-
SystemBus
3 days ago • 0 commentsThere are two copies of SystemBus, both paralely conected. Either one, or both may be used to stack with other PCBs like retrocomputer or another cards together. I will use female/male connectors (socket with long legs) in the inner position, but it is also possible to use pins downwards and socket upwards, alternation positions, if the F/M connectors are ont available or practical.
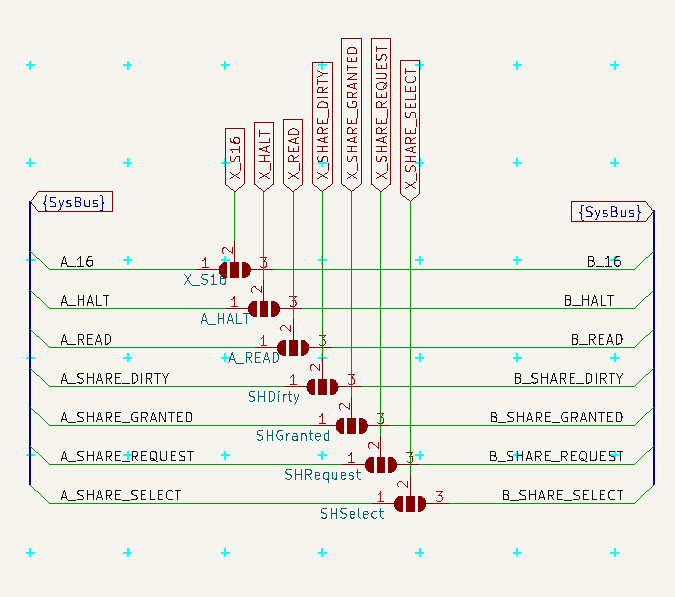
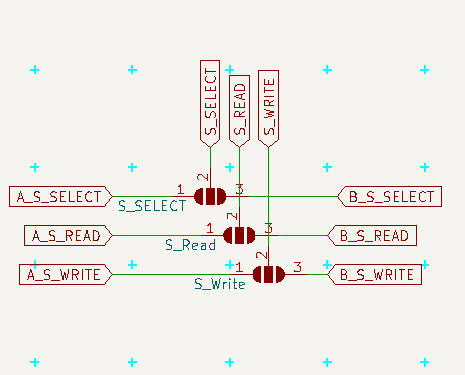
The SystemBus contains the usual common power, 8bits Data and 16bits Address, then communication with GLUE divided to A and B parts and rest of pins is reserved for signals (like MasterReset).
MasterReset is used for reseting all connected PCBs, while normal Reset resets only this PCB without affecting others.
![]() |SystemBus-schema.png|
|SystemBus-schema.png|![]()
|SystemBus-side.png| view from side with sockets in outer and pins in inner holes
-
Configuration
12/28/2025 at 15:01 • 0 commentsThis PCB can be used in different ways and different configurations. There are a lot of solder-jumpers (some open, some bridged by default) to customize it for your needs.
Serial connection
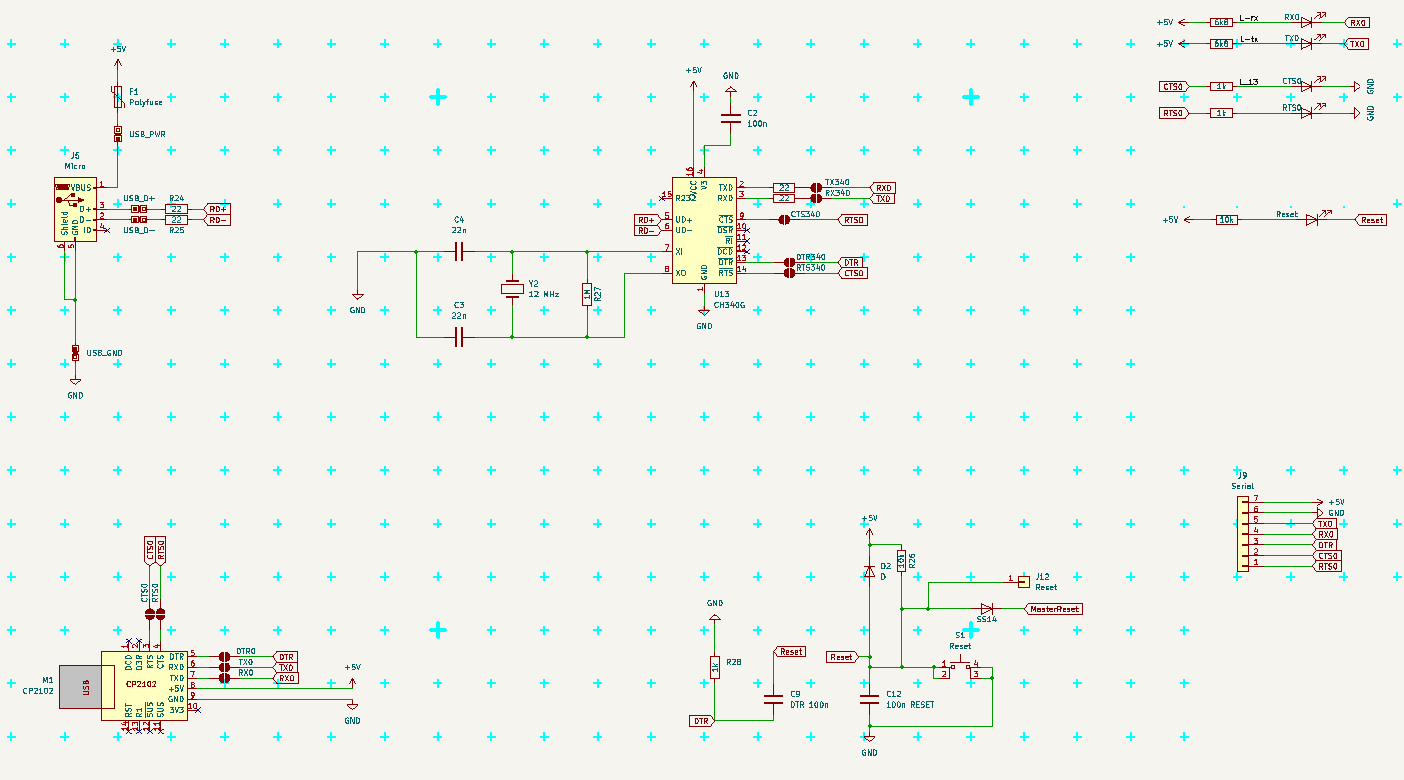
RX/TX are on pins PE0/PE1, CTS/RTS are on pins PB4/PB5, all 4 are at their respective ports pins. DTR is connected to Reset block directly.
Together they are on Serial connector on top edge for connecting any external Serial source (default).
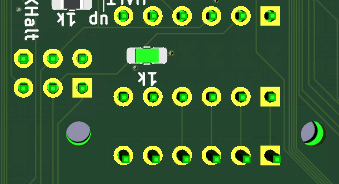
![]() |USB-Serial_pinhead.png|
|USB-Serial_pinhead.png|Solder-jumpers there enable connection to CH340G USB-Serial convertor.
![]()
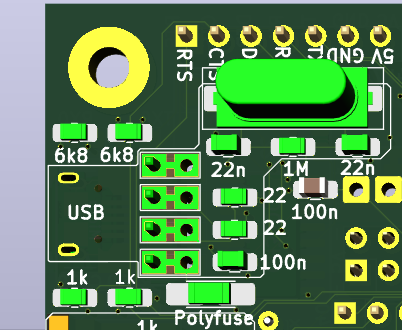
|USB-Serial_CH340G_top.png|
Another set of Solder-jumpers is under CP2102 module and allowe use of that module.
