In my last post, I listed the components needed to build a reflow-oven and the components I chose for my design.
In this post, I will outline the steps I used to build my reflow-oven along with some photos.
As mention, I am using a BLACK & DECKER Model TRO355. In order to make room inside for the SSR and because it was no longer needed, I had to remove the temperature controls. There were some pre-stamped holes in the back and bottom of the metal housing of the oven. I used one of them to feed the thermocouple through and used Aluminum Foil Tape to seal the hole and secure the wires along the back side.
 Nice oven! No controls!Side open, dials removed, controls bypassed and SSR in placeCloser view of the compartment
Nice oven! No controls!Side open, dials removed, controls bypassed and SSR in placeCloser view of the compartmentReferring to the photos above, in the left photo, the thermocouple can be seen “hanging down” as it needs to be near the PCB’s. In the middle and right photos, the SSR is mounted at the bottom-front of the compartment. The black Bakelite “block” with the leaf-springs is the door-disconnect safety switch, which I left in place as a precaution since it immediately cuts power to the heating elements when the door is opened. I also had to bypass the temperature control using 10 gauge single-strand wire but the method cannot be readily seen in the photos.
 Back of LCD with custom cable modCP2103-based USB-2-Serial BridgeCP2103-based USB-2-Serial Bridge
Back of LCD with custom cable modCP2103-based USB-2-Serial BridgeCP2103-based USB-2-Serial BridgeReferring to the photos above; the individual modules that make up the PID controller needed to fit in a plastic enclosure.
The LCD was not a direct-connection to the ROCKET SCREAM PID controller shield, so a connector had to be fitted (left photo). Also, the LCD had a flex-strip for its interface cable, so I had to directly solder individual 30 gauge KYNAR wires to the flex connector then crimp the other ends into an IDC connector to mate to the LCD connector on the PID controller shield.
I used a CP2102-based USB-to-Serial bridge to interface with the AVR-based “Mini-Ultra” module. The USB-to-Serial bridge comes with a USB “type-A” connector, which I removed. I wanted to use a USB “Mini-B” connection instead, so I needed to fashion a daughter-board to mate it with that also supply 5 volts from the USB bus (middle and right photos).
The reflow controller shield came with an 8×2 LCD, 3 on-board switches (w/ hardware debounce circuitry) for “RESET”, “SW1” and “SW2”, two LEDS and a beeper. There is also a 6-position mini-terminal block for the thermocouple, Heat SSR and (cooling) Fan SSR connections. The included LCD detaches and a “standard” 16 pin (2×8) LCD header is available to “extend” the LCD somewhere else. I planned to use the 16×2 LCD, so having the LCD connector available was the best option.
The only issues I had with the design layout of the reflow controller shield was that if one wants to use external switches through the reflow controller shield (like me), then there is no way to attach them in parallel to those on-board. Nor is there any way to attached external LEDs for front panel display. So that required a little bit of hacking by soldering the external switch and LED wires directly to to the reflow controller shield.
 “Mini-Ultra” and PID controller shield; mates for life!LCD and PushbuttonsUSB Mini-B and hole for SSR and Thermocouple wiresAll modules mounted in the enclosure
“Mini-Ultra” and PID controller shield; mates for life!LCD and PushbuttonsUSB Mini-B and hole for SSR and Thermocouple wiresAll modules mounted in the enclosureReferring to the photos above; a 6 x 3 x 2 inch project box was used but it needed some holes cut into before the components could be mounted. I needed a rectangular cutout for both the LCD (middle-left photo) and the USB Min-B connector access (middle-right photo).
After assembling the “Mini-Ultra” PCB and leaving the 3.3V regulator off, I was able to hard-solder the D13:0 pins of the “Mini-Ultra” right to the reflow controller shield’s D13:0 pins and stretch some connect wires for power, ground, reset, etc. Thus the “Mini-Ultra” and PID controller shield were “mated” together with a minimum of effort and holes were drilled in the enclosure for mounting them (left photo). All modules and components fit into the enclosure with some room to spare (right photo).
 Enclosure mounted to side of ovenEnclosure mounted to side of oven
Enclosure mounted to side of ovenEnclosure mounted to side of ovenReferring to the photos above; the oven was reassembled with the thermocouple and SSR wires routed outside the oven “control compartment” and the enclosure was mounted to the side of the oven. The themocouple and SSR wires were threaded into the enclosure and fastened to their respective terminal block connections on the PID controller shield.
