Someone in the United States has a stroke every 40 seconds, and every 80 seconds one stroke takes place in Russia. The spasticity is the most common post stroke consequence. Post-stroke rehabilitation can make people healthy again, and the faster the rehabilitation begin the more effective it is. The Rehab Helper can make rehabilitation faster and more effective.
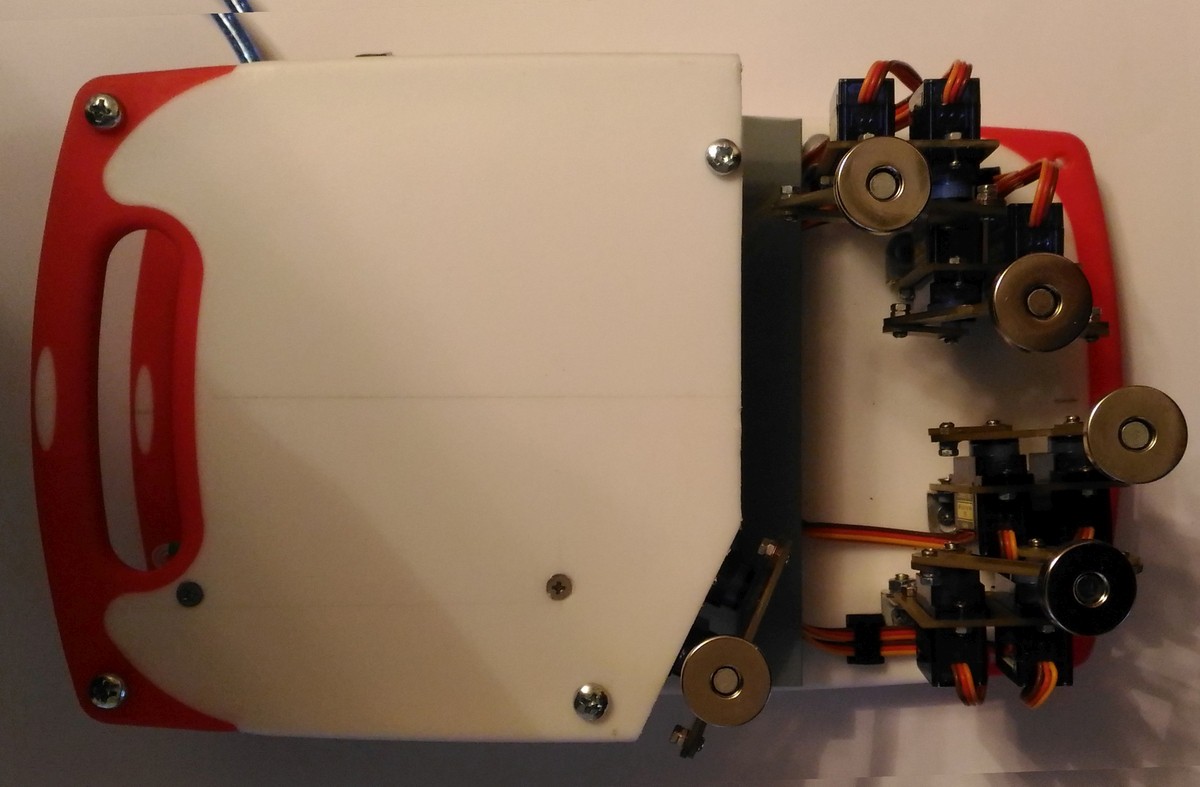
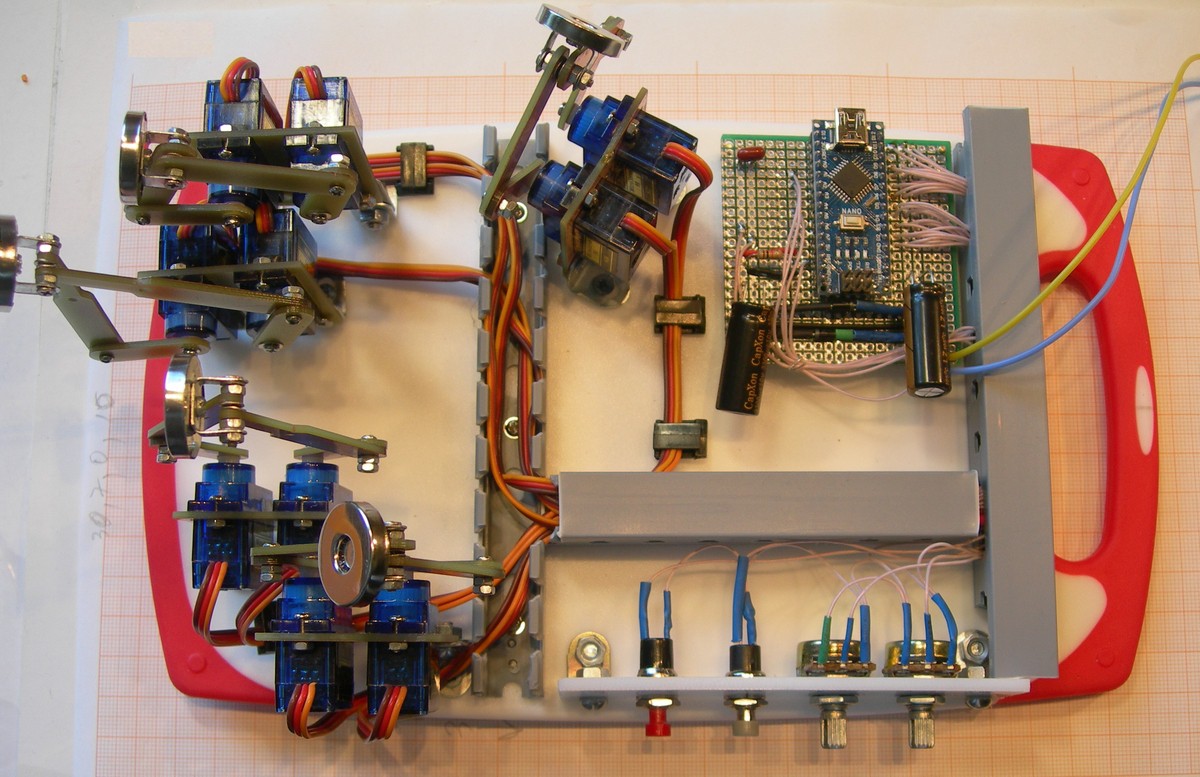
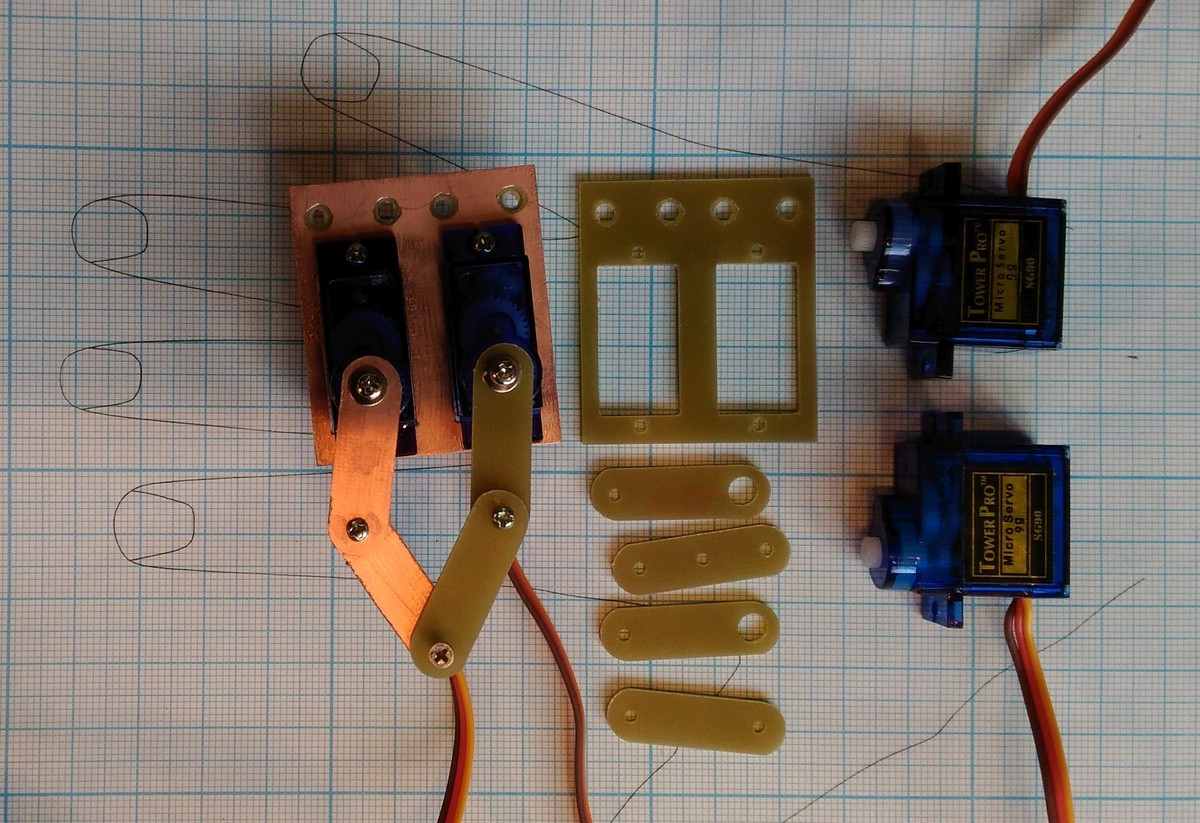
