Figure 1: Grove – Infrared Transmitter
On the transmission side, the transmitter will send IR SONY data. For more details, please refer to SB-Projects’ topic of IR Remote Control Theory to learn the theory of IR remote controls operation and a collection of IR protocol descriptions. In this example, we are going to use Sony as the transmission protocol.
Sony Features
• 12-bit version, 7 command bits, 5 address bits.
• Pulse width modulation.
• Carrier frequency of 40kHz.
• Bit time of 1.2ms or 0.6ms.
Sony SIRC Modulation
The SIRC protocol uses pulse width encoding of the bits. The pulse representing a logical “1” is a 1200us long burst of the 40kHz carrier, while the burst width for a logical “0” is 600us long. All bursts are separated by a 600us long space interval as shown in Figure 2 below.
Figure 2: Sony SIRC Modulation

Protocol
Figure 3: 12-bit Sony SIRC protocol

The Figure 3 above shows a typical pulse train of the 12-bit SIRC protocol. With this protocol the LSB is transmitted first. The start burst is always 2.4ms wide, followed by a standard space of 0.6ms. Apart from signalling the start of a SIRC message this start burst is also used to adjust the gain of the IR receiver. Then the 7-bit Command is transmitted, followed by the 5-bit Device address. In this case Address 1 and Command 19 is transmitted.
Commands are repeated every 45ms (measured from start to start) for as long as the key on the remote control is held down.
 pammyleong
pammyleong Pin configuration of the IR Emitter and BW16
Pin configuration of the IR Emitter and BW16 Pin configuration of the IR Emitter and BW16 type C
Pin configuration of the IR Emitter and BW16 type C Pin configuration of the IR Emitter and AW-CU488 Thing Plus
Pin configuration of the IR Emitter and AW-CU488 Thing Plus


 Jac Goudsmit
Jac Goudsmit
 Tryst
Tryst
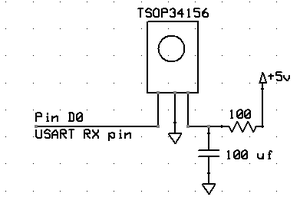
 Bruce Land
Bruce Land