-
1Video Walkthrough
![]()
The optional Bluetooth feature can be used to manually toggle & control the water pump wirelessly from your smartphone.
Develop: Are you a programmer, engineer or designer who has a great idea for a new feature/design in Sprout? Maybe you're just a beginner or you've spotted a bug? Feel free to grab our code, schematics, 3D design files & laser cutting files from Github and tinker with it.
-
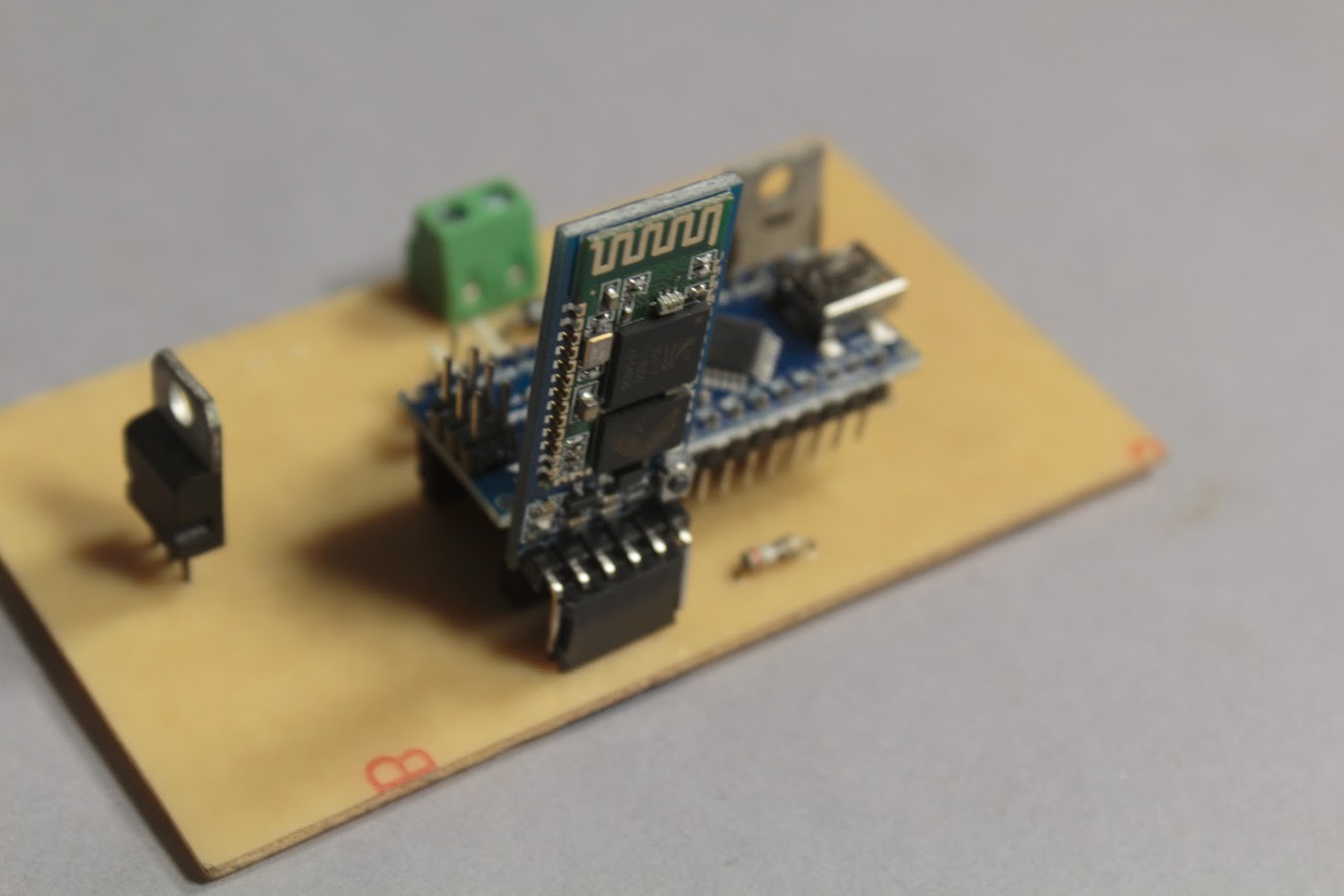
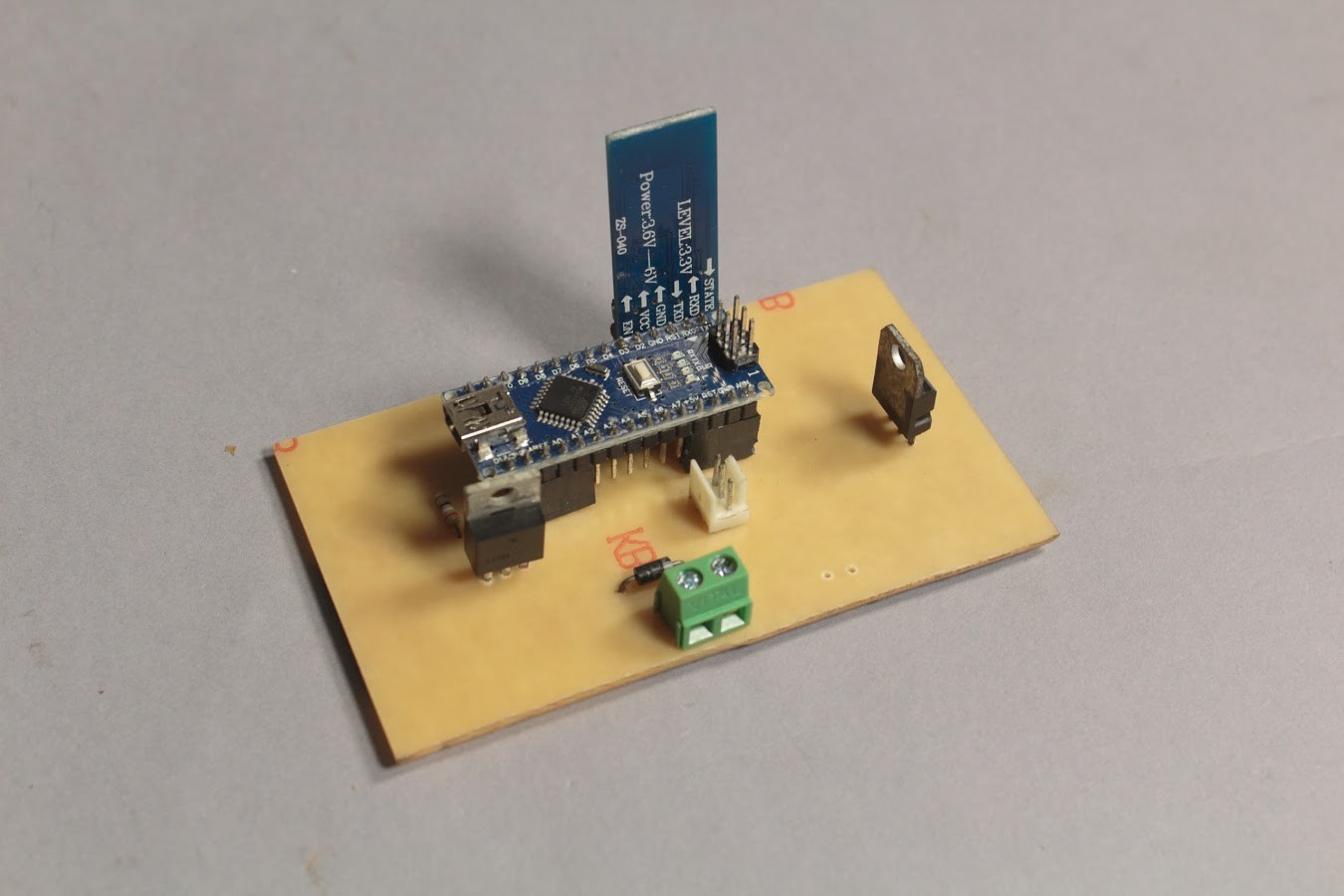
2Electronic Design
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
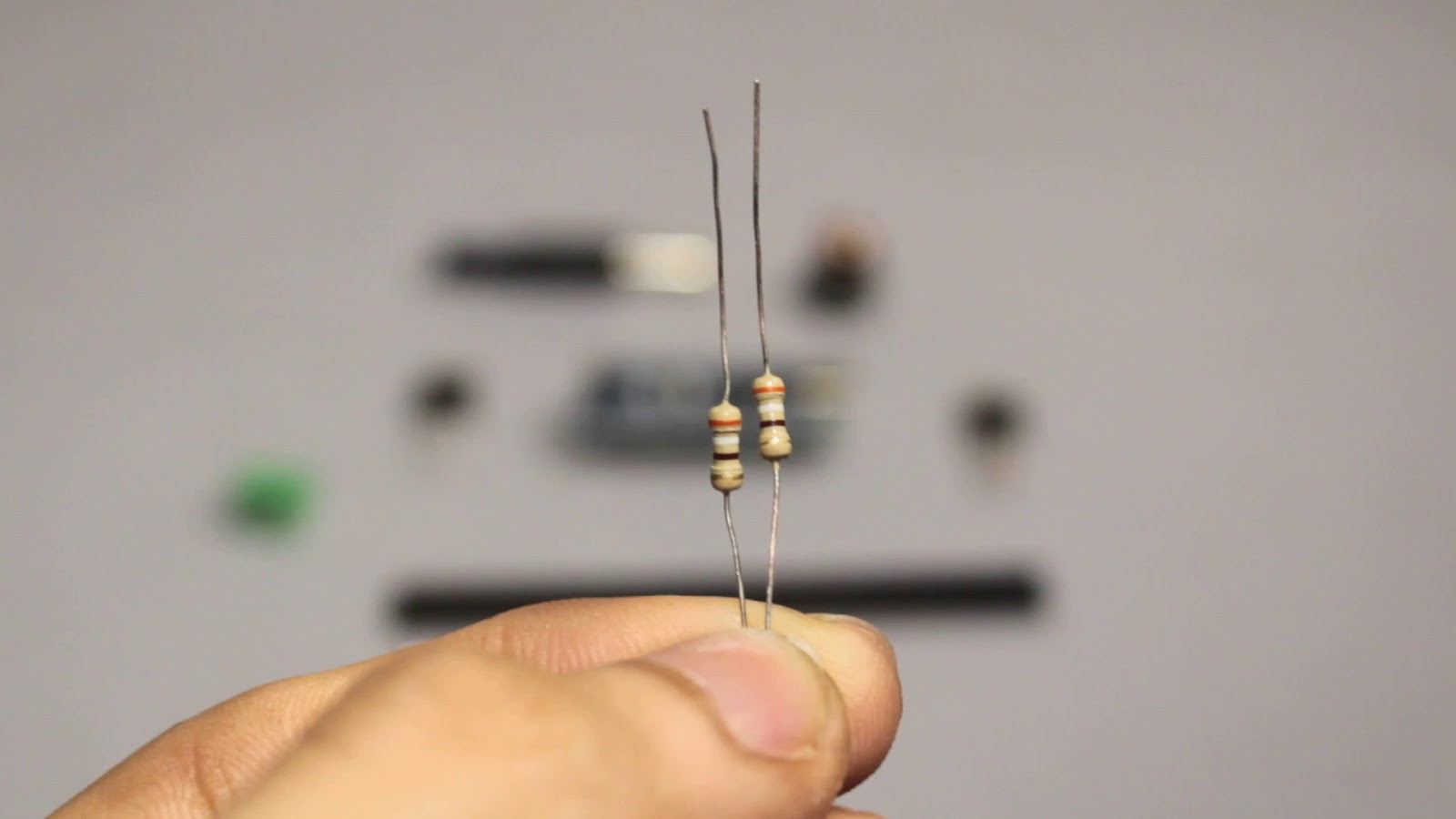
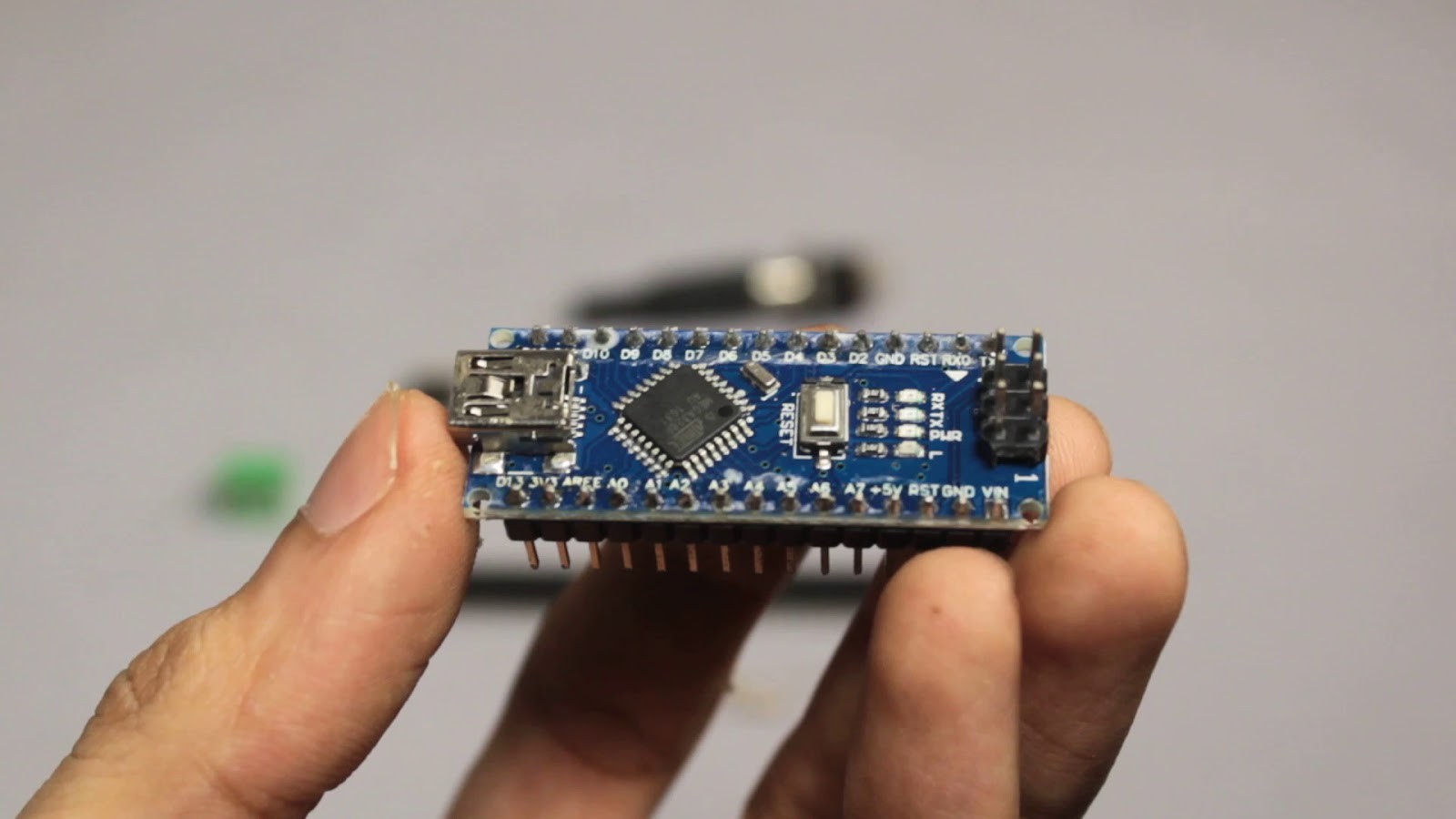
