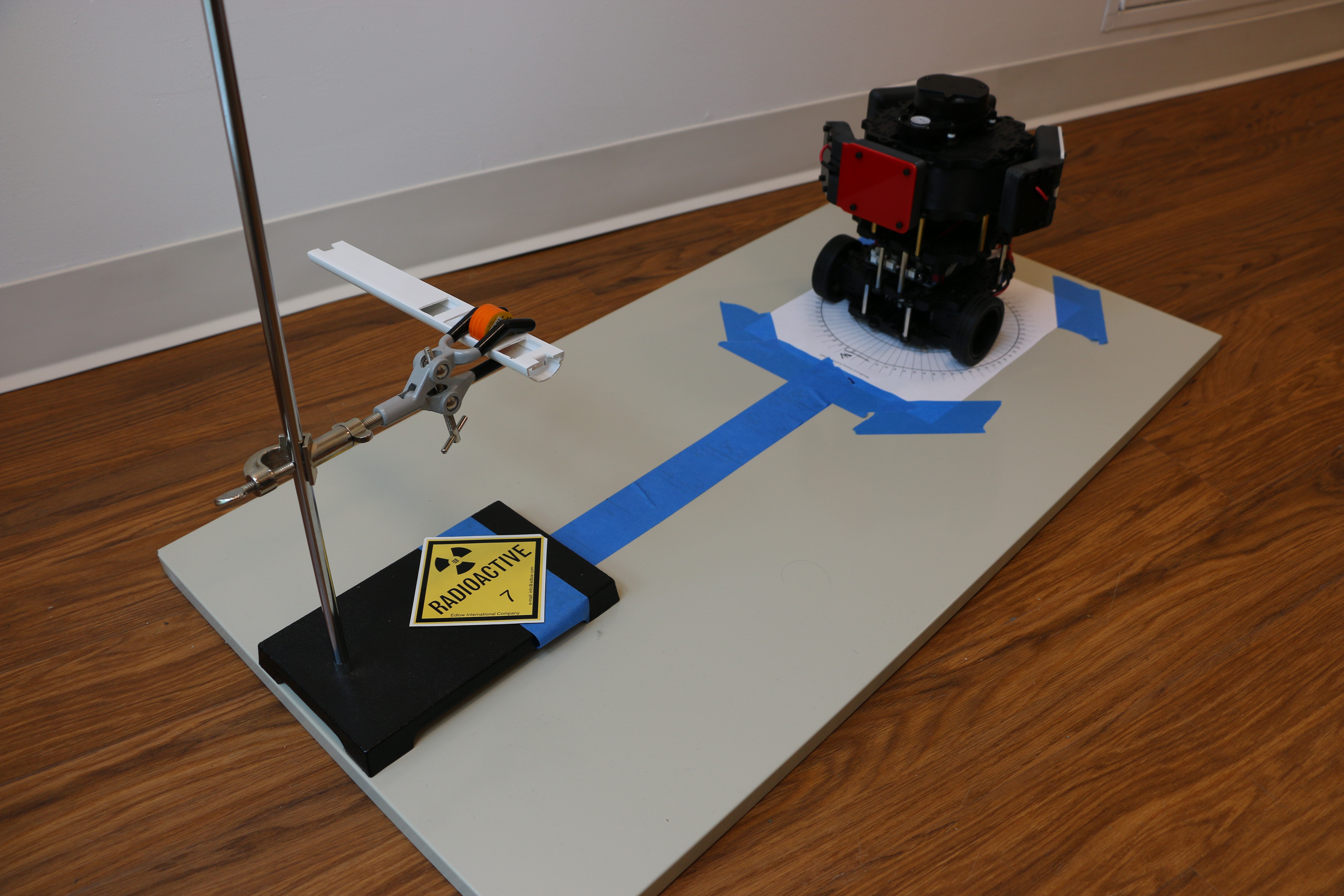
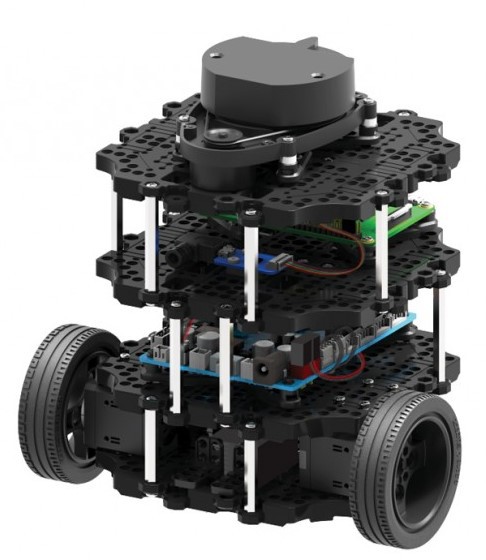
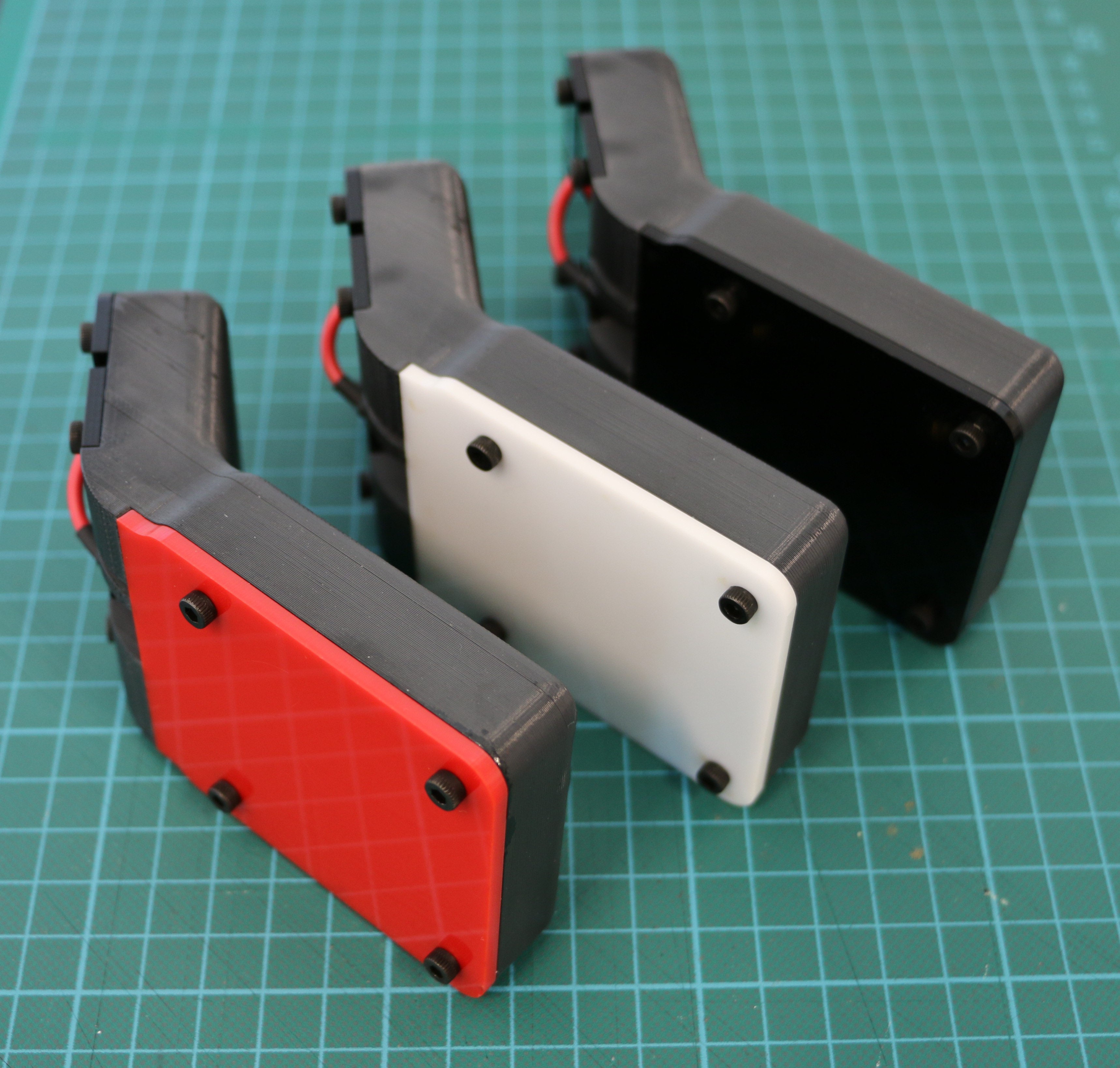
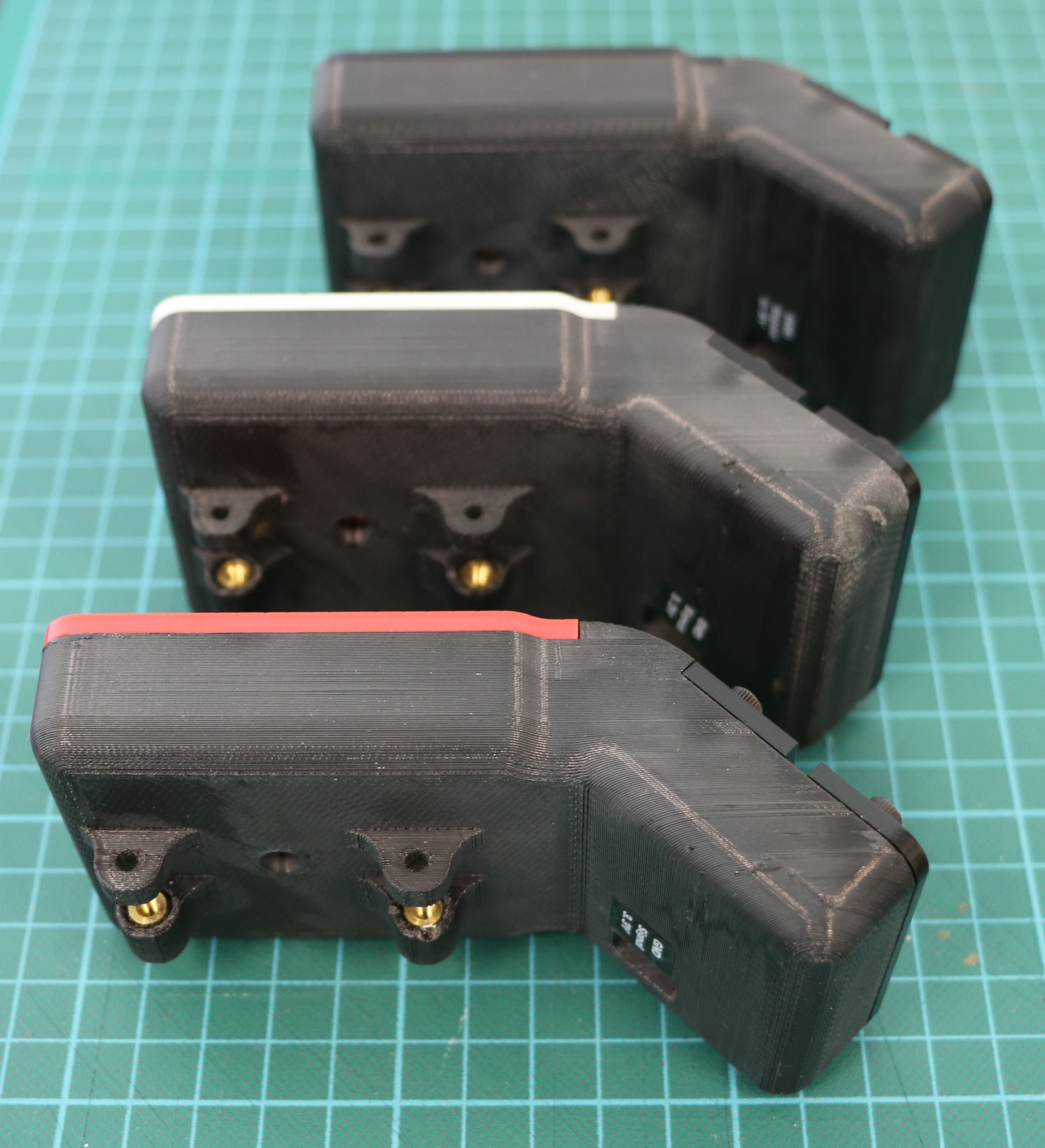
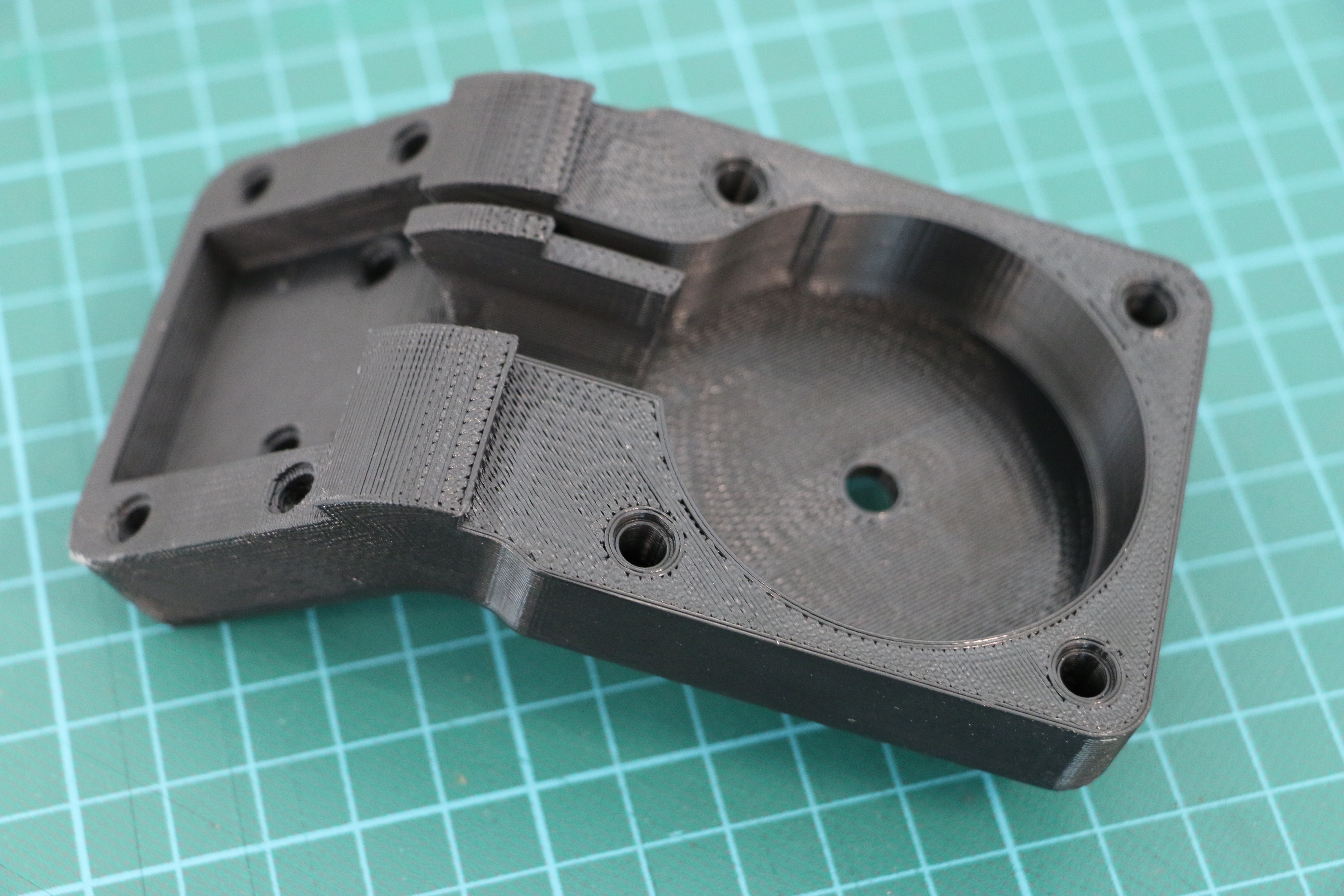
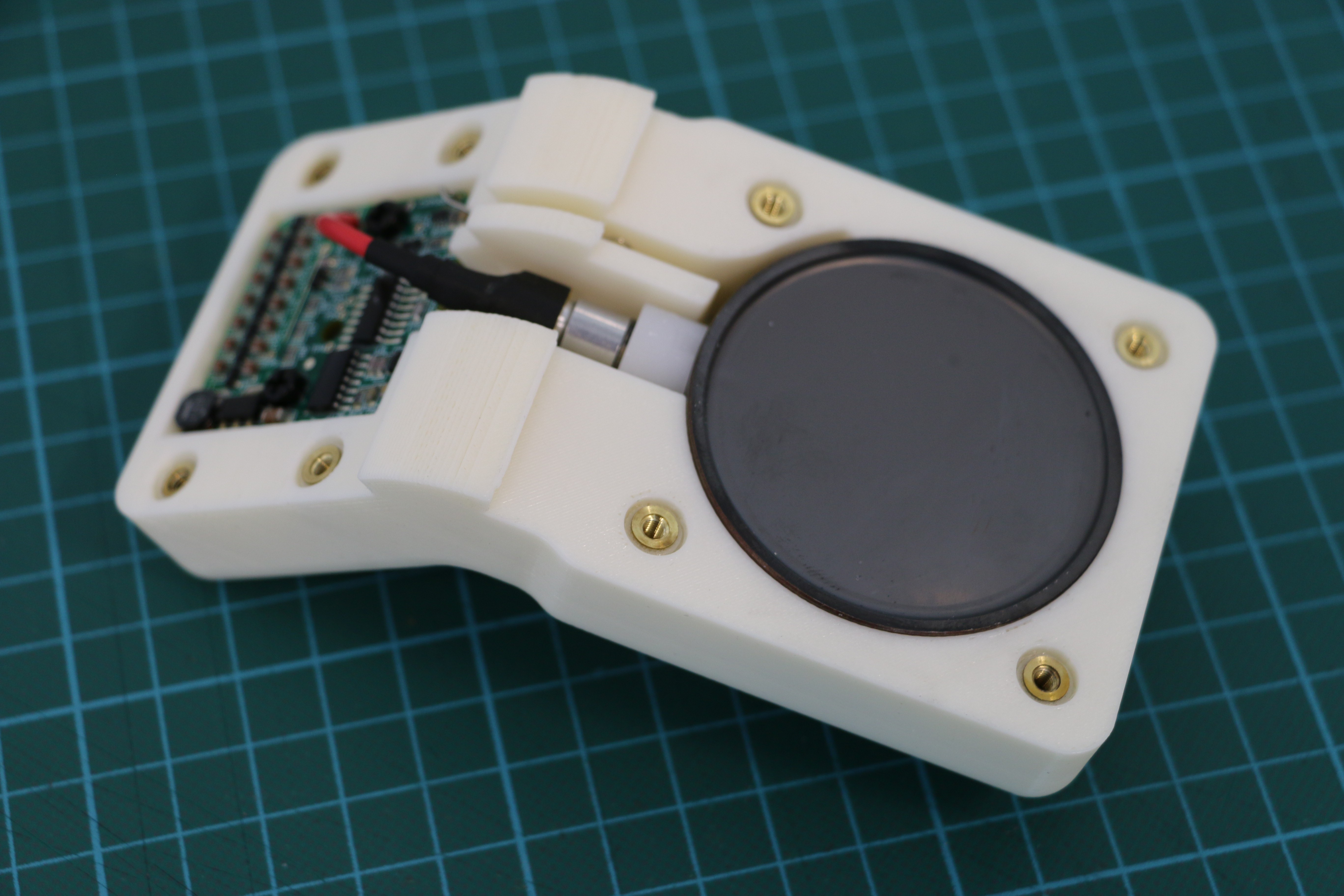
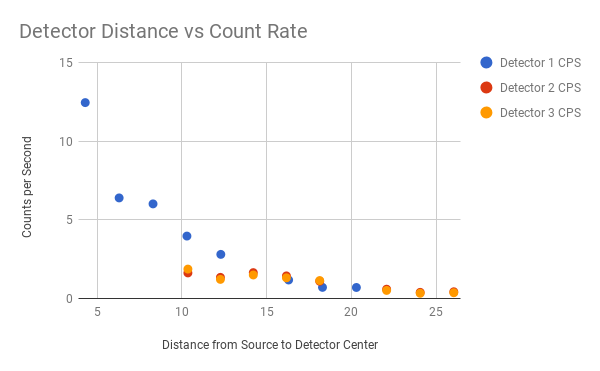
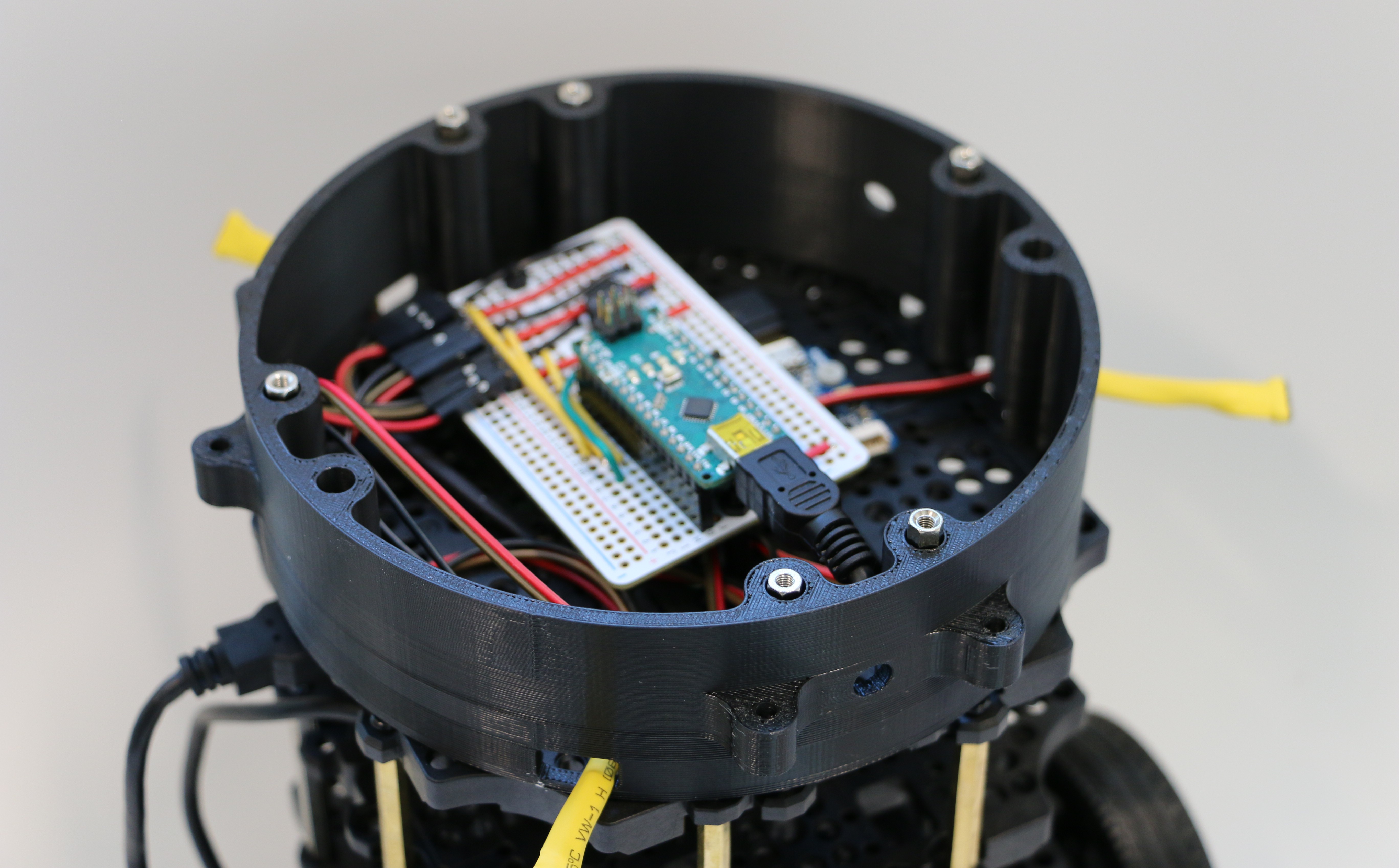
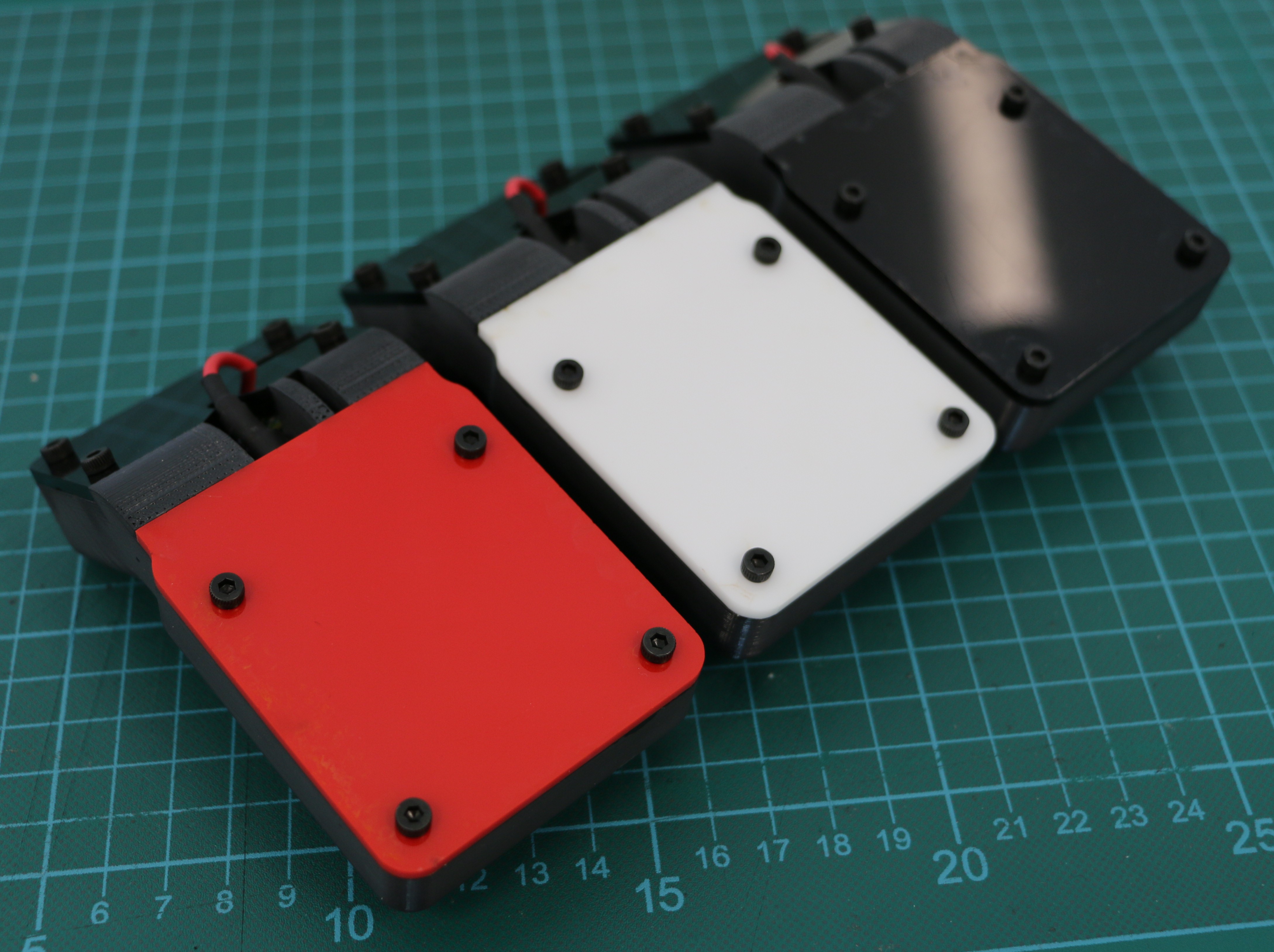
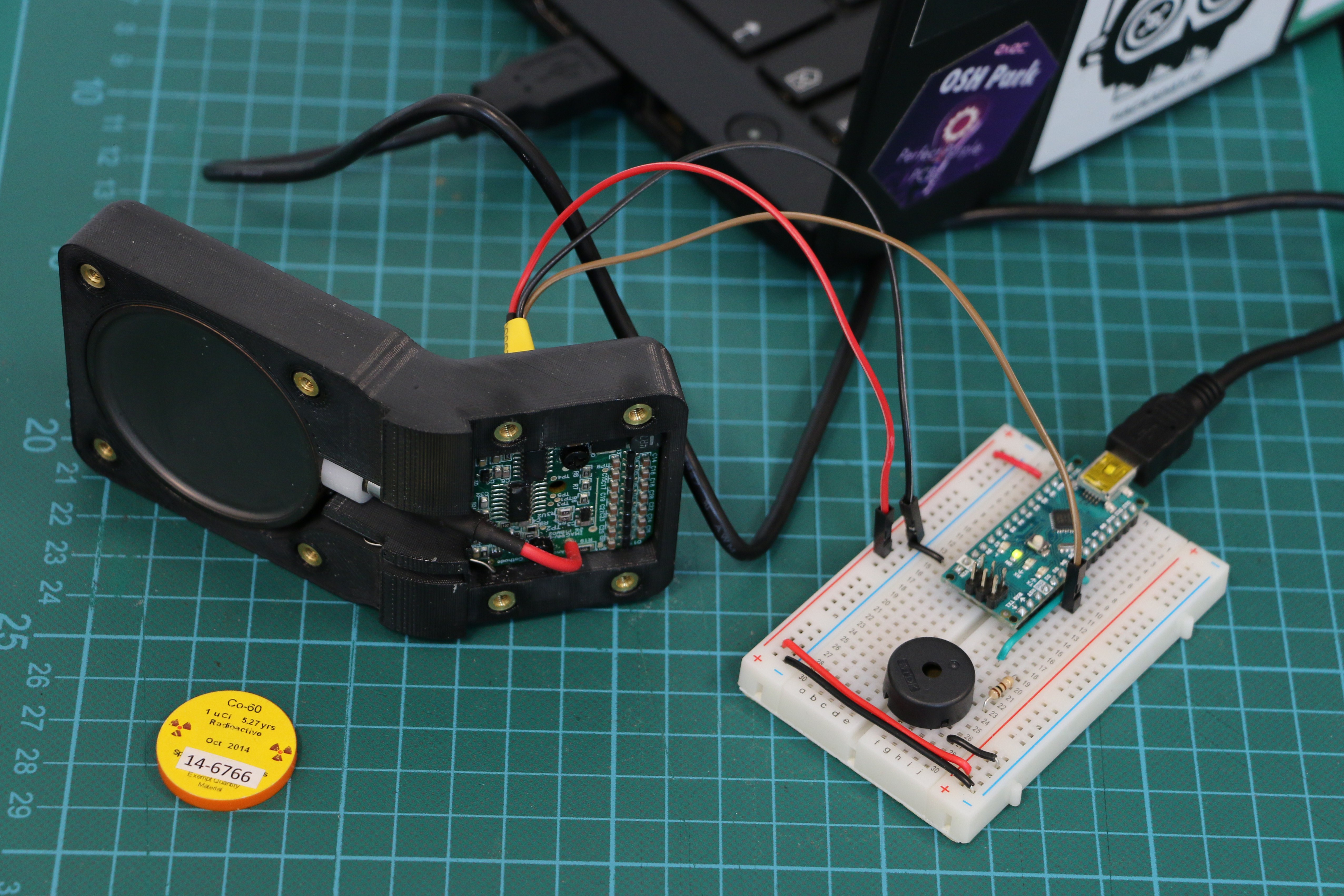
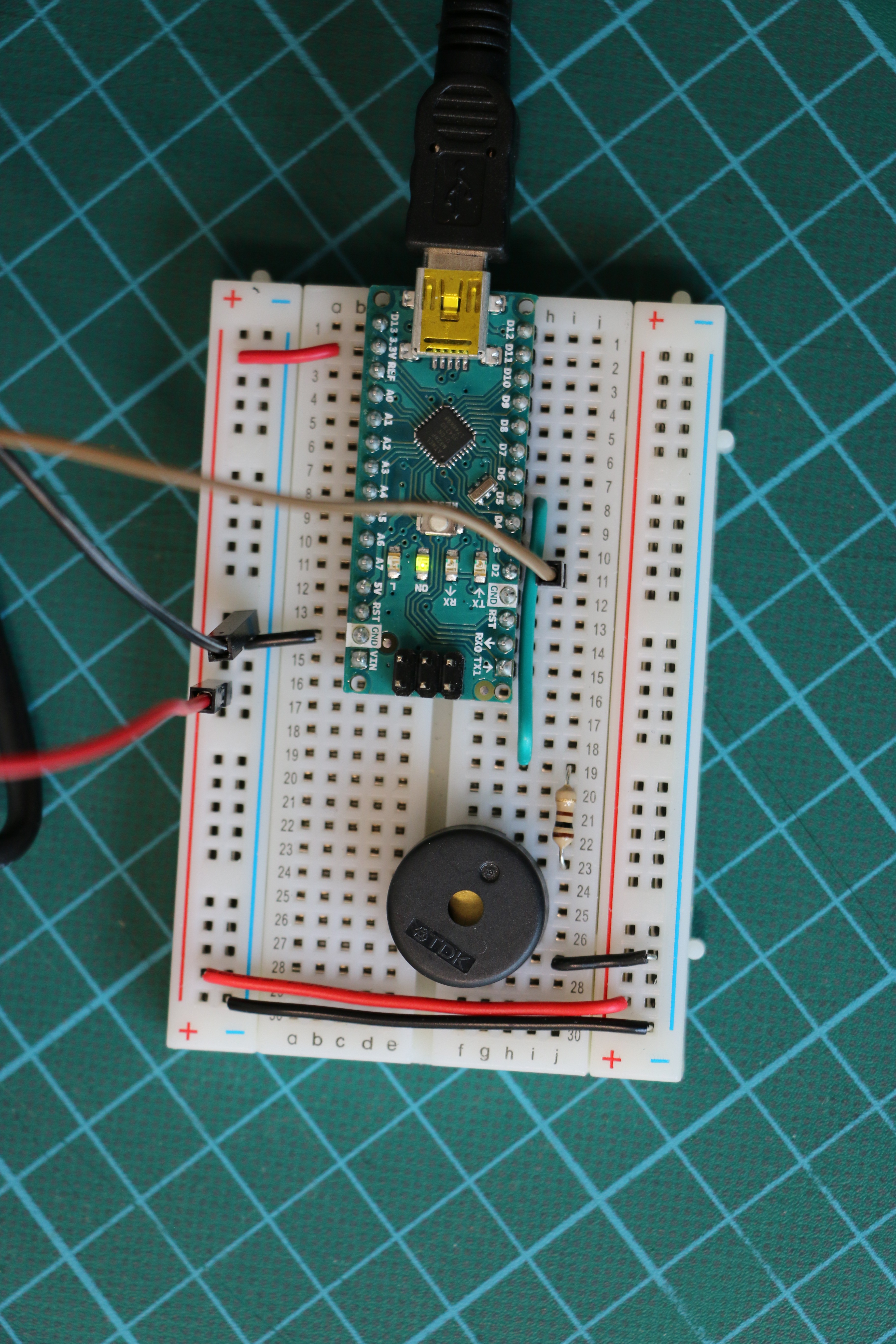
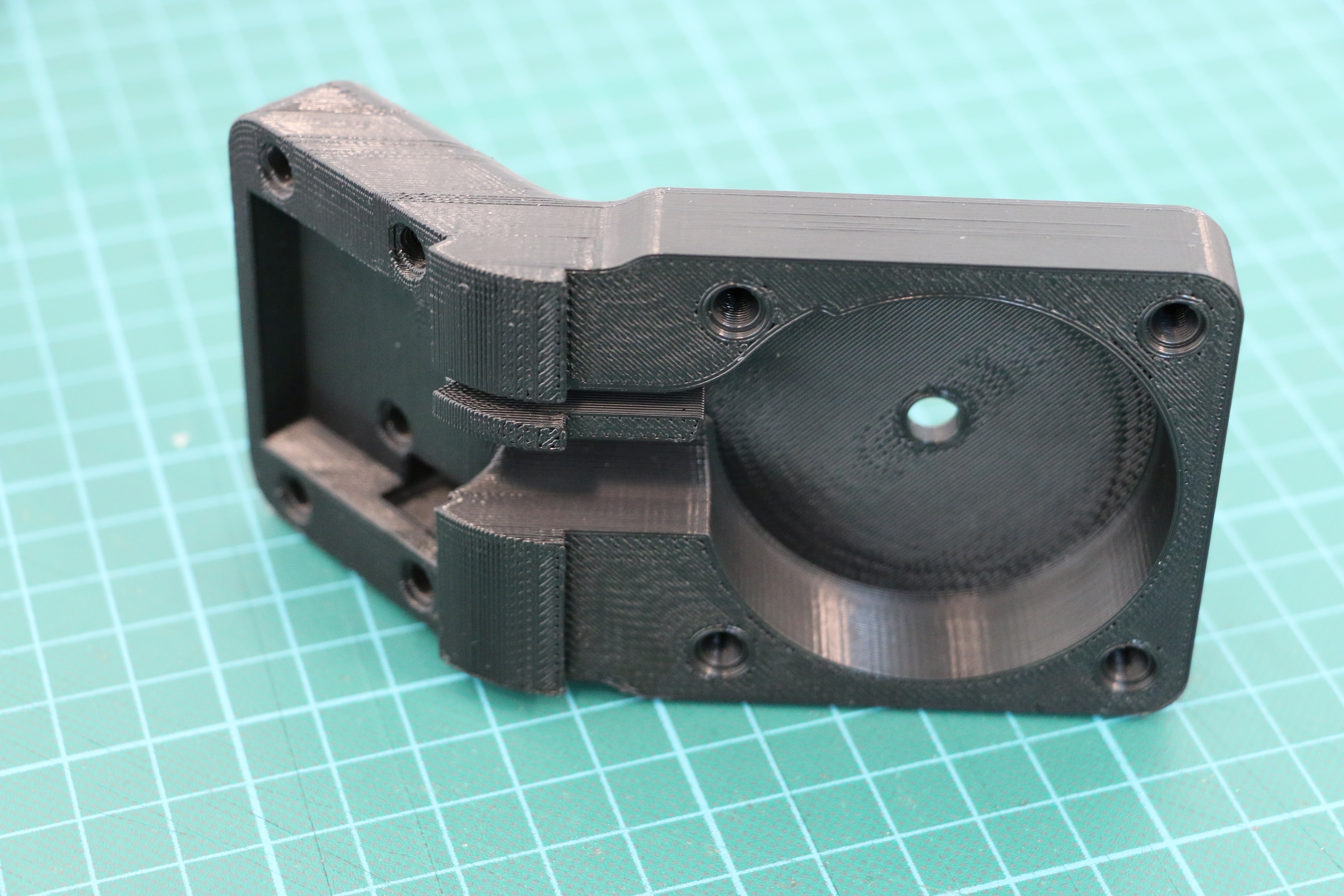
