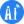
1. Running the Example
cd ~/mcu/Ameba-rtos/ameba-rtos
source ameba.sh
cd amebadplus_gcc_project
1) Configure using menuconfig.py
CONFIG BT ---> [*] Enable BT ---> [*]BT Example Demo --> [*] BLE Peripheral
2) Build and Flash
build.py flash.py -p /dev/ttyCH341USB0
3) Run
Open a serial tool with baud rate 1500000. To enable BLE Peripheral mode, send the AT command:
AT+BTDEMO=peripheral,1
You will see several SERVICES become active:
Open a BLE debugging app on your phone: Search for RTK_BT_PEIPHERA and connect.
You will see the services provided by the example, and you can read a characteristic:
2. Feature Expansion
In the original example, BLE Peripheral must be enabled using an AT command, which is not convenient.
1) Enable BLE Peripheral in Code
cd ~/mcu/Ameba-rtos/ameba-rtos/component/bluetooth/example/ble_peripheralCreate two new files: ble_led.c and ble_led.h
ble_led.c
#include "platform_autoconf.h"#include "ameba_soc.h"#include "os_wrapper.h"#include "ble_led.h"
extern int ble_peripheral_main(uint8_t enable);
void raw_gpio_demo(void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct_LED;
// init LED control pins
GPIO_InitStruct_LED.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_LED_PIN1;
GPIO_InitStruct_LED.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_OUT;
GPIO_Init(&GPIO_InitStruct_LED);
GPIO_InitStruct_LED.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_LED_PIN2;
GPIO_Init(&GPIO_InitStruct_LED);
GPIO_InitStruct_LED.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_LED_PIN3;
GPIO_Init(&GPIO_InitStruct_LED);
GPIO_InitStruct_LED.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_LED_PIN4;
GPIO_Init(&GPIO_InitStruct_LED);
GPIO_InitStruct_LED.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_LED_PIN5;
GPIO_Init(&GPIO_InitStruct_LED);
// Enable BLE Peripheral mode
ble_peripheral_main(1);
rtos_task_delete(NULL);
}
void app_example(void)
{
if (RTK_SUCCESS != rtos_task_create(NULL, "RAW_GPIO_DEMO_TASK",
(rtos_task_t)raw_gpio_demo, (void *)NULL, (128 * 16), (1))) {
printf("Create RAW_GPIO_DEMO_TASK Err!!!\n");
}
}
void turn_off_leds(void)
{
GPIO_WriteBit(GPIO_LED_PIN1, 0);
GPIO_WriteBit(GPIO_LED_PIN2, 0);
GPIO_WriteBit(GPIO_LED_PIN3, 0);
GPIO_WriteBit(GPIO_LED_PIN4, 0);
GPIO_WriteBit(GPIO_LED_PIN5, 0);
}
void set_led(uint8_t i, u32 val)
{
switch (i) {
case 1: GPIO_WriteBit(GPIO_LED_PIN1, val); break;
case 2: GPIO_WriteBit(GPIO_LED_PIN2, val); break;
case 3: GPIO_WriteBit(GPIO_LED_PIN3, val); break;
case 4: GPIO_WriteBit(GPIO_LED_PIN4, val); break;
case 5: GPIO_WriteBit(GPIO_LED_PIN5, val); break;
}
}
This enables BLE Peripheral automatically by calling:
ble_peripheral_main(1);
ble_led.h
#ifndef BLE_LED_H#define BLE_LED_H
#include "ameba_soc.h"
#define GPIO_LED_PIN1 _PB_17#define GPIO_LED_PIN2 _PB_18#define GPIO_LED_PIN3 _PB_19#define GPIO_LED_PIN4 _PB_20#define GPIO_LED_PIN5 _PB_21
void turn_off_leds(void);void set_led(uint8_t i, u32 val);
#endif
Add ble_led.c to CMakeLists.txt
ameba_list_append...
Read more »
 Ai-Thinker
Ai-Thinker
 Mahesh Venkitachalam
Mahesh Venkitachalam
 Guillermo Perez Guillen
Guillermo Perez Guillen