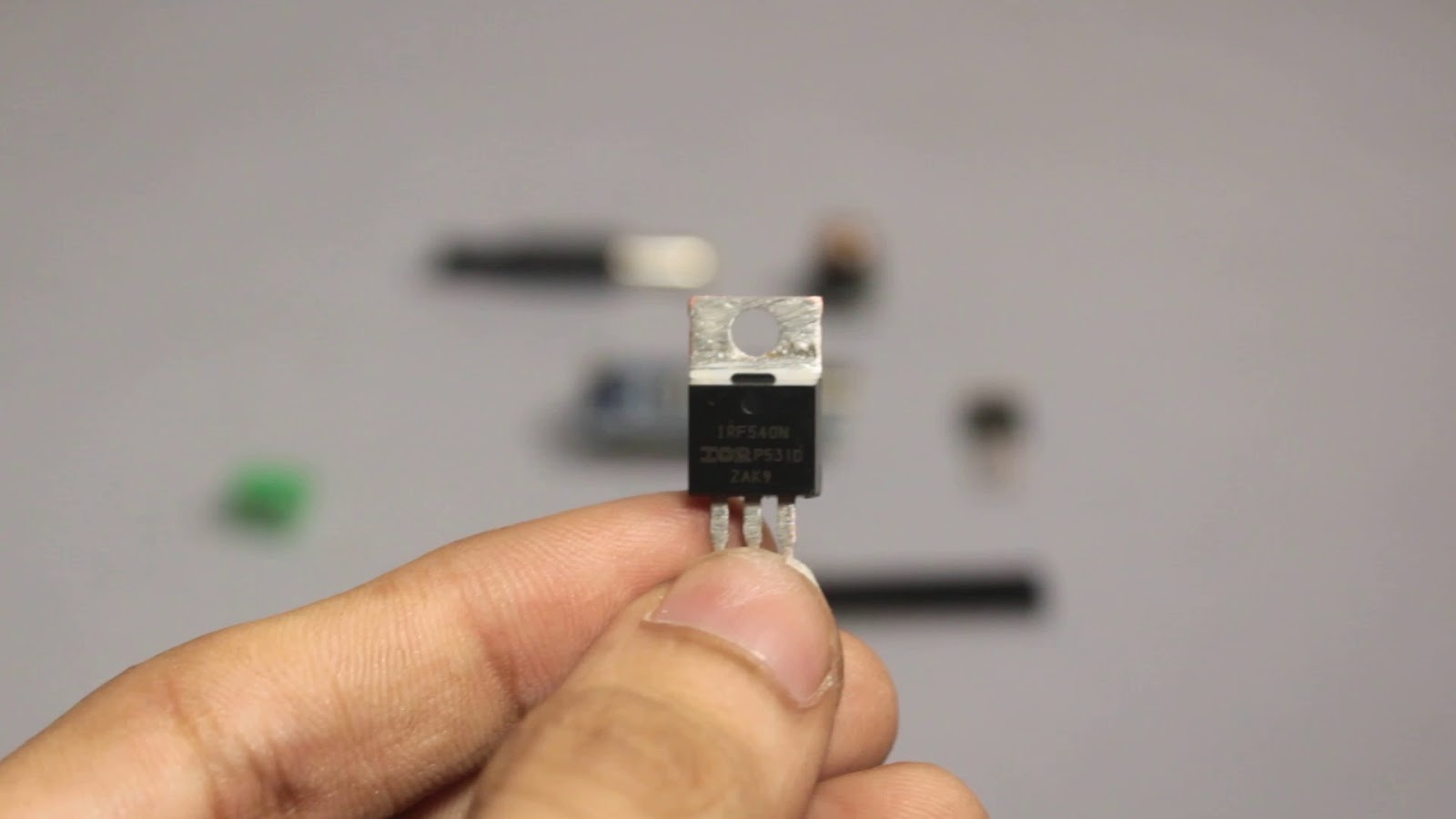
Electronic Components Required:
1x Arduino Nano/ Arduino Pro Mini
1x DC Water Pump 12V or 9V
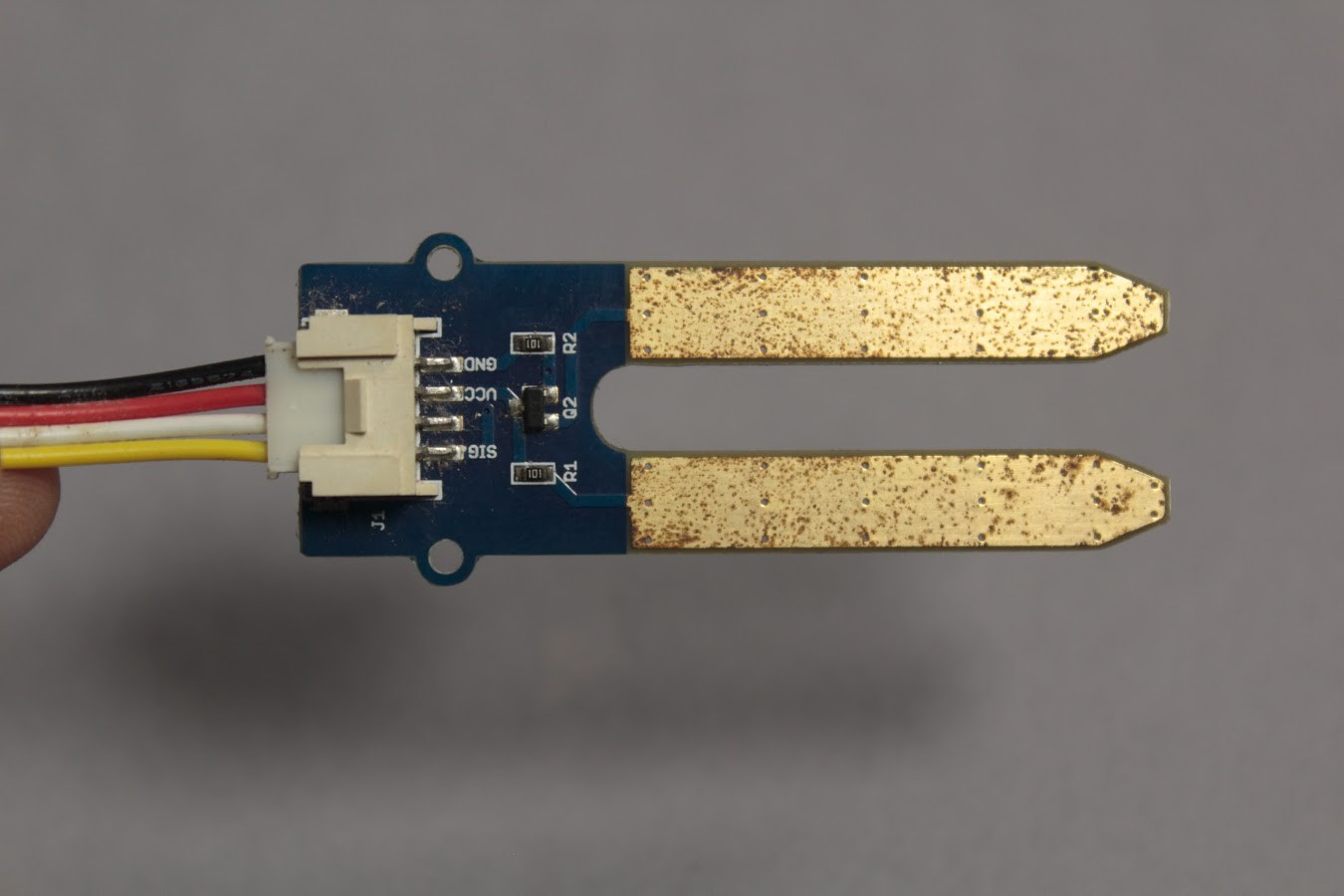
1x Soil Moisture Sensor
1x LM7805 Voltage Regulator
1x IRF540 MOSFET
1x 220 Ohm Resistor
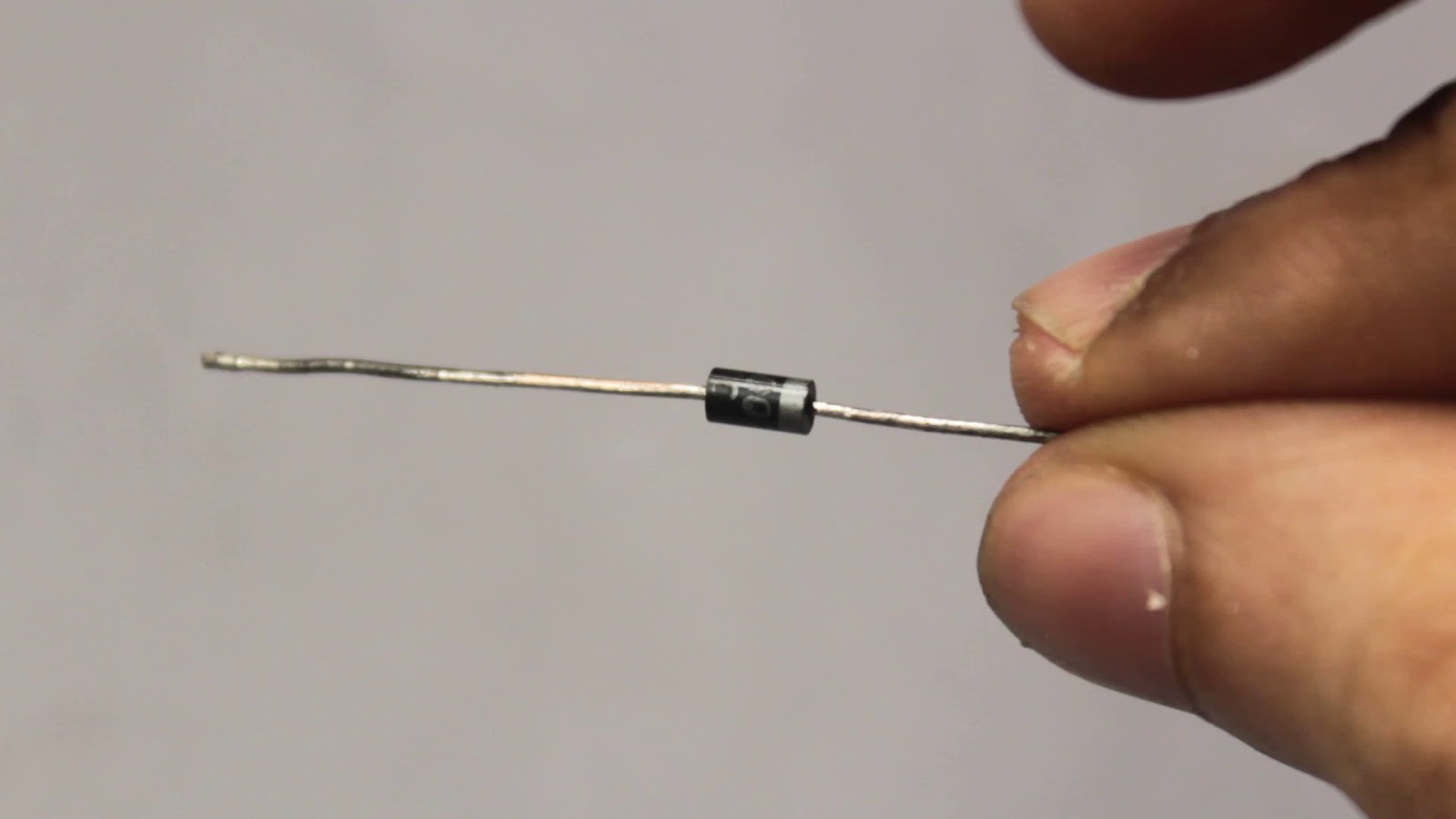
1x IN4001 Diode
1x Header Pins Strip
1x 2-Pin Screw Terminal
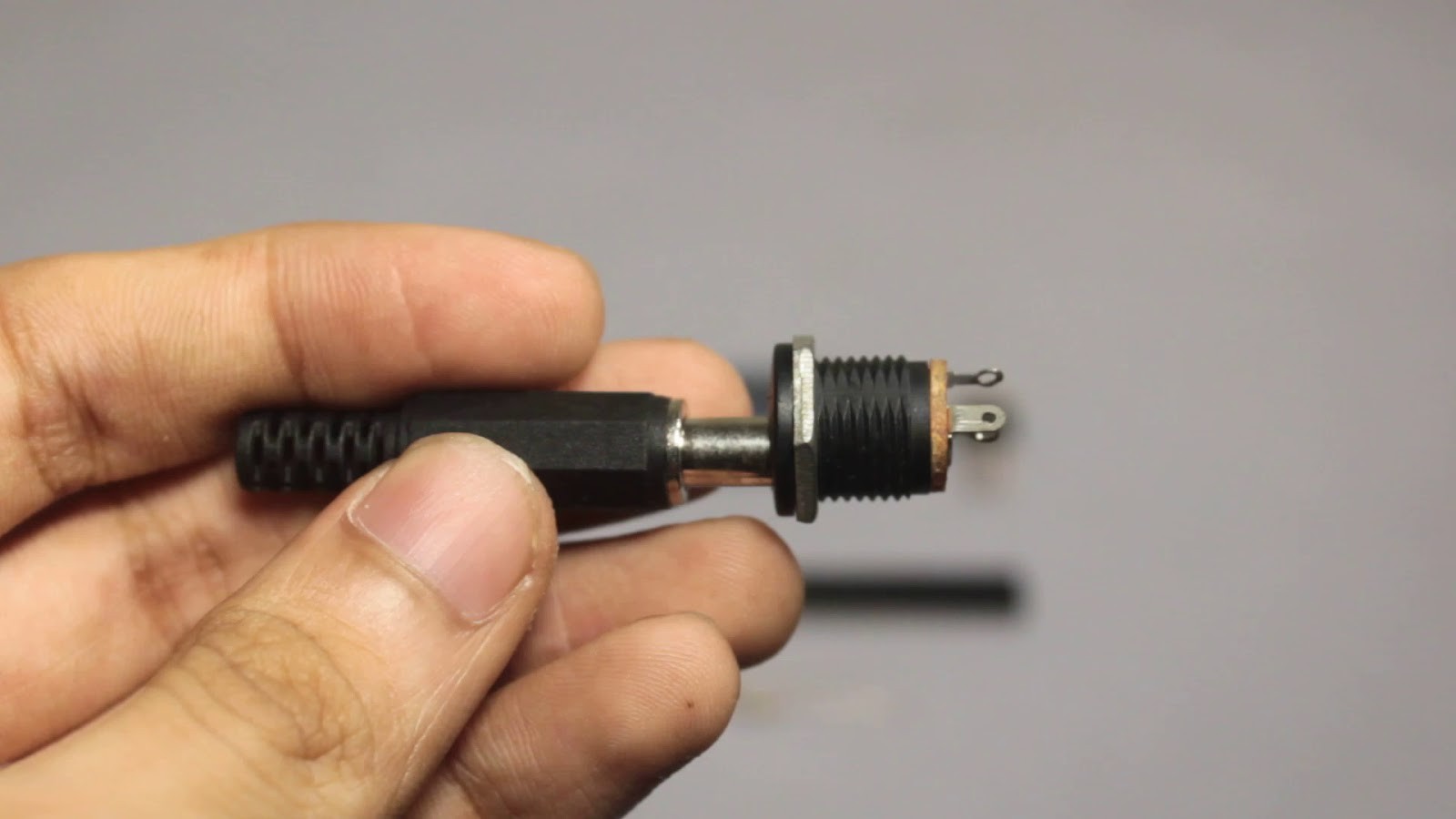
1x DC Power Jack (Male + Female)
Optional: 1x HC-05 Bluetooth Module
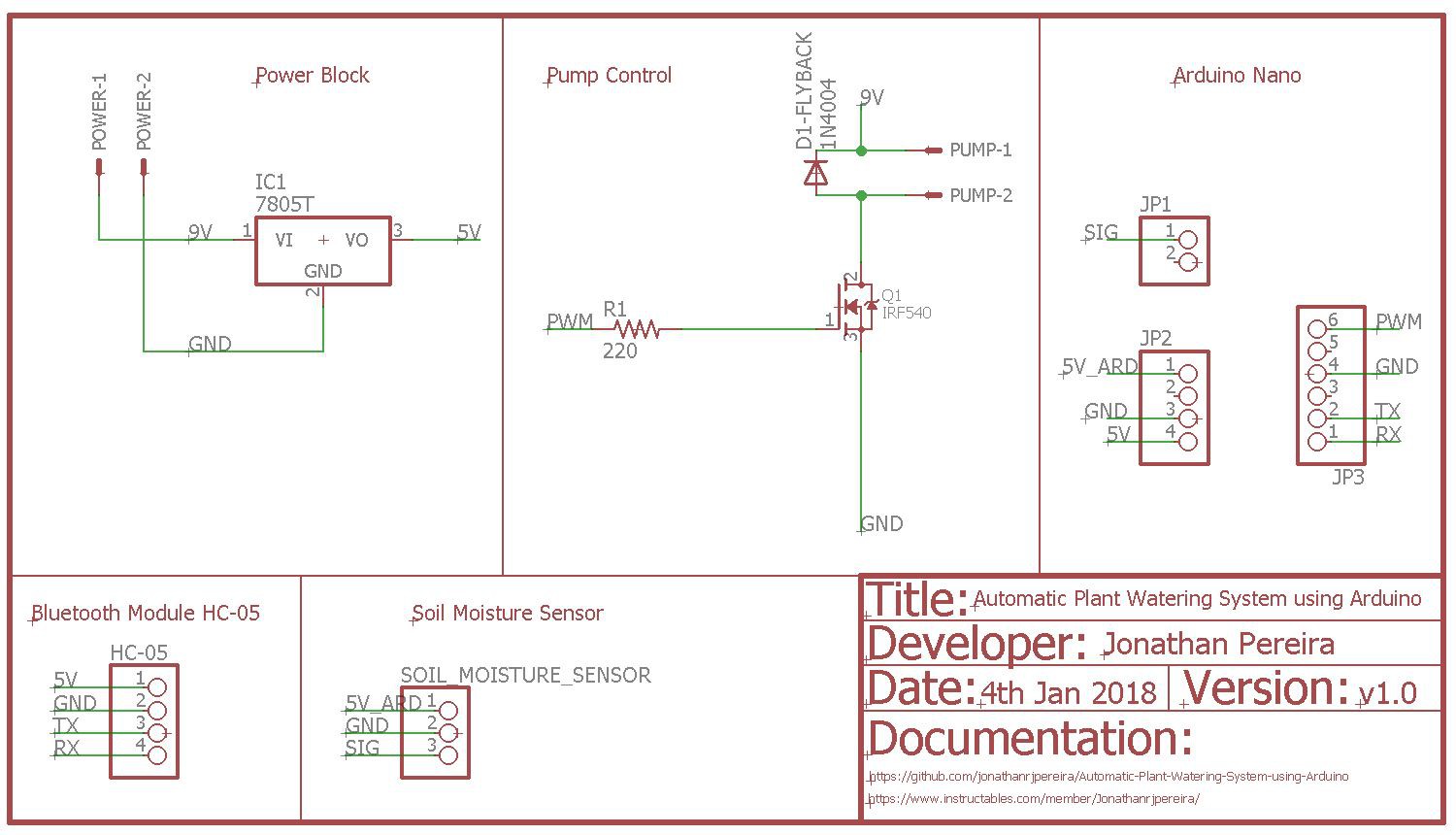
Power Block
The 7805 regulates the supply voltage and reduces it to a constant 5V making it suitable to run the Arduino & Soil Moisture Sensor.
