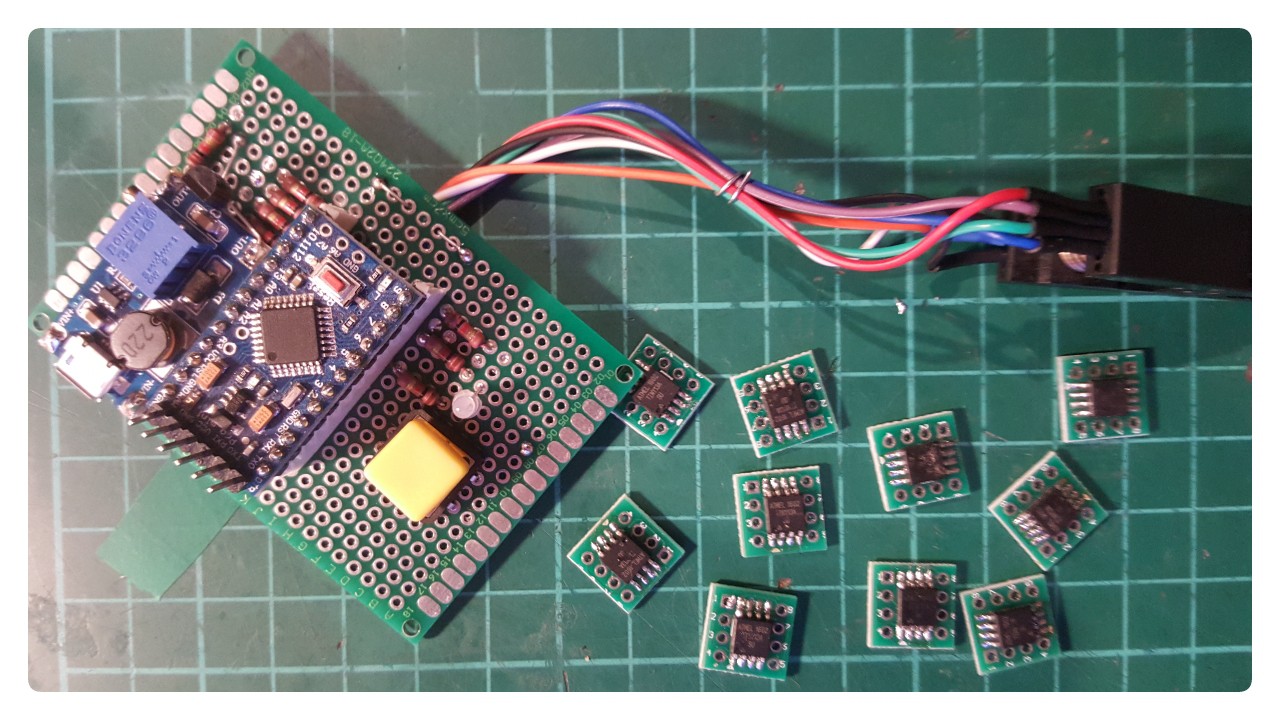
to fix almost all my tiny13a's I had to build this, but it definitely fixed all 10 boards :) for the tinies you don't need any parallel connections, so it's basically SPI + 12V on reset. I've hooked up a boost converter, added a button and "some" LEDs (bicolor), worked them in the code and now basically have a "power on and fix" stand alone fuse resetter for soic Attinies. That's not highly specialised at all. BUT IT WORKS AND THEY WORK! Now I need to clean up my desk.
http://www.engbedded.com/fusecalc/
https://arduinodiy.wordpress.com/2015/05/16/high-voltage-programmingunbricking-for-attiny/
// AVR High-voltage Serial Fuse Reprogrammer
// Adapted from code and design by Paul Willoughby 03/20/2010
// http://www.rickety.us/2010/03/arduino-avr-high-voltage-serial-programmer/
// Fuse Calc:
// http://www.engbedded.com/fusecalc/
// slightly edited by davedarko in 2017
#define RST 13 // Output to level shifter for !RESET from transistor
#define SCI 12 // Target Clock Input
#define SDO 11 // Target Data Output
#define SII 10 // Target Instruction Input
#define SDI 9 // Target Data Input
#define VCC 8 // Target VCC
#define BUTTON 3 // Target VCC
#define LED_RED 7 // