-
More Amplifier Selection Ramblings
03/21/2018 at 18:50 • 0 commentsI have previously ruled out the Apex PA314 as not having the power desired for this project. It turns out that they have even more crazy solutions, including the PA03 (among others). https://www.apexanalog.com/products/pa03.html
Look at the Package on this thing
![]()
It dissipates 500W thermal, and can supply ±75V at 30A Pk. This is designed for, among other things, driving sonar. The only downside here is price tag, clocking in at nearly $600 dollars on Digikey.
it can be had cheaper on eBay, and they do make some more "down market" offerings that should also work.
Part of me wants to just shell out ~$150 for one of these premo solutions and be done with this. Buys power, voltage, low harmonic distortion, etc...
On the other hand there's replicating some of the work that's been done by others in the hobbyist community with half bridge FET solutions. The main downside to these is the high harmonic content (I.E. square wave generation), which makes tuning more difficult.
-
High Power Op Amps
03/17/2018 at 23:13 • 1 commentSo I've been stalled on selecting the power amplifier for this project for a while. because of the high frequencies (40kHz, possibly higher), class-D amplifiers (i.e. PWM) aren't really viable. Many other projects have just used power MOSFETs that produce square waves and either filter that or just eat the harmonic distortion.
I may yet go with the power FETs due to their expense, but I really wanted to have reasonably sinusoidal outputs.
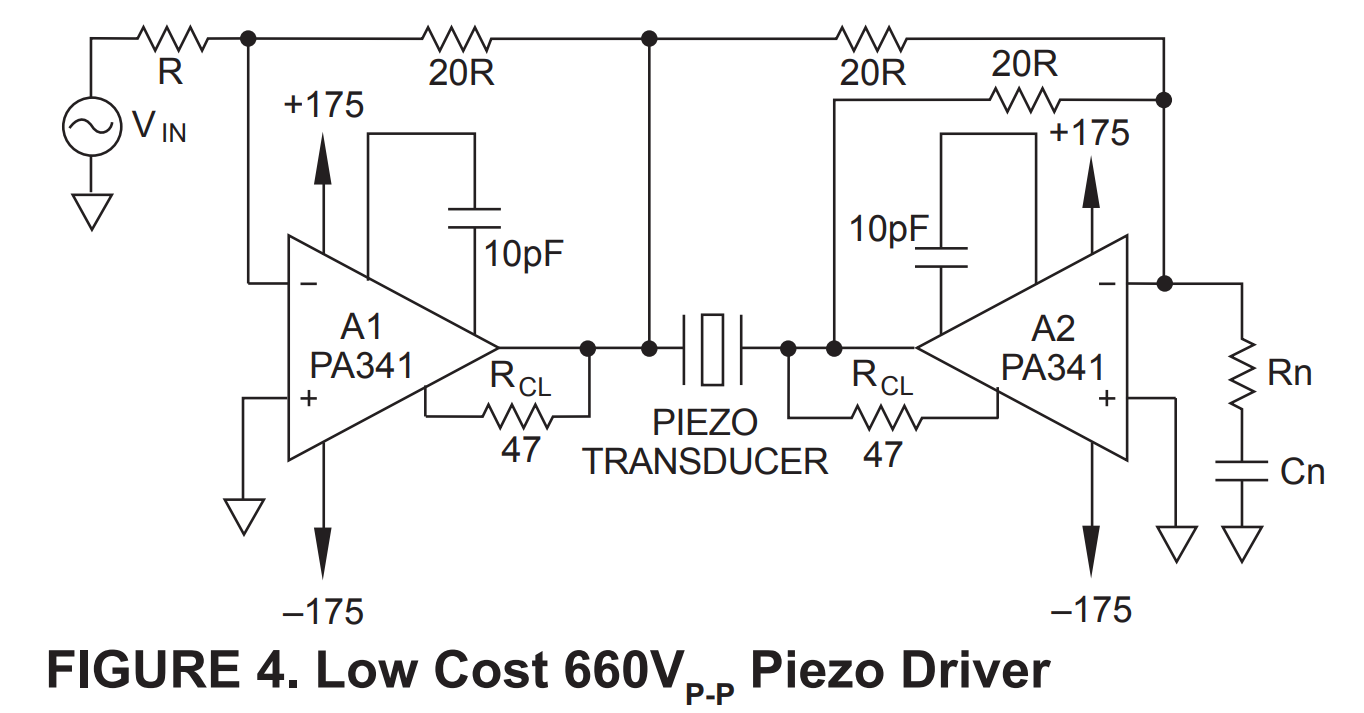
Enter the Apex PA341, which purpose built for power ultrasonic devices. Here's the suggested implementation from the datasheet.