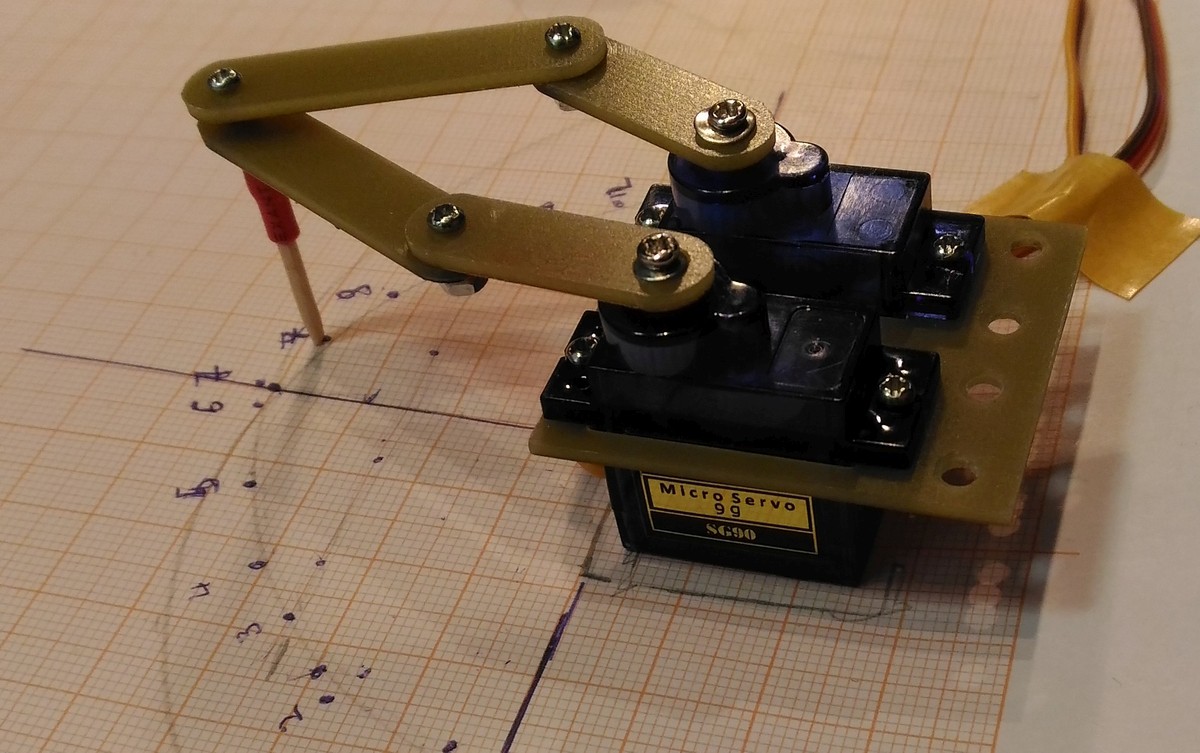
- We design five-bar mechanism to convert rotational movements of servos to 2- dimensional movement of patient's fingers. Hand- therapy system of 5 mechanisms is constructed.