Pump Control
The MOSFET acts as a switch which is controlled by the Arduino. We use the MOSFET since the Arduino cannot directly power the DC Pump. The resistor connected to the gate of the MOSFET prevents the MOSFET from getting damaged. The flyback diode connected across the pump provides a path for dissipation of stored energy when the pump is switched off.
Moisture Sensor The sensor feeds an analog value to the Arduino. The threshold level of moisture is calibrated by the user depending on the type of plant used and the typical h
Bluetooth Module
Uses Serial Communication to transfer data between the Arduino and your Smartphone.
-
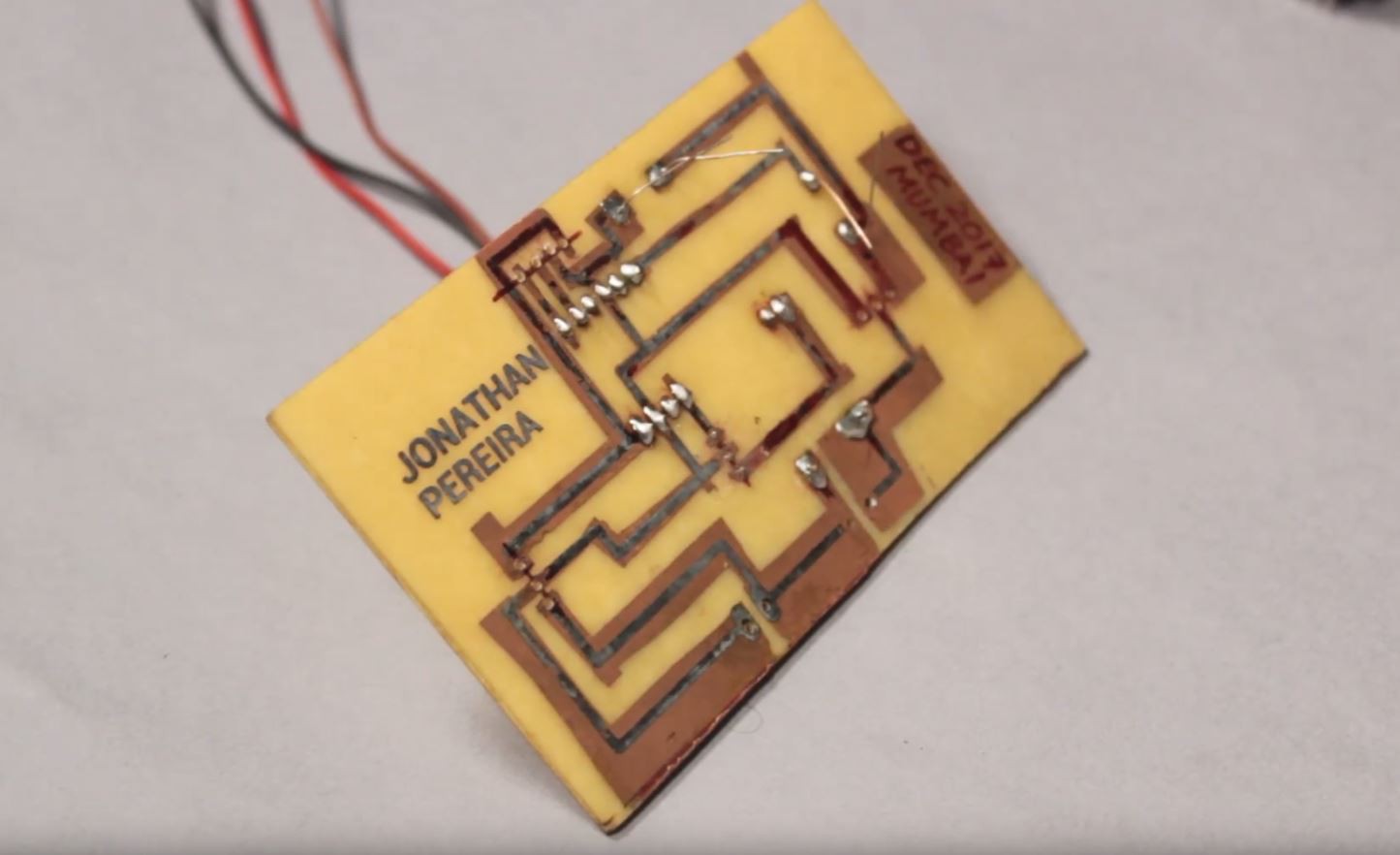
3Electronic Assembly
![]()
![]()
A 1x Scale printable PCB as well as the board view and schematic is available in the GitHub repository.
The repository also contains an A4 size PDF which contains multiple PCB's on a single page. This can be used to make multiple PCB's at a time for mass production
Solder all the components according to the given Schematics.
The editable Eagle files are available below.
-
4Software & Bluetooth Configuration
Software
The Moisture Sensor is connected to an Analog Input pin of the Arduino. A threshold value determines whether the Pump should be ON/OFF.
You can find the code at Sprout: GitHub/Code
Feel free to modify & contribute to the GitHub repository.
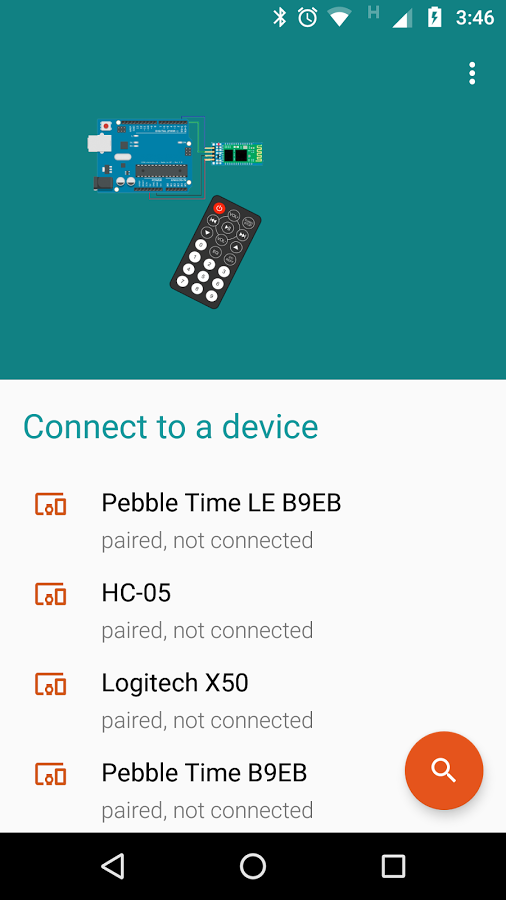
Smartphone App & Bluetooth Configuration
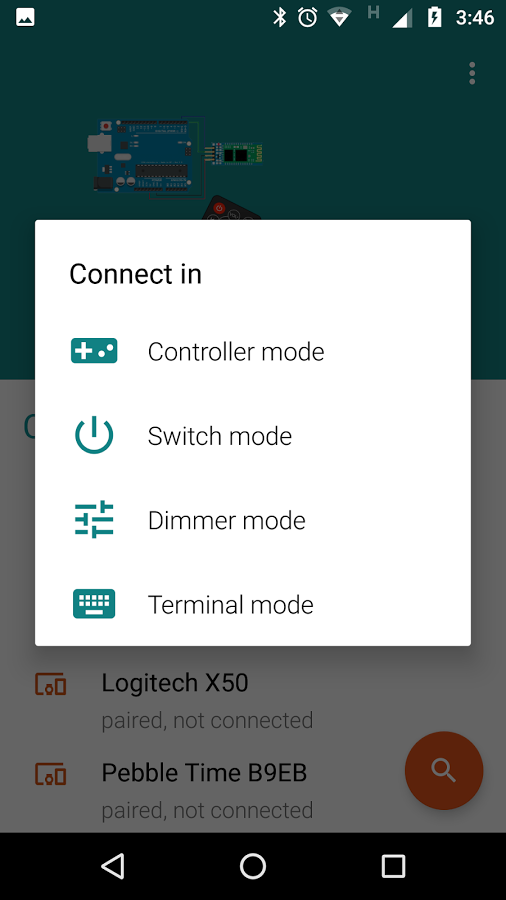
The HC-05 Bluetooth module is the intermediate block between the Smartphone & Arduino. It uses Serial Communication to send data from the Smartphone to the Arduino & acts as a Remote Control.
The app transmits the value '48' or '49' which represent 'ON' & 'OFF' respectively. The pump can hence be controlled wirelessly.
![]()
![]()
Simply open the app, scan for discoverable devices & pair with the HC-05 module. then click on 'Switch Mode' and toggle the onscreen button.