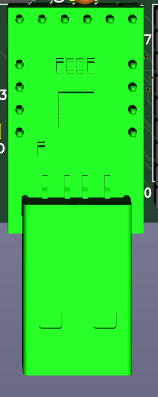
![]() |USB-Serial_CP2102_bottom.png|
|USB-Serial_CP2102_bottom.png|CH340G and CP2102 cannot be used together, or with external Serial (signals will conflict).
SBC config
To use Shared RAM in SBC configuration is needed access to its signals (otherwise managed by GLUE) and maybe to its gates to SystemBus too - simply solder all jumpers in this part and use the new scheme
![]()
|Shared_RAM_top.png|
![]()
|config_SBC.png|
AxB SystemBus connection - Graphic Card
Graphic Card configuration is the final goal - this PCB would serve as Input/output for retrocomputer - SystemBus is connected to other PCB, where is retrocomputer and its GLUE is managing Shared RAM and some more signals.
There may be 2 such cards in system (one for VGA/RCA where screen takes 90% of time, other for SD card, PS/2 and Serial, where some transmission needs be uninterrupted by screen). One card will be named A and other will be named B and GLUE will talk to each separately. To became Card A solder left part of each of 10 jumpers, to became card B solder right part. (And in both cases unsolder SBC configuration.)
![]()
|config_GLUE_top.png|
![]()
|config_GLUE_top_A.png|
![]()
|config_GLUE_top_B.png|
![]()
|config_GLUE.png| This is communication from MCU to GLUE.
![]()
|config_gates.png| Here is communication from GLUE to gates
![]()
|config_shared.png| and here communication from GLUE to Shared RAM
Notice, that in order to read/write shared RAM the MCU need ask GLUE to set related signals (and GLUE will do it only if the Shared RAM is owned by MCU)
HALT + LED
For proper boot of retrocomputer may be needed to fill its RAM with the "ROM" part before it is started. To do so the HALT should be pulled DOWN (it is active low) and hold there until is all ready.
If this PCB is supposed to do that, it would be good to solder pulldown resistor (and not pullup), after boot actively hold down the line and after setting the RAM (open gates via GLUE, manipulate A0..A16 and D0..D7 and set write signal via GLUE) hold it UP.
If this PCB is suppose to do that, but does not want to doo it, solder pullup resistor (and not pulldown), cut the XHalt jumper and use HALT LED for anything else (like SYSTEM_LED, but beware, it is also active low)
If this PCB is not suppose to do that (the other (AxB) card should do it), do not solder any pull* resistor, cut the XHalt and use LED as you want.
On SBC configuration this line is used to to write to Shared RAM, so do not solder pull* resistors, do not cut XHalt, but you may cut out the HaltLed or leave it to indicate writes to Shared RAM.
Also you may cut the HaltLed and solder any output to this inverted LED or use the invertor for anything else.
![]()
|config_HALT.png|
![]() |config_HALT_bottom.png|
|config_HALT_bottom.png|PS/2 Direct access + Inside
If you want read the PS/2 direct and process it, solder the 2 jumpers near SPI/SD card (and change the two marked resistors to 1 kOhm ) Also you may want to cut the Inside jumper, as it is probabelly of no use in such scenario. It also interfere with SPI, which needs address in SW.
![]()
|PS2_direct_top.png|
SD Card
SD Card may be cut off SPI and managed separatelly via its header, but it is probabelly of no use
RCA source 40 x 80
This pinhead selects source of graphic data for RCA - the pins are 40,signal,80 and the center (signal) should be connected to one of the sides - 40 selects the UART1 output (and classical driver with 40 characters per line), but I want to test sending there data in similar way as for VGA, so the 80 selects output from VGA module (which may or may not be able to provide 80 characters per line). Now I recomend to use 40.
-
Debug LEDs
11/18/2025 at 19:01 • 0 commentsAs I need feedback while testing things, I usually use LEDs on Arduino, but LEDs needs IO pins and forgotten code may affect function later, so I decided to use one pin (PD4) for 6 Neopixel WS2812B which are serial driven. Setting different colors may indicate different states and should I accidentally forget somewhere some testing code, it will reveal soon and in non harmfull way.
---------- more ----------They share pin with X_SHARE_GRANTED signal, but it should not be problem, as this signal is input for MCU and LEDs are output and both are separated by resistor. GLUE, which set this signal does not read it, so it will not be bothered with data for LEDs and LEDs need some specific protocol, so they will ignore ocassional changing in the signal.
My plan it to dedicate some RAM for the values of these LEDs and simply let system resend it after each screen (60 times per second), so programs will just put values there and forgot it (like with videoRAM),
Here is the scheme
![]() Debug LEDs are only on top of PCB (and I did not found more place for them, so I did not place there more of them). There are their numbers, you may populate just few with lower numbers
Debug LEDs are only on top of PCB (and I did not found more place for them, so I did not place there more of them). There are their numbers, you may populate just few with lower numbers ![]()
-
RAM (External + Shared)
11/15/2025 at 06:18 • 0 commentsExternal RAM may be used to have visible 64kB RAM inside MCU (but those 56kB extra is 1 tick slower to access).
Shared RAM may be shared with retrocomputer or used as just storage with slower time then RAM but faster then anything else.
Both are 128kB chips CY7C109D, as I found them to be cheap, accessible and 5V friendly. The truth is, that their output is lower then 3.4V, but Atmega should be able use it anyway. 74HC245 gate may need power little lower than +5V, so I added resistor there to slightly decrease it (or maybe Schottky diode). I will see, if it is really needed.
Note that near the RAM datalines may be permutated any way, as well as adderss lines, because it does not matter, the permutation will negate when the data are readed back. So it may be used to have better physical traces there (as I did).
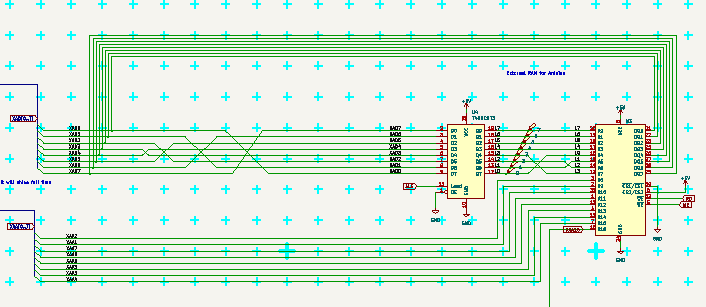
---------- more ----------External RAM is connected to ports PA and PC, where PA is latched by 74AHC573 fast octal D-latch. It must be enabled in SW and managed by PG0-2. I will use PG3 to select in which half of chip it resides.
It can be accessed also manually if the automatic is not enabled, by setting low address to PA, latch it and then use PA as data line. This way any byte in 128kB may be used at slower access time. I will probabely use it for futher expansion of FORTH memory. those 8 squares around it are probes of D-latch output, so it could be tested too. D-latch is placed under the PCB to have short lines to RAM.