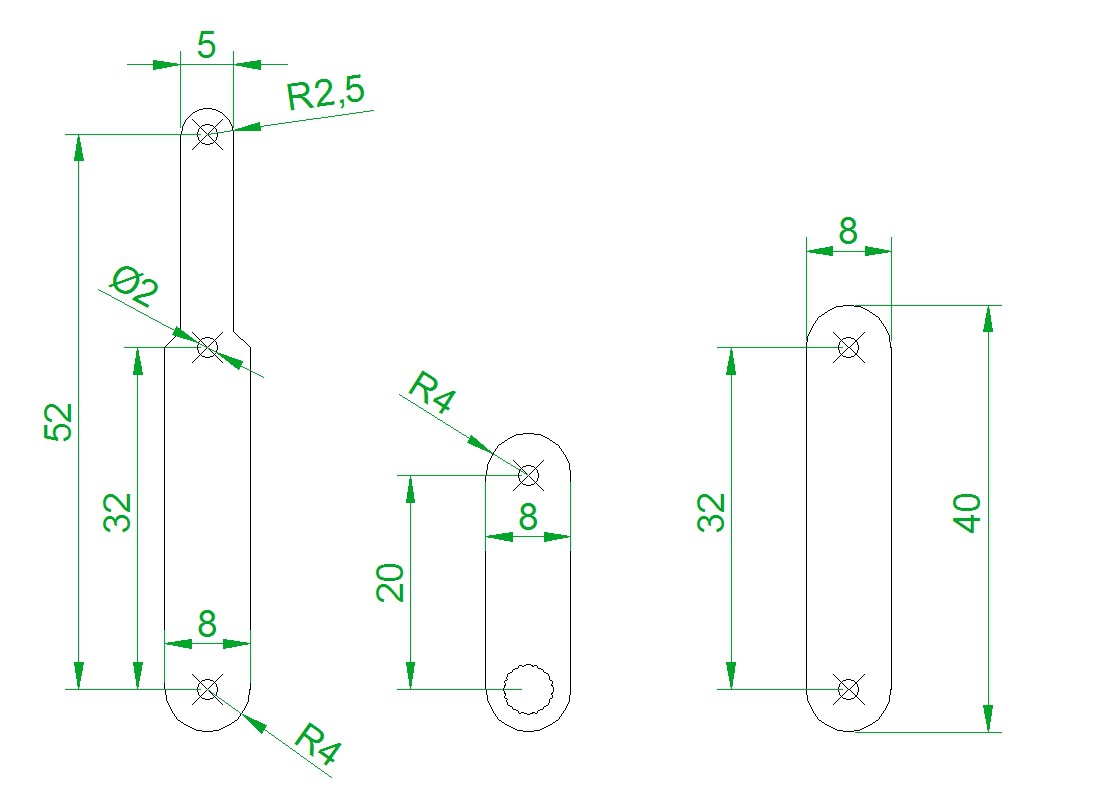
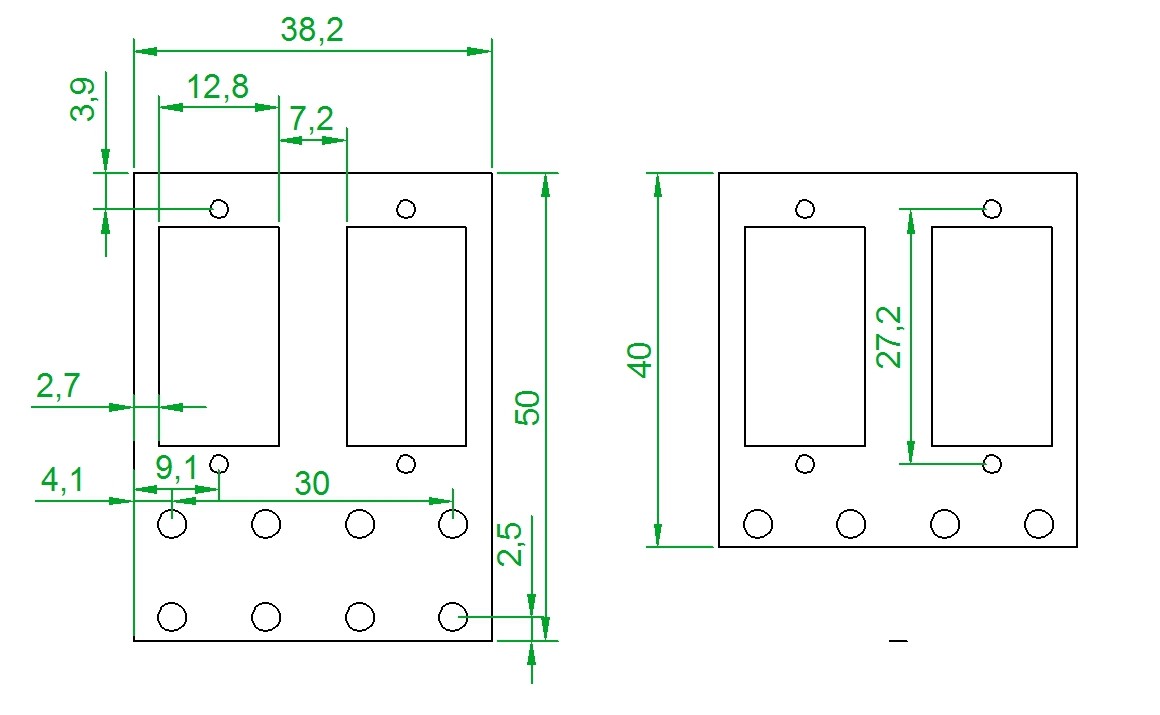
- We use servos, Arduino Nano controller board, LED MAX7219 display shields, lever arms and base, that can be made using 3d printer, miller or simply with Knife for cardboard and drill.
- The device is powered by 5 V DC power source. The current can be up to 2-3 Amperes.
- We calculate approximation functions to calculate the servo angles as a function of finger base position without complex time-consuming trigonometric calculations.
- We wrote simple Arduino - compatible code to control 10 servos.
- It is 17 modes of movement: horizontal, vertical and mixed (arc). The modes can be selected by pressing push button.
- Frequency and smoothness can be changed by two potentiometers.
- The LED Display shows the mode, the number of swipes, smoothness (number of points in interpolation) and time in milliseconds between points.
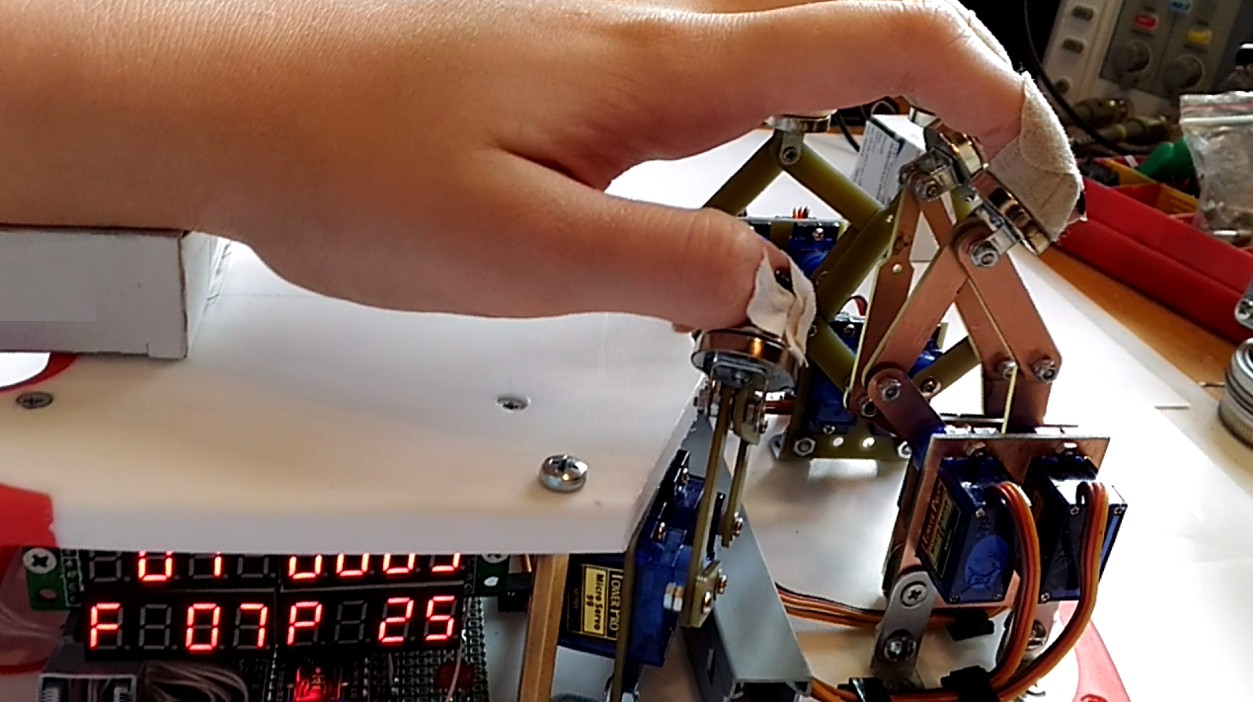
- Patient’s fingers are fixed with adhesive bandage to magnetic clasp.