The app is available at Bluetooth App
-
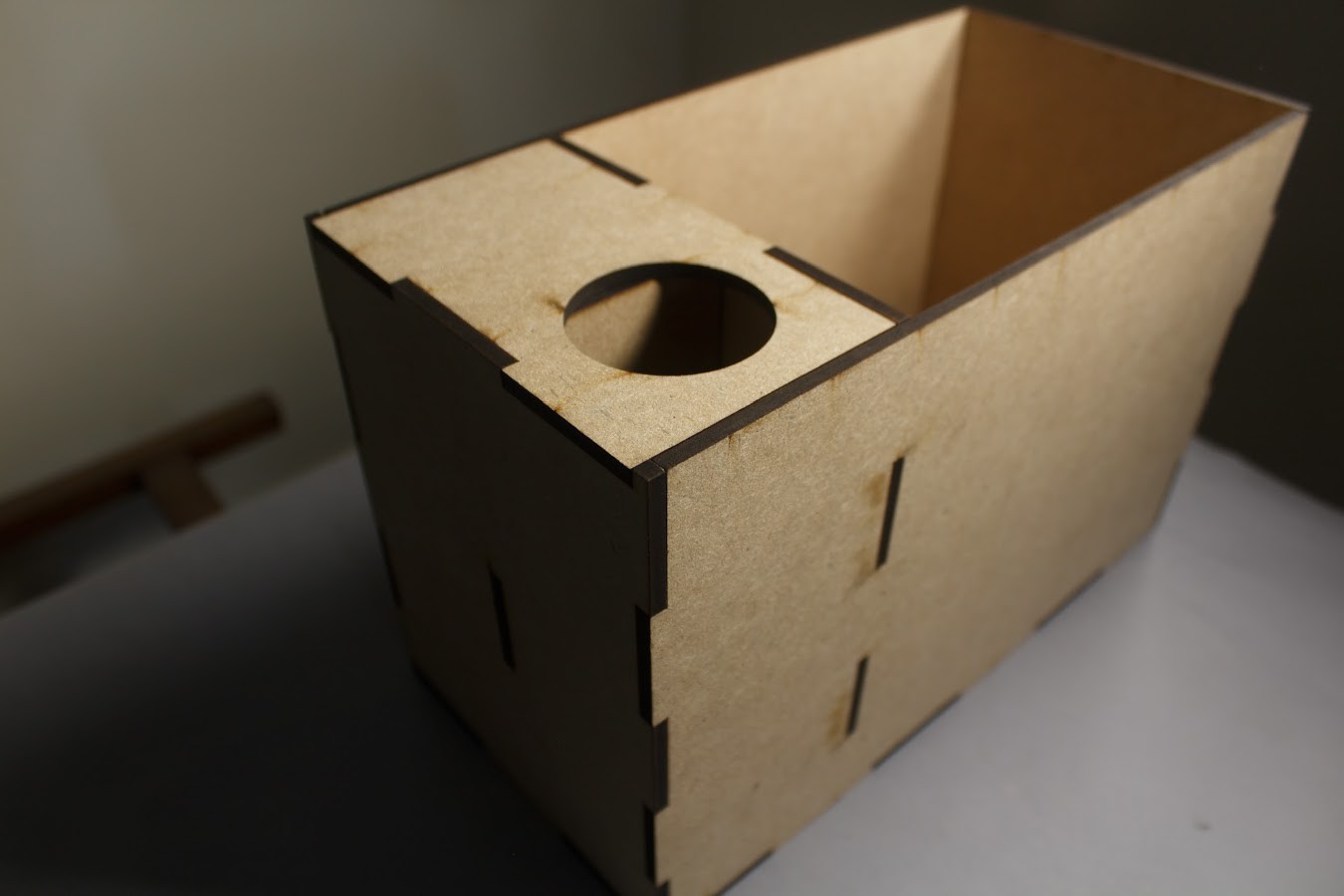
5Mechanical Design
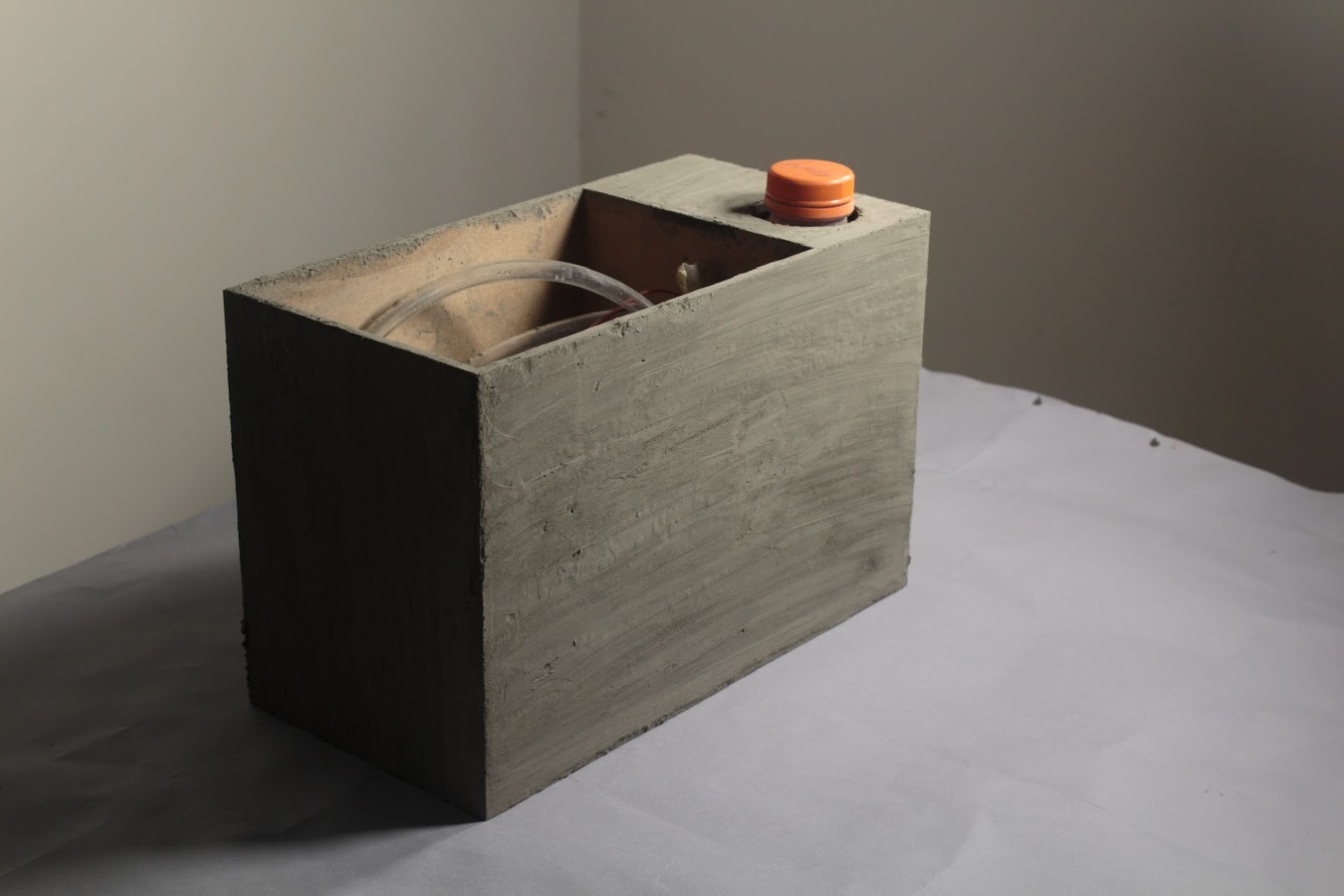
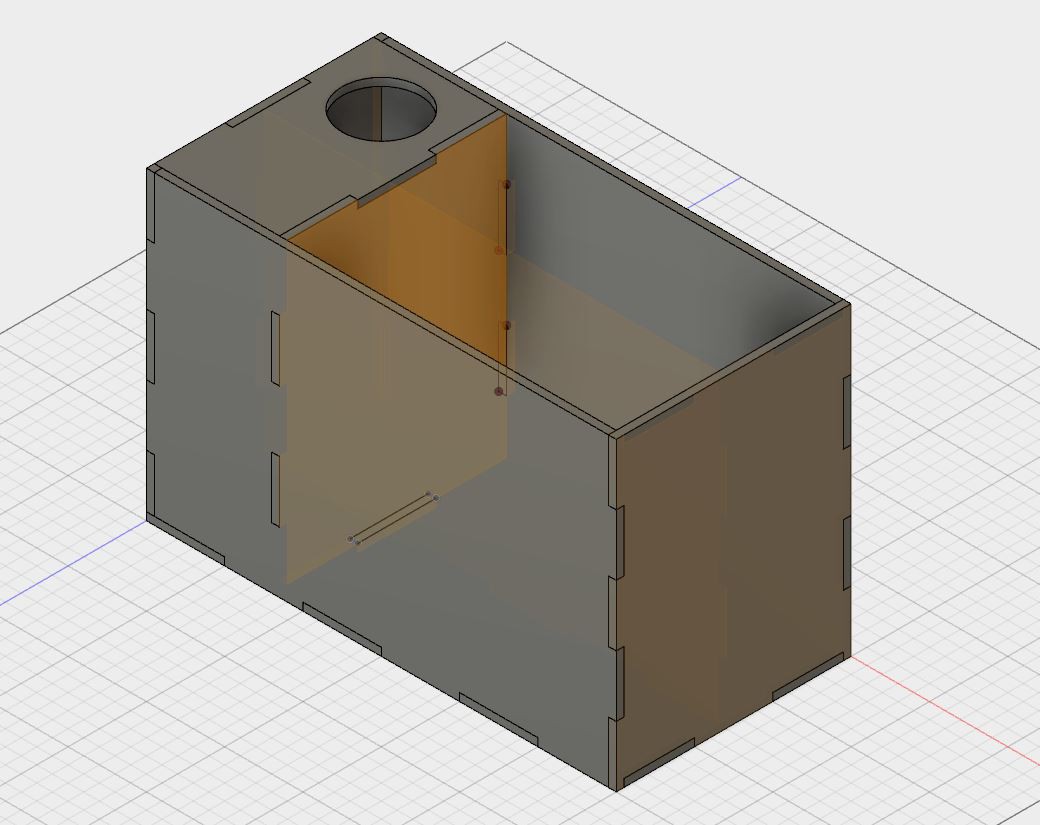
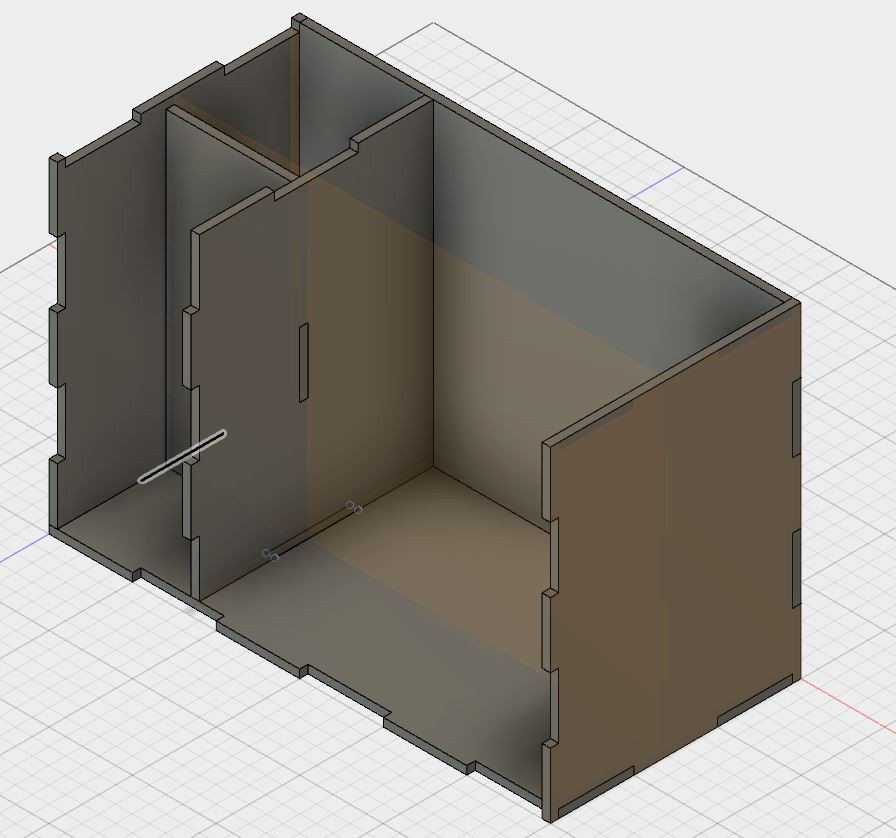
The main body of Sprout is a 30cm X 15cm X 19cm Box made out of MDF.
All Mechanical Design steps have been clearly demonstrated in the video attached at the start of the Instructable. You can also check it out at Sprout: Video/Mechanical Design
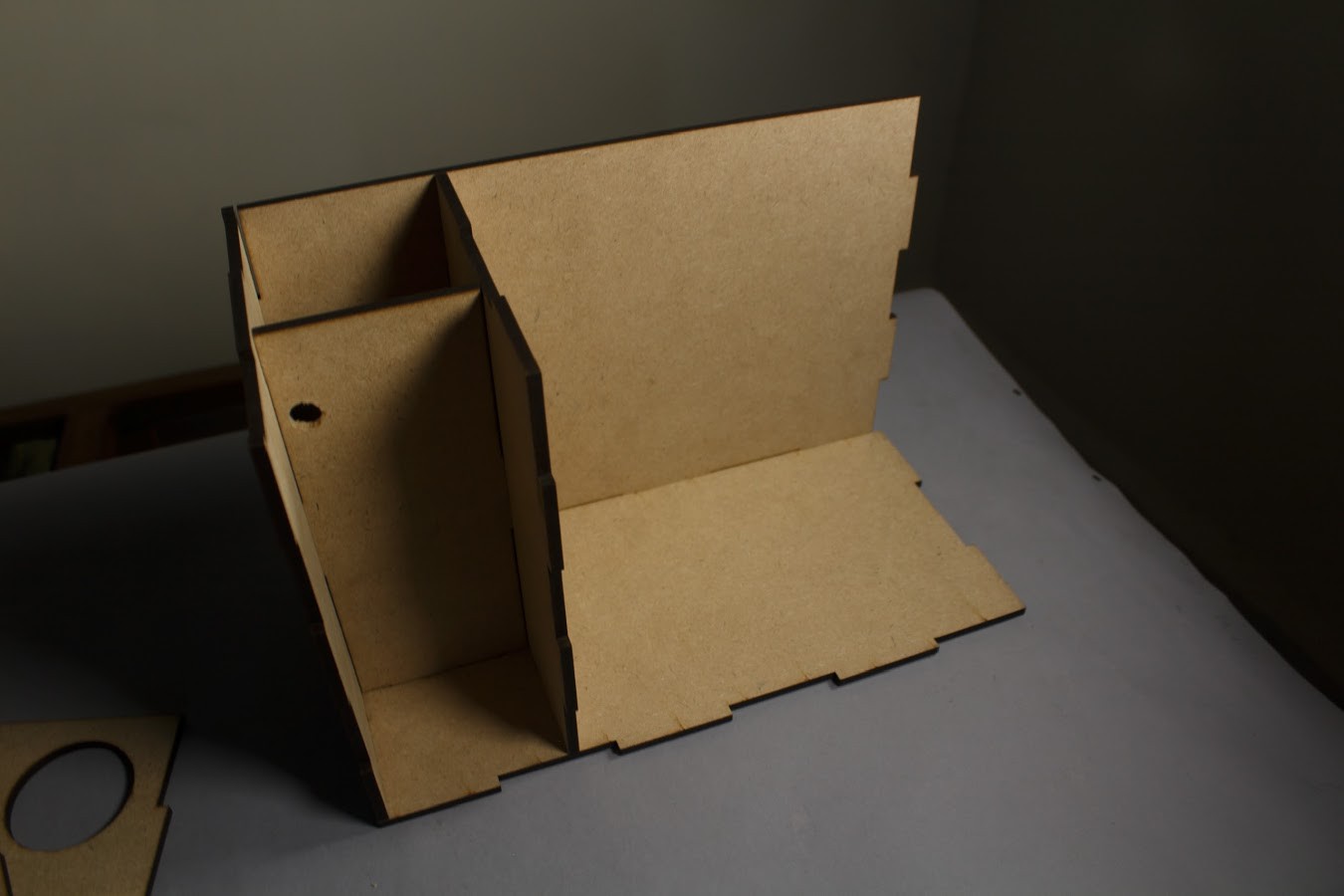
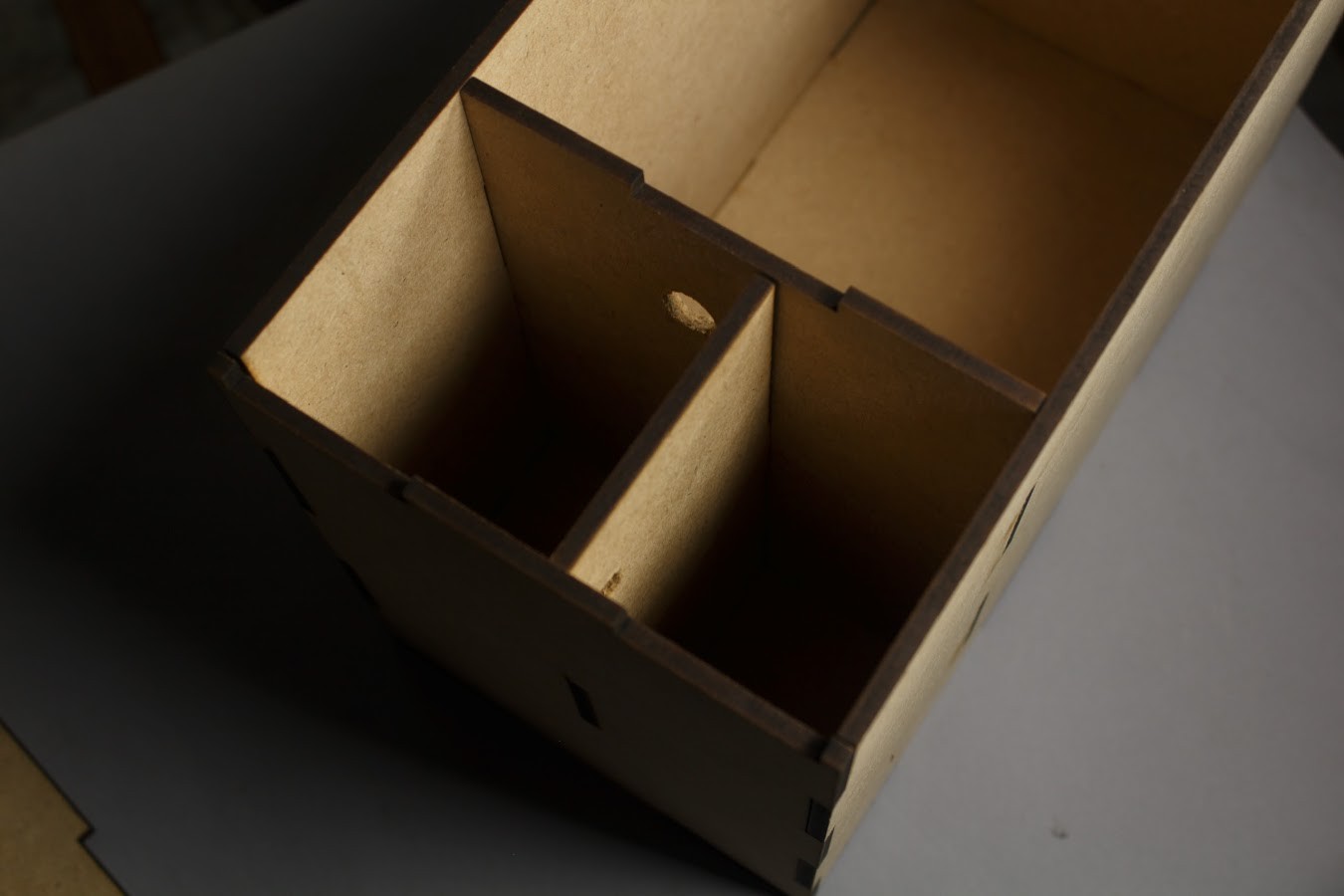
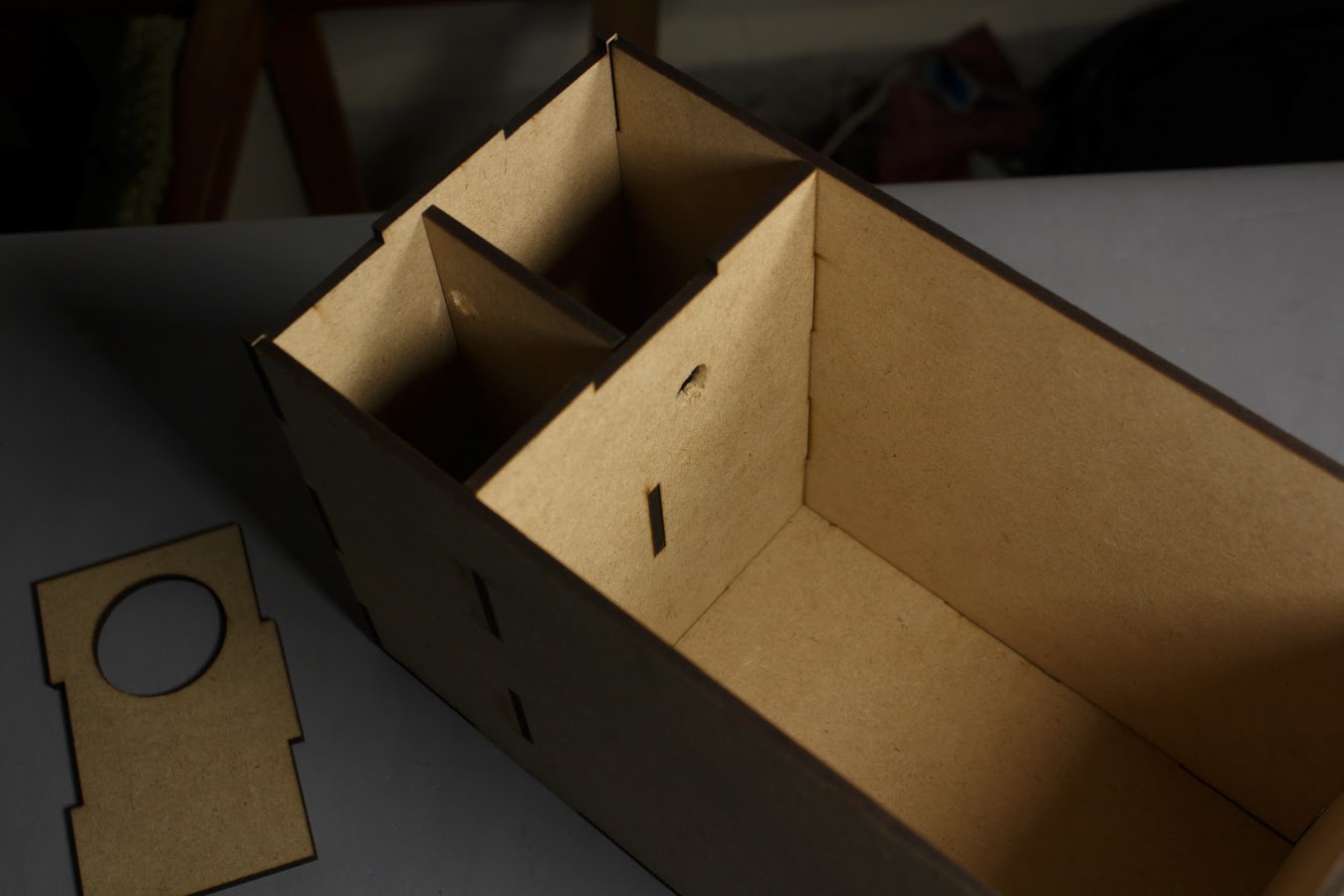
The box is divided into two sections:
- The larger section contains the Soil & Plants
- The smaller section is further divided into two more sections such that one section contains the Circuit Board while the other contains the Water Reservoir.
