-
1Watch My Project Working
-
2Get All the Material
To start, make sure you have all of the following:
- An Arduino microcontroller board, UNO is preferred.
- An L298N dual H-bridge motor driver board.
- 6 male to male jumper wires.
- 7 male to female jumper wires.
- A screwdriver.
- A 12 volt-DC power supply adapter.
- A track segment with IR proximity sensor attached on the underside(I used a Kato S62 track)
-
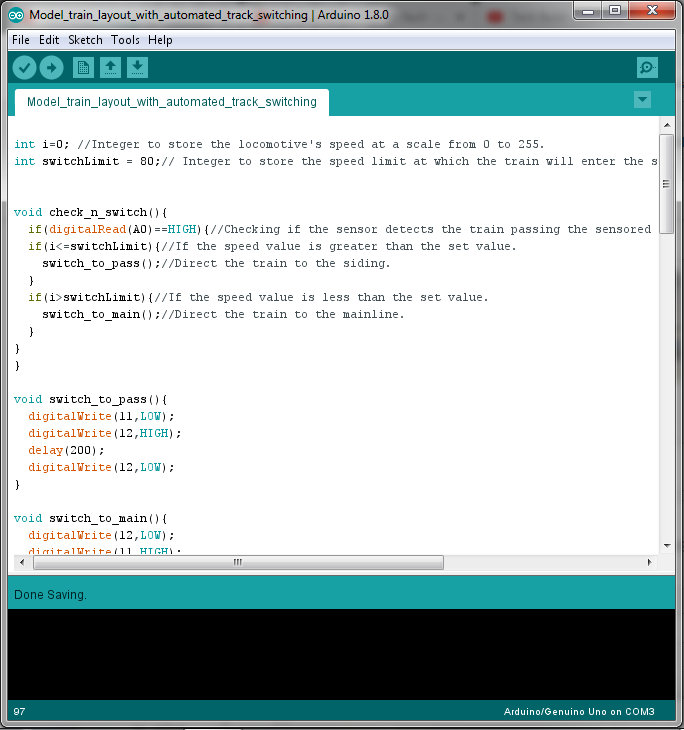
3Upload the Program to the Arduino Board
Download the Arduino IDE from here if you don't have it on your computer. Then download and open the given code:
int i=0; //Integer to store the locomotive's speed at a scale from 0 to 255. int switchLimit = 80;// Integer to store the speed limit at which the train will enter the siding. void check_n_switch(){ if(digitalRead(A0)==HIGH){//Checking if the sensor detects the train passing the sensored track. if(i<=switchLimit){//If the speed value is greater than the set value. switch_to_pass();//Direct the train to the siding. } if(i>switchLimit){//If the speed value is less than the set value. switch_to_main();//Direct the train to the mainline. } } } void switch_to_pass(){ digitalWrite(11,LOW); digitalWrite(12,HIGH); delay(200); digitalWrite(12,LOW); } void switch_to_main(){ digitalWrite(12,LOW); digitalWrite(11,HIGH); digitalWrite(11,HIGH); delay(200); digitalWrite(11,LOW); } void setup() { pinMode(A0,INPUT); pinMode(9,OUTPUT); pinMode(10,OUTPUT); pinMode(11,OUTPUT); pinMode(12,OUTPUT); } void loop() { switch_to_pass();//Switching turnouts to the siding since the train will start the journey fro