This balanced driver pushes 660V at 60 mA continuous! This means I can just take an eBay AD9851 DDS source and just push that out. Sadly that doesn't get me to the 400+ W I was hoping for.
https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/apex-microtechnology/PA341CE/598-1918-ND/2700702
That said, this is a really cool part for higher precision power ultrasonic devices such as motors or similar.
-
Dusting this off, cables in
03/16/2018 at 18:38 • 0 commentsFinally got around to ordering an SHV cable, and it finally arrived from HK.
Just ran the eBay ultrasonic cleaning supply with the Branson welding converter. They are not in tune, but it does make a noise and make some weird currents when immersed in water.
Next up: tuning and alternative power supplies.
-
Piezos are in!
11/22/2017 at 20:15 • 0 commentsI bought two different transducers: an el-cheapo langevian and a proper Branson converter. Both are 40kHz units.
Not much to see here. The piezo is 4.4nF. Here is a first draft of the schematic of the single layer driver board, with as many components marked as I could get with a bit of googling.
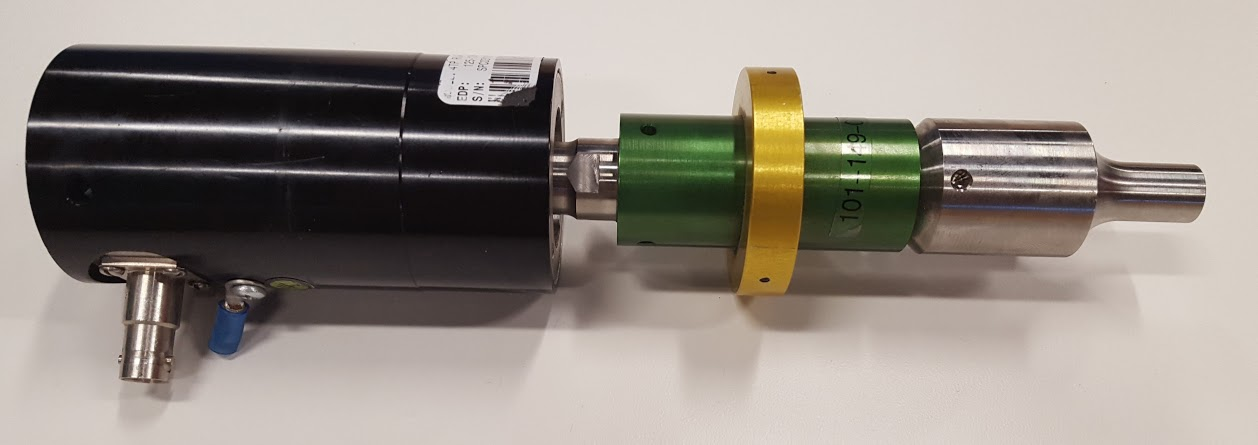
On to the real prize: Made in 'Murica! Branson 4TP RF converter. my google fu has largely failed to turn up a datasheet for the specific model number, but a 4TP unit is listed as compatible with the Branson 2000BDC 40:.8 power supply, which is a 450W continuous, 800W peak output unit. The input connector shows 5.7 nF, which leads me to believe there are be 3 or more piezo elements inside.