The schematic for the module and component interconnections is below. A full-sized JPEG schematic is here.
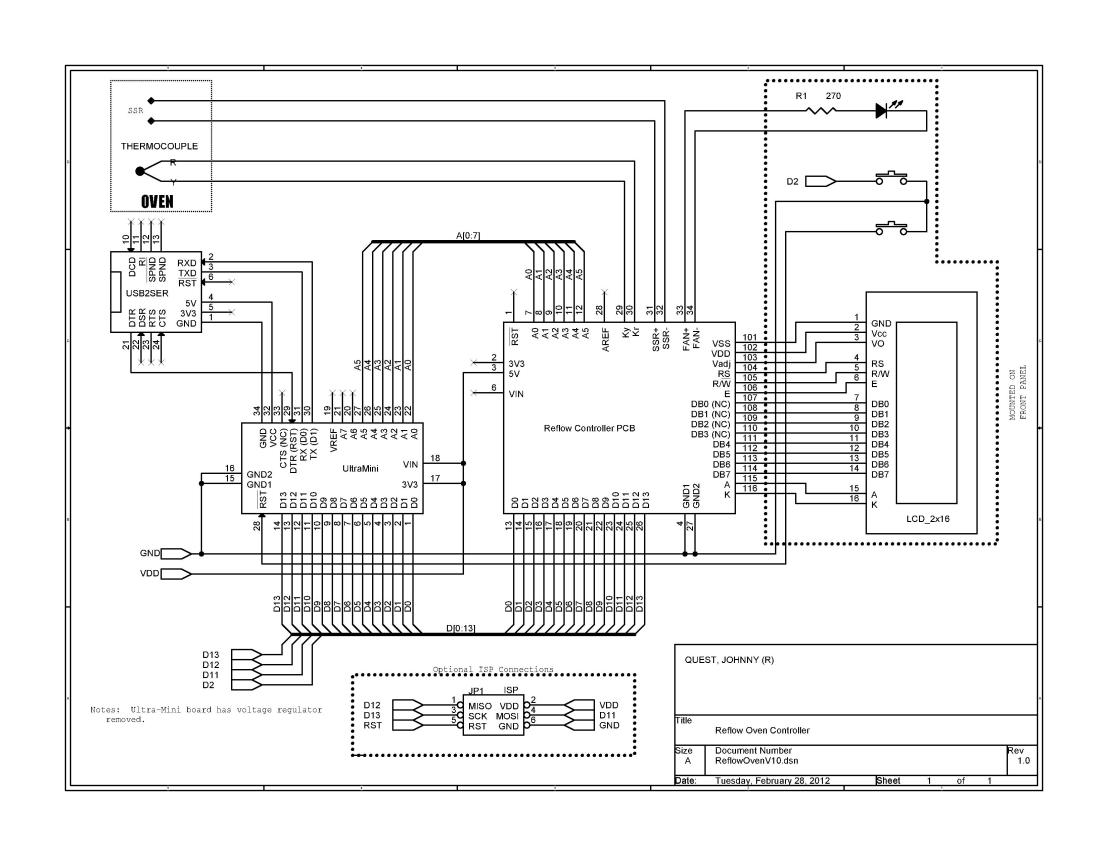 Module Interconnections
Module InterconnectionsThe modified ARDUINO sketch is posted below.
/*******************************************************************************
Title: Reflow Oven Controller
Version: 1.31
Date: 2016-0618
Company: Rocket Scream Electronics
Website: http://www.rocketscream.com
==============================================================================
Additional modifications: (2012) Johnny Quest (ksv_prj [at] gmx [dot] com
==============================================================================
Revision Description
======== ===========
1.31 JQ – Moved message strings to PROGMEM, which was not
really necessary.
Uses: “Arduino Pro Mini” w/ Mega328p @8MHz
1.30JQ – Forgot what I did!.
1.20JQ – Added support for 16×2 “external display”.
Added support for displaying real-time temperature slope
Added support for remaining “soak time”
Added support for elapsed time at “wet zone” temperature
1.10 Arduino IDE 1.0 compatible.
1.00 Initial public release.
********************************************************************************
Brief
=====
This is an example firmware for our Arduino compatible reflow oven controller.