there. for(i=0;i<=40;i++){//Increasing the speed of the locmotive to 40, at this speed the lights turn on but the train remains at rest. analogWrite(9,i); delay(10); } delay(1000); for(i=40;i<=90;i++){//Increasing the speed of the locomotive to 90 analogWrite(9,i); check_n_switch(); delay(500); } delay(4000); for(i=90;i<=180;i++){//Increasing the speed of the locomotive to 180. analogWrite(9,i); check_n_switch(); delay(250); } delay(5000); for(i=200;i!=90;i--){//Decreasing the speed of the locmotive back to 90. analogWrite(9,i); check_n_switch(); delay(500); } delay(5000); while(digitalRead(A0)==LOW){//Wait for the train to cross the sensored track. } switch_to_pass();//Switch the turnouts to direct the train to the siding. delay(10000);//Wait for the train to enter the siding. for(i=90;i!=50;i--){//Reduce the speed of the train gradually, bringing it to a halt. analogWrite(9,i); delay(500); } delay(2000); for(i=50;i!=0;i--){ analogWrite(9,i); delay(62); } delay(5000);//Wait for 5 seconds before repeating the whole process again. } -
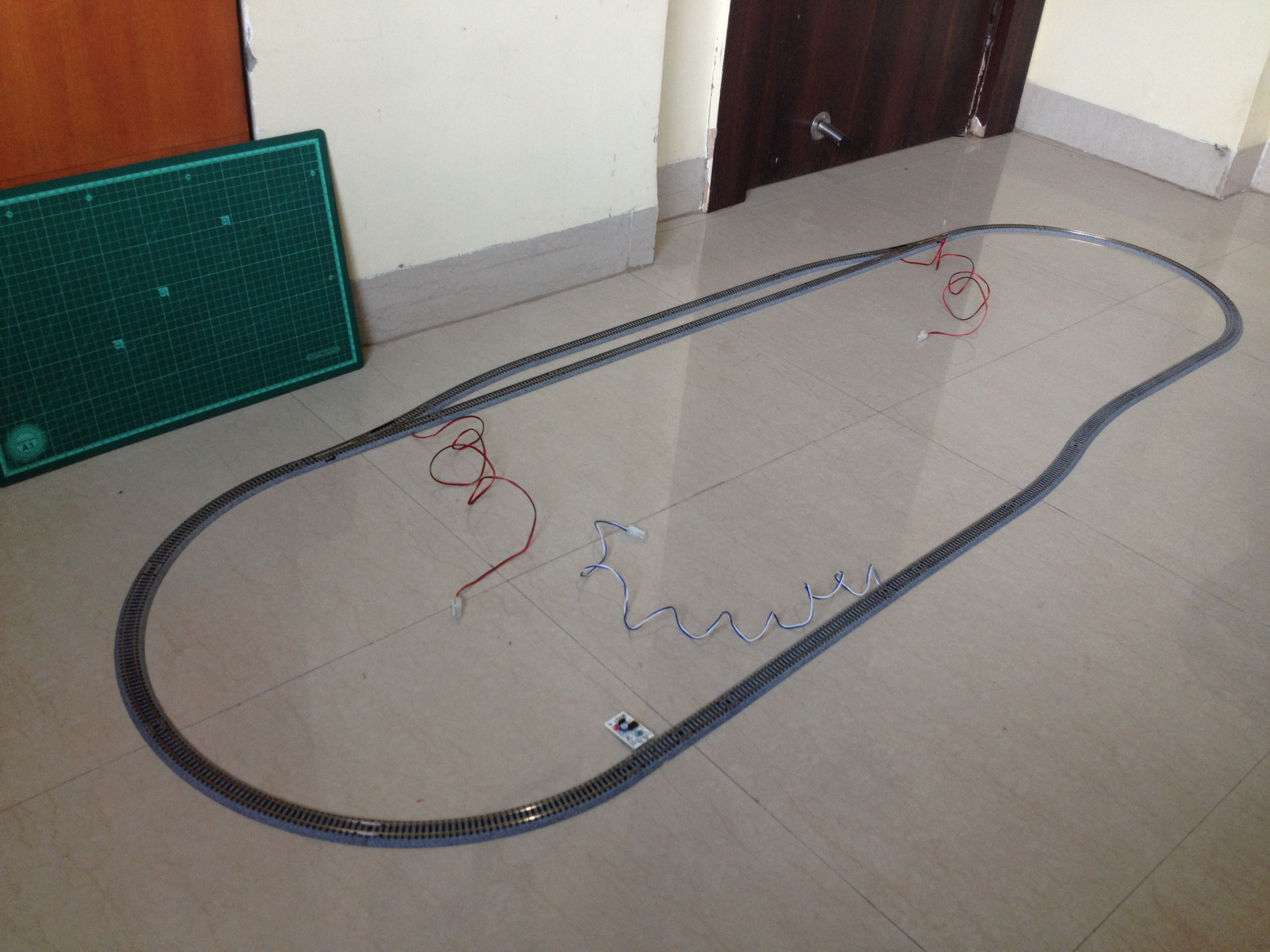
4Lay the Tracks and Make the Layout
Make an oval loop with a passing siding somewhat as shown above. Make sure the distance between the sensor track and the first turnout the train will cross after crossing the sensor track is greater than the length of the train such that no part of the train is over the sensor track when it crosses the turnout.
-
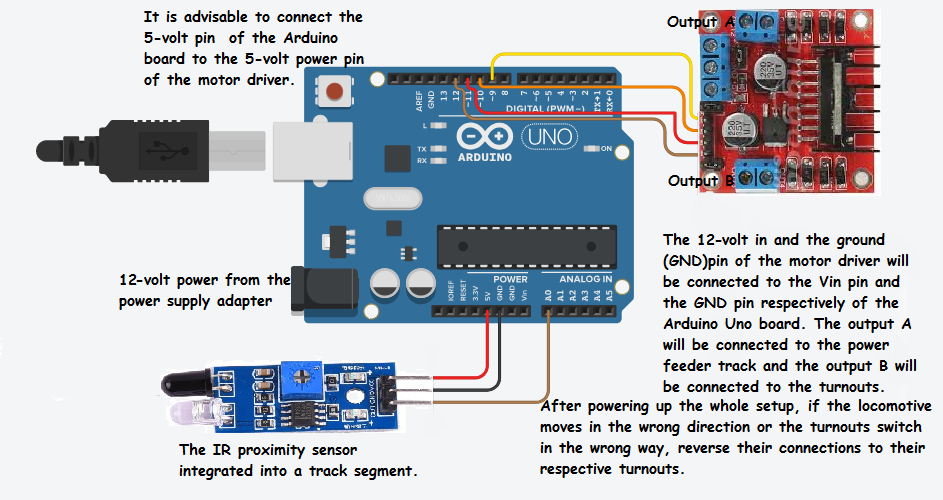
5A Circuit Schematic Is Always Helpful
![]()
Make sure you go through the full circuit schematic and all of the details before proceeding.
