pass delay time (in ms) between frames. void theaterChaseRainbow(int wait) { int firstPixelHue = 0; // First pixel starts at red (hue 0) for(int a=0; a<30; a++) { // Repeat 30 times... for(int b=0; b<3; b++) { // 'b' counts from 0 to 2... strip.clear(); // Set all pixels in RAM to 0 (off) // 'c' counts up from 'b' to end of strip in increments of 3... for(int c=b; c<strip.numPixels(); c += 3) { // hue of pixel 'c' is offset by an amount to make one full // revolution of the color wheel (range 65536) along the length // of the strip (strip.numPixels() steps): int hue = firstPixelHue + c * 65536L / strip.numPixels(); uint32_t color = strip.gamma32(strip.ColorHSV(hue)); // hue -> RGB strip.setPixelColor(c, color); // Set pixel 'c' to value 'color' } strip.show(); // Update strip with new contents delay(wait); // Pause for a moment firstPixelHue += 65536 / 90; // One cycle of color wheel over 90 frames } } } -
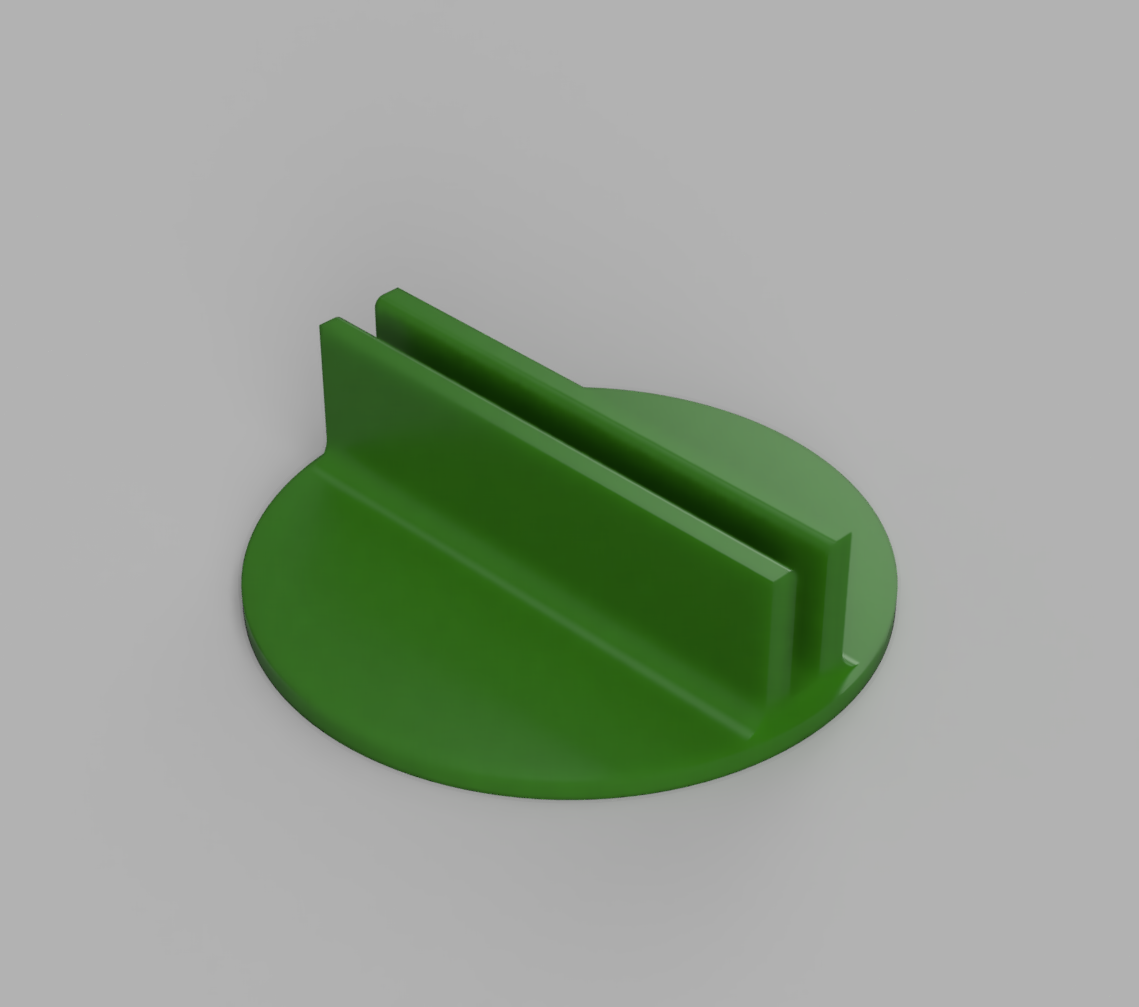
9Make a base
I 3d printed a base to keep the Christmas tree up. You can find the STL under the files section.