The reflow curve used in this firmware is meant for lead-free profile
(it’s even easier for leaded process!). Please check our wiki
(www.rocketscream.com/wiki) for more information on using this piece of code
together with the reflow oven controller.
Temperature (Degree Celcius) Magic Happens Here!
245-| x x
| x x
| x x
| x x
200-| x x
| x | | x
| x | | x
| x | |
150-| x | |
| x | | |
| x | | |
| x | | |
| x | | |
| x | | |
| x | | |
30 -| x | | |
|< 60 – 90 s >|< 90 – 120 s >|< 90 – 120 s >|
| Preheat Stage | Soaking Stage | Reflow Stage | Cool
0 |_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _|_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _|_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Time (Seconds)
This firmware owed very much on the works of other talented individuals as
follows:
==========================================
Brett Beauregard (www.brettbeauregard.com)
==========================================
Author of Arduino PID library. On top of providing industry standard PID
implementation, he gave a lot of help in making this reflow oven controller
possible using his awesome library.
==========================================
Limor Fried of Adafruit (www.adafruit.com)
==========================================
Author of Arduino MAX6675 library. Adafruit has been the source of tonnes of
tutorials, examples, and libraries for everyone to learn.
Disclaimer
==========
Dealing with high voltage is a very dangerous act! Please make sure you know
what you are dealing with and have proper knowledge before hand. Your use of
any information or materials on this reflow oven controller is entirely at
your own risk, for which we shall not be liable.
Licences
========
This reflow oven controller hardware and firmware are released under the
Creative Commons Share Alike v3.0 license
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
You are free to take this piece of code, use it and modify it.
All we ask is attribution including the supporting libraries used in this
firmware.
*******************************************************************************/
// ***** INCLUDES *****
#include
#include
#include <avr/pgmspace.h>
#include
#include
#define TEST 0 // set to “1” to enable test code/constants
#define DEBUG 0 // set to “1” to enable debug via Serial
// ***** TYPE DEFINITIONS *****
typedef enum REFLOW_STATE {
REFLOW_STATE_IDLE,
REFLOW_STATE_PREHEAT,
REFLOW_STATE_SOAK,
REFLOW_STATE_REFLOW,
REFLOW_STATE_COOL,
REFLOW_STATE_COMPLETE,
REFLOW_STATE_ERROR,
REFLOW_STATE_TUNE
}
reflowState_t;
typedef enum REFLOW_STATUS {
REFLOW_STATUS_OFF,
REFLOW_STATUS_ON
}
reflowStatus_t;
typedef enum DEBOUNCE_STATE {
DEBOUNCE_STATE_IDLE,
DEBOUNCE_STATE_CHECK,
DEBOUNCE_STATE_RELEASE
}
debounceState_t;
// ***** CONSTANTS *****
// set “1” if LCD has “degree” character, else “0”
#define HAS_DEGREE 0
// set “1” if LCD has “delta” character, else “0”
#define HAS_DELTA 0
// This is the temperature at which the “complete” signals at
#if !TEST
#define TEMPERATURE_ROOM 50
#else
#define TEMPERATURE_ROOM 80
#endif
#define TEMPERATURE_SOAK_MIN 150
#define TEMPERATURE_SOAK_MAX 155
#define SOAK_TEMPERATURE_STEP 5
#if !TEST
#define SOAK_MICRO_PERIOD 240000 // 4 minutes (240 seconds) to soak
#else
#define SOAK_MICRO_PERIOD 300000 // 5 minutes to soak
#endif
#define TEMPERATURE_REFLOW_MIN 180 // spec’d wet region start
#define TEMPERATURE_REFLOW_MAX 230
#if !TEST
#define TEMPERATURE_COOL_MIN 60
#else
#define TEMPERATURE_COOL_MIN 80
#endif
// soak-to-reflow beeper “on” duration in mS
#define BEEPDURATION_REFLOW 250
// reflow-to-cool beeper “on” duration in mS
#define BEEPDURATION_COOL 2000
// cool-to-complete beeper “on” duration in mS
#define BEEPDURATION_COMPLETE 3000
#define DEBOUNCE_PERIOD_MIN 50
#define THERMOCOUPLE_DISCONNECTED 10000
#define SENSOR_SAMPLING_TIME 1000
#define PID_SAMPLE_TIME 1000
// Define PWM @ 100% window size in mS
// Note: 2000mS appears to be a crucial value
#if !TEST
#define PWMWINDOW 2000
#else
#define PWMWINDOW 2500
#endif
// ******************* PID PARAMETERS *******************
// ***** PRE-HEAT STAGE *****
#define PID_KP_PREHEAT 40
#define PID_KI_PREHEAT 0.025
#define PID_KD_PREHEAT 20
// ***** SOAKING STAGE *****
#define PID_KP_SOAK 200 // These work well!