-
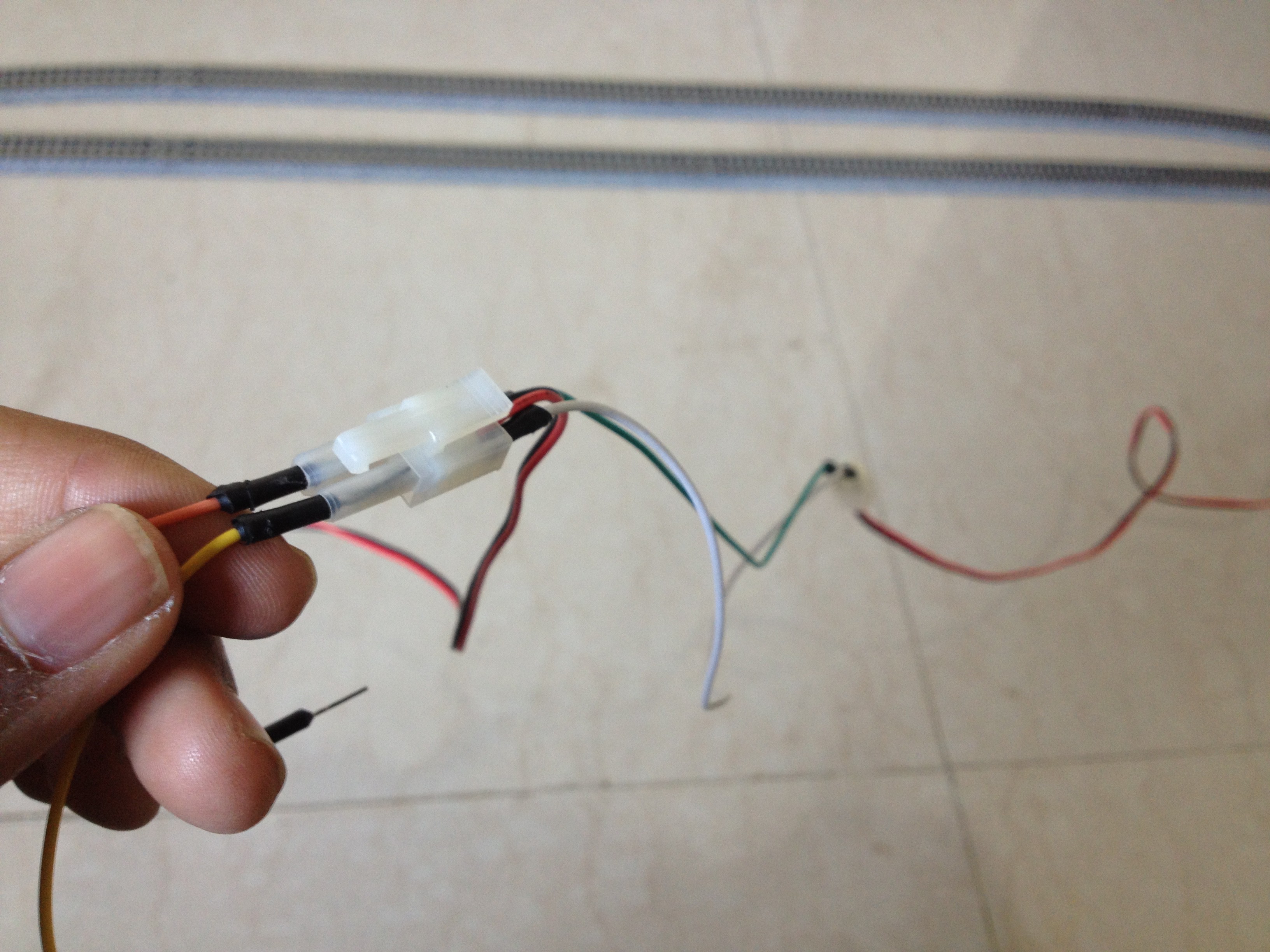
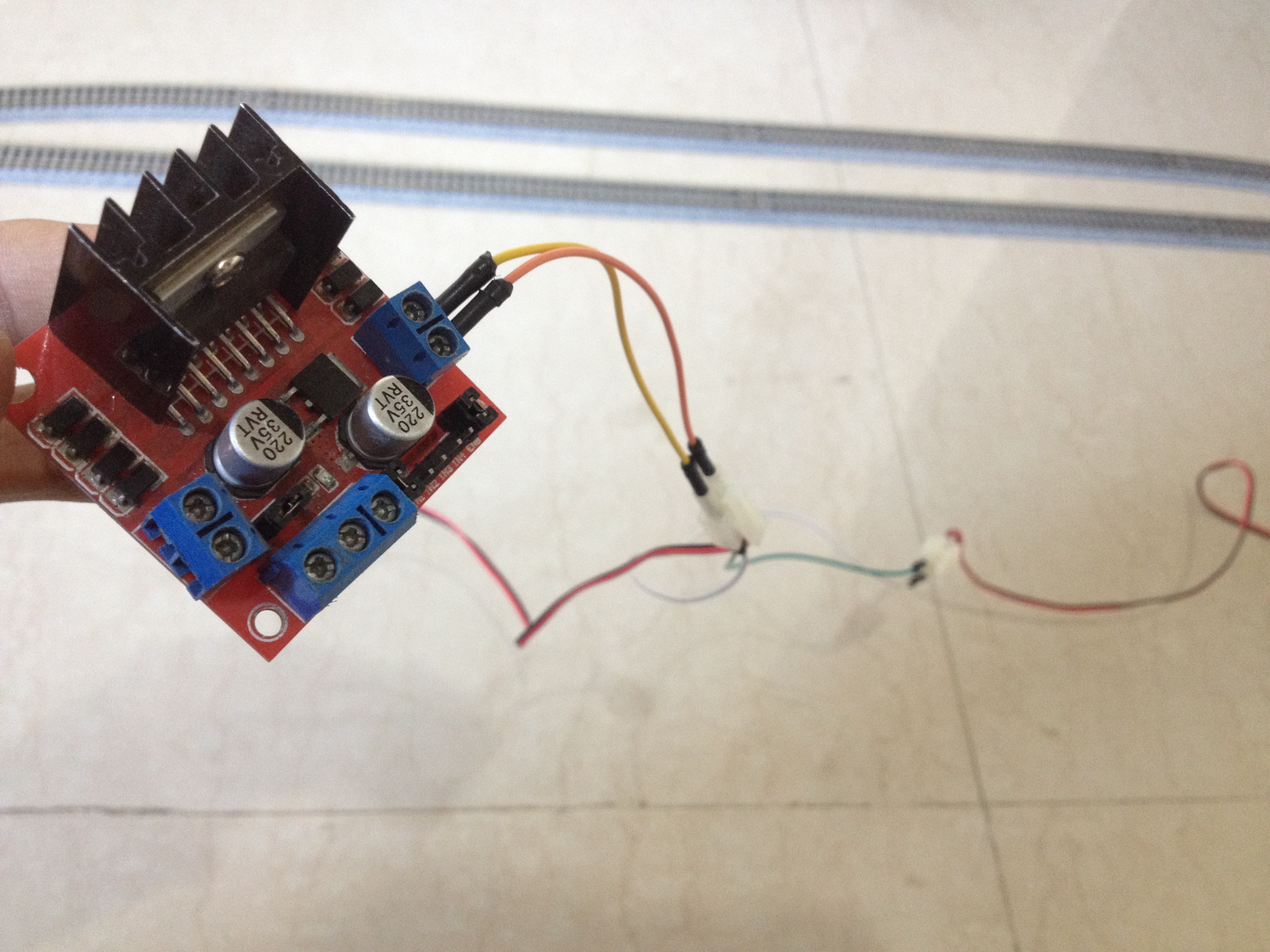
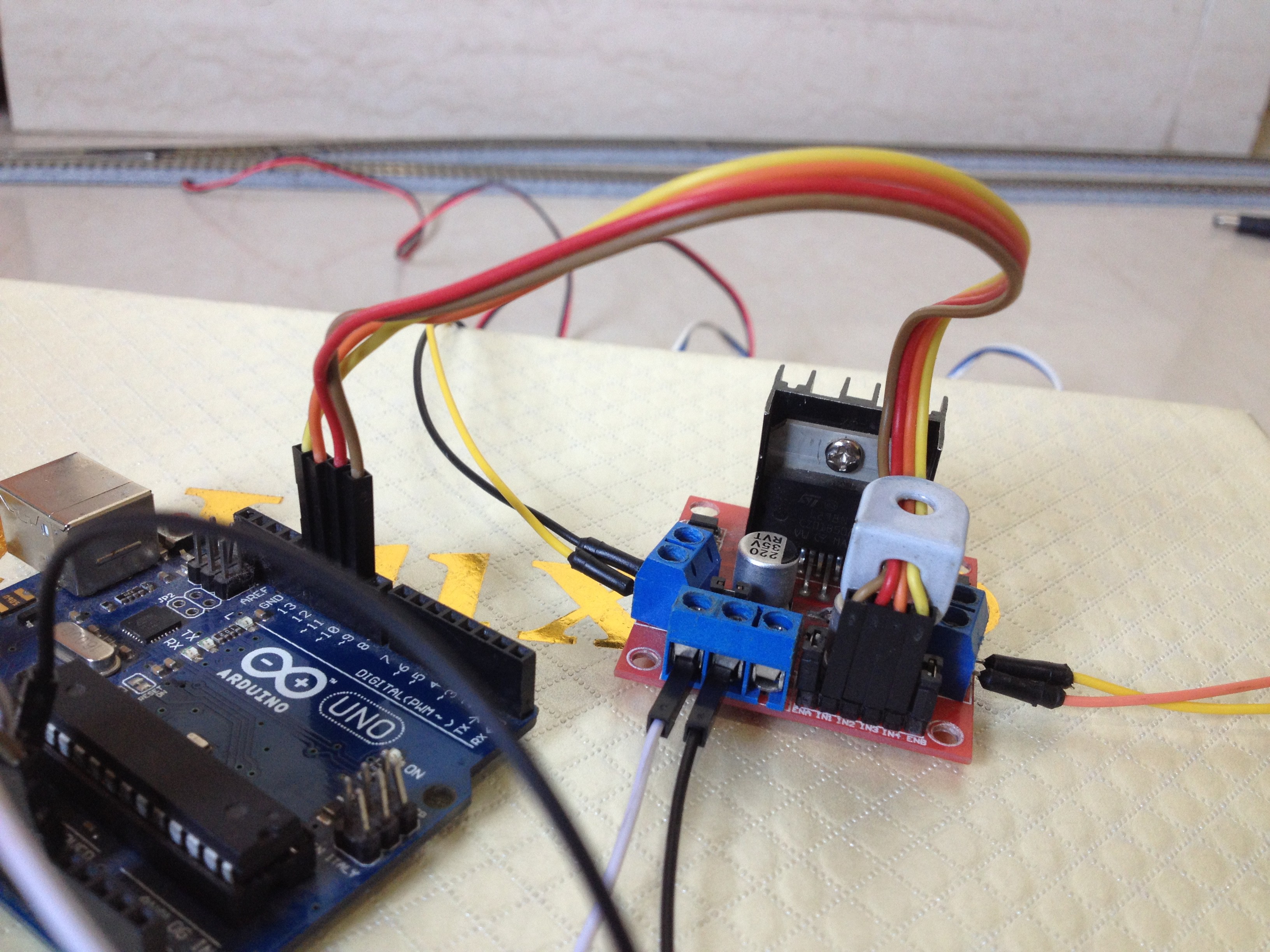
6Connect the Turnouts to the Output of the L298N Driver Board
Connect the red and the black wires of both the turnouts