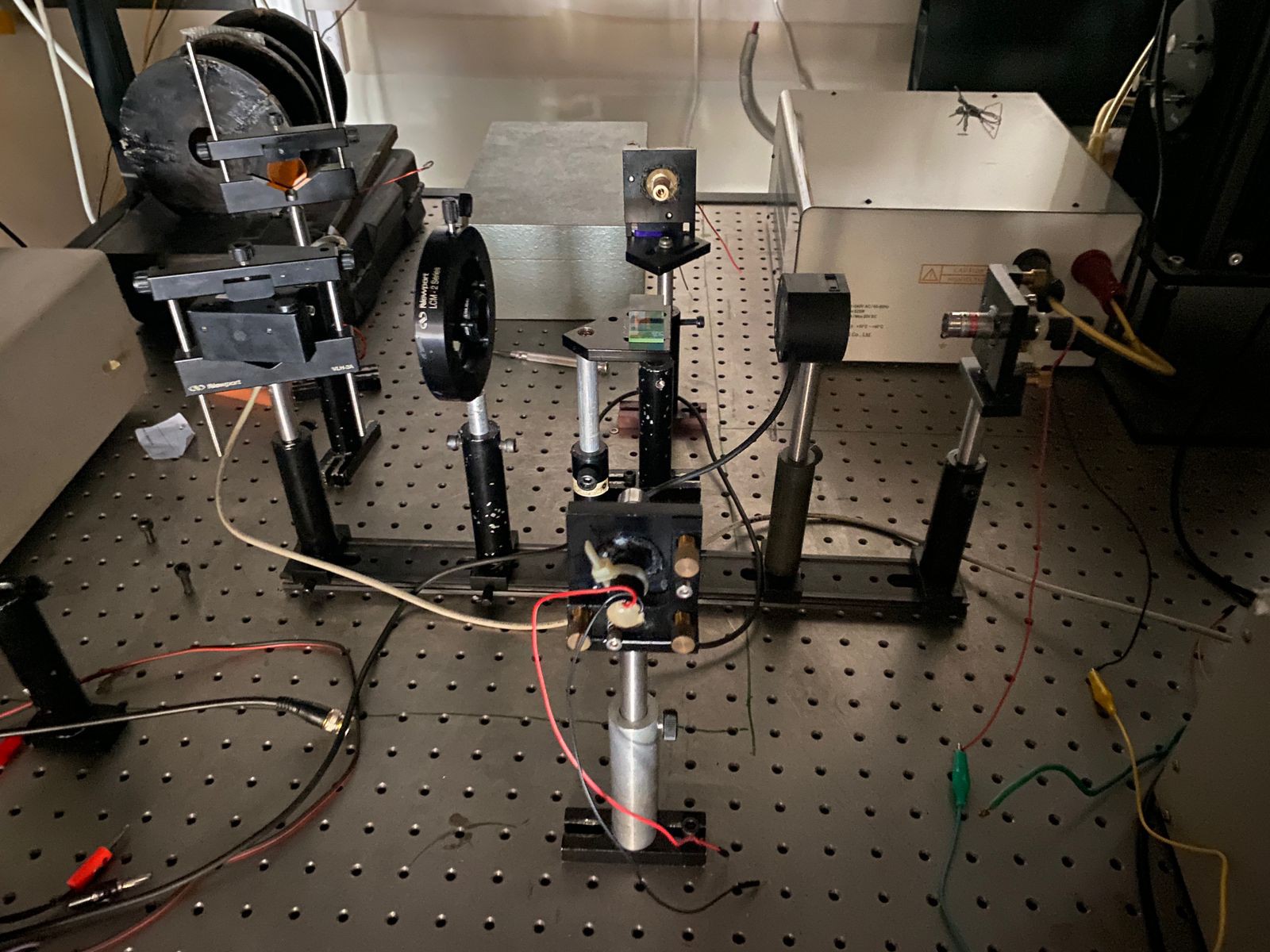
My setup

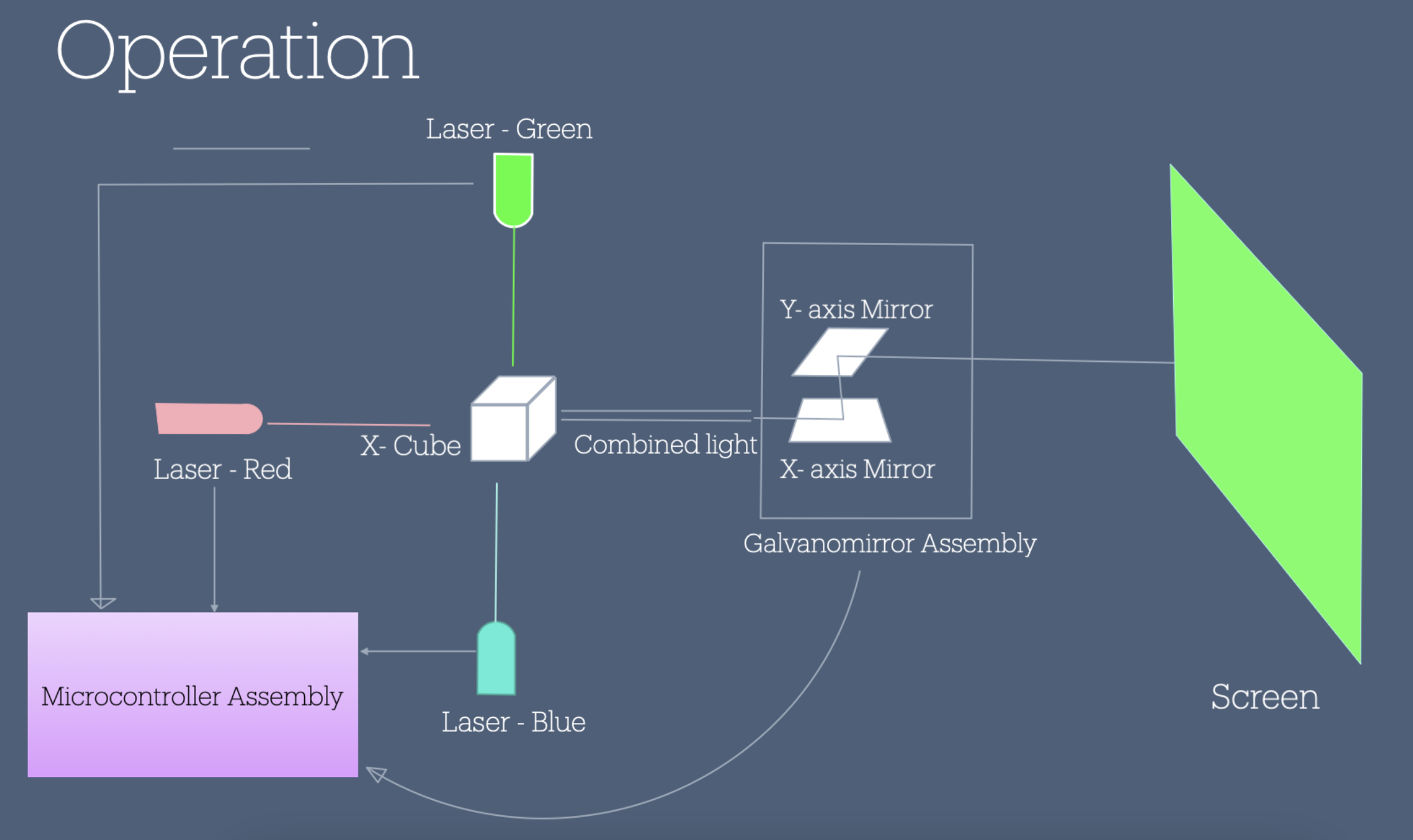
The plan of action is the following, Get the hardware working to control the power of the lasers, get the galvo working with DAC and appropriate circuitry to project the laser onto a screen. write software that will take care of projection and decoding and encoding images.
Hardware Setup
I realise PWM works a bit differently than with Arduino mainly because of the abstraction. so i'm looking into making it work with STM.
NOTES STM Timer module
Timer module in be in several different types
1- Timer mode TCNT register gets incremented by 1 after every clock cycle. the oscillating source goes through prescaler and then increments after every clock cycle. this mode can give an overflow interrupt when register is full. usually at 80Mhz and 1:1024 prescaler it's 0.89seconds. but if we want the interrupt to occure every 1 second.. we can use the preloader to not start the count from 0 but from some other value.
2- Counter mode Instead of clock source can take any input and at rising or falling edge of signal the TCNT register increments by one. note that in this mode it also goes through the prescaler so we can set that to 1:1 to get real value
3- General timer module all timer module consists of counter register, Auto-reload register with a preload register access and prescaler register.
PWM Mode of timer module In PWM mode, the timer module is clocked from an internal clock source and produces a digital waveform on the output channel pin called the PWM signal. By using output compare registers (OCR), the incrementing timer’s register value is constantly compared against this OCR register. When a match occurs the output pin state is flipped until the end of the period and the whole process is repeated.
The timer in PWM mode will produce a PWM signal at the specified frequency the user chose. The duty cycle is also programmatically controlled by its register. The PWM resolution is affected by the desired FPWM and other factors as we’ll see in the dedicated tutorials for PWM generation.
I'll be following "Discovering the STM32 Microcontroller" by Geoffrey Brown to get a better understanding of this controller.. too many concepts are flying right over my head as of right now.
 Shoaib Mustafa
Shoaib Mustafa
Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.