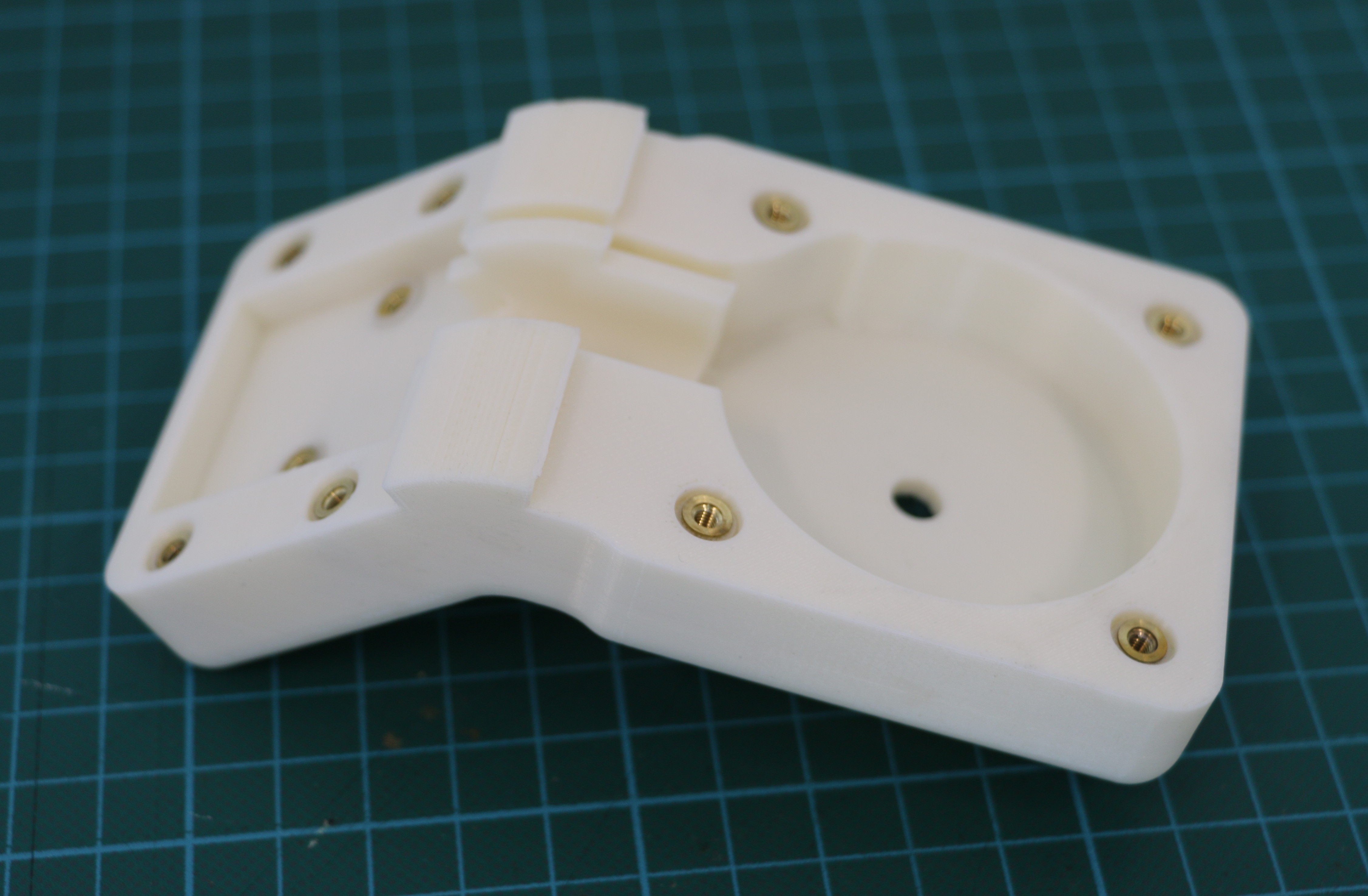
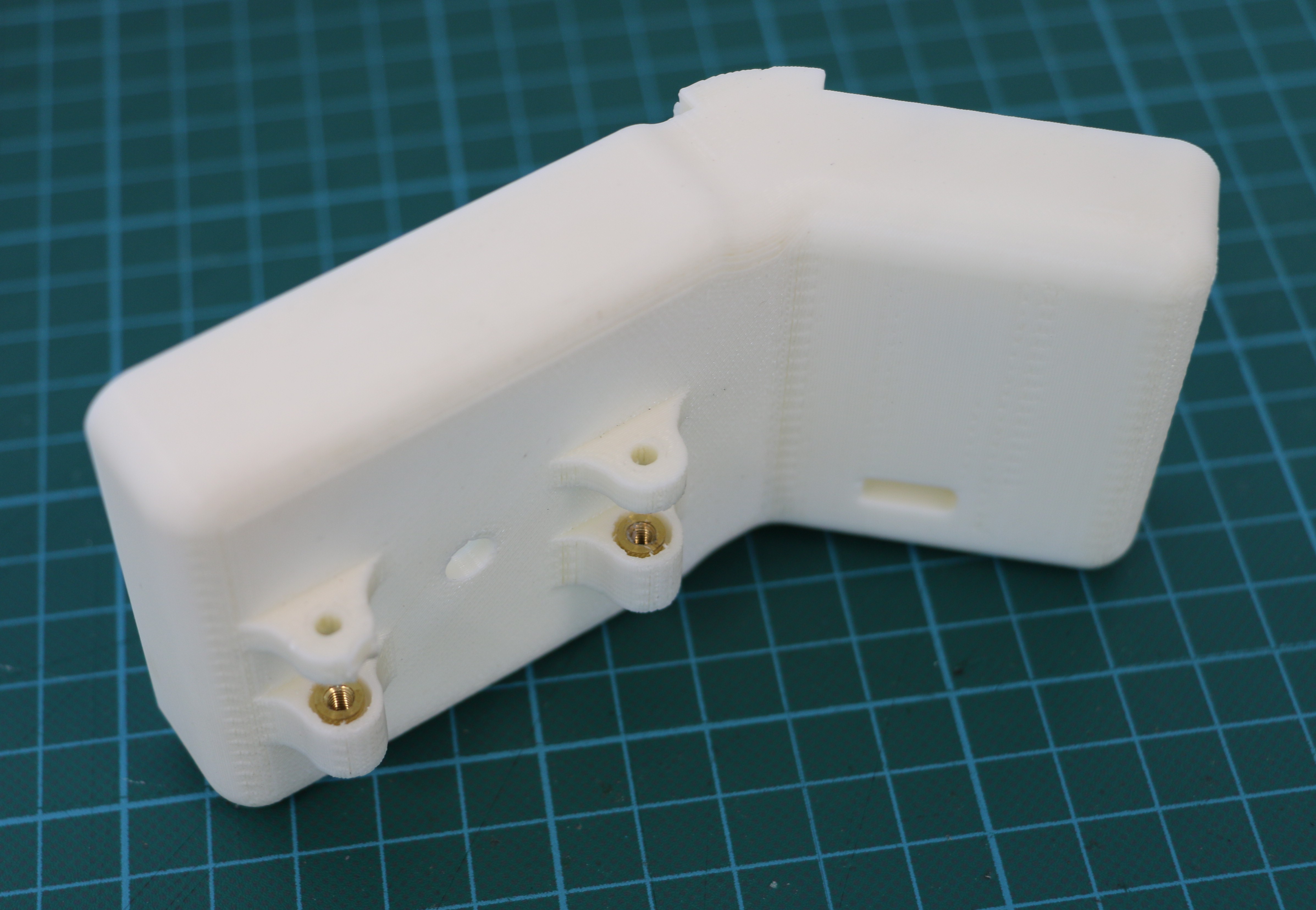
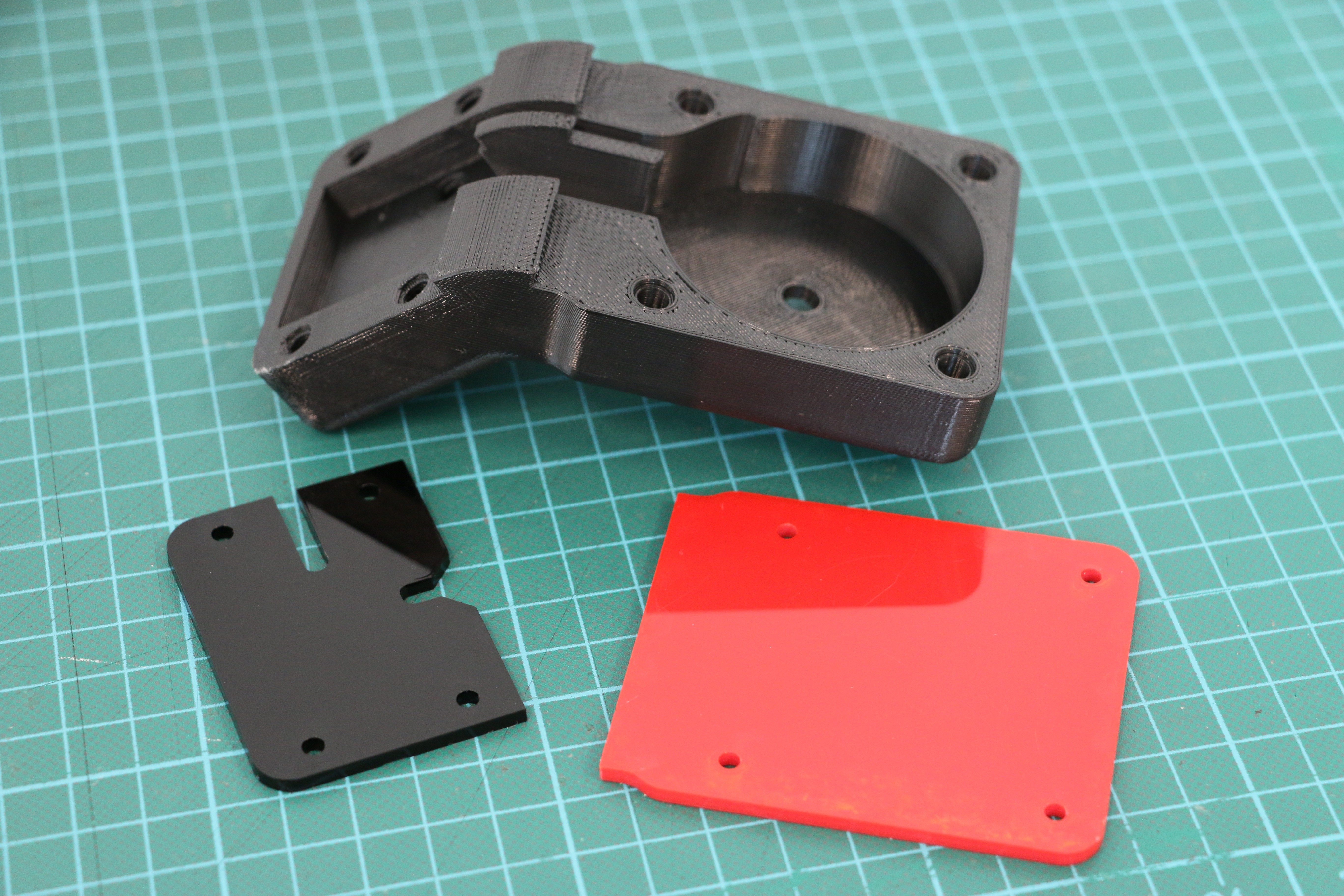
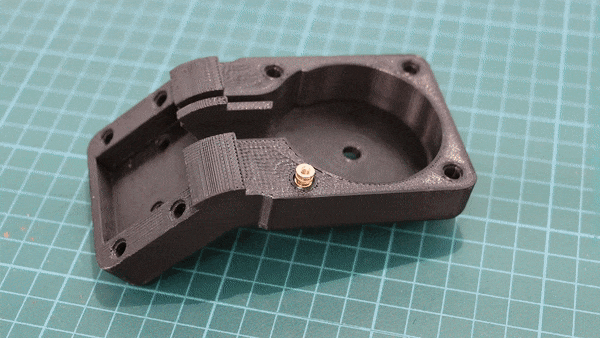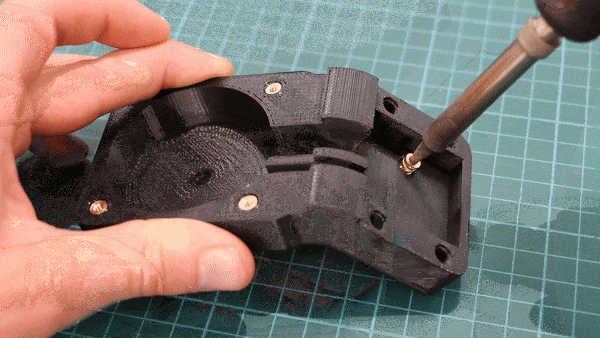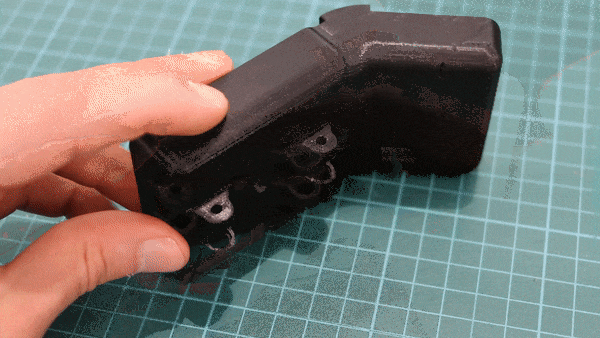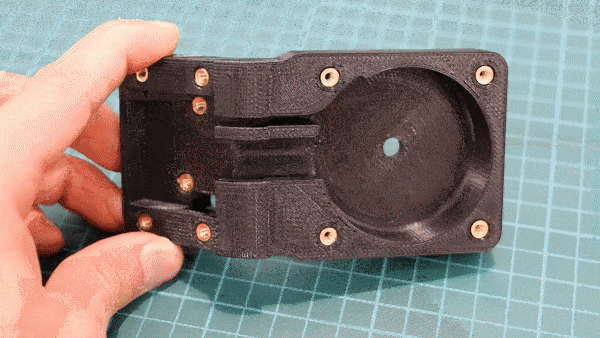
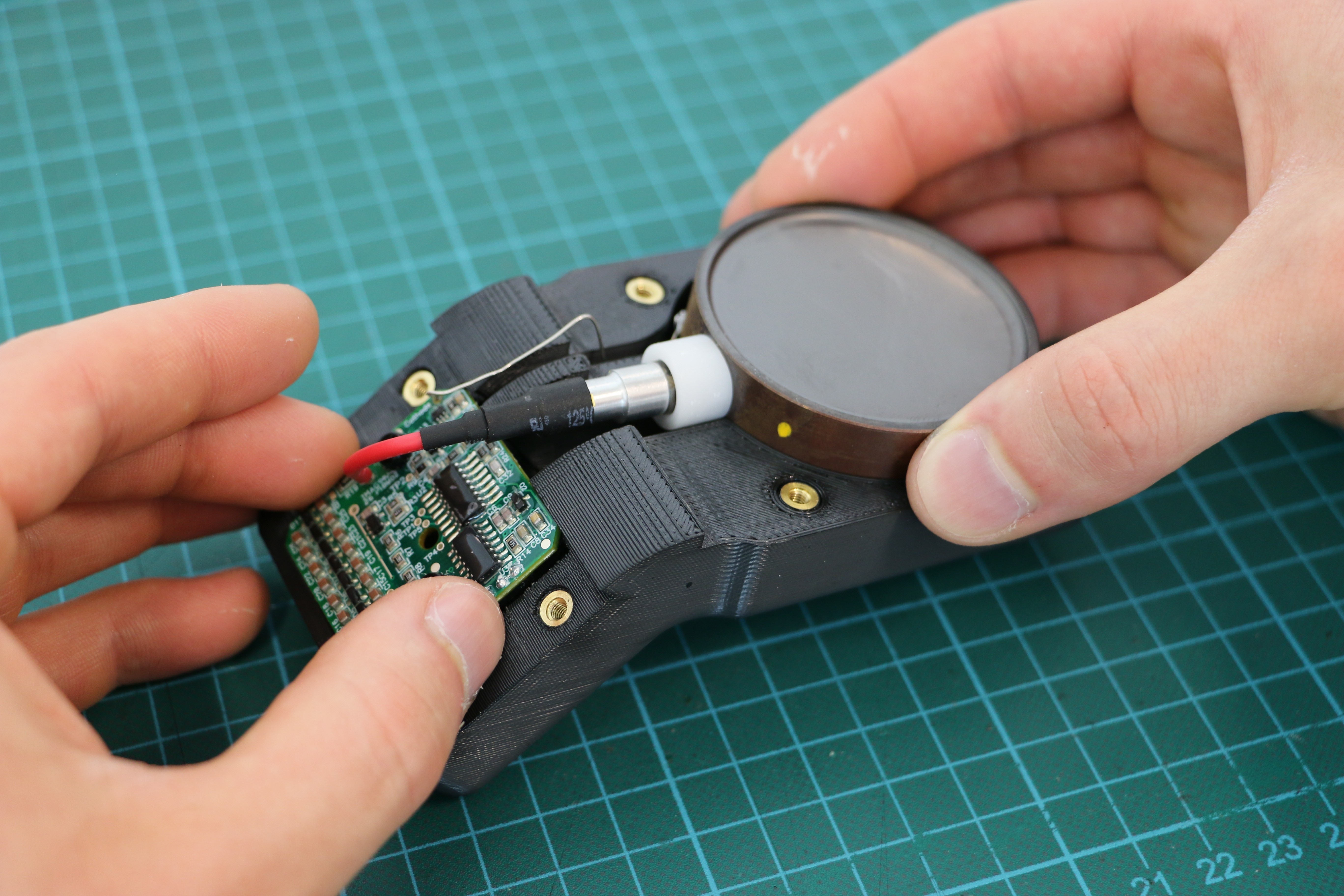
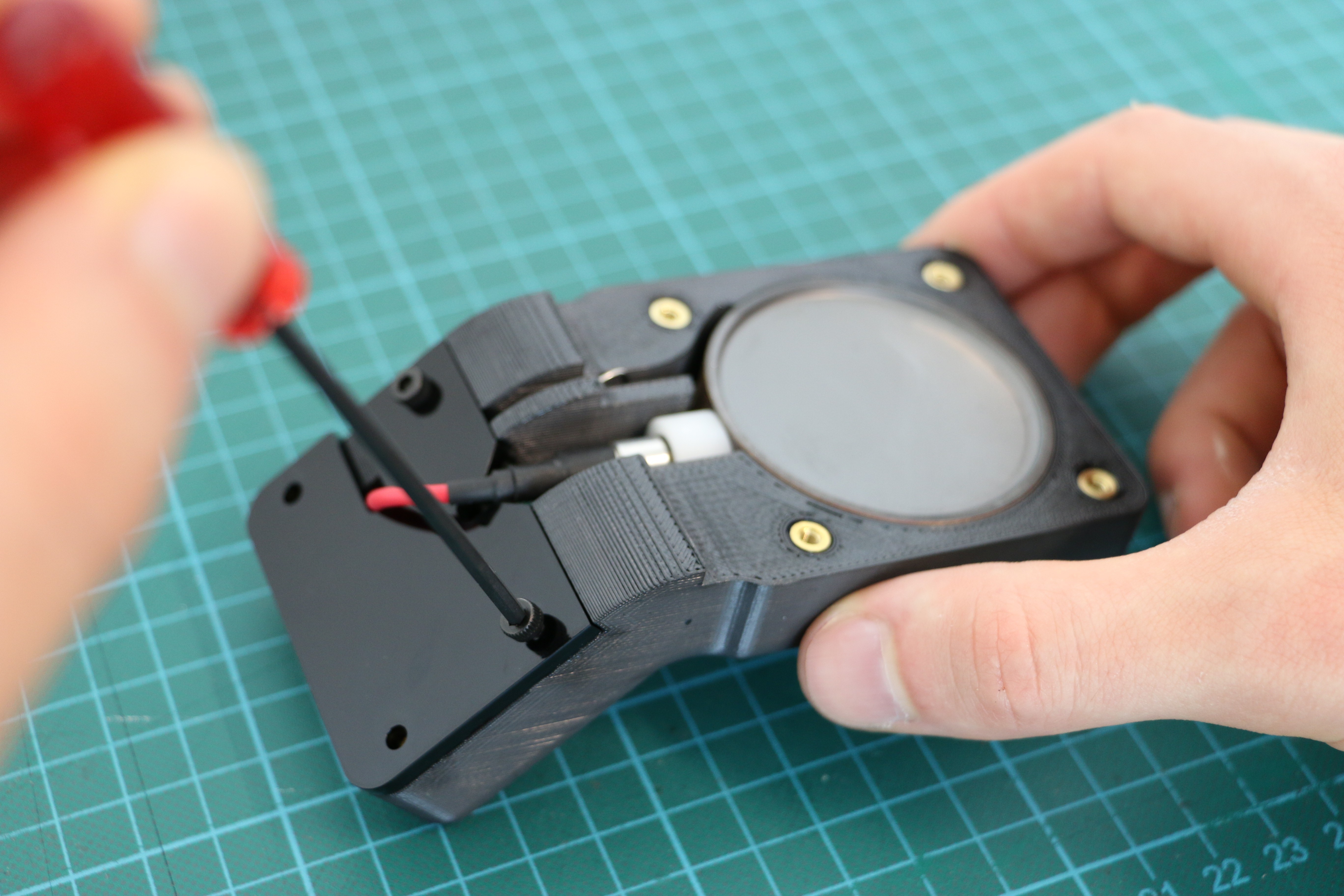
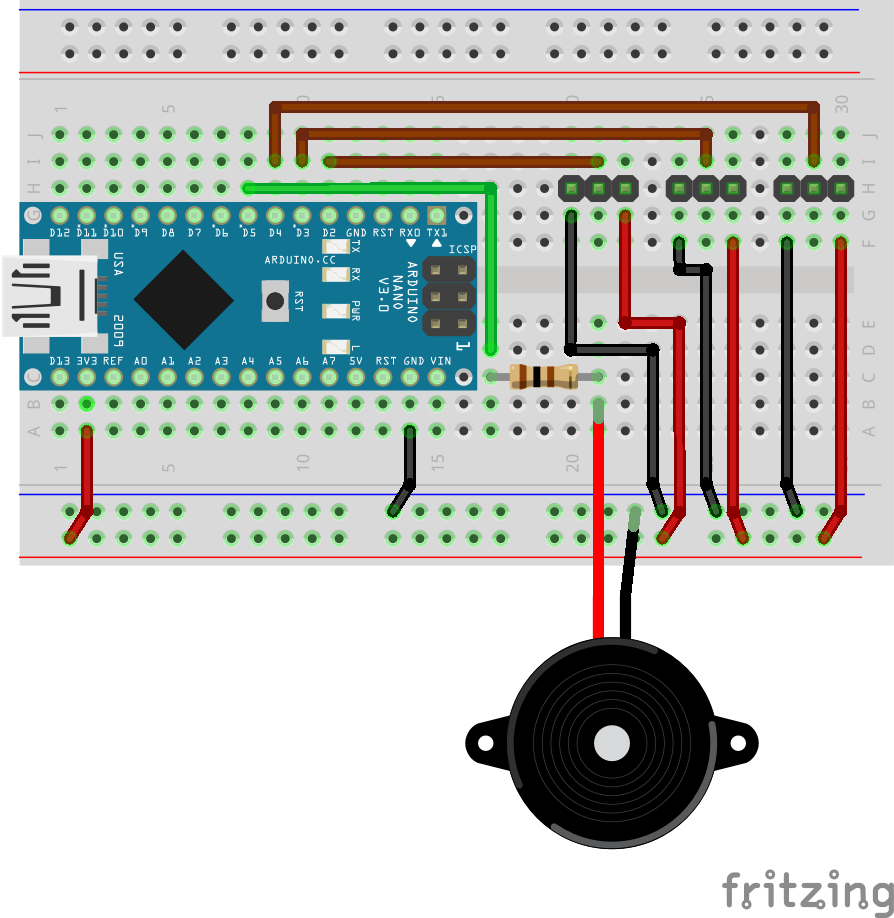
Geiger counters are the easiest possible way to detect ionizing radiation. The main part of a Geiger counter