respectively to each other, resulting in a parallel connection.
Then, connect the red wires to the out4 and the black wires to the out3 terminal of the motor driver board.
-
7Connect the Power Feeder Track to the Other Output of the L298N Driver Board
Connect the power feeder's white wire to the out1 and the blue wire to the out2 terminal of the motor driver board.
-
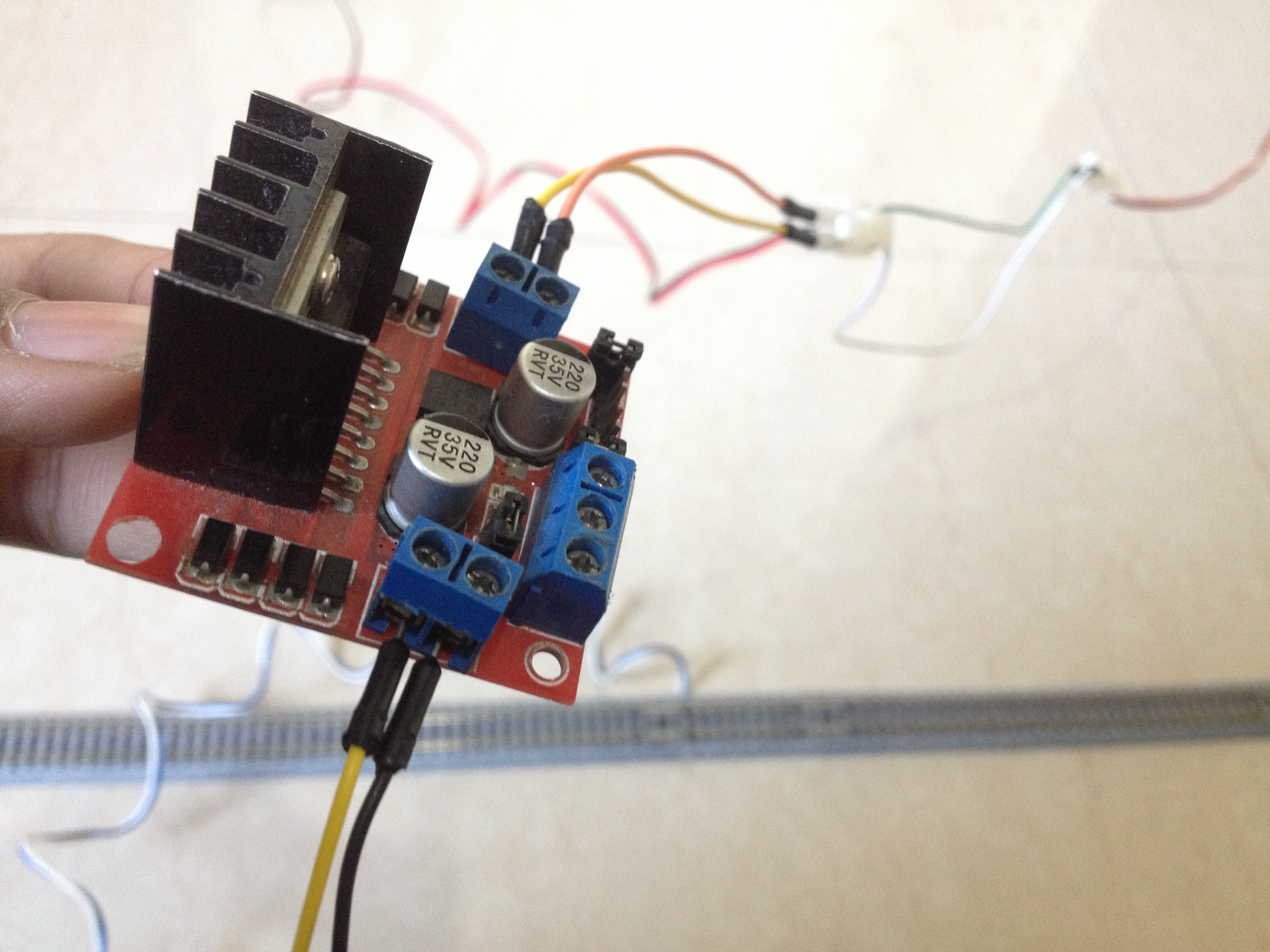
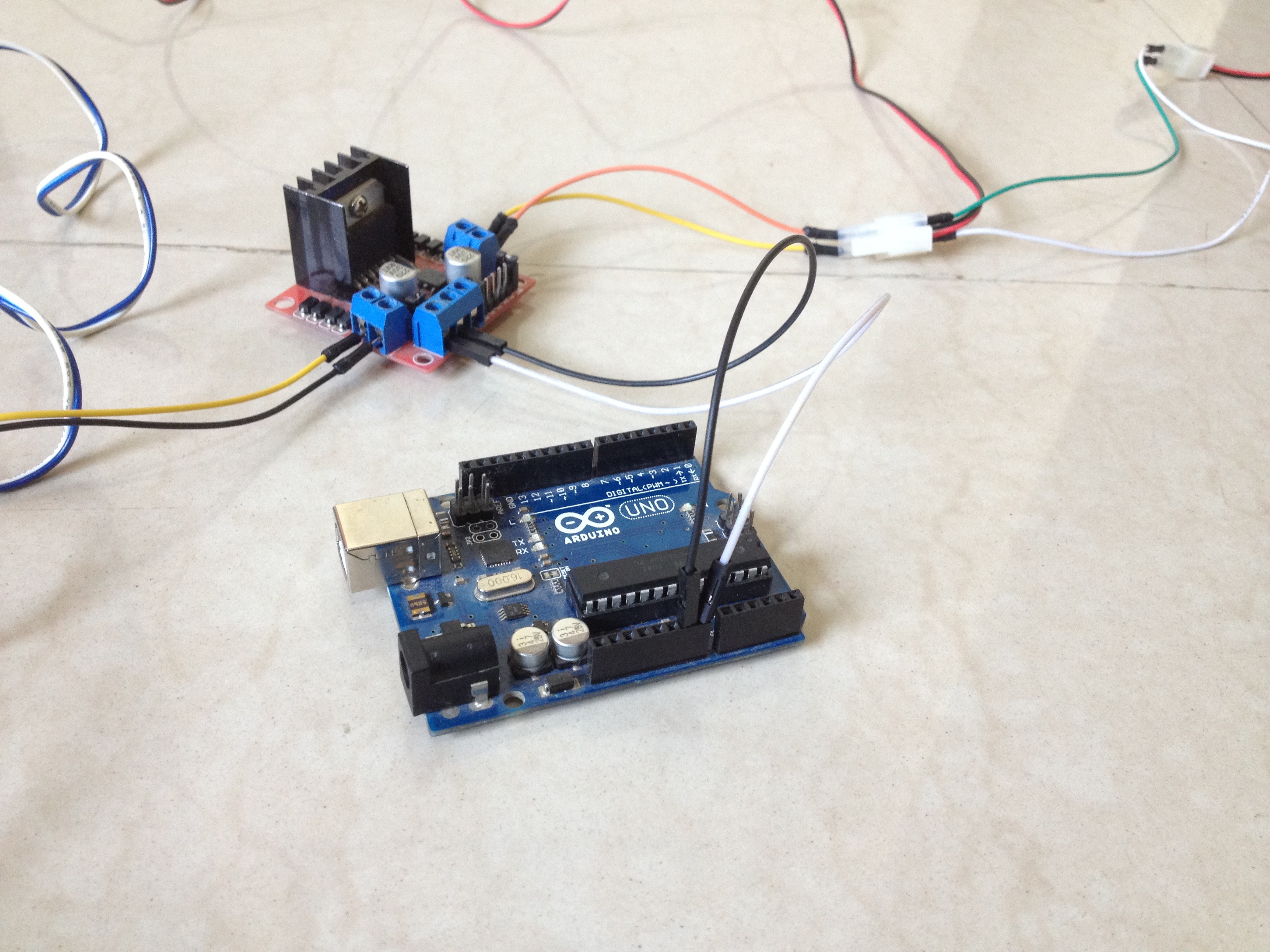
8Connect the L298N Driver Board to the Power Pins of the Arduino Board
Connect the 12-volt pin to the VIN pin of the Arduino board, the GND pin to the GND pin of the Arduino board, and preferably, the 5-volt pin of the motor driver to the 5-volt pin of the Arduino board.