#define PID_KI_SOAK 0.015
#define PID_KD_SOAK 50
// ***** REFLOW STAGE *****
#define PID_KP_REFLOW 100
#define PID_KI_REFLOW 0.025
#define PID_KD_REFLOW 25
// ***** LCD MESSAGES *****
// Strings in PROGMEM
const char lcdMessagesReflowStatus1[] PROGMEM = ” Ready” ;
const char lcdMessagesReflowStatus2[] PROGMEM = ” Pre-heat” ;
const char lcdMessagesReflowStatus3[] PROGMEM = ” Soak” ;
const char lcdMessagesReflowStatus4[] PROGMEM = ” Reflow” ;
const char lcdMessagesReflowStatus5[] PROGMEM = ” Cool” ;
const char lcdMessagesReflowStatus6[] PROGMEM = ” Complete” ;
const char lcdMessagesReflowStatus7[] PROGMEM = ” Error” ;
const char lcdMessagesReflowStatus8[] PROGMEM = ” Tuning” ;
const char * const lcdMessagesReflowStatusPtr[] PROGMEM = {
lcdMessagesReflowStatus1 ,
lcdMessagesReflowStatus2 ,
lcdMessagesReflowStatus3 ,
lcdMessagesReflowStatus4 ,
lcdMessagesReflowStatus5 ,
lcdMessagesReflowStatus6 ,
lcdMessagesReflowStatus7 ,
lcdMessagesReflowStatus8 ,
};
char buffer[10]; // make sure this is large enough for the largest string it must hold
// ***** DEGREE SYMBOL FOR LCD *****
#if !HAS_DEGREE
unsigned char degree[8] = {
140, 146, 146, 140, 128, 128, 128, 128
};
unsigned char degree_char = 0; // custom char code “1”
#else
unsigned char degree_char = 0xDF;
#endif
// ***** DELTA SYMBOL FOR LCD *****
#if !HAS_DELTA
unsigned char delta[8] = {
B00000, B00100, B01010, B10001, B10001, B11111, B00000, B00000
};
unsigned char delta_char = 1; // custom char code “1”
#else
unsigned char delta_char = 0xE8;
#endif
// ***** PIN ASSIGNMENT *****
int button1 = 2;
int button2 = 3;
int fan = 4;
int ssr = 5;
int buzzer = 6;
int lcdRs = 7;
int lcdE = 8;
int lcdD4 = 9;
int lcdD5 = 10;
int lcdD6 = 11;
int lcdD7 = 12;
//
int ledGreen = A0;
int ledRed = A1;
int thermocoupleCLK = A3;
int thermocoupleCS = A4;
int thermocoupleSO = A5;
// ***** PID CONTROL VARIABLES *****
double setpoint;
double input;
double p_input;
double slope;
double output;
double kp = PID_KP_PREHEAT;
double ki = PID_KI_PREHEAT;
double kd = PID_KD_PREHEAT;
int windowSize;
unsigned long windowStartTime;
unsigned long nextCheck;
unsigned long nextRead;
unsigned long timerSoak;
unsigned long SoakStartTime;
unsigned long ReflowStartTime;
unsigned long ReflowDwellTime;
unsigned long buzzerPeriod;
// For Auto-Tuning
byte ATuneModeRemember = 0;
double kpmodel = 1.5, taup = 100, theta[50];
double outputStart = 5;
double aTuneStep = 50, aTuneNoise = 1, aTuneStartValue = 100;
unsigned int aTuneLookBack = 10;
boolean tuning = false;
unsigned long modelTime, serialTime;
// Reflow oven controller state machine state variable
reflowState_t reflowState;
// Reflow oven controller status
reflowStatus_t reflowStatus;
// Button debounce state machine state variable
debounceState_t debounceState;
// Button debounce timer
long lastDebounceTime;
// Button press status
boolean buttonPressStatus;
// Seconds timer
int timerSeconds;
// Specify PID control interface
PID reflowOvenPID(&input, &output, &setpoint, kp, ki, kd, DIRECT);
// Specify PID Auto-tune interface
PID_ATune aTune(&input, &output);
// Specify LCD interface
LiquidCrystal lcd(lcdRs, lcdE, lcdD4, lcdD5, lcdD6, lcdD7);
// Specify MAX6675 thermocouple interface
MAX6675 thermocouple(thermocoupleCLK, thermocoupleCS, thermocoupleSO);
void setup()
{
// SSR pin initialization to ensure reflow oven is off
digitalWrite(ssr, LOW);
pinMode(ssr, OUTPUT);
// Buzzer pin initialization to ensure annoying buzzer is off
digitalWrite(buzzer, LOW);
pinMode(buzzer, OUTPUT);
// LED pins initialization and turn on upon start-up (active low)
digitalWrite(ledRed, LOW);
digitalWrite(ledGreen, LOW);
pinMode(ledRed, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledGreen, OUTPUT);
// Push button pins initialization
pinMode(button1, INPUT);
pinMode(button2, INPUT);
// Start-up splash
digitalWrite(buzzer, HIGH);
lcd.begin(16, 2);
#if !HAS_DEGREE
lcd.createChar(0, degree);
#endif
#if !HAS_DELTA
lcd.createChar(1, delta);
#endif
lcd.clear();
lcd.print(“Reflow Oven 1v31”);
digitalWrite(buzzer, LOW);
delay(2500);
lcd.clear();
// Serial communication at 57600 bps
Serial.begin(57600);
// Turn off LED (active low)
digitalWrite(ledRed, HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledGreen, HIGH);
if (digitalRead(button1) == LOW)
{
// Valid button press
reflowState = REFLOW_STATE_TUNE;
}
// Set window size
windowSize = PWMWINDOW;
// Initialize time keeping variable
nextCheck = millis();
// Initialize thermocouple reading varible
nextRead = millis();
}
void loop()
{
// Current time
unsigned long now;
// Time to read thermocouple?
if (millis() > nextRead)
{
// Read thermocouple next sampling period
nextRead += SENSOR_SAMPLING_TIME;
// Read current temperature
p_input = input ; //save previous reading
input = thermocouple.readCelsius();
slope = (input – p_input); // calculate the slope
// If thermocouple is not connected
if (input == THERMOCOUPLE_DISCONNECTED)
{
// Illegal operation without thermocouple
reflowState = REFLOW_STATE_ERROR;
reflowStatus = REFLOW_STATUS_OFF;
}
}
if (millis() > nextCheck)
{
// Check input in the next seconds
nextCheck += 1000;
// If reflow process is on going
if (reflowStatus == REFLOW_STATUS_ON)
{
// Toggle red LED as system heart beat
digitalWrite(ledRed, !(digitalRead(ledRed)));
// Increase seconds timer for reflow curve analysis
timerSeconds++;
if ( !DEBUG )
{
// Send temperature and time stamp to serial
if (timerSeconds < 10) Serial.print(” “) ;
if (timerSeconds < 100) Serial.print(” “);
Serial.print(timerSeconds);
Serial.print(” “);
Serial.print(setpoint);
Serial.print(” “);
Serial.print(input);
if ( slope >= 0 ) {
Serial.print(” “);
}
else
{
Serial.print(” “);
}
Serial.print(slope);
Serial.print(” “);
Serial.println(output);
}
else
{
Serial.print(“T: “);
if (timerSeconds < 10) Serial.print(” “) ;
if (timerSeconds < 100) Serial.print(” “);
Serial.print(timerSeconds);
Serial.print(” “);
strcpy_P(buffer, (char*)pgm_read_byte(&lcdMessagesReflowStatusPtr[reflowState]));
Serial.print(buffer);
Serial.print(” In:”);
Serial.print(int(input));
Serial.print(” RST:”);
Serial.print(ReflowStartTime);
Serial.print(” RDT:”);
Serial.print(ReflowDwellTime);
Serial.println();
}
}
else
{
// Turn off red LED
digitalWrite(ledRed, HIGH);
}
// Clear LCD
lcd.clear();
// Print current system state
strcpy_P(buffer, (char*)pgm_read_byte(&lcdMessagesReflowStatusPtr[reflowState]));
lcd.print(buffer);