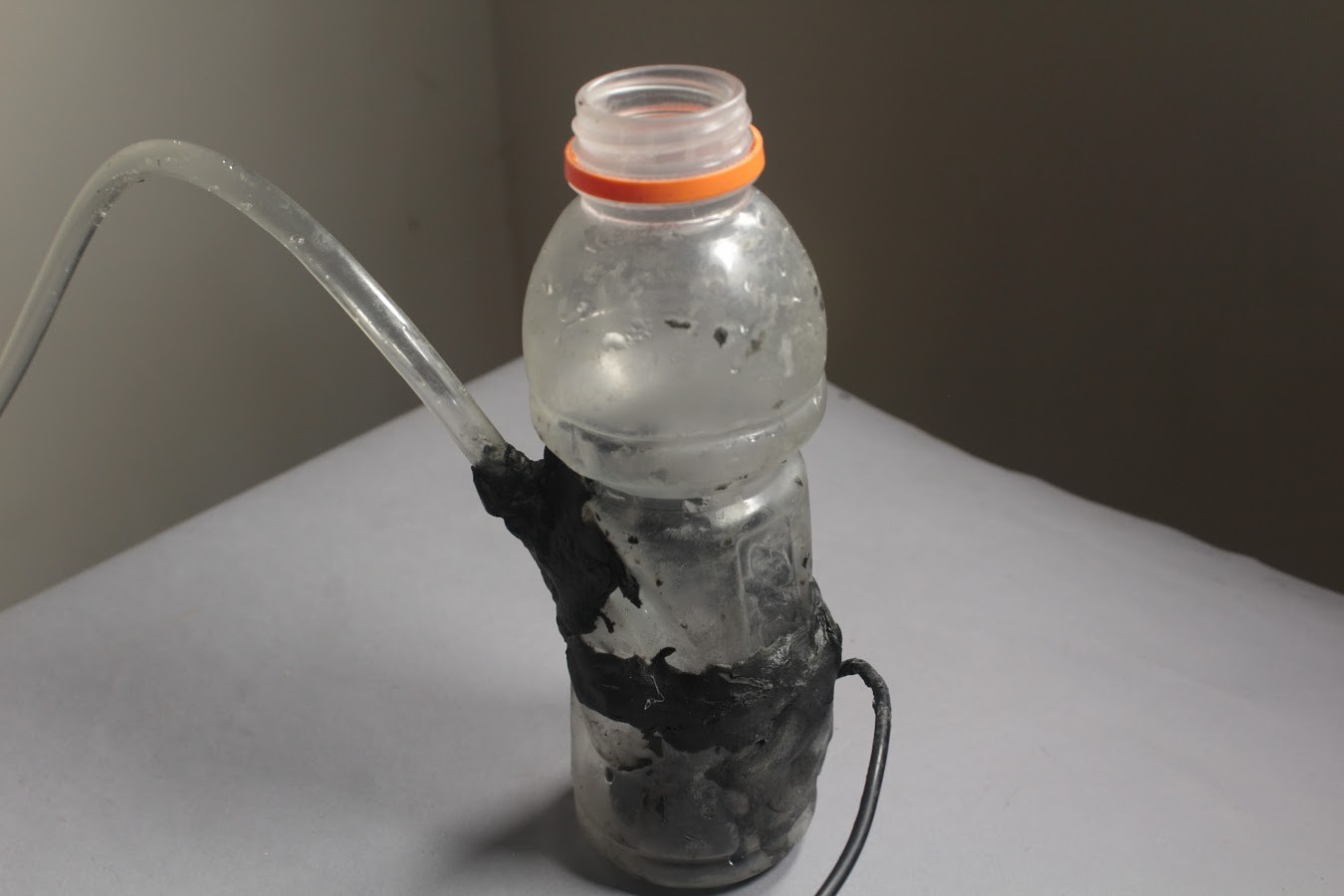
The water reservoir is a 500ml plastic bottle.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The MDF box has 8 separate interlocking faces which can be laser cut and slotted into each other.
The Laser Cutting files, Fusion 360 Design file (3D Design file), isometric as well as orthogonal views of each face can be found at Sprout: GitHub/Mechanical Design
You can also find editable Illustrator files in the GitHub repository which can be modified to your specific requirements/dimensions and then can be laser cut.
-
6Mechanical Assembly: Bottle Preparation
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
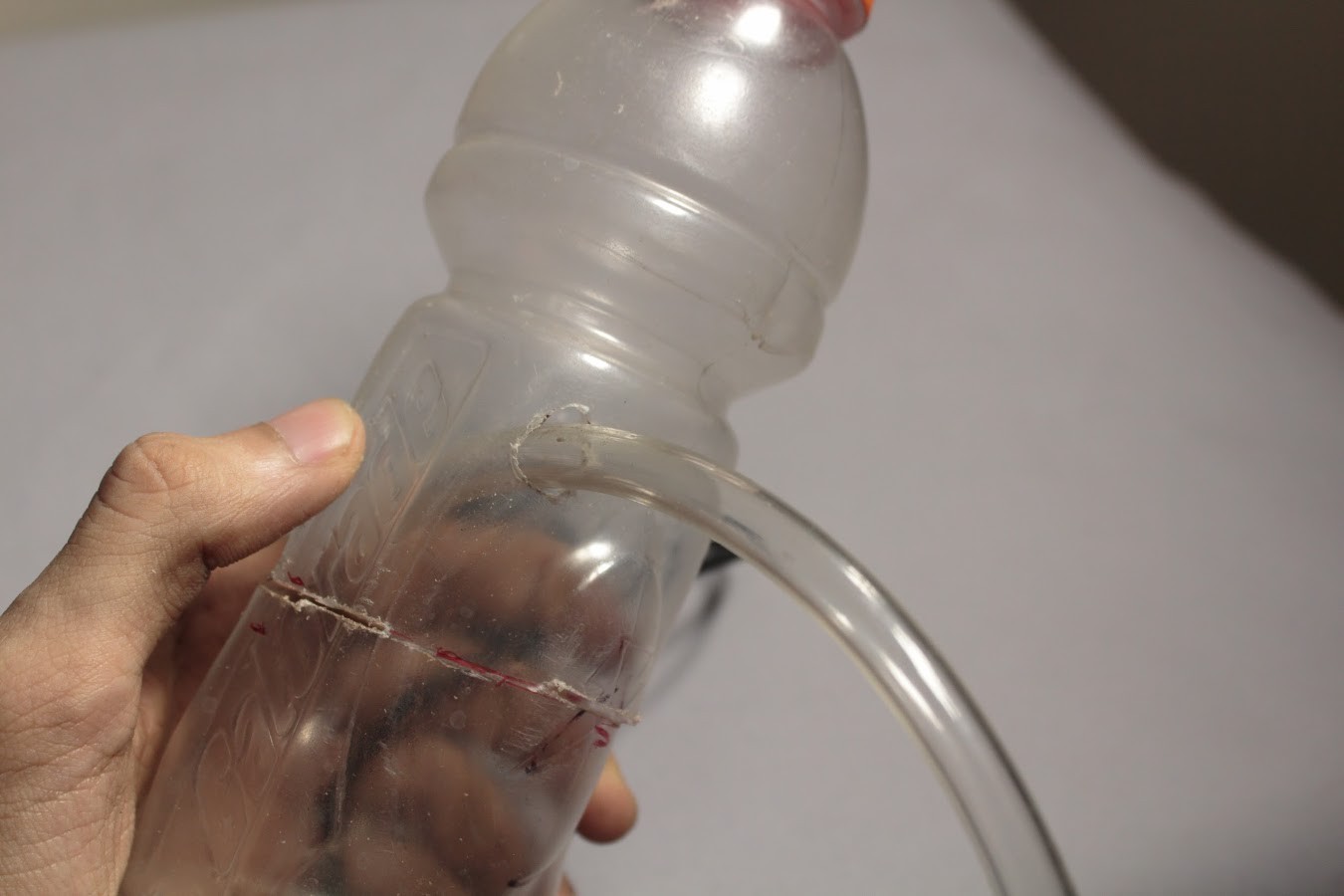
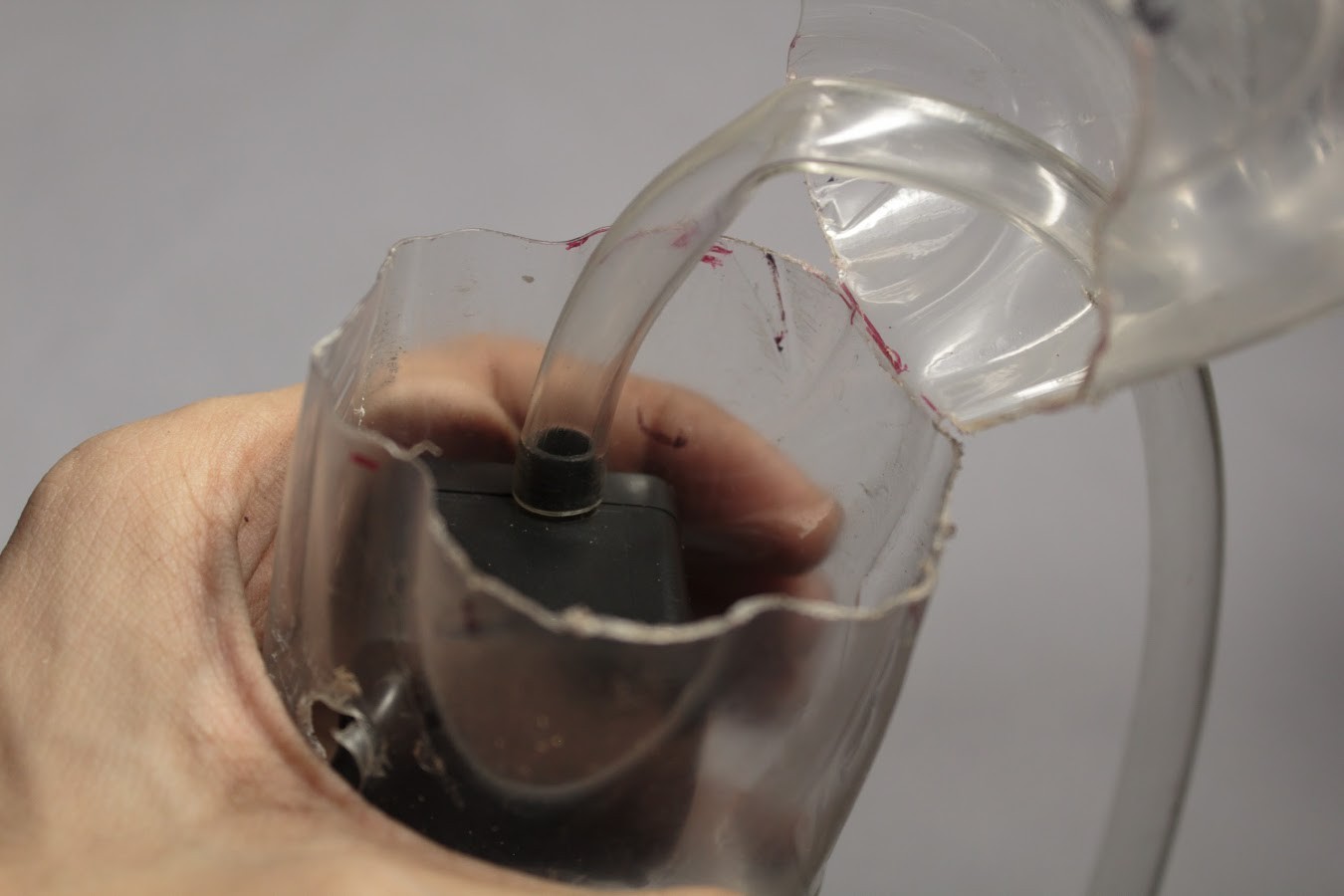
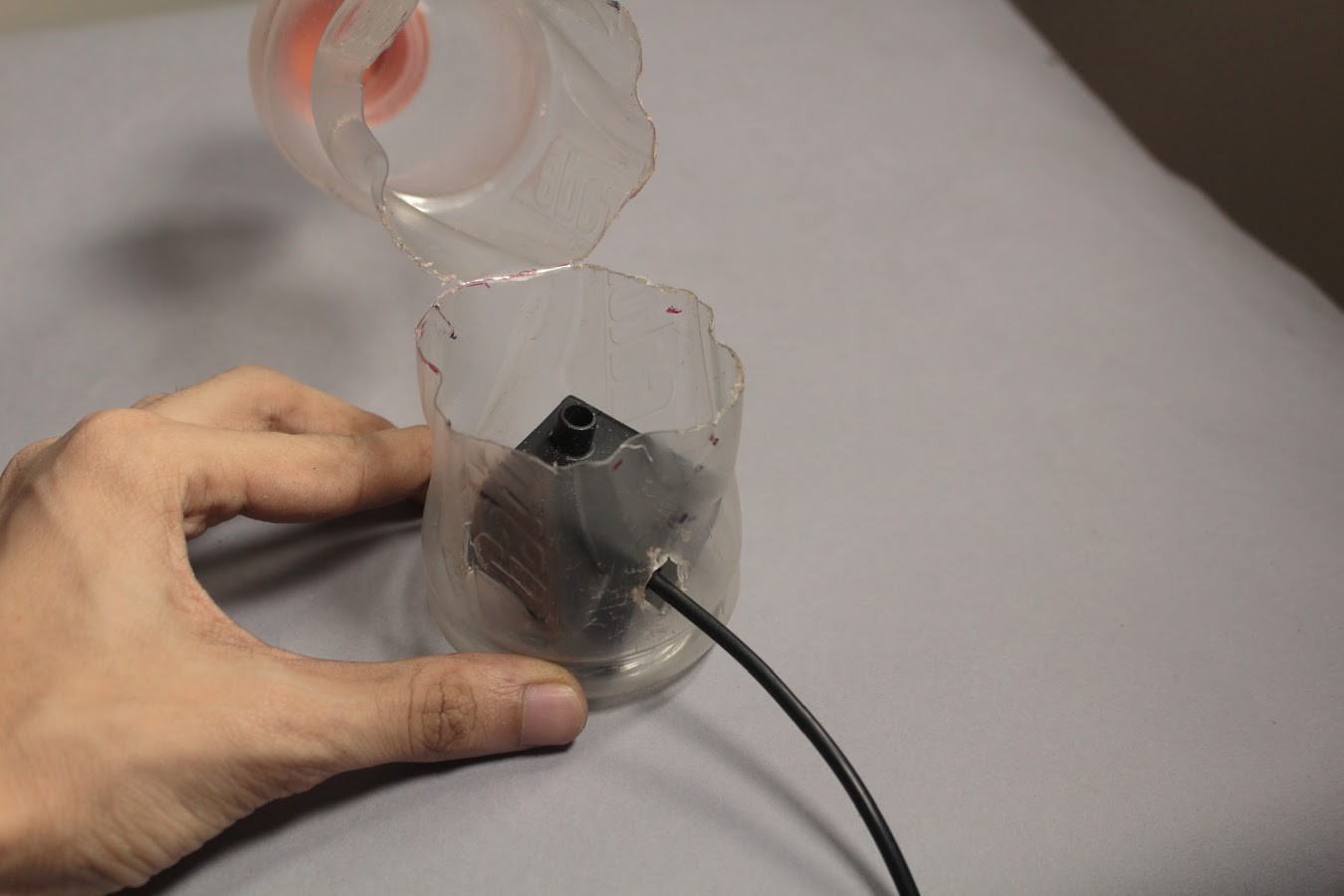
The water reservoir is a 500ml plastic bottle. A typical 500ml plastic Soda bottle can be used for this.