![]()
![]()
![]()
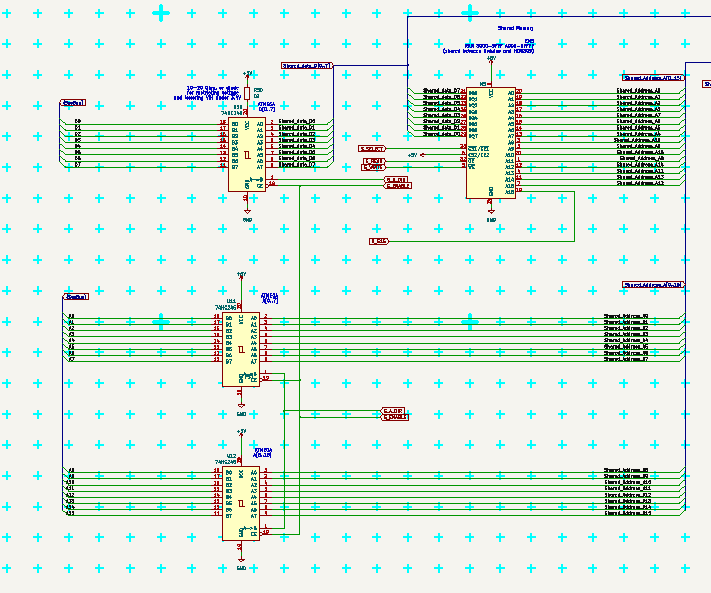
Shared RAM is connected to ports PJ, PK and PL, and in graphic card configuration is managed in cooperation with GLUE. In SBC configuration the MCU need to manage it itself, so all SBC solder jumpers should be soldered. If output to System Bus is not needed, also gates may be unpopulated.
![]()
![]()
![]()
-
SD Card + SPI + ISCP
11/15/2025 at 05:27 • 0 commentsSD card formated with FAT system serve for storing and reading files.
Currently it uses SPI and Arduino library, but as I use timers, I update millis() just each screen refresh to make illusion of time for its timeouts.
SPI have its LED and pinheader placed near SD card and may be separated by cutting solder jumpers (default connected). MISO/MOSI may serve also for PS/2 serial input when its (default open) solderjumpers are solrdered.
ISCP connector is also there with pin 1 marked by white rectangle under SD reader.
---------- more ----------![]()
ISCP is ATmega/Arduino Standard and may be used for programming MCU. As there is not much space free, the Silkscreen is placed above (+5V GND), bellow (white mark visible from angle under SD card reader, Sck and Rst) and by sides (MISO left down, ISP right) for correct orientation of connector.
SD Card Reader may be cut out for freeing CS/SS PB0, or other pin may be used for SPI chip select.
SPI LED is connected to SCK and placed just above SD Card Reader near the SPI pinheader.
SD Card Reader should have level shift to 3V3 and fixed CS to disable MISO, when not active. See my comments here and original discussion.
![]()
![]()
(only resistor for LED visible here).
I tried classic Arduino SD library for reading SD card and it works, but need somehow advancing millis(), so I just incremented the value in VGA library. Also I tried only to read one byte at new screen, as I did not know the timing of the library, which was slow, but worked. I will make my own version with much better approach some time later (I hope).
-
Serial + USB
11/14/2025 at 19:36 • 0 commentsCommon
All marks are from MCU signal side of view. (RX is input, TX output, CTS is input, RTS is output, DTR is input).
Default Serial uses USART0 (RX0/TX0 - PE0/PE1 pins) and RTS/CTS (PB5/PB4 pins) and DTR connected to Reset.
There are 3 possible sources for Serial Communication
- Serial pinhead - always conected to MCU, need all signals to be attached
- CH340G with micro USB from Arduino Mega Pro - need to solder connect (RTS/CTS does not work with usual drivers)
- CP2102 module with USB A - need to solder connect
There can be two modes of communication
- full with RTS/CTS flow controll - recomended - protect agains buffer overflow, when PC transmits more data (like a file, or Copy-Paste larger block)
- simply RX/TX like on Arduino, buffer may overflow, cannot paste longer lines
---------- more ----------For RTS/CTS the pins must be connected and driver must use it.
Connect RX to TX on of the other part communicating (USB-Serial module, PC, other Arduino ...).
(And TX to RX; CTS to RTS; RTS to CTS; DTR to DTR.) Typical crossing of lines.
The Serial pinhead is already connected to MCU.
CTS is "Clear To Send" and is INPUT, when is low, MCU can send data over TX, when it is high MCU should not send anything
RTS is "Ready To Send", (in new era it is RTR "Ready To Receive") and is OUTPUT, when is low, the other side can send us data, if it is hight, the other side should stop sending
If buffer is too full, set RTS to HIGH until the buffer is empty again.
(It is critical to good communication, as PC have gigabytes of memory, large buffers and fast communication, while ATmega is realitively slow, have small buffer and processing data may take some time. So we need temporaly stop PC from sending more, until we can receive it.)
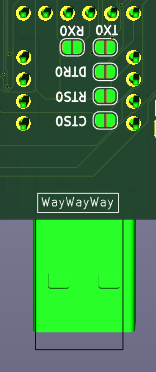
![]()
Serial pinhead
It is "easier" Serial connection as it is just pinhead. It contains all the signals and what is there connected is up to user.
There are LEDs for RX, TX, RTS, CTS near micro USB connector, so communication should be visible. RTS and CTS LEDs are active when the signals are HIGH, which means the direction is BLOCKED. (So use of red LEDs make good sense here.)
DTR is near Reset buton, and does not have LED, the Reset LED indicate any Reset
![]()
CH340G
This came from Arduino Mega Pro, where RTS/CTS are not used. If you prefere this behavior, solder only RX, TX and DTR jumpers.
There are problems with drivers for CH340G using RTS/CTS, if it does not work, look for some patch or different driver.
I had problem with the Micro USB connector, that it does not had good and reliable contact and was too easy to damage/rip off. So I added some pinholes for its pins, so I can solder piece of PCB with USB A connector there when problem arise. There are actually two lines of holes, one connected to Micro USB, annother connected to CH340G chip. They are connected on BOTH sides of PCB, so to cut it would need cut on BOTH sides. (I do not think, that it would be needed anyway.)
In case you want use this connector for power only, then populate only the connector and polyfuse (or cut the D+ and D- on both sides of PCB)
![]()
![]()
CP2102 module
This module have all signals connected to pins, and have solid USB A connector. To use this module for communication, solder the jumpers on the bottom side of PCB. To use it just as power souce, simply solder the module in.
![]()
![]()
Notice, that signals should came from max one module at time, so solder/desolder and cut the solderjumpers as needed.
Also notice, that normal Arduino Serial does not use CTS/RTS signals, so in this case is better leave them unconnected.
Also notise, that RTS/CTS flow controll usually need be allowed on the PC side in communication program (Serial terminal and so), Arduino IDE cannot use it at this time.
-
PS/2
11/14/2025 at 08:02 • 0 commentsErrata
- all 10 kΩ resistors in PS/2 (8+2) should be rather 1 kΩ (otherwise it take too long for reading values, like 10 clock cycles)
PS/2
PS/2 have 2 lines - Clock and Data. See https://wiki.osdev.org/PS/2_Keyboard
Clock runs at 10-17 kHz, 11 pulses (normal High, active LOW), data came as
- 1 start bit (always 0)
- 8 data bits (least significant bit first)
- 1 parity bit (odd parity)
- 1 stop bit (always 1)
The clock/data can be connected directly to PB2/PB3 MOSI/MISO via solder jumpers (default OPEN, solder to USE) and decoded as serial communication, but I will use two shift registers and R-C to detect, if we are Inside the packet or not, so I could read the data as one byte on port PF, when I do not use it as VGA data output.
Inside signal (connected via closed solder jumper, cut if not wanted) is HIGH when clock is changing, LOW, when clock stops and PSDat is valid.
PS-OE is active LOW and let the captured PS data go to port PF
---------- more ----------(In next version I may redirect PS Clock BEFORE fixing its edges by Schmitt 74HC14, so it would be possible also send data like status LEDs (Caps,Num,Scrl) to keyboard)
The plan is to check at end of VGA line, if the Inside went LOW, then set port PF ro read, set PS2-OE LOW, read PF and set PS2-OE HIGH again. Inside is way longer than VGA line and pause between two PS/2 blocks is also long enought for it.
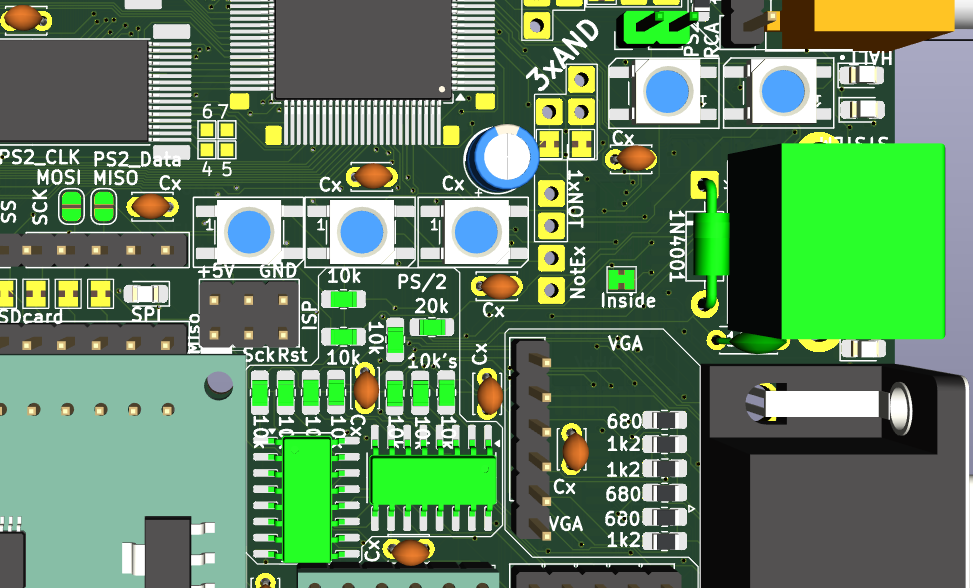
The schema is distributed over more places.
The main part with shif registers:
![]() Connection to data:
Connection to data:![]()
Inside signal:![]()
Serial clock+data signals:![]()
Top PCB:![]() Bottom:
Bottom:![]()
-
Composite output
11/13/2025 at 10:43 • 0 commentsThe composite output is currently done via USART running on half system clock.
One line is 64 uS long.
Sync pulse should be 0 V, black should be 0.3 V and white should be 1 V.
---------- more ----------![]()
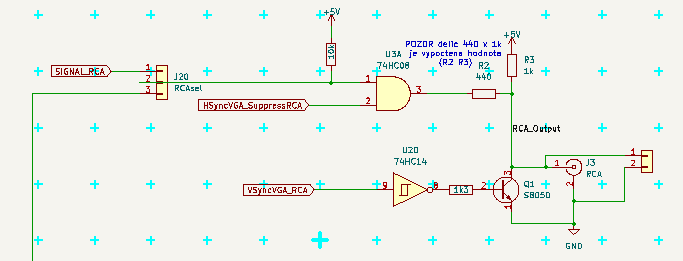
Logic signal goes to resistor divider over 440 Ohm to joint of 1k pullup to +5V and the 50 Ohm screen input. This was computed to make the requested 0.3 - 1 V levels.
Sync goes transistor (over NOT gate and 1k3 resistor) to pull that to 0 V. (and the resisors of divider limits the current from gates.)
As the USART lets its pin to flow, when disabled, the USART output goes via AND gate and Suppress signal keep the output LOW when no data are transmited.
In future (in this version) I want try to feed it from 74HC166 in similar way as VGA does it, to have 2x faster data here (same as system clock)
The jumper 40-80 selects the source, either USART (marked as 40 chars per line) or the 74HC166 output (marked 80 chars)
Here is the part on PCB
![]()
(top)
![]()
(bottom)
The RCA uses 1/4 AND gates of 74HC008 (the rest is avaiable as 3xAND blocks for future use) and 1/6 NOT gates of 74HC14 (4/6 are used by PS/2 and HALT, 1/6 is avaiable here too)
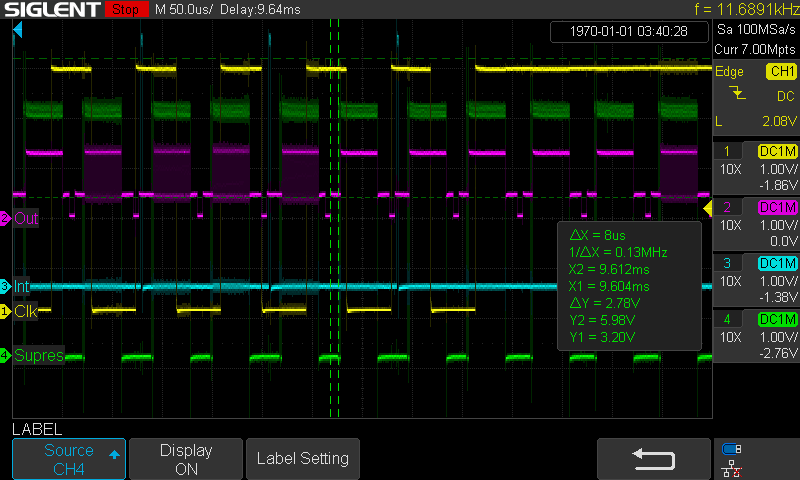
Here is osciloscope showing the RCA signal (magenta Out), Supress (green) and clock from PS/2 (yellow). The cyan Int is some debug.
![]()
Here we see the PS/2 traffic - pulses of similar width as RCA lines, but no synchronisation possible. Magenta Out show 0V sync pulses and 0.3V-1V data accompanied dark area before and after visible line.
Here is osciloscope of 3 full screens and 8 PS/2 codes - around vertical sync is blank area bellow and above visible screen and the sync is way longer there.
![]()
There is no time to produce both RCA and VGA signals at the same time, but it is possible to switch the output on the fly. But the monitors are slow and take few seconds to adjust and start showing incomming signal, so no smart tricks probabelly possible here.
-
VGA
11/07/2025 at 12:32 • 0 commentsVGA need Vertical Sync (at start of each screen), Horizontal Sync (at start of each line) and Signal (inside the line, it is the pixels).
Vertical Sync is generated by timer on pin PE4 (every 16.64 mS ~ 60 Hz)
Horizontal Sync is generated by timer on pin PB6 (every 32 uS)
VGA signal is generated in interrupt on timer overflow (every 32 uS = each 512 clock ticks)
It needs pin PE7, where 16MHz (system clock) can be configured. As Arduino Mega does not have this pin connected, this was the main reason for making this PCB.
---------- more ----------Here are some osciloscope snaps, the magenta line is VSync, yellow line is HSync and green is Signal (sorry for wrong naming in picture)
![]() (4 screens at 60Hz)
(4 screens at 60Hz)![]() (1 line with pixels, 32uS)
(1 line with pixels, 32uS)
The main idea came from Squeezing Water from Stone 3: Arduino Nano + 1(!) Logic IC = Computer with VGA and PS/2 from slu4coder - short macro in assembler take character from videoram, take its definition from Flash, puts it as byte to port (PF here) and let 74HC166 to clock it out as 8 pixels. The macro take 8 clock ticks and is repeated 40x to output full line.
Each line is shown 2x so the visible area is 320x400 pixels, but is managed as 320x200 points (25 text lines) for readability and data size (character set takes 256 chars x 8 lines per character = 2kB of Flash.)
The numbers are: 32uS x 16MHz = 512 ticks. 40 characters x 8 ticks = 320 ticks, 512 - 320 = 192 ticks for everything else. When interrupt happens and interrupts are allowed (SEI) the MCU will finish instruction first, then serve the interrupt. This waiting for instruction end may take 1-3 ticks itself, so the interrupt may happen not really regularry and is necesery to adjust for that (macro check in my code). Also it needs to save registers, compute all adresses and offsets and manage possible PS/2 during the line. That may take approx 150 ticks together, leaving like 42 ticks between lines for user code to run in (means 8% speed only).
Then there are the black borders above and below the displayed image (only lines 60 .. 460 are visible), where the user program is mainly executed (which give like 20% of MCU power). It is not much, but a lot of work can be done anyway.
I set not only the Vertical Sync, but also the Horizontal sync to timers, so it does not depend on code exuting, which solved problem where VGA monitor sometimes went blank for few seconds (because some other interrupt or CLI..SEI section moved HSync pulse out of place and monitor get "confused and blank"). Now long uniterruptable section just make small glitch on screen, where pixels are horizontally moved for a frame (1/60 sec).
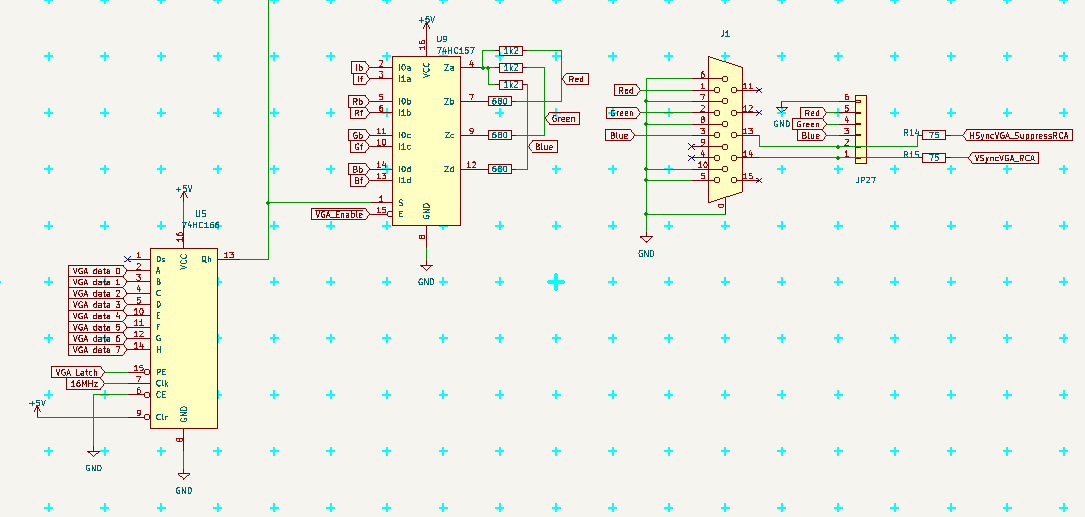
I also added 74HC157 IC to select foreground/background colors according to 74HC166 output, so now it is possible set foreground/background color for each line separately (I set it for all 16 lines of character the same now). The colors are set on port PH now at the start of visible line.
I also added VGA_ENABLE signal to cut off all pixels output in blank areas, so the ports (PF and PH) can be used for something else (I use PF for PS/2 input, leaving PH for user programs).
I also plan to make hooks on end of each visual line for "mini interrupts" and on end of last visible line (for "run at frame pause" synchronisation of larger blocks, like SD card) to run in interrupt context.
On user level the change of variable frames can be used for synchronisation of larger blocks or for timing events.
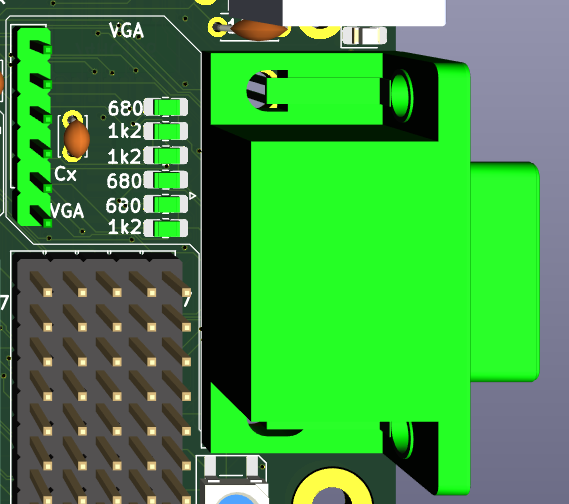
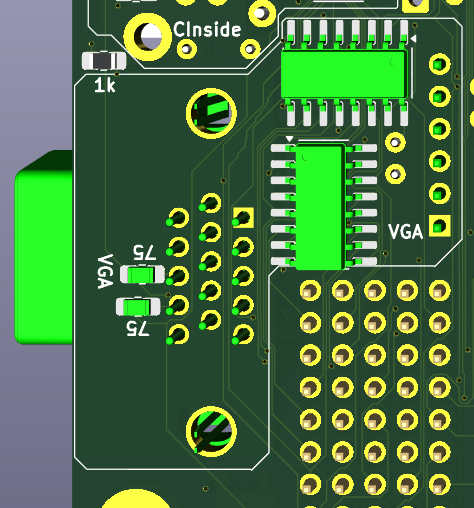
Here is schema and placement of the chips on PCB:![]()
![]()
![]()
Also note, that PB7 (VGA_Latch) is SYSTEM_LED on Arduino, so I placed LED between RCA and PS/2 connector near HALT LED and conected it here. When using VGA the LED will shine with approx 1/8 intensity. -
How it started
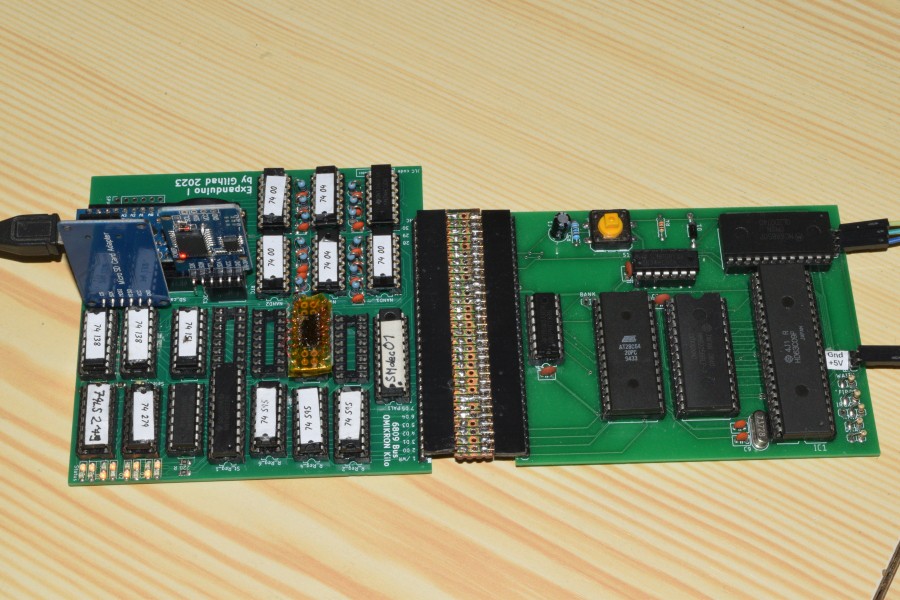
11/05/2025 at 12:46 • 0 commentsMany years ago I bought Omen Kilo (SBC with HD6309) and start to play with it. It worked, but did not anything visible (does it even run?), just communicated over Serial. Which was not so much satisfying.
---------- more ----------So I invented and constructed card for 8 serial channels and called it Expanduino (pages in Czech only and incomplete), as it was Arduino based.
![]()
It worked somehow, but was mechanically unreliable, slow and did not allowed for more extensions.
So I decided to make my own design from the start and make it simply extensible, so it culd have everything a computer needs - output to some monitor, input from keyboard, filesystem to store and load data and programs, ports and so on and so on. This was not SBC anymore.
I also found Composite video from Arduino UNO from ceptimus and Squeezing Water from Stone 3: Arduino Nano + 1(!) Logic IC = Computer with VGA and PS/2 from slu4coder which looked like solution for the video output. I use their ideas (and many others) and reworked it to system, which can switch between VGA and RCA even on runtime. This looked as good foundantion for videocard I wanted.
First public presentation was on 2024 Maker Faire in Prague, in form of Computer at price for dinner as proof of concept.
I then expanded it to FORTH driven breadboard computer NanoHomeFORTH and started work on even better version with more RAM and power.
![]()
I called the project MegaHomeFORTH, as it was based on Arduino Mega, but then I discovered, that the most importaint pin (16MHz clock) is not accessible on Arduino Mega, nor on Arduino Mega Pro, so I went to make my own board, where it will be all included.
On that time the PCBway reached to me and told me, that the project prom Maker Faire catched their interest and that they will sponsor me with PCB for it, should I make the plans. I offered the new project instead, as it made more sense for me and they agreed. It took me 2 months to came with the first version MHF-001 and they manufactured the board for it.
![]()
The PCB was nice, simple to use, soldering there was easy for normal parts, but I had problems with the MCU and the RAM as the footprints I used was for machine soldering, but I had to solder this with my hands and eyes. MCU went well