The following tools and materials were used in this project:
Tools and materials:
- Solder iron and wire. I had to solder some terminals to Nunchuk's wires in order to connect it to the Arduino;
- Shrinking tube. Some pieces of shrinking tube were used for a better isolation of the conductors;
- Screwdriver. The structure is mounted using some bolts and nuts;
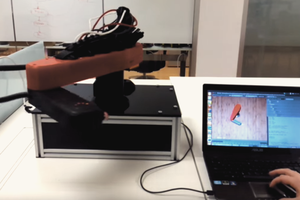
- 6-axis mechanical desktop robotic arm (link). This awesome kit already comes with several components as described bellow. It's reliable and easy to assemble;
- 12V power supply (2A or more);
- Nunchuk controller (link). It interfaces to the Arduino board, and it's used to control the robotic arm;
- Male jumper wires (4 wires);
- Arduino Mega (link / link / link). Notice that the robotic arm kit I've used also has a board and controller bundle that already comes with this Arduino board. If you you're not using on of those kits, you might use other Arduino boards as well;
I was informed later that there's a Nunchuk adapter that makes the connection to a breadboad easier (link / link). It's a good option if you want to same some time on soldering and doesn't want to destroy the original connector as described on Step 9.
Sain Smart 6-axis mechanical desktop arm already comes with the following components:
- Arduino Mega 2560 R3 (link)
- Control board shield (link)
- NRF24L01+ Wireless Transceiver Module (link)
- MPU6050 3-axis gyroscope and a 3-axis accelerometer (link)
- 71 x M3X8 screw
- 47 x M3 nut
- 2 x U bracket
- 5 x servo bracket
- 4 x 9kg servo (link)
- 2 x 20kg servo (link)
- 6 x metal servo tray
- 3 x U bracket
- 21 x right-angled bracket
- 3 x flange bearing
- 1 x gripper
You might find other robotic arm kits online, or even design your own. There are some awesome projects you can 3D print, for instance.
 igorfonseca83
igorfonseca83





 Alvaro Ferrán Cifuentes
Alvaro Ferrán Cifuentes
 ElectroScope Archive
ElectroScope Archive