- Magnetic force is strong enough to hold the fingers, but is weak enough to detach the fingers and do not any harm.
- Code is Arduino IDE compatible and can be changed to get any kind of finger base movement.
- The device can be replicated according to build instruction. Step-by-step build instruction and program code are free for download on git hub repository and from “Files” section of our hackaday page here.
- Some devices are in clinics now under investigating of the effectiveness.
We believe that the ReHub Helper can assist in neurological rehabilitation of the upper extremity in all the cases when manual therapy can help:
• Brain tumour
• Cerebral palsy (CP)
• cervical spine
• Chronic illnesses such as multiple sclerosis (MS)
• Fractures and injuries of the distal upper extremity (remodelling phase) • Meningitis, encephalitis
• Motor neuron diseases, e.g. amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
• Muscle dystrophy
• Parkinson's disease
• Signs of paralysis caused by slipped disc in the
• Spinal cord injuries
• Stroke (cerebral haemorrhage, ischaemic damage)
• Traumatic brain injury (TBI)
 Sergei V. Bogdanov
Sergei V. Bogdanov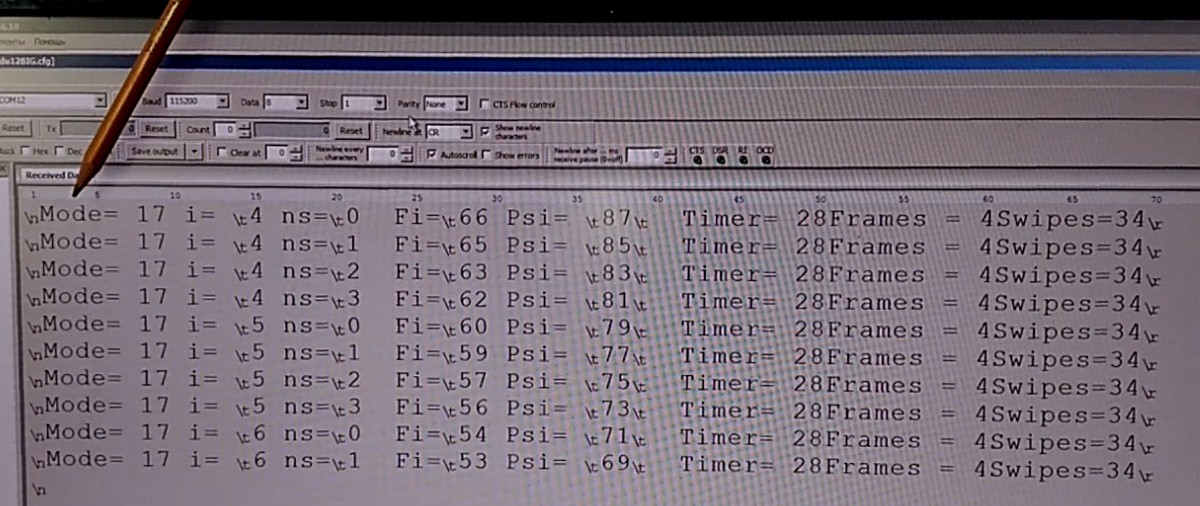




 Nicolas Guilbert
Nicolas Guilbert
 amr.mostaafaa
amr.mostaafaa
 mircemk
mircemk