Timer
Using timer in micropython is also simple. To use timer, we need to import Timer library first from machine importTimer
Basic usage:
Define Timer
tim=Timer(n)
Timer 3 is reserved for internal use. Timer 5 controls the servo drive. Timer 6 is used to signaling ADC / DAC read/write. It is recommended to use other timer in your program.
tim=Timer(1, freq=100)
tim=Timer(4, freq=200, callback=f)
Set frequency: tim.freq(100)
Define callback function (interrupt): tim.callback(f)
Disable callback function: tim.callback(None)
Introduction of Timer library
timer.counter([value])
Obtain or set timer counter
timer.freq([value]
Obtained or (if setting changes prescaler and period) set frequency timer
timer.init(*, freq, prescaler, period) initialize timer. Initialization must have frequency (Hz) or prescaler tim.init(freq=100), tim.init(prescaler=83, period=999) keyword parameter:
freq — Frequency with specified time period
Prescaler—Prescaler, [0-0xffff]. Timer frequency is system clock
(prescaler + 1). The highest frequency of timer 2-7 and 12-14 is 84MHz, that of timer 1, 8-11 is 168MHz
Period—Period value(ARR). Timer 1/3/4/6-15 is [0-0xffff]. Timer 2 and 5 is [0-0x3fffffff]
Check port no. from my computer. Right-click->my computer->management->device manager->port. Port No. is COM9.
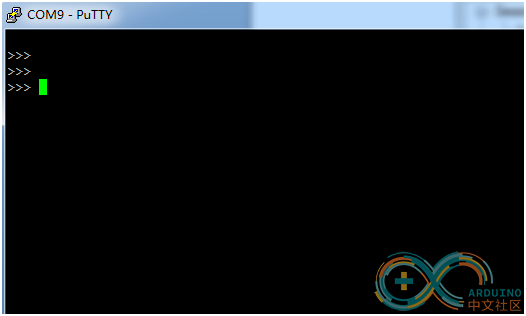
Open and run terminal putty of micropython. Select port no. (COM9), connection type (Serial)
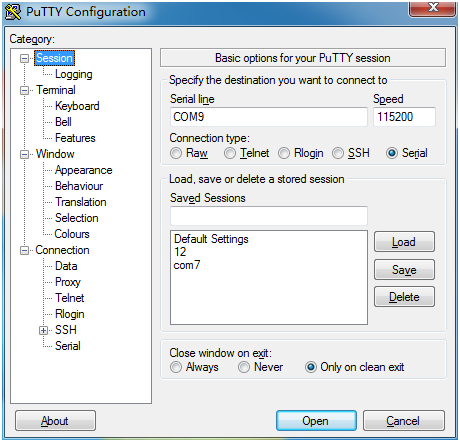 Other settings are shown below.
Other settings are shown below.Press enter key several times after Open. We can enter micropython language at putty terminal
Press Ctrl+E to access paste mode, and right-click in the mode to paste program. Press Ctrl+D to complete pasting. Micropython will execute pasting program
Example of Timer
Timing period output 1
from machine import Timer
tim = Timer(-1)
def func(t):
print (1)
tim.init(period=2000, mode=Timer.PERIODIC, callback=func)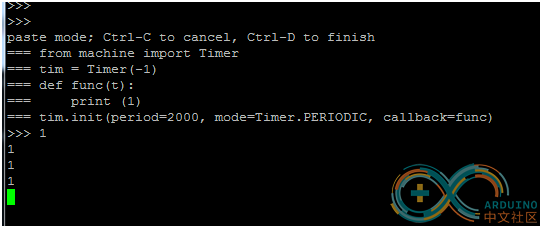
Timing one-time output 2
from machine import Timer
tim = Timer(-1)
def func(t):
print(2)
tim.init(period=2000, mode=Timer.ONE_SHOT, callback=func)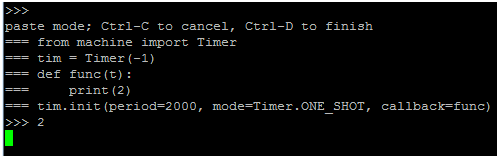
Breathing Light
from machine import Pin,Timer,PWM
pwm = PWM(Pin(14),100)
polar = 0
duty = 0
def setLed(t):
global duty,polar
if(polar == 0):
duty+=16
if(duty >= 1008):
polar = 1
else:
duty -= 16
if(duty <= 0):
polar = 0
pwm.duty(duty)
tim = Timer(1)
tim.init(period=10,mode=Timer.PERIODIC, callback=setLed)
try:
while True:
pass
except:
tim.deinit()
pwm.deinit()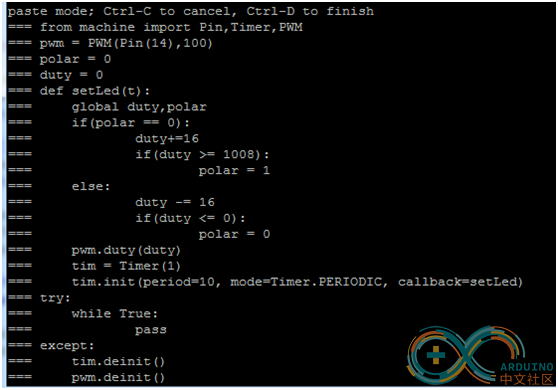
I2C
I2C is two-wire communication protocol between devices. It only needs two signal lines in the physical layer: SCL and SDA, which is clock and data line respectively.
I2C communication program between esp8266 and EEPROM Data Storage Module For Arduino
from machine import Pin, I2C
i2c =I2C(scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4), freq=100000)
b=bytearray(4)
b[0]=97
b[1]=98
b[2]=99
i2c.writeto_mem(0x50,0,b)
i2c.readfrom_mem(0x50,0,4) muzi
muzi
 Oliver
Oliver
 Luke Thompson
Luke Thompson
 W. Alex Best
W. Alex Best