// Move the cursor to the 2 line
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
// If currently in error state
if (reflowState == REFLOW_STATE_ERROR)
{
// No thermocouple wire connected
lcd.print(“No ThermoCouple!”);
}
else
{
unsigned int temp;
unsigned int minutes;
unsigned int seconds ;
// Print current temperature on 1st line
lcd.setCursor(9, 0);
if (input < 10) lcd.print(” “) ;
if (input < 100) lcd.print(” “) ;
lcd.print(int(input)) ;
lcd.print(“.”) ;
lcd.print(int( ( input – int( input ) ) * 10) );
lcd.write((uint8_t)degree_char); // Print “degree” symbol
lcd.print(“C”);
// Print remaining time and slope on 2nd line
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
if ( reflowState == REFLOW_STATE_SOAK ) {
lcd.print(“Rem:”);
temp = ( (SOAK_MICRO_PERIOD / 1000) – ( timerSeconds – SoakStartTime ) );
minutes = int(temp / 60 );
seconds = int(temp % 60 );
if (minutes < 10) lcd.print(” “) ;
lcd.print(minutes);
lcd.print(“:”);
if (seconds < 10) lcd.print(“0”) ;
lcd.print(seconds);
}
if ( (reflowState == REFLOW_STATE_REFLOW) || \
(reflowState == REFLOW_STATE_COOL) ) {
lcd.print(“Wet:”);
if (ReflowStartTime == 0) {
temp = 0; // display “0:00” till reflow min temp
}
else {
if (ReflowDwellTime == 0) {
temp = ( timerSeconds – ReflowStartTime );
}
else {
temp = ReflowDwellTime;
}
}
minutes = int(temp / 60 );
seconds = int(temp % 60 );
// if (minutes < 10) lcd.print(” “) ;
lcd.print(minutes);
lcd.print(“:”);
if (seconds < 10) lcd.print(“0”) ;
lcd.print(seconds);
}
if ( ( reflowState == REFLOW_STATE_PREHEAT ) || \
( reflowState == REFLOW_STATE_REFLOW ) || \
( reflowState == REFLOW_STATE_COOL) ) {
// Print slope
lcd.setCursor(9, 1);
lcd.write((uint8_t)delta_char); // print “delta” symbol
if ( slope < 0 ) {
lcd.print(“-“) ; // “-” if negative slope
}
else {
lcd.print(“+”) ; // “+” if positive slope
}
lcd.print(abs(int(slope))) ;
lcd.print(“.”) ;
lcd.print(abs( int( ( slope – int( slope ) ) * 10) ) ); // print slope
lcd.write((uint8_t)degree_char); // Print “degree” symbol
lcd.print(“C”);
}
}
}
// Reflow oven controller state machine
switch (reflowState)
{
case REFLOW_STATE_IDLE:
// If button is pressed to start reflow process
if (buttonPressStatus)
{
// Ensure current temperature is comparable to room temperature
// TO DO: To add indication that temperature is still high for
// reflow process to start
if (input <= TEMPERATURE_ROOM)
{
if ( !DEBUG )
{
// Send header for CSV file
Serial.println(“Time Setpoint Input Slope Output”);
}
else {
Serial.println(“Debugging!”);
}
// Intialize seconds timer for serial debug information
timerSeconds = 0;
// Initialize PID control window starting time
windowStartTime = millis();
// Ramp up to minimum soaking temperature
setpoint = TEMPERATURE_SOAK_MIN;
// Tell the PID to range between 0 and the full window size
reflowOvenPID.SetOutputLimits(0, windowSize);
reflowOvenPID.SetSampleTime(PID_SAMPLE_TIME);
// Turn the PID on
reflowOvenPID.SetMode(AUTOMATIC);
// Proceed to preheat stage
reflowState = REFLOW_STATE_PREHEAT;
}
}
break;
case REFLOW_STATE_PREHEAT:
reflowStatus = REFLOW_STATUS_ON;
// If minimum soak temperature is achieve
if (input >= TEMPERATURE_SOAK_MIN)
{
// Chop soaking period into smaller sub-period