after lot of effort, but I could not solder the RAM reliably even after many attempts. It sometime worked, sometime not and sometime helped to press it with fingers. The pads for its pins was too small for me to make it reliable. The PCB itself managed well even when I repeatedly solder and desolder the pins, the problem was my handwork. Anyway it prove the concept, the RAM worked well sometimes.
Also other parts worked, it generated nice VGA signal with color lines, it generated RCA signal too, it read PS/2 keyboard and it even was able to read SD card while doing all the previous at the same time (I was using some Arduino library, where I hacked the millis() mechanism, as I used the interrupt for other purposes, I read one byte at time at each frame to do not collide with the VGA, so it got speed 50 char/sec, but it proved the concept).
I also published it as project there.
There was problems with USB connector, mainly because small footprint, it was torned from the PCB more time due my manipulation and was not as reliable as I wanted, but the desing did not allowed for other connection to MCU (except for ISP programming), so new concept for that was included to the new step too.
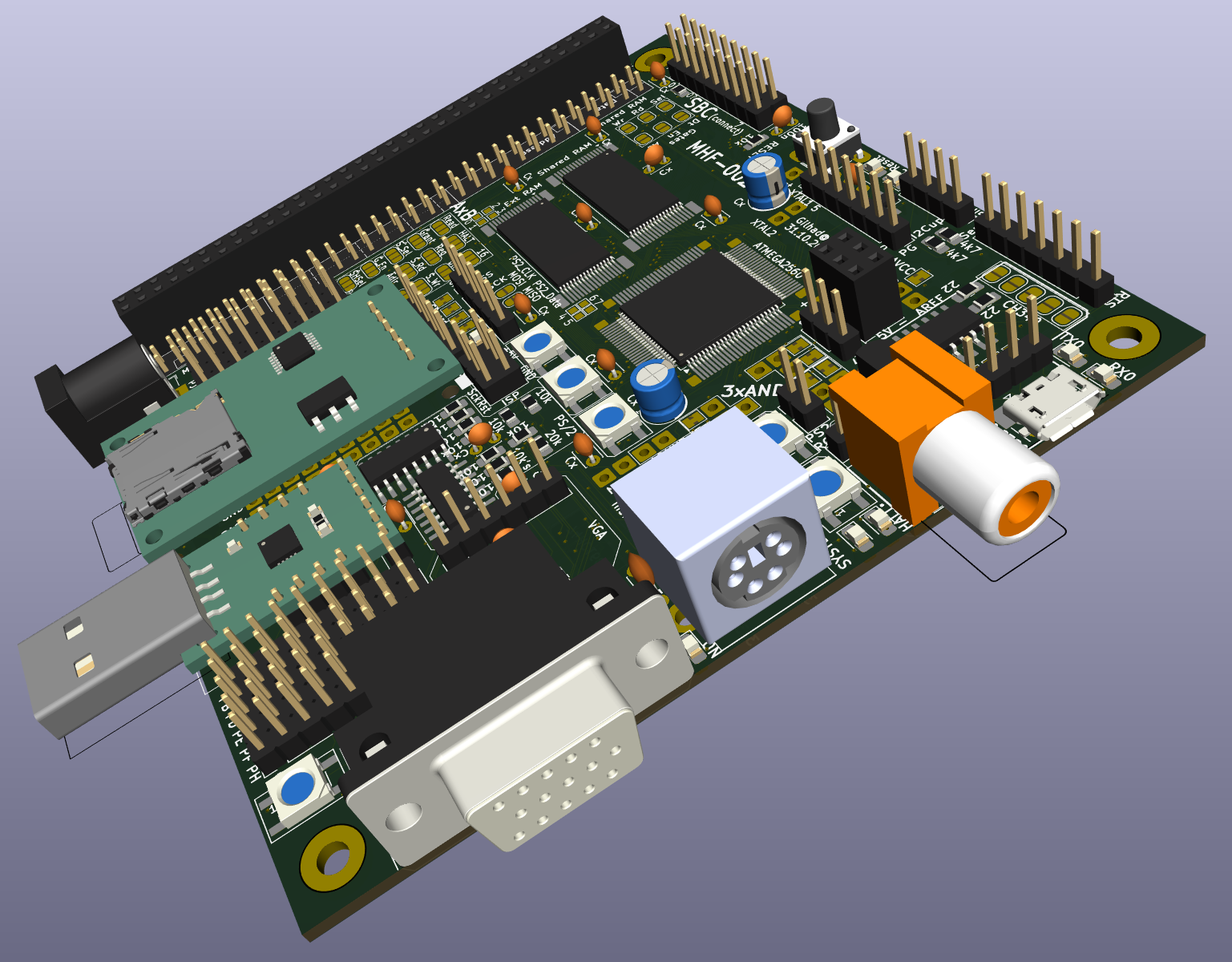
So I took another 2 moths to redesign it, added more features, made more logical configuration, and improved everything I could and now I am here, with MHF-002, which have more circuits on it, new module for USB, debug NeoPixel LEDS and so on and so on, which PCBway also offered to manufacture for free as sponsoring - and it is just manufactured as I write this lines :)
