Configuring I2C(Raspberry Pi)
Run sudo raspi-config and follow the prompts to install i2c support for the ARM core and linux kernel Go to Interfacing Options
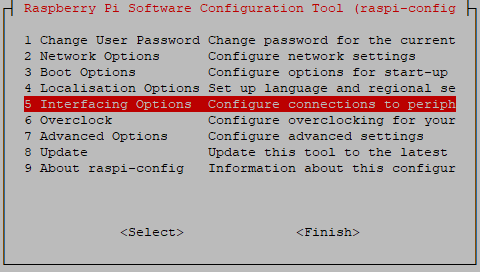
then I2C
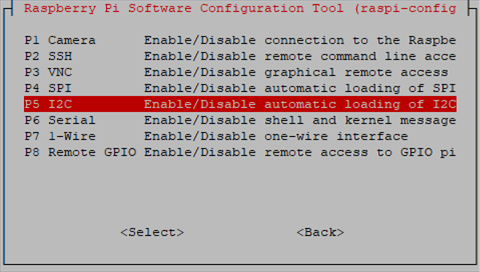
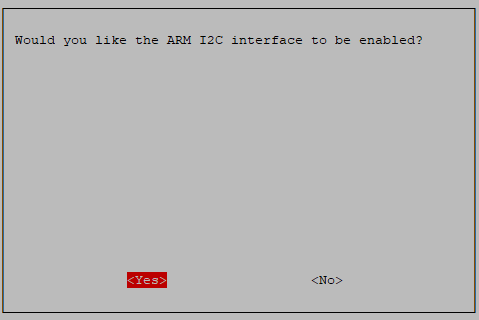
Enable!
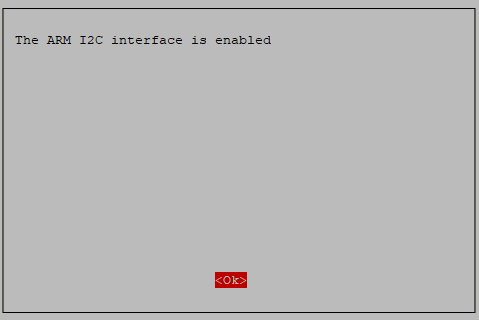
Done!
Replace /boot/overlays/sc16is752-i2c.dtbo(Raspberry Pi)
Replace /boot/overlays/sc16is752-i2c.dtbo file with this file: File:Sc16is752-i2c.zip
Modify /boot/config.txt file and add following parameter:
dtoverlay=sc16is752-i2c
How to use GPS Module with gpsd(Raspberry Pi)
A) First, replace the /boot/overlays/sc16is752-i2c.dtbo and make sure I2C is working properly.
- Replace sc16is752-i2c.dtbo
- Configuring I2C
B)Install gpsd tools.
sudo apt install gpsd gpsd-clients
C)Modify /etc/default/gpsd file and add following parameters:
DEVICES="/dev/ttySC1" GPSD_OPTIONS="-F /var/run/gpsd.sock"
D)Enter command i2cset -y 1 0x16 0x23 0x40 to reset the GPRS module.
E)Python Script For Open GPS:
import serial
import os
import time
# Restart gpsd service.
os.system("sudo systemctl restart gpsd.socket")
# Open serial port ser = serial.Serial('/dev/ttySC0', 115200)
i = 0
if ser.isOpen == False:
ser.open()
try:
print("Turn on GPS...")
while True:
ser.write(str.encode("AT+GPS=1\r"))
size = ser.inWaiting()
if size != 0:
ticks = time.time()
response = ser.read(size)
gps = str(response,encoding="utf-8")
if(gps.find("OK") != -1):
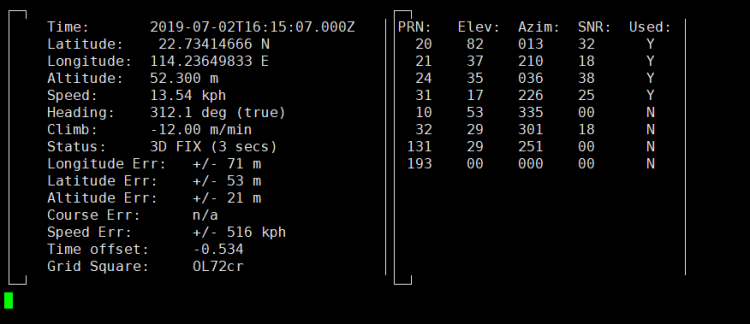
os.system("sudo cgps -s")
exit()
else:
i = i + 1
print("Waiting GPS Enable, If the time is too long, Please test outdoors:" + str(i))
ser.flushInput() time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
ser.flushInput()
ser.close()
F)Save it and execute it:
python3 GPS.py
How to use GPS Module with C(Raspberry Pi)
A)Install gpsd tools.