timerSoak = millis() + SOAK_MICRO_PERIOD;
// Set less agressive PID parameters for soaking ramp
reflowOvenPID.SetTunings(PID_KP_SOAK, PID_KI_SOAK, PID_KD_SOAK);
// Ramp up to first section of soaking temperature
setpoint = TEMPERATURE_SOAK_MIN + SOAK_TEMPERATURE_STEP;
// Proceed to soaking state
reflowState = REFLOW_STATE_SOAK;
SoakStartTime = timerSeconds ; // set Soak Start Time
}
break;
case REFLOW_STATE_SOAK:
// If micro soak temperature is achieved
if (millis() > timerSoak)
{
timerSoak = millis() + SOAK_MICRO_PERIOD;
// Increment micro setpoint
setpoint += SOAK_TEMPERATURE_STEP;
if (setpoint > TEMPERATURE_SOAK_MAX)
{
// Set agressive PID parameters for reflow ramp
reflowOvenPID.SetTunings(PID_KP_REFLOW, PID_KI_REFLOW, PID_KD_REFLOW);
// Ramp up to first section of soaking temperature
setpoint = TEMPERATURE_REFLOW_MAX;
// Proceed to reflowing state
reflowState = REFLOW_STATE_REFLOW;
ReflowStartTime = 0;
buzzerPeriod = millis() + BEEPDURATION_REFLOW ;
digitalWrite(buzzer, HIGH); //enable beeper
}
}
break;
case REFLOW_STATE_REFLOW:
if (millis() > buzzerPeriod) // turn off buzzer
{
digitalWrite(buzzer, LOW);
}
// We need to avoid hovering at peak temperature for too long
// Crude method that works like a charm and safe for the components
if ( (input >= TEMPERATURE_REFLOW_MIN) && (ReflowStartTime == 0 ) )
{
ReflowStartTime = timerSeconds ; // set Reflow Start Time
}
if (input >= (TEMPERATURE_REFLOW_MAX – 5))
{
// Set PID parameters for cooling ramp
reflowOvenPID.SetTunings(PID_KP_REFLOW, PID_KI_REFLOW, PID_KD_REFLOW);
// Ramp down to minimum cooling temperature
setpoint = TEMPERATURE_COOL_MIN;
// Proceed to cooling state
reflowState = REFLOW_STATE_COOL;
buzzerPeriod = millis() + BEEPDURATION_COOL;
digitalWrite(buzzer, HIGH);
}
break;
case REFLOW_STATE_COOL:
if (millis() > buzzerPeriod) // turn off buzzer
{
digitalWrite(buzzer, LOW);
}
// Since we’re cooling off, let’s keep track of the “Wetting” time
if ( (ReflowDwellTime == 0) && (input <= TEMPERATURE_REFLOW_MIN) ) {
ReflowDwellTime = ( timerSeconds – ReflowStartTime );
}
// If minimum cool temperature is achieve
if (input <= TEMPERATURE_COOL_MIN)
{
// Retrieve current time for buzzer usage
buzzerPeriod = millis() + BEEPDURATION_COMPLETE;
// Turn on buzzer and green LED to indicate completion
digitalWrite(ledGreen, LOW);
digitalWrite(buzzer, HIGH);
// Turn off reflow process
reflowStatus = REFLOW_STATUS_OFF;
// Proceed to reflow Completion state
reflowState = REFLOW_STATE_COMPLETE;
}
break;
case REFLOW_STATE_COMPLETE:
if (millis() > buzzerPeriod)
{
// Turn off buzzer and green LED
digitalWrite(buzzer, LOW);
digitalWrite(ledGreen, HIGH);
// Reflow process ended
reflowState = REFLOW_STATE_IDLE;
}
break;
case REFLOW_STATE_ERROR:
// If thermocouple is still not connected
if (input == THERMOCOUPLE_DISCONNECTED)
{
// Wait until thermocouple wire is connected
reflowState = REFLOW_STATE_ERROR;
}
else
{
// Clear to perform reflow process
reflowState = REFLOW_STATE_IDLE;
}
break;
case REFLOW_STATE_TUNE:
Serial.println(“Tuning”);
// Clear to perform reflow process
reflowState = REFLOW_STATE_IDLE;
break;
}
// If button is pressed
if (buttonPressStatus == true)
{