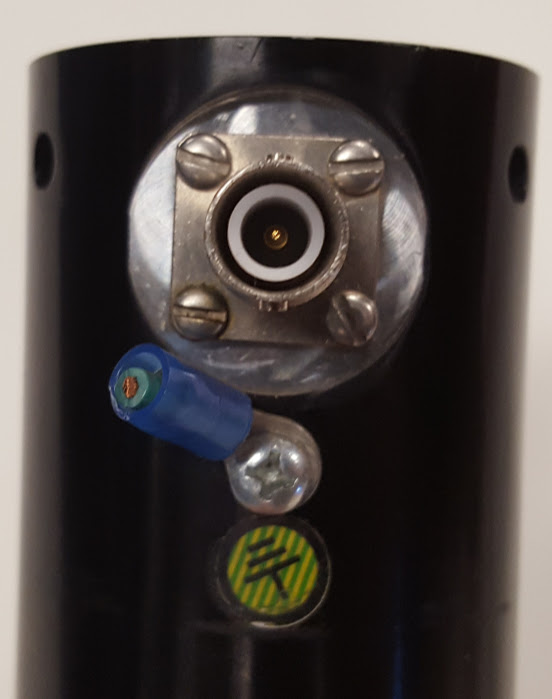
She's a beauty to be sure. The green booster is 1:1.5, and the output horn appears to be a high amplitude gain step horn. Of course, the used equipment purchasing experience wouldn't be complete without weird incompatibilities, so while it looks like it takes BNC, the connector is actually a reverse polarity SHV connector.
the output horn is threaded with 1/4" fine (28 tpi) threads, and the hole is about 5/8" deep, so it takes hardware store bolts as viable working tips. I'll be using these once I get a tuning rig in place. I'm hoping that a longer bolt will work as a 1/2 wavelength element and can be used as the working tip for sonifying liquids.
-
Impedance Matching Woes
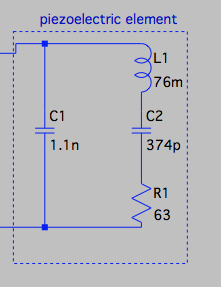
11/16/2017 at 22:29 • 1 commentPiezoelectric element modeling
Here is an electrical model of a power piezo transducer. I pulled the component values from the following video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EAFNjyx3uX0. This matches behaviorally with what I’ve read. C3 is representative of the electrical capacitance of the piezo element and electrodes, and the series LCR circuit composed of L1, C4 and R3 is representative of the mechanical domain inertia and compressive spring forces.
![]()
An AC sweep reveals the following current response:Note the resonance at 28kHz where current is maximized, and the anti-resonance at 34kHz where current is minimized. The goal for most ultrasonic drivers is to drive at either resonance or antiresonance, depending on application.
Drive circuit modeling
I am starting with the power driver from: http://www.imajeenyus.com/electronics/20110514_power_ultrasonic_driver/index.shtml
To increase output power I’m turning the half bridge to an H bridge, which will approximately double the drive voltage. Here is a spice model of an h-bridge driver, piezo transducer, and matching network. The H-bridge will approximately generate a square wave output voltage.
You can see the issue that is addressed at the top of the above article: namely lack of matching network. This causes huge current spikes in the mosfets on switching and poor drive voltage, as shown below:
The problem
So clearly I need some sort of matching network, or a sinusoidal driver. The major advantage of an H-bridge is that the FETs are nearly always in saturation, which greatly reduces the heat they produce. That said, I’m fairly confused about how to go about matching this. The fundamental frequency is already tuned to match the fundamental of the transducer. From playing around with spice a bit, I now suspect it has to do with matching higher-order harmonics of the drive waveform. The impedance of the transducer is inductive for anything much higher than the anti-resonant frequency. I added an LC matching network that puts a resonance at the 3rd harmonic (87kHz). Here is the full model with matching network and the current response with and without the network.
This barely shifts the primary resonance, but does substantially change the impedance to the 3rd harmonic. I would expect this to improve my current spikes, but instead, it does nothing:
Here is the network added to the total model, and the resulting current through M1:
I’m not really sure what to do from here. I’m having trouble finding useful results on google as most searches for “impedance matching” and variations thereof turn up RF matching systems. These mostly discuss matching resistive loads to the intrinsic impedance of a transmission line, not inductive loads in a lumped element system.
I’ll verify these model results with some real world devices when I have all the parts necessary. If i come up with anything, I’ll post it here. In the meantime, any ideas would be great.
-
Purchasing Power ultrasonics - Demystified
11/14/2017 at 21:15 • 0 commentsIf you are looking to build an at-home power ultrasonics system, there are a lot of options available to you, and deciding what you need can be confusing.Power ultrasonics are heavy industrial tools with heavy industrial price tags, especially if you look to do anything with high power greater than about 50 watts. Here is a quick breakdown of what you need, and what’s available.