The maximum diameter of the bottle should be 74mm. The maximum diameter of the cap of the bottle should be 50mm. The maximum height from the base of the bottle to the lowest part of the cap should be 18.5 cm.
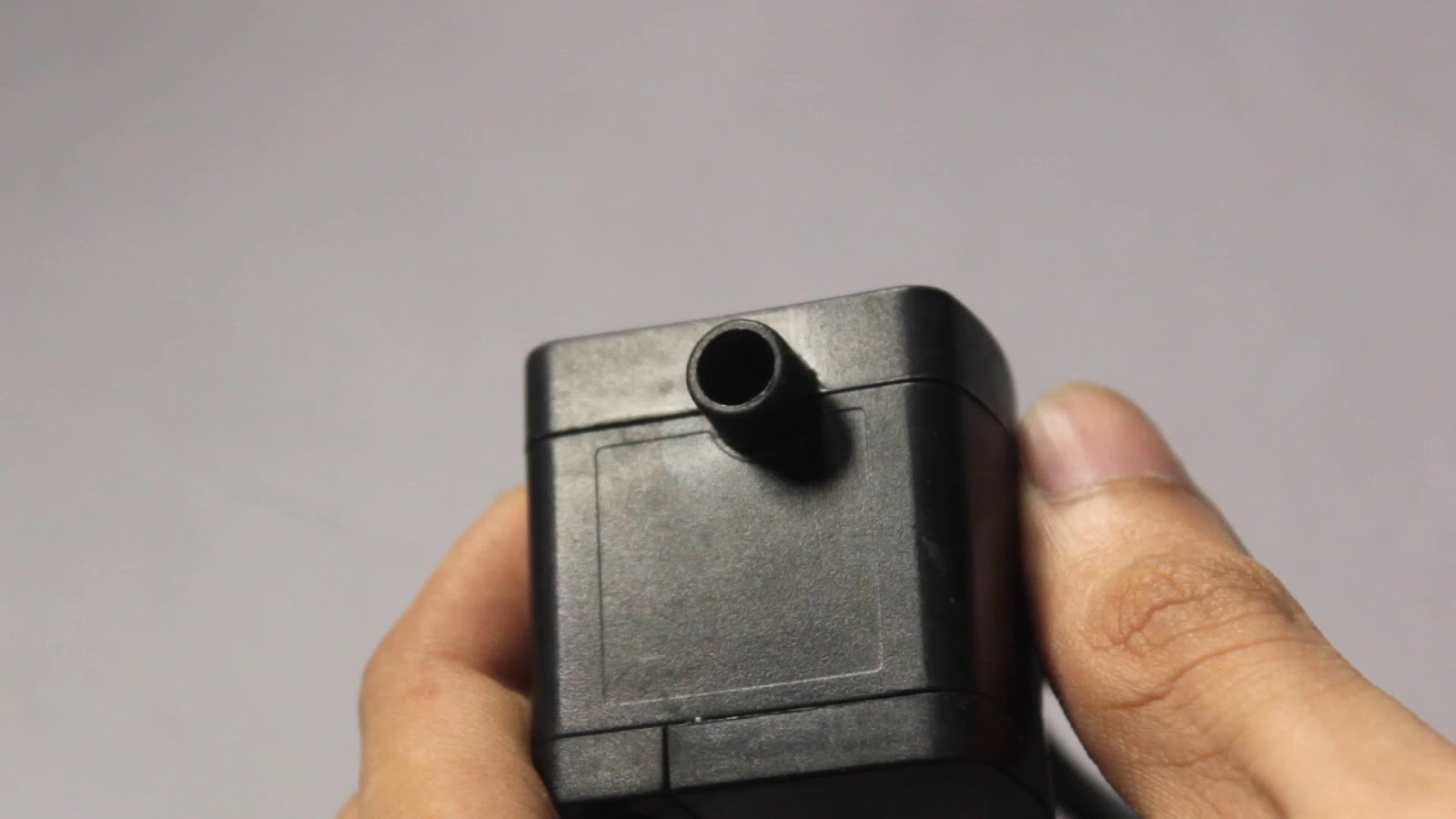
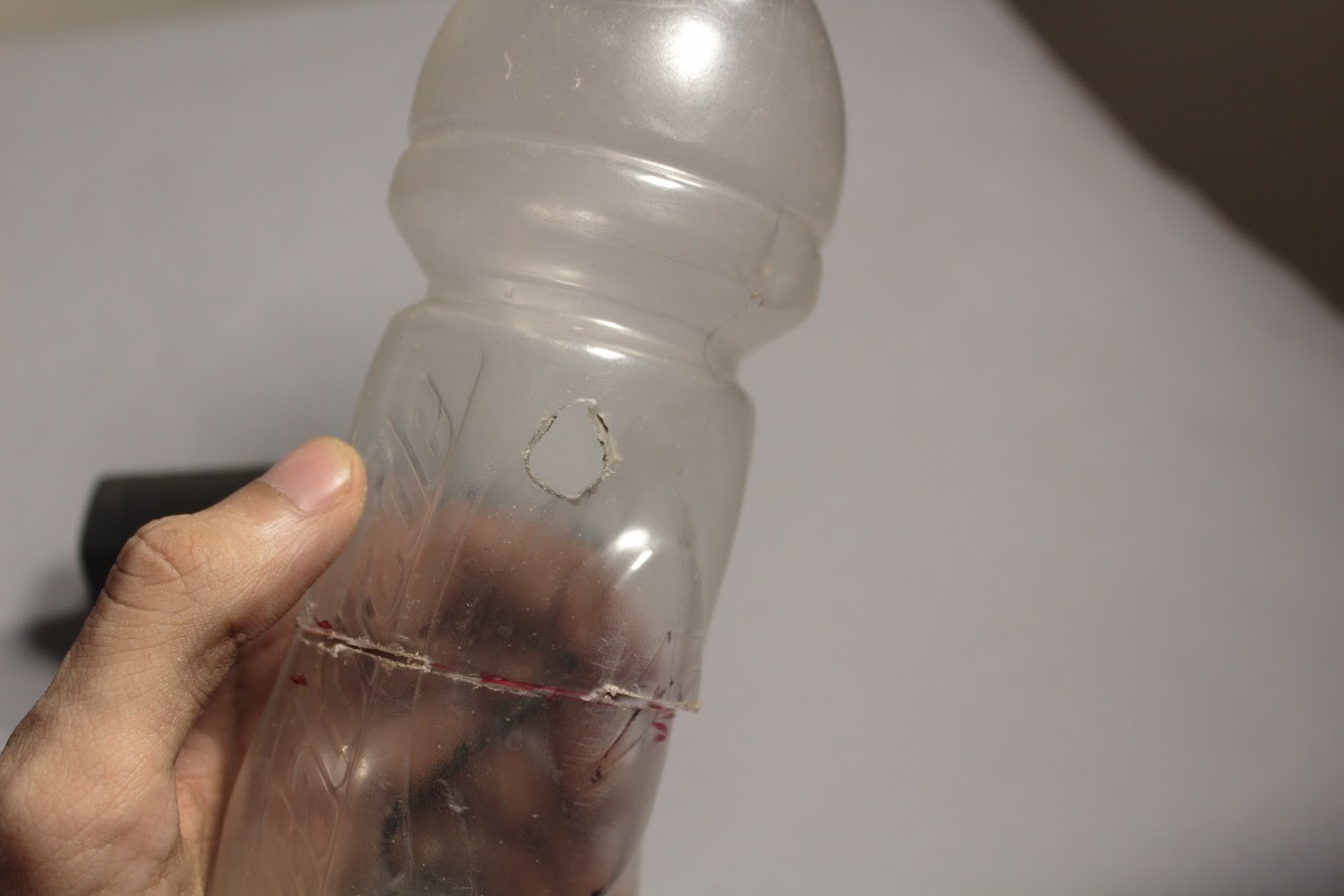
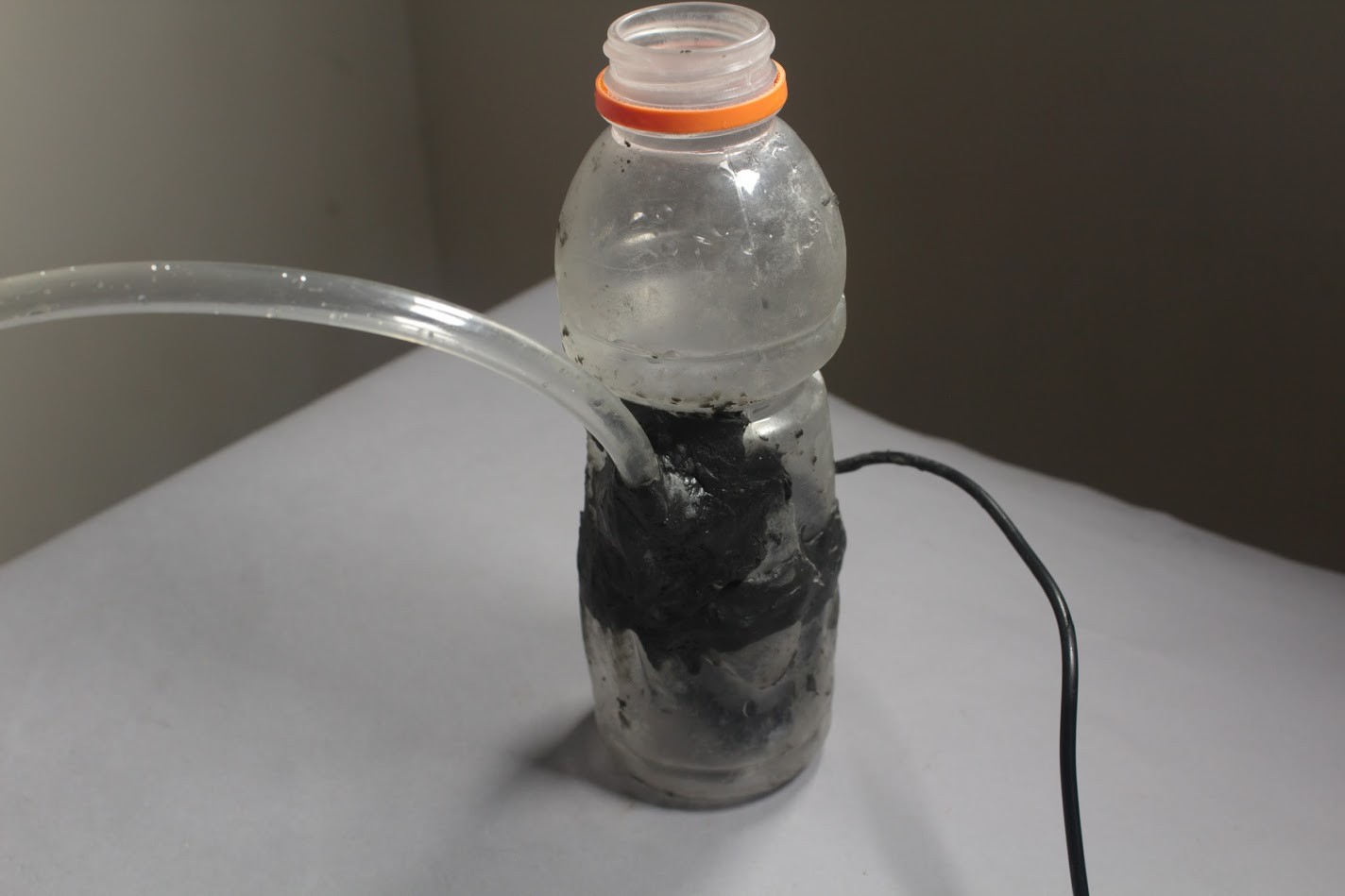
The bottle must be cut about 50mm above its base so that the pump can be placed within it. Holes must be cut into the bottle such that the Outlet Pipe and Power wires can be fed through the bottle.