sudo apt-get install libgps-dev
B)Create source code and name it "gps.c"
#include <gps.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{ int rc;
struct timeval tv;
struct gps_data_t gps_data;
if ((rc = gps_open("localhost", "2947", &gps_data)) == -1)
{
printf("code: %d, reason: %s\n", rc, gps_errstr(rc));
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
gps_stream(&gps_data, WATCH_ENABLE | WATCH_JSON, NULL);
while (1)
{
/* wait for 2 seconds to receive data */
if (gps_waiting(&gps_data, 2000000))
{
/* read data */
if ((rc = gps_read(&gps_data)) == -1)
{
printf("error occured reading gps data. code: %d, reason: %s\n", rc, gps_errstr(rc));
}
else
{
/* Display data from the GPS receiver. */
if ((gps_data.status == STATUS_FIX) && (gps_data.fix.mode == MODE_2D || gps_data.fix.mode == MODE_3D) && !isnan(gps_data.fix.latitude) && !isnan(gps_data.fix.longitude))
{
/* gettimeofday(&tv, NULL); EDIT: tv.tv_sec isn't actually the timestamp! */
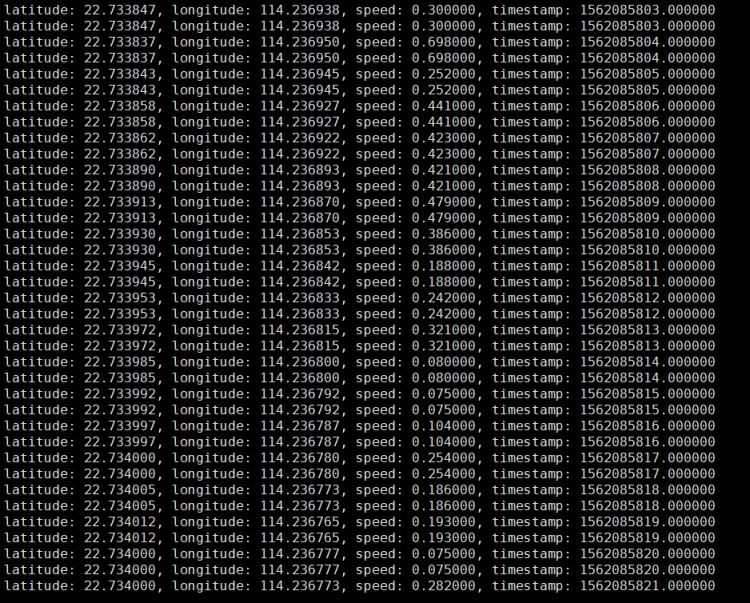
printf("latitude: %f, longitude: %f, speed: %f, timestamp: %lf\n", gps_data.fix.latitude, gps_data.fix.longitude, gps_data.fix.speed, gps_data.fix.time);
//EDIT: Replaced tv.tv_sec with gps_data.fix.time
}
else
{
printf("no GPS data available\n");
}
}
}
sleep(3);
}
/* When you are done... */
gps_stream(&gps_data, WATCH_DISABLE, NULL);
gps_close(&gps_data);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Compile!
gcc gps.c -lm -lgps -o gps
Exec It!
./gps
How to use GPS Module with Python(Raspberry Pi)
The following code is recommended to be executed using Python 3 and install the gpsd-py3 library and GPS 2D/3D Fix:
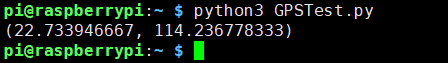
import gpsd # Connect to the local gpsd gpsd.connect() # Get gps position packet = gpsd.get_current() # See the inline docs for GpsResponse for the available data print(packet.position())
 yoyojacky
yoyojacky
 AlfredC
AlfredC
 Kutluhan Aktar
Kutluhan Aktar
 simon
simon
 Kevin Kingsbury
Kevin Kingsbury