-
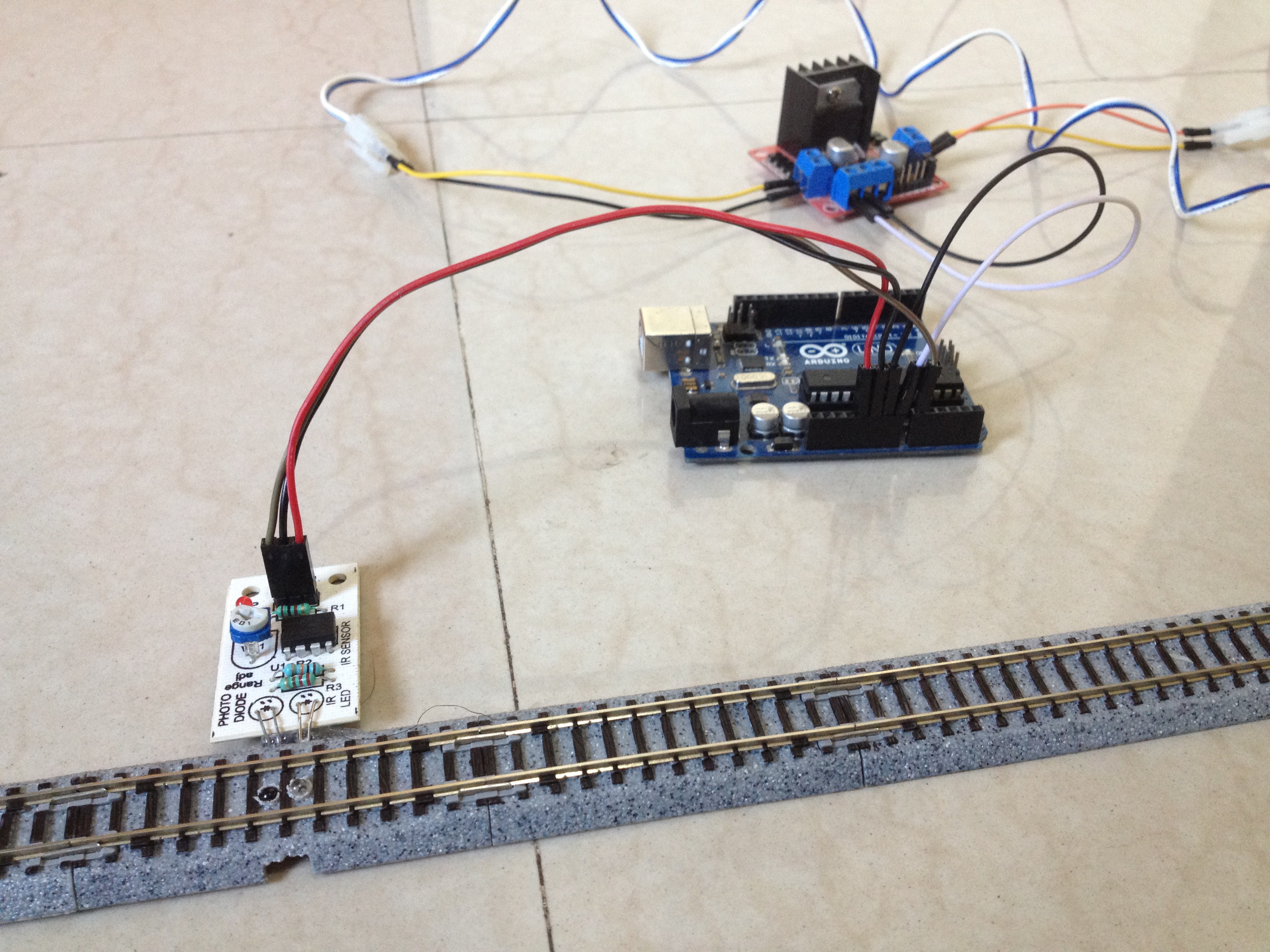
9Connect the Sensor to the Arduino Board
Connect the VCC pin of the sensor to the 5-volt pin of the Arduino board, GND pin to GND pin of the Arduino board, and the OUT pin to the A0 pin of the Arduino board.