![]()
![]()
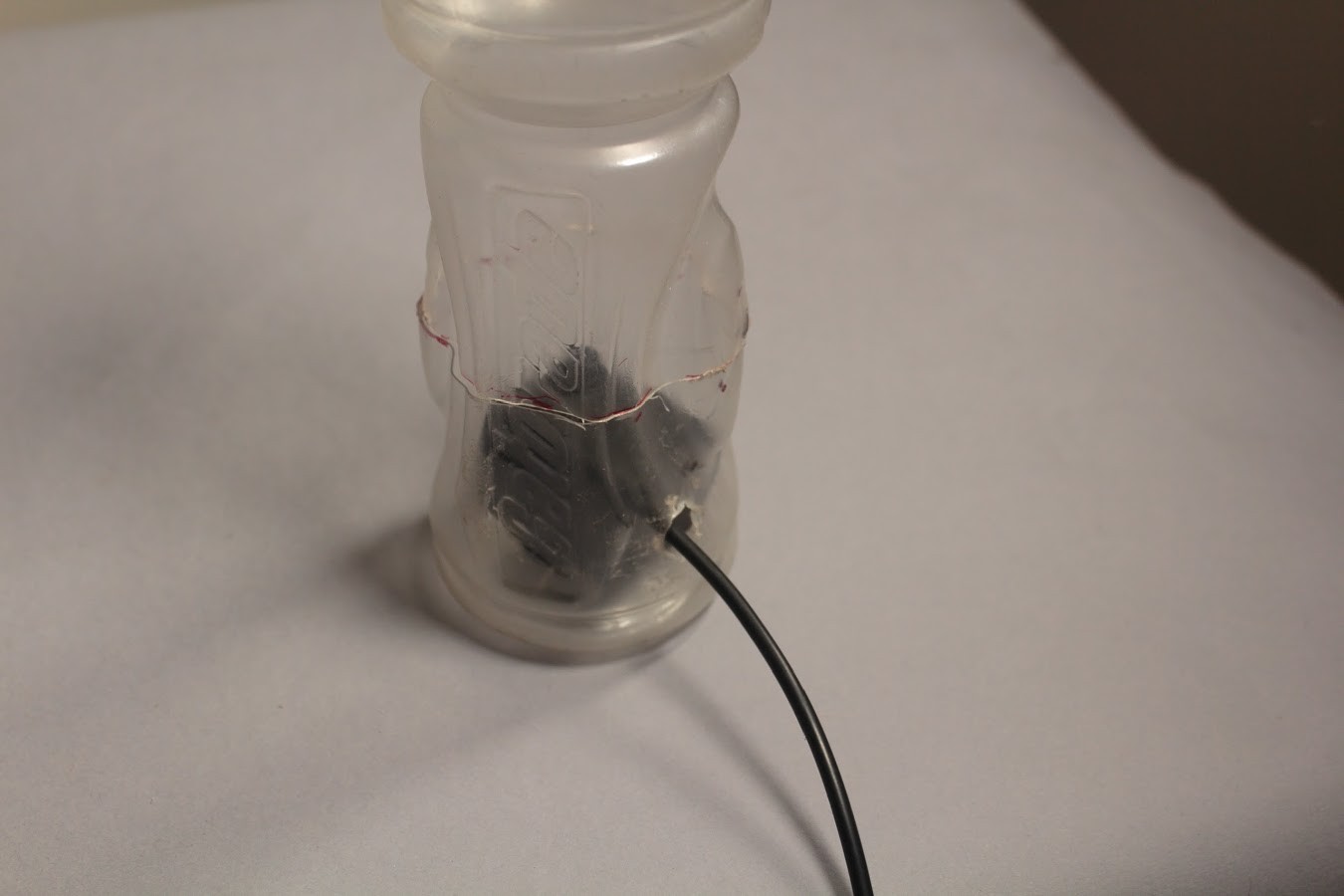
Once the Outlet Pipe and wires have been taken out through their respective holes, the bottle can be sealed again. To seal the bottle we must use an Epoxy Compound which will harden within a few hours. This will prevent any water from leaking out.
The water can be refilled from the top of the bottle by simply opening its cap.
-
7Mechanical Assembly: Box Preparation
-
8Mechanical Assembly: Cement
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
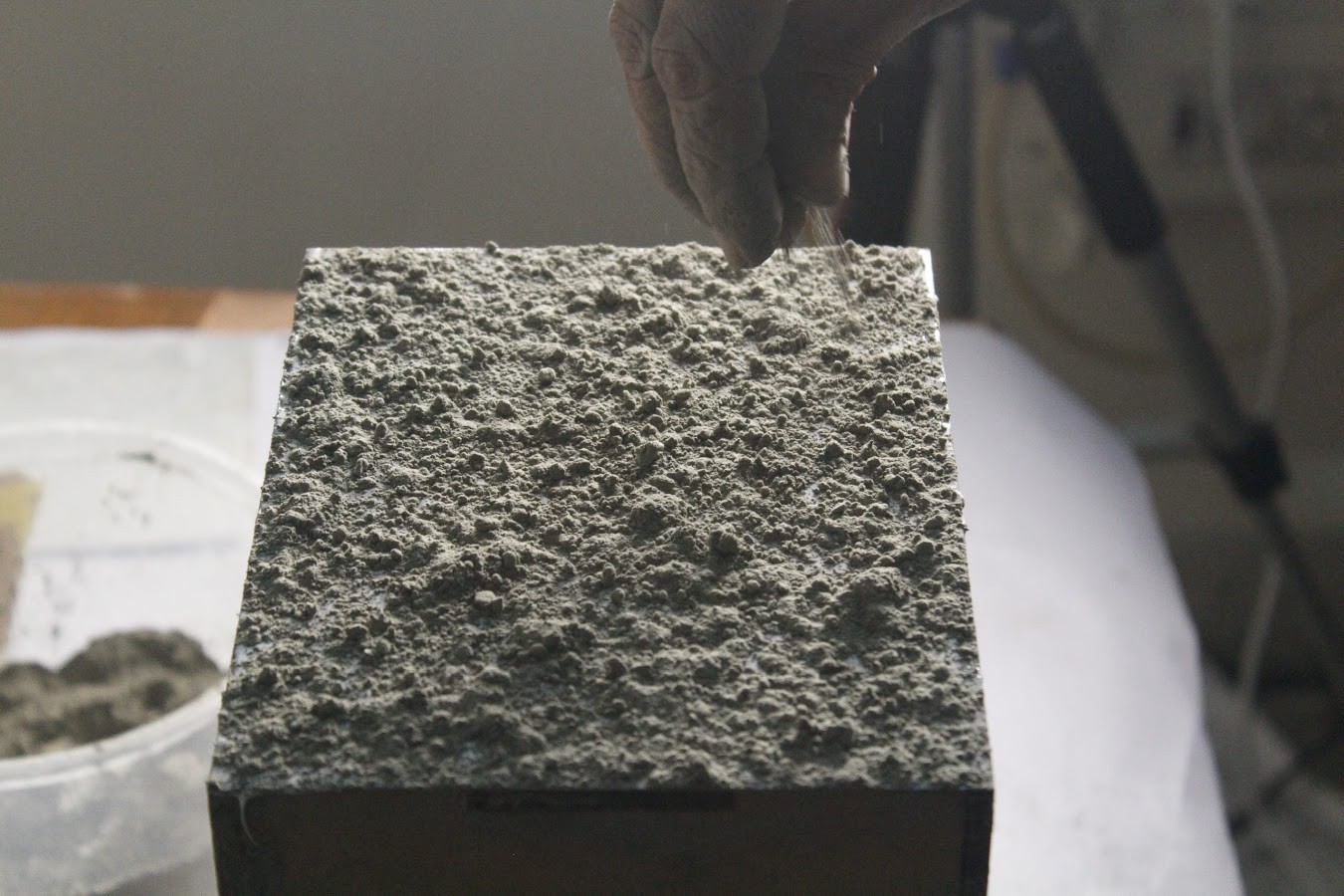
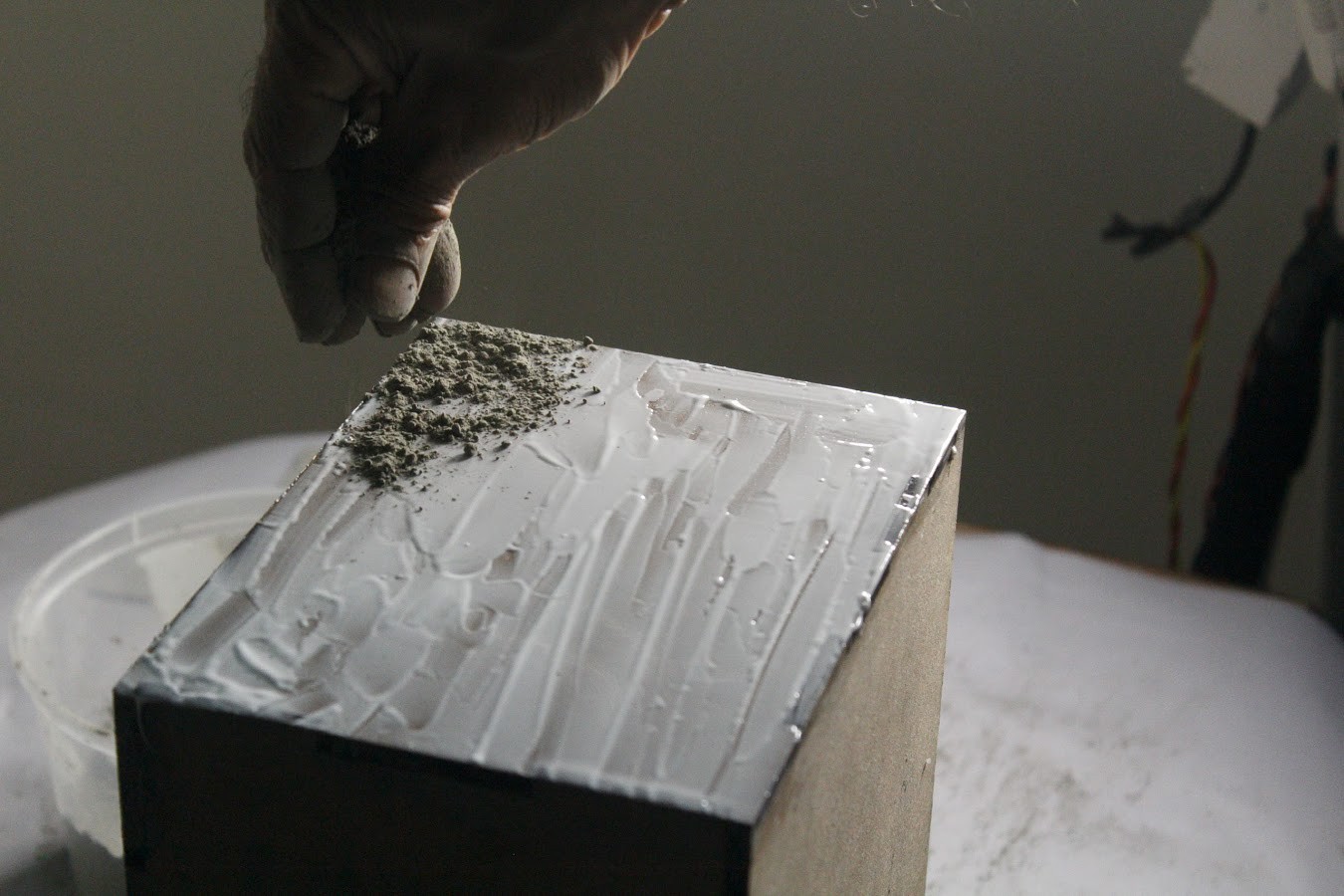
This step will determine the out texture & final finish of the box as well as give the planter another protective coating.
Apply glue to each face of the box. Then sprinkle some cement over the glue. Use the remaining circular MDF piece which was cut from the Top Plate to smoothen the cement across the surface of each face of the box. Repeat this step for each face of the box as demonstrated in the video.
Once the cement dries, sprinkle with water every 6 hours for 1 day. This will allow the cement to cure, with no cracks and will also prevent water from leaking.
-
9Add the Soil & Plants
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
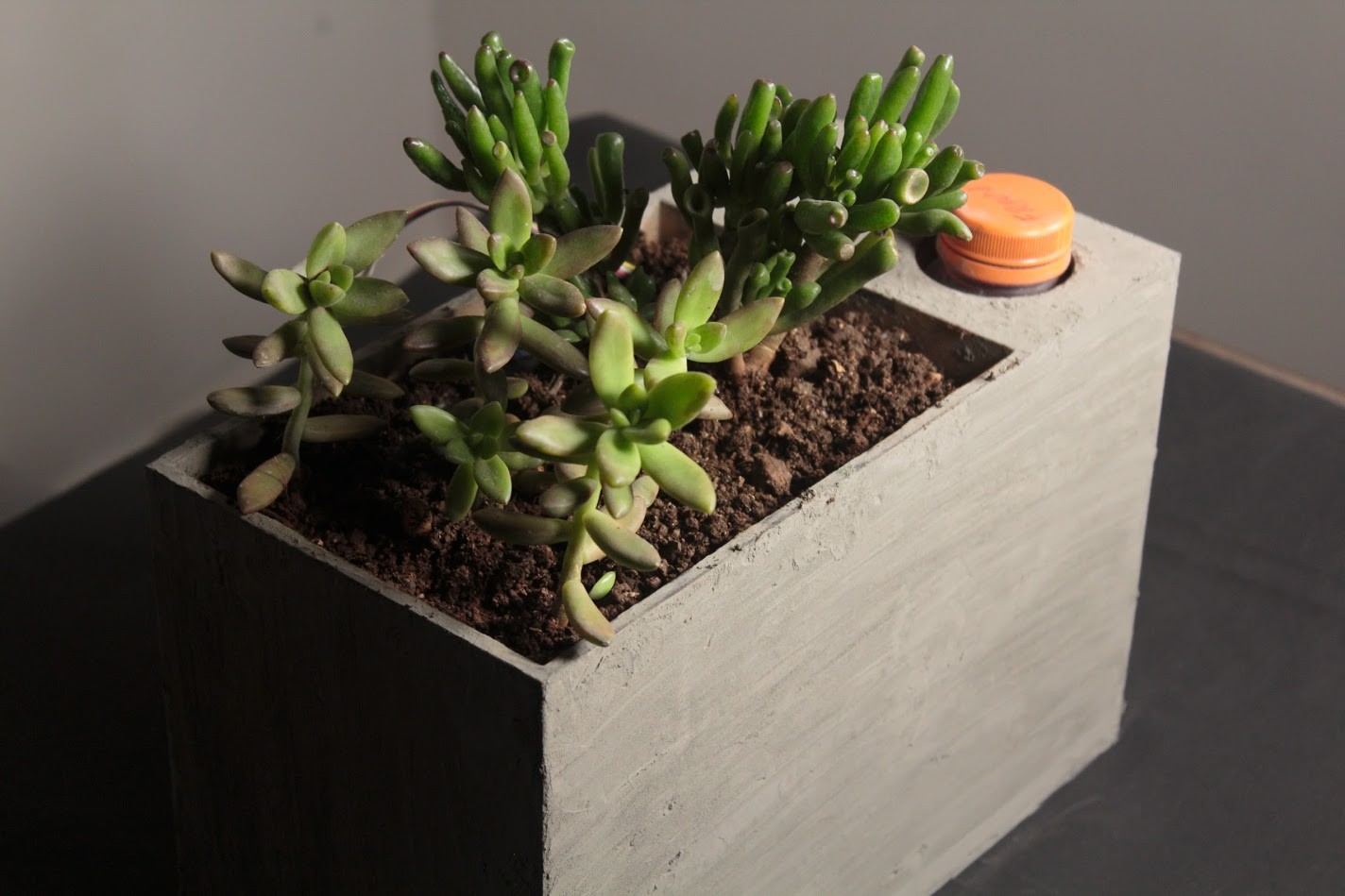
Once the cement has cured, fill the box with soil.