A power ultrasonic system has 3 main components. These often come bundled together as either completed or partial systems. The components are:
- Power supply
- Ultrasonic transducer
- Output horn or mechanical coupling
These three components generate electrical power, convert electrical power to mechanical vibrations, and direct the vibrations into your target.
Power supply:
A power supply needs to provide high voltage, high power AC at the resonant or anti-resonant frequency of the transducer system. The main things to consider are: drive frequency, drive power, user friendliness, and safety of the design. Your transducer must match the resonant frequency of the transducer for best results and longest tool life. High quality industrial systems will provide features that automatically detect the resonant frequency and adjust their output accordingly. This will control for drift due to tool wear, cleanliness, loosening of fasteners, temperature shifts, component aging, and the like. This can also provide a warning to the operator if the system has gone out of tune and needs maintenance, repair, or replacement. High quality systems also permit reliable adjustment and measurement of output power to permit process control, especially for sonochemical or cell disruption processes. Safety consists of fuses, grounding, isolation, and other common high power safety systems. When I get my hands on some physical units, I will determine how safe these various options are.
You have three main options for power supplies:
- Chinese ultrasonic cleaner power supplies. These cost around $30, output a fixed frequency of 28kHz or 40Khz, and have have no frequency adjustment, power adjustment, or any other “nice” features built in. They are by far the easiest and cheapest option available. I have purchased one and will be experimenting with it soon. Sources: ebay, alibaba, and ilk.
- Real industrial systems. These are the high end “cadillac” option. Common brands include Dukane and Branson, but others are available. You can pick whatever features, frequency, and power output you want, but they will cost you. I have not done an exhaustive search of actual sale price, but they typically list for around $1000 used, often more. These may be a viable option for a small company, but they are solidly out of my price range as a hobbyist.
- DIY. I’m still investigating the price point you can expect out of this, but this is what I perceive to be the only viable option for >100W supplies at sub $1k prices.
Transducer
The transducer is a large piezoelectric element. They come as “raw” ceramic components, or completed assemblies that stack several ceramic elements, electrodes, and possibly mechanical preload screws, mounting enclosures, cooling elements, and mounting fasteners.
Power systems require mechanical preload. Almost all piezo elements are made from a ceramic material called lead zirconate titanate, or PZT. Like other ceramics, it is brittle, and does not handle large changes in shape without cracking. Preload means clamping the ceramic to allow large forces to be created without large changes in physical size, thus decreasing the tendency to crack or break. The most common design is the Langevin, which uses annular ring ceramics clamped between two pieces of steel with a bolt. Here is a cross section image sourced from http://techblog.ctgclean.com/2012/01/ultrasonics-transducers-piezoelectric-hardware/:
Purchasing options
- Flat, raw element ultrasonic bath disk transducers. ~$3, 35W, 40Khz. No housing, cooling, or even wiring. This is just a chunk of PZT with some metallic contacts. I have purchased a couple of these, and haven’t done to much with them yet. Buy from ebay, alibaba, et. al.
- Ultrasonic bath Langevin transducer. ~$15, 50W-100W, 28kHz or 40kHz.These are the most common transducer you will find, and the basis of most hobbyist projects you’ll find. They consist of a piezoelectric stack, typically 2 elements, as well as steel mounting that provides heat sink, output coupling, and mechanical preload. These can be purchased with a cheapo supply in a kit and have you up and running in no time. Purchase from ebay, alibaba, et. al.
- Industrial transducers. Price is highly variable, typically >$50, >500W, 28kHz or 40kHz. These tend to be “full featured” systems. The main brands you’ll find are Branson and Dukane, and are designed for industrial use in industrial environments. These are often referred to as “converters” or “RF converters”. They have a housing that you can mount to, cooling ports to force air flow, and are typically capable of 500W - 2kW, and have preload built in. As a hobbyist you will only find these used. They often come with output boosters and horns. Pro tip: at time of writing most sellers are re-listing these repeatedly. These vary rarely sell on ebay for list price. You can lowball sellers with counteroffers and they will accept offers 20% below list price. Do your homework on the output horns and extras before bidding as you can get a good deal on packaged extras. Usual haggling algorithm of “you want 100%, I’ll bid 60%. How about 90%? How about 70%? How about 80%? Sold!” applies.