is a Geiger-Müller tube, which can turn that radiation into a voltage pulse. The tube needs a supply voltage of several hundred volts. GeigerROS uses three simple geiger counter setups, controlled by an Arduino Nano. The nano provides the measurements as ROS topics. By using three detectors, it is not only possible to measure radiation at a given point but also to estimate the direction of the source. Because of limited range of alpha and beta radiation in air, we expect the detectors to mainly detect gamma radiation.
We currently install the sensor on a TurtleBot 3 "Burger" robot. Our final goal is to create a prototype that can autonomously create a radiation & room map in an indoor setting. The map will not only include the strength of radiation, but also some information about directionality.
For the project, we selected the same Geiger-Müller tubes and control/high voltage electronics that have been used in devices developed Safecast Project, e.g. the bGeigie nano. The Safecast project was founded after the Fukushima nuclear accident and aims to provide crowd sourced radiation maps, it is still active today.
The development of our ROS enabled radiation detection sensor is part of a bigger project that aims at developing robots for nuclear weapons disarmament and non-proliferation (preventing new countries from getting nuclear weapons). For non-proliferation applications robots could be employed in existing facilities use for the purpose of civilian nuclear energy production. Already today, these facilities are regularly inspected by human inspectors to make sure that no civilian material is diverted for the purpose of building a nuclear weapon. Usually, the number of inspectors allowed to inspect a facility is limited, and inspection time is typically regulated. In the future, robots might support human inspectors by carrying out search tasks. Our robot equipped with Geiger counters is a small test-bed for a bigger robot that will be equipped with neutron detectors to search for neutron sources.
Besides the ability to search for existing radiation sources, the robot could also be used to make sure that there are no radioactive sources present in a room. Of course, there will always be background radiation, but our setup should enable us to distinguish this from point-like additional sources. A nuclear arms control application would be the check of a room for "emptiness" before the room would be used for example to dismantle a nuclear weapon.
Besides nuclear disarmament and non-proliferation there are other applications for a robotic radiation sensor - it is easy to imagine a similar setup for radiation safety applications. Robots could check contaminated areas after nuclear accidents. For high levels of radiation though all electronics would have to be hardened against radiation damage - likely other robotic platforms than TurtleBot 3 would be needed.
See the Files page for relevant license information, buy in short all the work we've done is CC-BY-SA.