ADULTERATION
The Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic (FD&C) Act 2888) states that food is "adulterated" if it meets any one of the following criteria:
- It bears or contains any "poisonous or deleterious substance" which may render it injurious to health.
- It bears or contains any added poisonous or added deleterious substance (other than a pesticide, food additive, color additive, or new animal drug, which are covered by separate provisions) that is unsafe.
- Its container is composed, in whole or in part, of any poisonous or deleterious substance which may render the contents injurious to health.
- It bears or contains a pesticide chemical residue that is unsafe.
Food also meets the definition of adulteration if:
- It is, or it bears or contains, an unsafe food additive.
- It is, or it bears or contains, an unsafe new animal drug.
- It is, or it bears or contains, an unsafe color additive.
- It consists, in whole or in part, of "any filthy, putrid, or decomposed substance" or is otherwise unfit for food.
Further, food is considered adulterated if:
- It has been irradiated and the irradiation processing was not done in conformity with a regulation permitting irradiation of the food in question.
- It contains a dietary ingredient that presents a significant or unreasonable risk of illness or injury under the conditions of use recommended in labeling (for example, foods or dietary supplements containing aristolochic acids, which have been linked to kidney failure, have been banned).
- A valuable constituent has been omitted in whole or in part or replaced with another substance; damage or inferiority has been concealed in any manner; or a substance has been added to increase the product's bulk or weight, reduce its quality or strength, or make it appear of greater value than it is.
- It is offered for import into the United States and is a food that has previously been refused admission, unless the person reoffering the food establishes that it is in compliance with U.S. law [21 U.S.C. § 342].
AVAILABLE METHODS FOR DETECTING ADULTERATION
Milk: Add a drop or two of iodine solution to a few drops of milk. If the solution turns blue then, it contains starch (which is used to give it a thick, rich texture).
Butter/ghee: Take small amount of ghee or butter in test-tube and heat it up. Take a small amount of sugar and dissolve it in 10 ml of hydrochloric acid (Hcl). Now, add the solution to the mixture of butter and ghee. If it turns red, then the ghee or butter is adulterated.
Mustard oil: Take small amount of mustard oil in a test-tube, add a few drops of nitric acid to it. Shake and heat the mixture for 2-3 minutes. Appearance of red colour indicates that argemone oil is added to mustard oil.
Turmeric powder, dals and pulses: Take a spoon of dal, turmeric or besan powder and let it dissolve in lukewarm water. Add a few drops of hydrochloric acid to it. If it turns pink, violet or purple, it shows that Metanil yellow is present in it.
Sugar: Take a spoon of sugar, dissolve it in water and allow it to settle. While sugar will dissolve in water, chalk will not and thus will remain as residue at the bottom.

PROPOSED SOLUTION
This "AI based adulteration detector" device consists of a micro-controller, a camera module and power supply. The OS must be programmed in a such a way that it must start image processing as soon as the device is powered up. The High Definition (HD) pictures of original and pure substances are obtained and their characteristics & properties are analysed and these data are stored in the SD card of Raspberry Pi. The pictures of test samples are then captured through an camera module attached to that of Raspberry Pi. Several filters are applied to the test sample because various...
Read more » G.Vignesh
G.Vignesh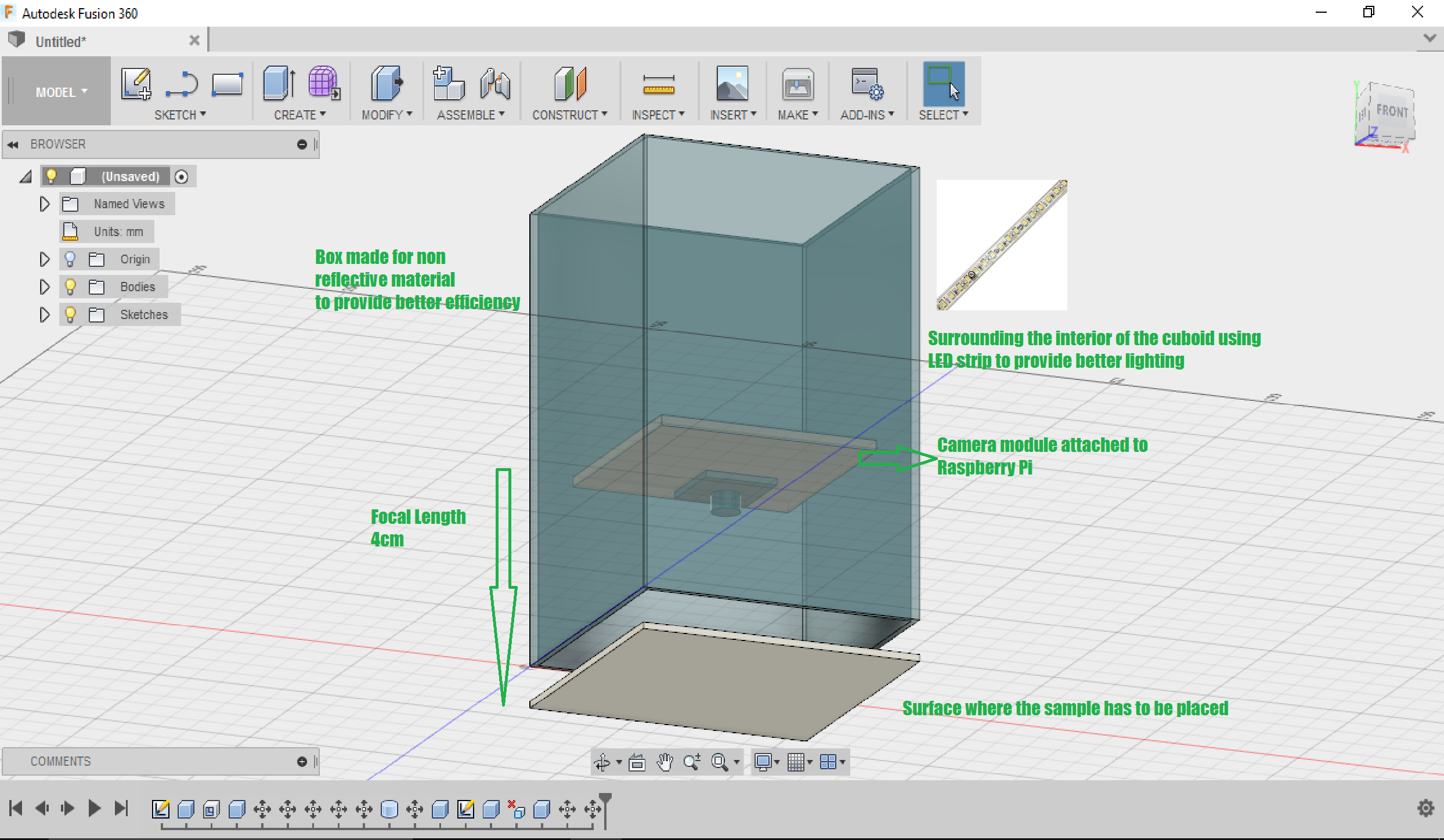


 To install the camera support enter the code in a terminal.
To install the camera support enter the code in a terminal.






















 hanno
hanno
 Eugene
Eugene
 Myrijam
Myrijam
 vedanshi.shah
vedanshi.shah
Perfect project man, Can you tell us more about the program and dataset you used to train the model? Thank you