// If currently reflow process is on going
if (reflowStatus == REFLOW_STATUS_ON)
{
// Button press is for cancelling
// Turn off reflow process
reflowStatus = REFLOW_STATUS_OFF;
// Reinitialize state machine
reflowState = REFLOW_STATE_IDLE;
}
}
// Simple button debounce state machine (for button #1 only)
// TO DO: To be replaced with interrupt version in next revision
switch (debounceState)
{
case DEBOUNCE_STATE_IDLE:
// No valid button press
buttonPressStatus = false;
// If button #1 is pressed
if (digitalRead(button1) == LOW)
{
// Intialize debounce counter
lastDebounceTime = millis();
// Proceed to check validity of button press
debounceState = DEBOUNCE_STATE_CHECK;
}
break;
case DEBOUNCE_STATE_CHECK:
// If button #1 is still pressed
if (digitalRead(button1) == LOW)
{
// If minimum debounce period is completed
if ((millis() – lastDebounceTime) > DEBOUNCE_PERIOD_MIN)
{
// Proceed to wait for button release
debounceState = DEBOUNCE_STATE_RELEASE;
}
}
// False trigger
else
{
// Reinitialize button debounce state machine
debounceState = DEBOUNCE_STATE_IDLE;
}
break;
case DEBOUNCE_STATE_RELEASE:
if (digitalRead(button1) == HIGH)
{
// Valid button press
buttonPressStatus = true;
// Reinitialize button debounce state machine
debounceState = DEBOUNCE_STATE_IDLE;
}
break;
}
// PID computation and SSR control
if (reflowStatus == REFLOW_STATUS_ON)
{
//unsigned long now;
now = millis();
reflowOvenPID.Compute();
if ((now – windowStartTime) > windowSize)
{
// Time to shift the Relay Window
windowStartTime += windowSize;
}
if (output > (now – windowStartTime)) digitalWrite(ssr, HIGH);
else digitalWrite(ssr, LOW);
}
// Reflow oven process is off, ensure oven is off
else
{
digitalWrite(ssr, LOW);
}
}
void changeAutoTune()
{
if (!tuning)
{
//Set the output to the desired starting frequency.
output = aTuneStartValue;
aTune.SetNoiseBand(aTuneNoise);
aTune.SetOutputStep(aTuneStep);
aTune.SetLookbackSec((int)aTuneLookBack);
AutoTuneHelper(true);
tuning = true;
}
else
{ //cancel autotune
aTune.Cancel();
tuning = false;
AutoTuneHelper(false);
}
}
void AutoTuneHelper(boolean start)
{
if (start)
ATuneModeRemember = reflowOvenPID.GetMode();
else
reflowOvenPID.SetMode(ATuneModeRemember);
}
void SerialSend()
{
Serial.print(“setpoint: “);
Serial.print(setpoint);
Serial.print(” “);
Serial.print(“input: “);
Serial.print(input);
Serial.print(” “);
Serial.print(“output: “);
Serial.print(output);
Serial.print(” “);
if (tuning) {
Serial.println(“tuning mode”);
}
else {
Serial.print(“kp: “);
Serial.print(reflowOvenPID.GetKp());
Serial.print(” “);
Serial.print(“ki: “);
Serial.print(reflowOvenPID.GetKi());
Serial.print(” “);
Serial.print(“kd: “);
Serial.print(reflowOvenPID.GetKd());
Serial.println();
}
}
void SerialReceive()
{
if (Serial.available())
{
char b = Serial.read();
Serial.flush();
if ( (b == ‘1’ && !tuning) || (b != ‘1’ && tuning) ) changeAutoTune();
}
}
void DoModel()
{
//cycle the dead time
for (byte i = 0; i < 49; i++)
{
theta[i] = theta[i + 1];
}
//compute the input
input = (kpmodel / taup) * (theta[0] – outputStart) + input * (1 – 1 / taup) + ((float)random(-10, 10)) / 100;
}
 Scott
Scott







Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.