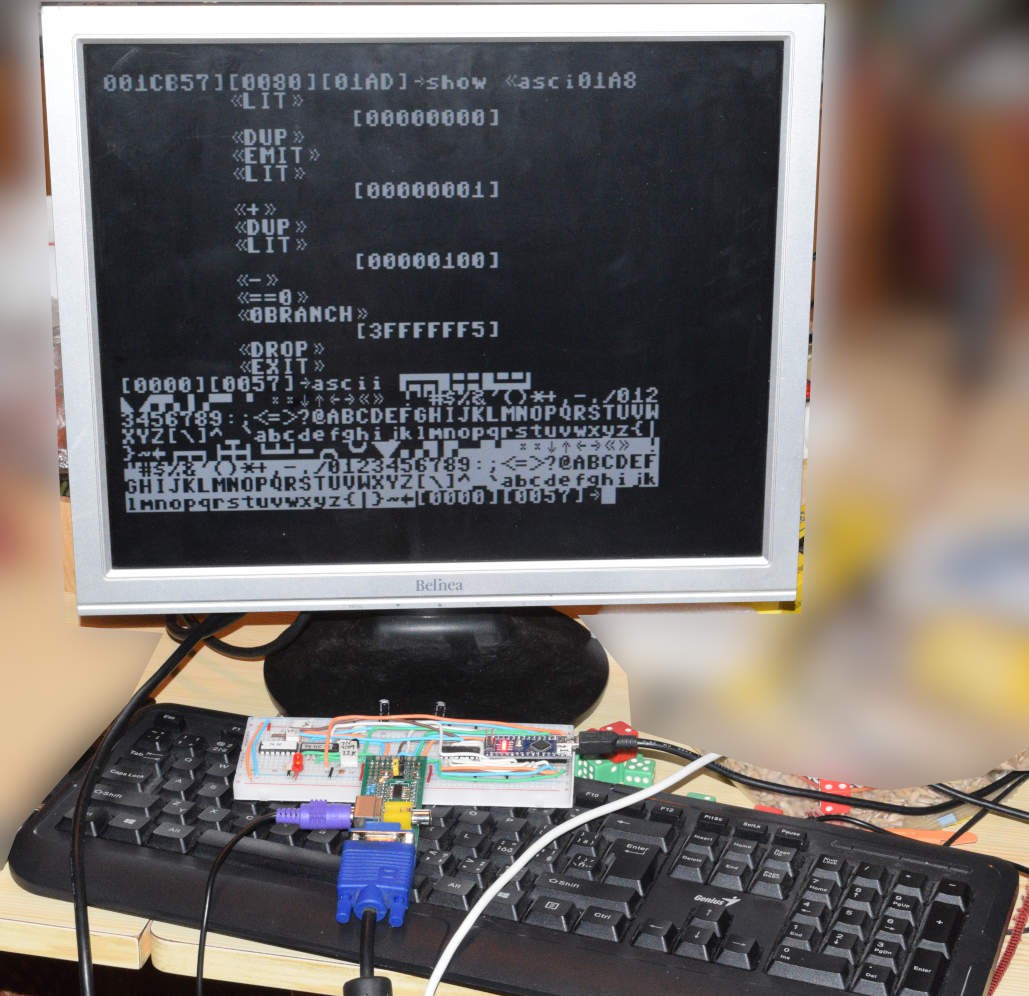
Here is 3D model, how it will look fully assembled:
![]()
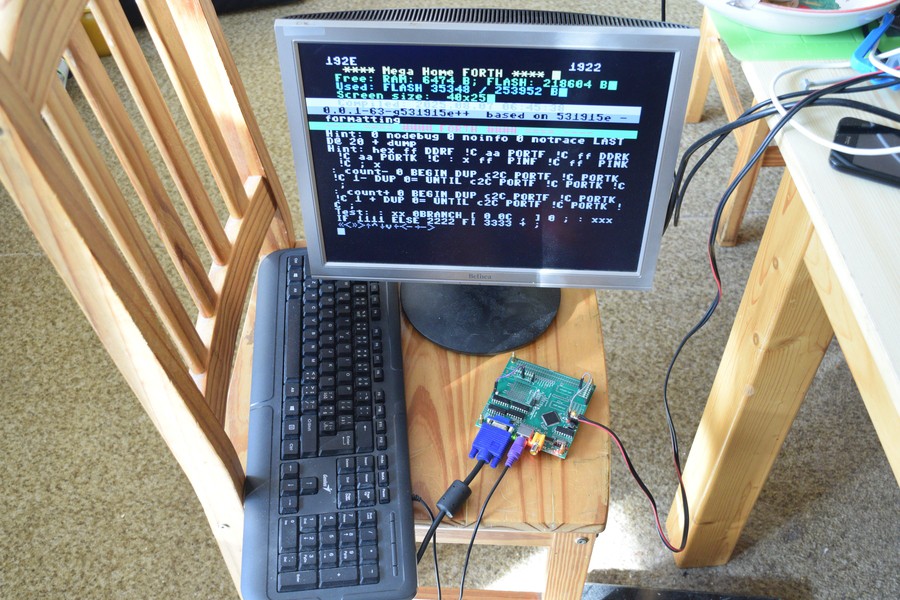
I am looking for bring real photo soon :)
MHF-002 (Mega Home FORTH)
ATmega2560 based SBC with VGA, PS/2 and SD cards - meant to run FORTH now and serve as graphic card later.
 Gilhad
Gilhad |SystemBus-schema.png|
|SystemBus-schema.png|
 |USB-Serial_pinhead.png|
|USB-Serial_pinhead.png|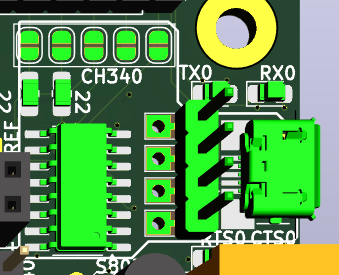
 |USB-Serial_CP2102_bottom.png|
|USB-Serial_CP2102_bottom.png|






 |config_HALT_bottom.png|
|config_HALT_bottom.png|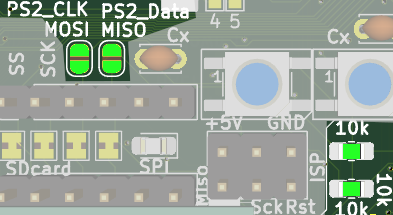
 Debug LEDs are only on top of PCB (and I did not found more place for them, so I did not place there more of them). There are their numbers, you may populate just few with lower numbers
Debug LEDs are only on top of PCB (and I did not found more place for them, so I did not place there more of them). There are their numbers, you may populate just few with lower numbers 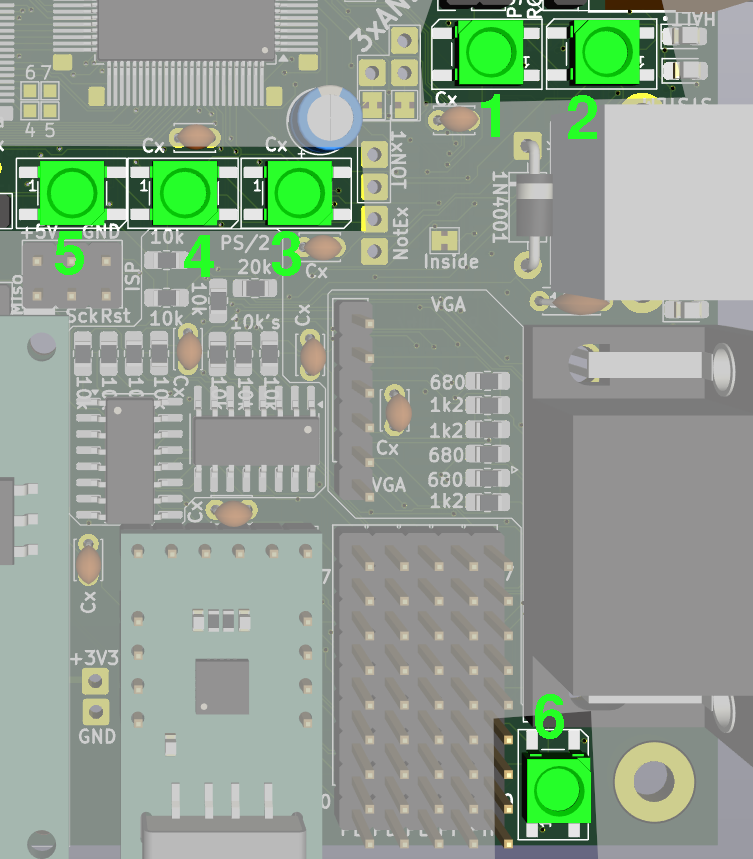



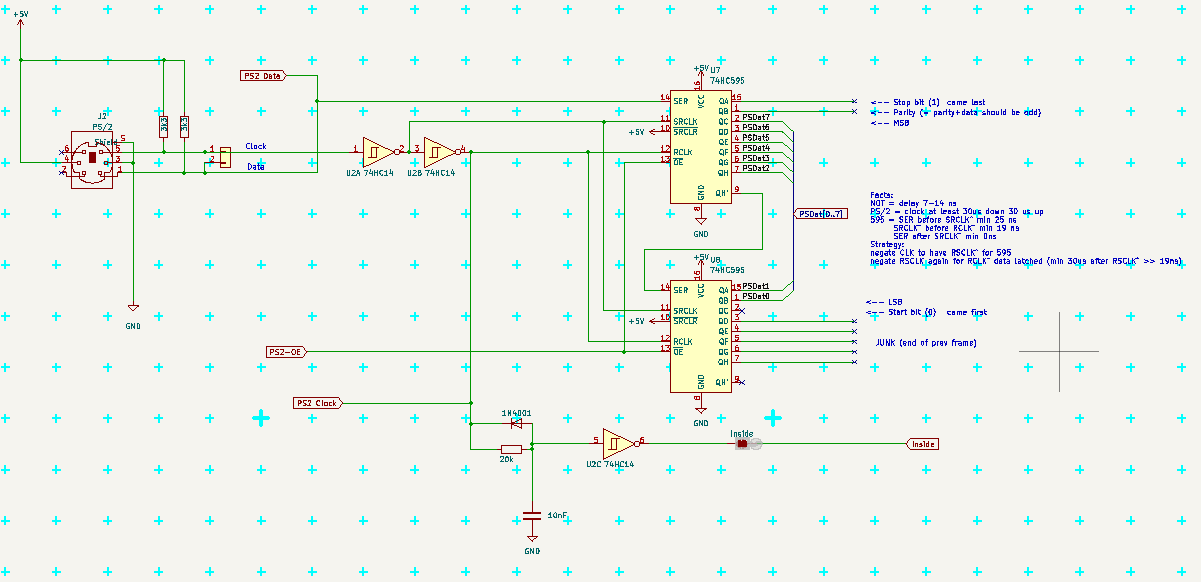 Connection to data:
Connection to data: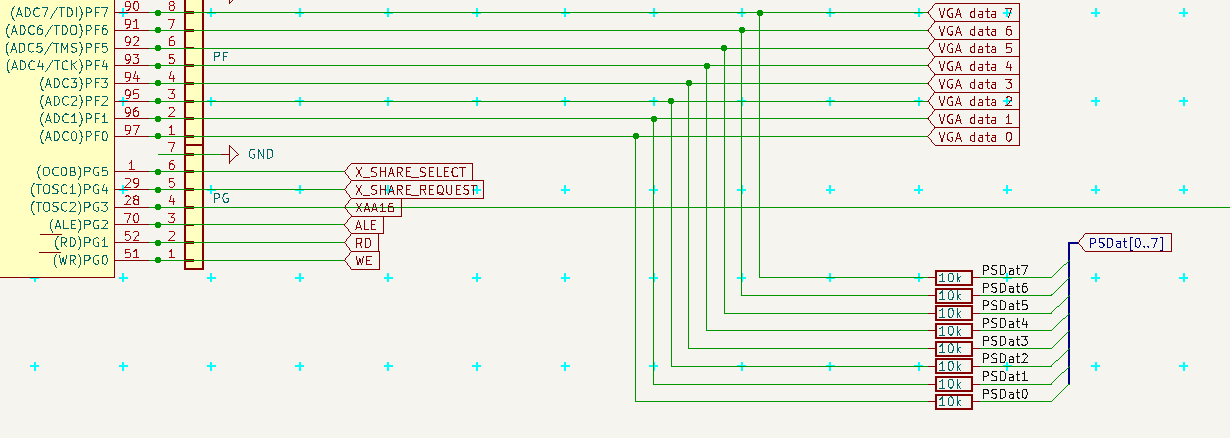


 Bottom:
Bottom:
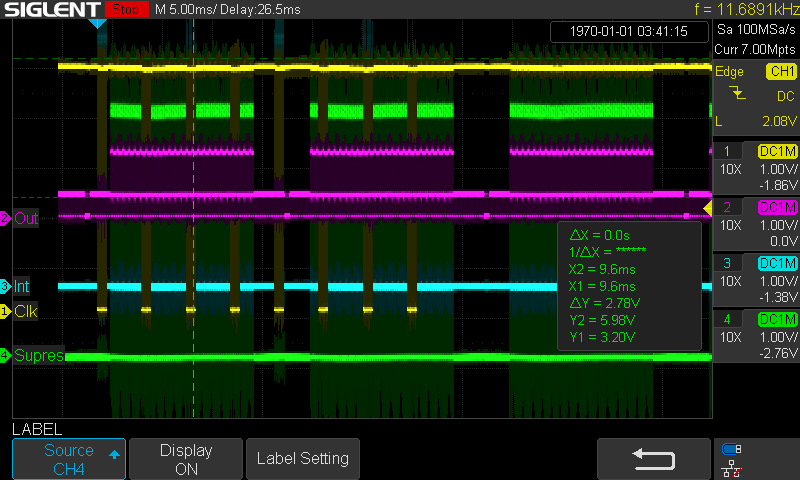
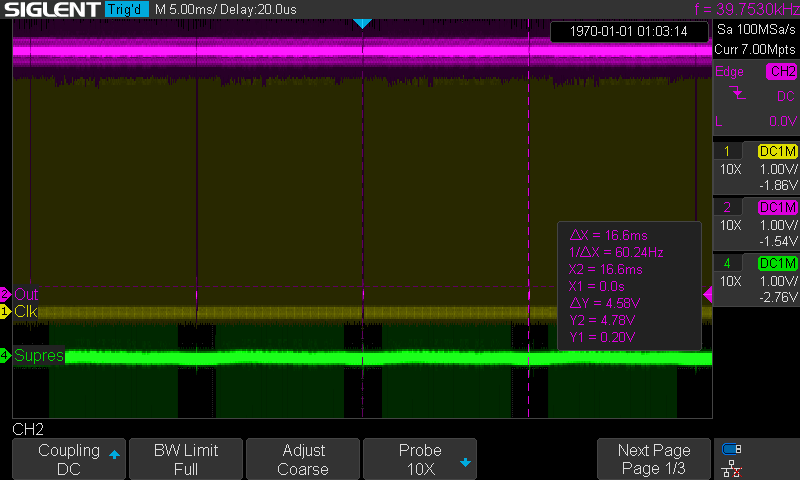 (4 screens at 60Hz)
(4 screens at 60Hz)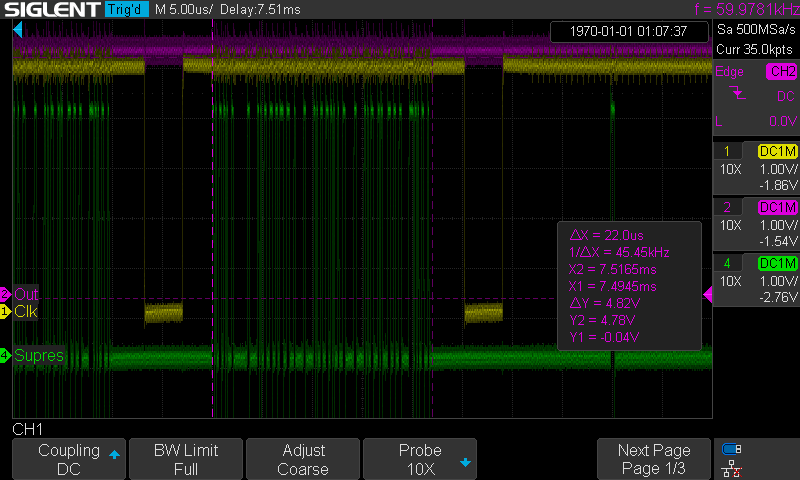 (1 line with pixels, 32uS)
(1 line with pixels, 32uS)