-
10Connect the Input Pins of the Motor Driver to the Arduino Board
Connect the digital pins of the Arduino board to the input pins of the motor driver board as follows:
- D9 to IN1
- D10 to IN2
- D11 to IN3
- D12 to IN4
Model Railway Layout With Automated Siding
Automating a model railroad layout with a passing siding using Arduino.
 KushagraK7
KushagraK7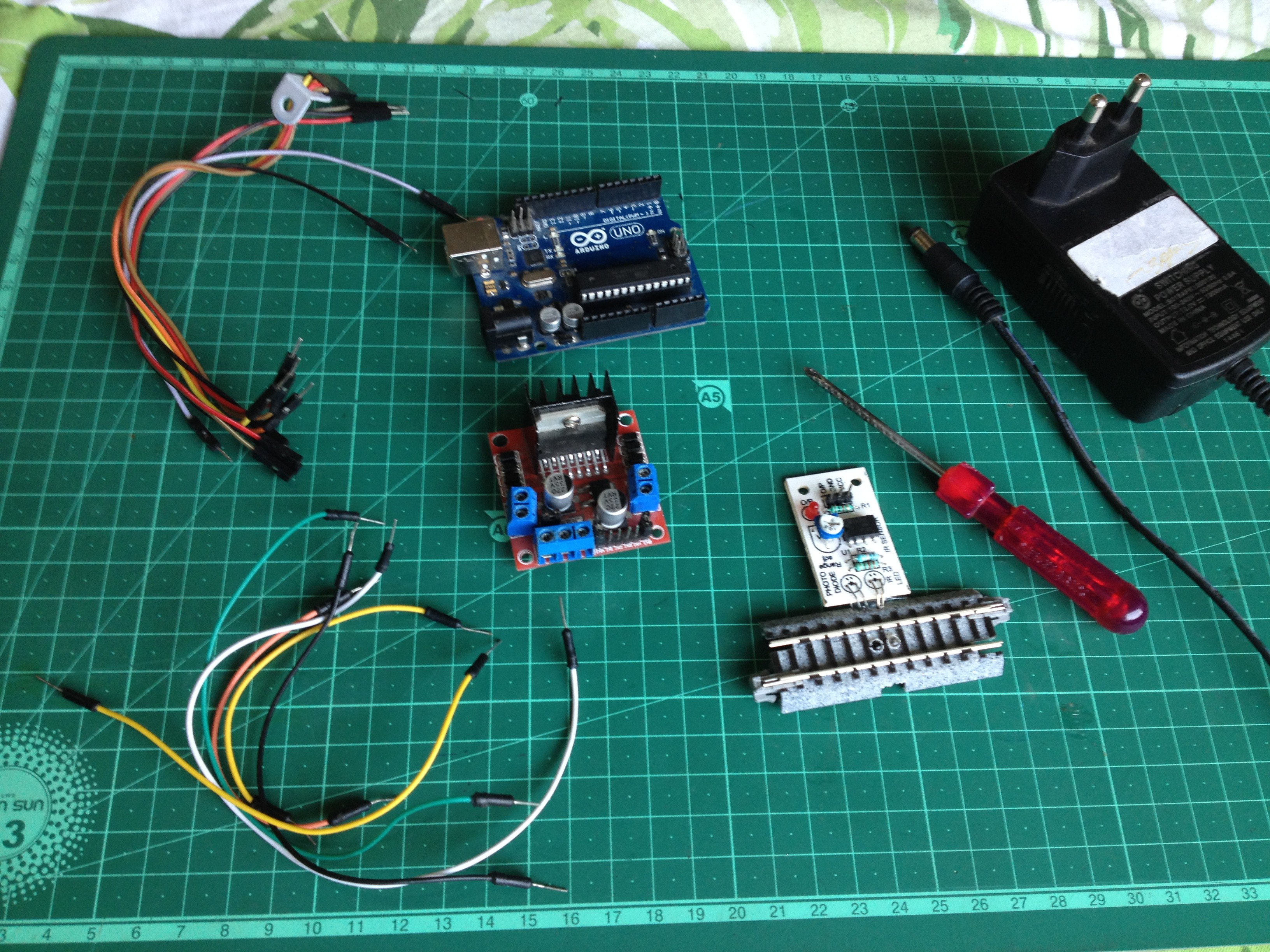



Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.