![]()
-
10Glue the Arduino
I glued the Arduino to the back of the Christmas tree using some hot glue.
Wooden Christmas tree with addressable LEDs
A wooden Christmas tree with addressable LEDs (WS2812 / Neopixels)
 Maarten Schipper
Maarten Schipper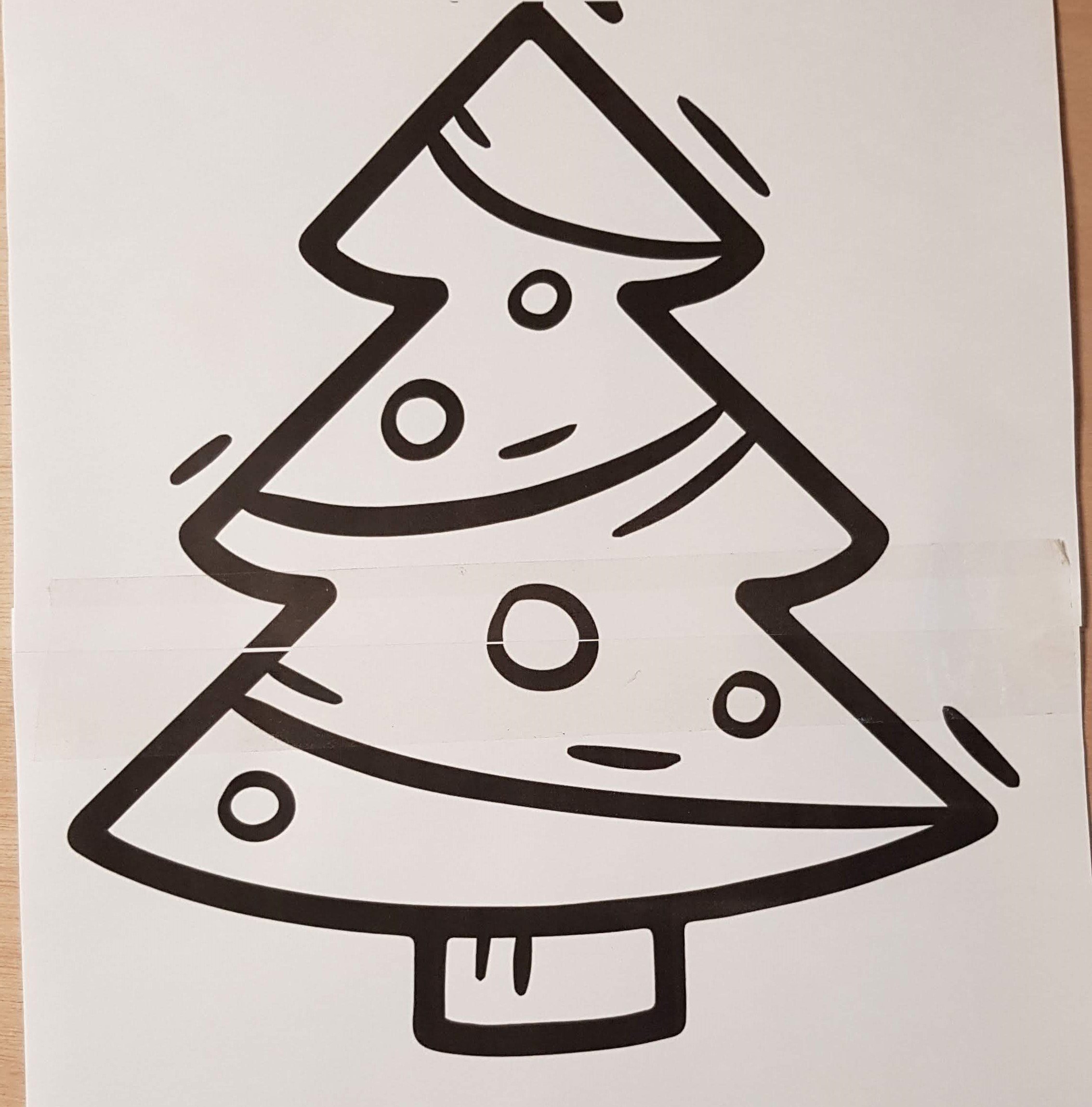







Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.