- “Specialty” items. I’m not going to go into a lot of detail here, but there is a huge variety of specialty piezo transducers available. These aren’t really available on common marketplaces like ebay, and you really have to go to specialty suppliers. These may come as raw piezo elements or packaged systems. Here’s a quick, non-exhaustive list of some available components:
- hemi-spherical transducers
- conical transducers
- shear element plates
- piezo benders disks, and bars
- piezo fans
- spherical resonators
- tubular elements
- multi-axis positioners stacks.
See: https://www.steminc.com/PZT/en/ for examples.
Output Coupling; Horns, Boosters, Tips, and Others
This is where you will find the most variety for power systems, and what you need will greatly depend on your intended application. These are passive mechanical elements that direct the ultrasound energy from your transducer into your workpiece/sample. There is a specialty variant of this for every possible use, and industrial customers often make custom tooling for their specific application. If you go that route, you will really have spend some time with finite elements methods and some textbooks. There is free software available, but I have not used it: http://www.sonoanalyzer.com/Downloads. Fortunately many applications don’t need that level of detail. For another writeup on this topic see: http://usblog.dukane.com/2010/03/how-does-your-ultrasonic-probestack.html
Probe Horns
These are the workhorse design for most power applications hobbyist would look to do. Again, the main brands are Branson, Dukane, and Emerson. Applications for variations on this design include: emulsification / cell disruption, welding, drilling, and cutting. These often come with a threaded tip so that the tip can be replaced as it wears down, or changed to permit multiple applications.
Considerations for purchasing: resonant frequency, probe size, horn material, and gain. These must match the resonant frequency of the transducer to work well. The probe size will be determined by your application, and basically boils down to “will it fit”. If you are looking to sonicate small liquids or components, double check that your tip will match your size. Brand name horns are typically made from steel or titanium. This affects what they react with chemically, how fast they wear out, and their physical size. Gain is the amount that horn increases the output amplitude. Piezo transducer stacks typically expand and contract by about 20um. These horns can increase the amplitude by as much as a factor of 3 depending on their output profile. In general, the more abruptly the diameter of the horn decreases, the higher the gain.
Purchasing recommendations
You can buy these on ebay, alone or bundled with industrial transducers for less than $100. Wear will vary greatly, and only you can decide if the wear is acceptable for your project and budget. Key phrases to search for include “ultrasonic horn”, “catenoidal horn”.
Caveat emptor on horn tips
Many power ultrasonic applications involve pushing >100W of ultrasonic energy through the fairly small tip of the output horn. This causes wear on the tip much faster than any other part of the system. In industrial applications, the tip is considered a wear item. Be careful when buying used horns without replaceable tips as these may be worn or broken unacceptably. These may also deposit small amounts of tip material into your workpiece or mixture.
Boosters
Boosters attach between the transducer and an output horn. These serve two main purposes: increased gain and adding an additional mounting point. Many boosters are designed with a ring at a nodal point, where the vibrations are 0 amplitude, that permits them to be mounted to other machinery. Like horns, they can also amplify the vibrational amplitude. Combining a booster and a horn multiplies the amplitude several times. For instance, you might have a 1:1.5 booster and a 1:2 horn. For 20um of piezo amplitude the booster increases this to 30um at the horn input, and the horn to 60um at the output.
Other types of horns
You can find a wide variety of horns for specialty applications. Some common examples include:
- Slitting horns, which are shaped like knives for ultrasonic cutting
- Large “blocks” for welding large components.
- “Feed through” horns. Which have pipes to mix or sonicate liquids.
- Some have specialty couplings to attach them to various industrial equipment, such as a pipe to help move or settle granular material.
- You may occasionally find discarded horns that have entire product outlines that may designed to assemble a completed item from time to time.
Go forth and have fun! Post in the comments if you make anything cool so I can watch! Post if you have questions and I can be just as confused as you!
Playing with Power Ultrasonics
Aimless exploration with power ultrasonic applications
 JasMoH
JasMoH