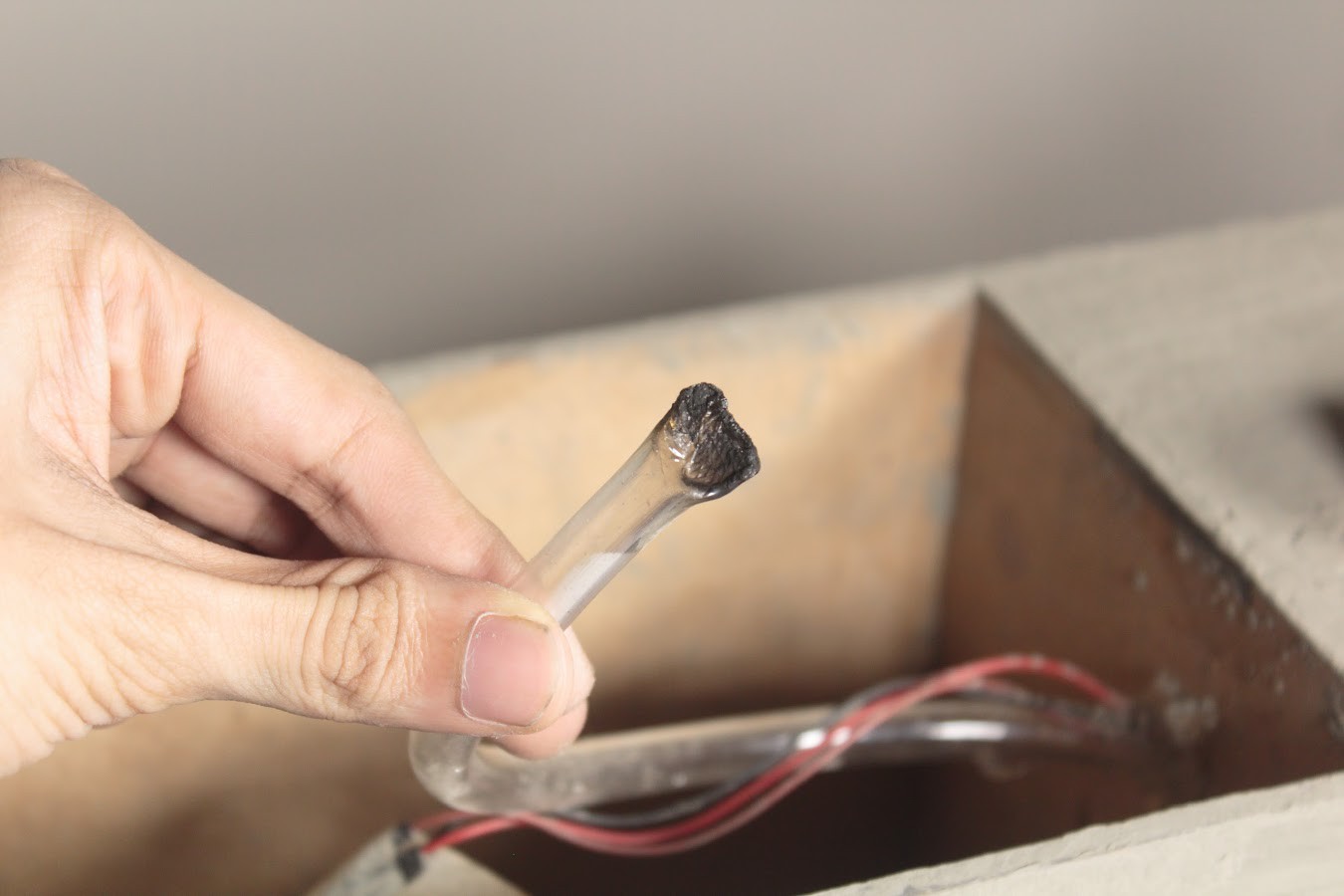
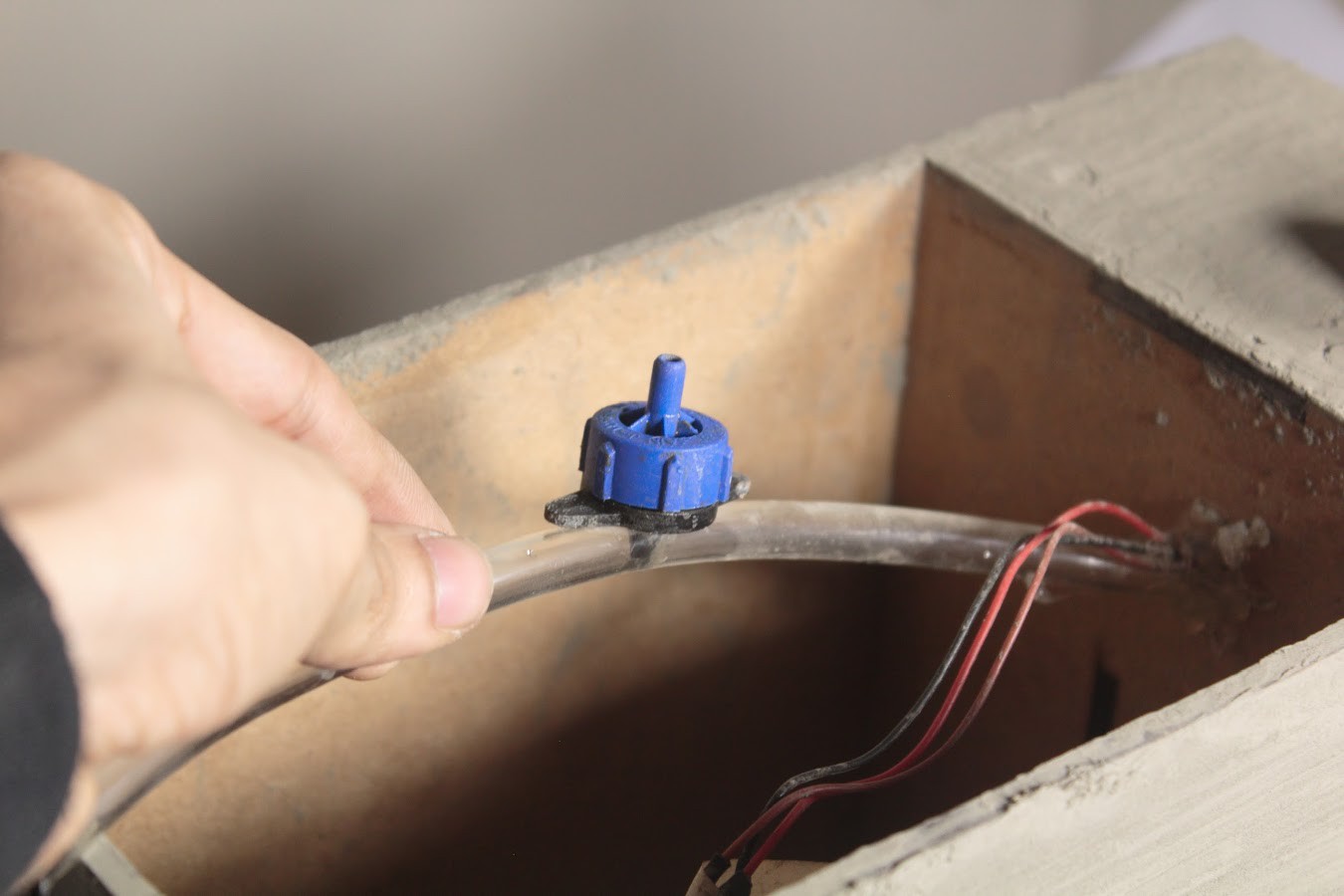
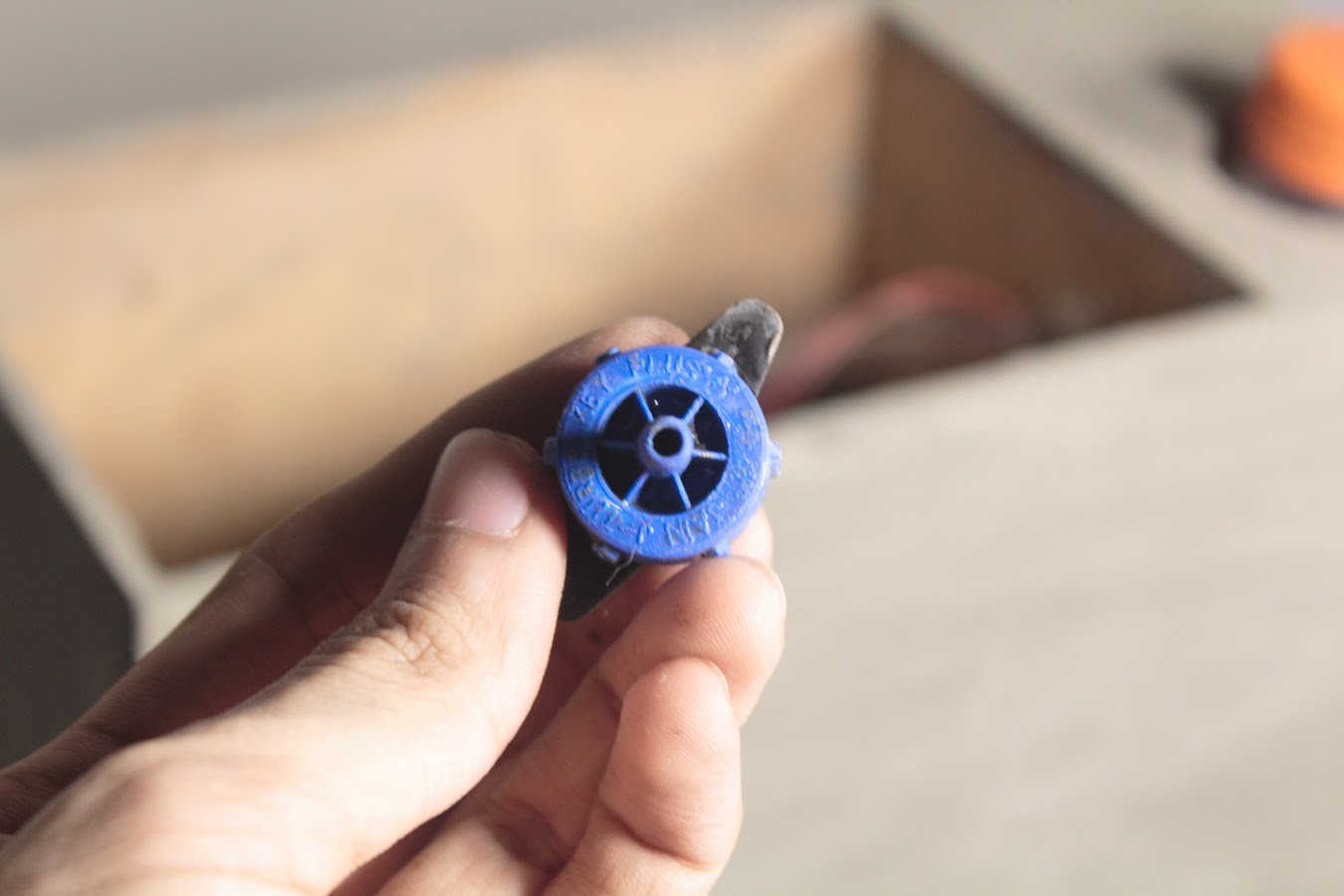
Remember to heat seal the end of the Outlet pipe before making a hole in it for the dripper. The dripper is used to regulate the water coming out of the pipe so that the water does not flow out of the planter.
Place the Soil Moisture Sensor inside the soil.
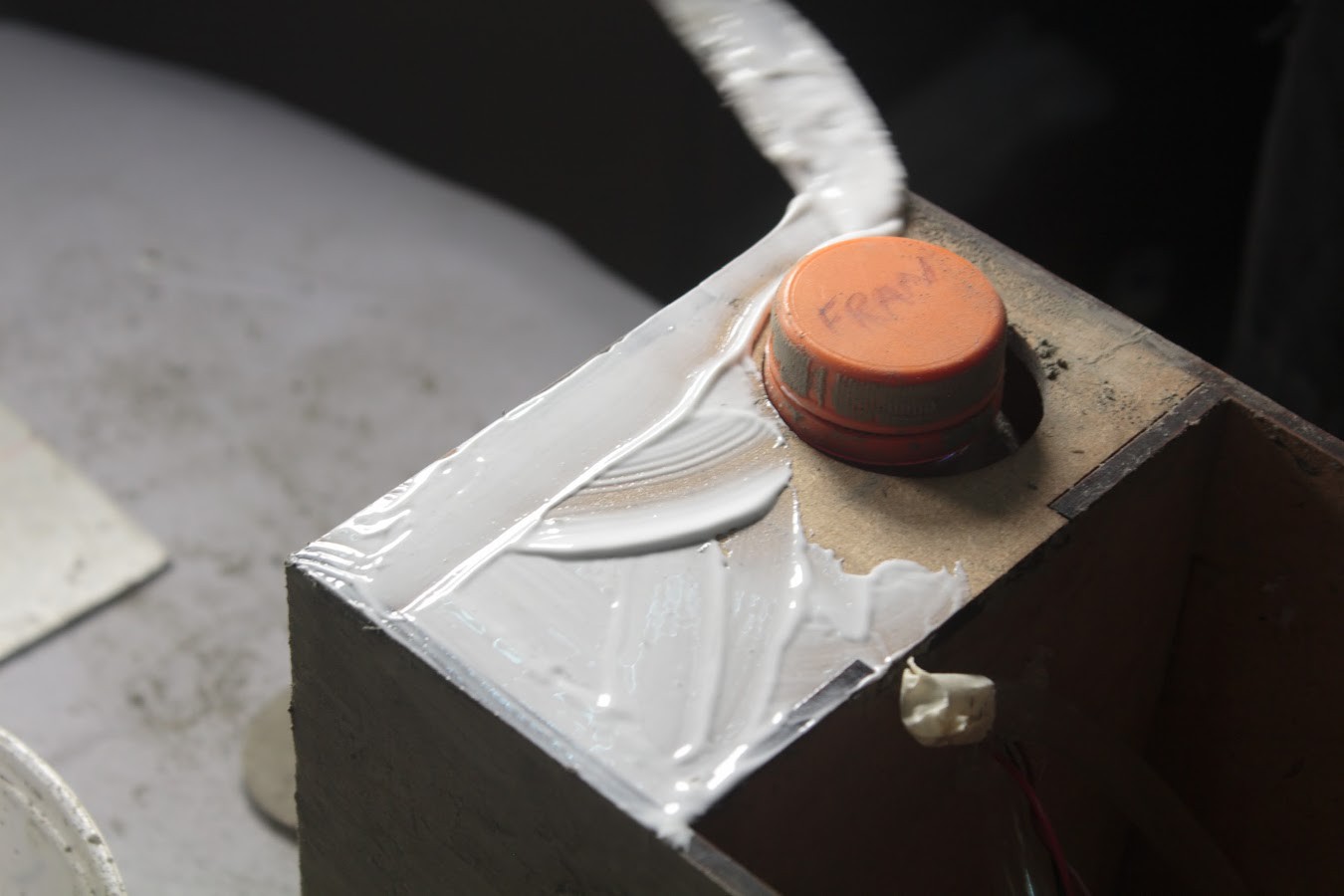
Power Sprout through the Power Jack at the Back Plate & make sure fill the water reservoir to the full level.
Test whether everything works and you should be done.
Sprout: Modern Indoor Self Watering Planter
Sprout is a Modern Indoor Planter which automatically waters your plants, herbs, vegetables, etc and will revolutionize your gardening game.
 Jonty
Jonty






















Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.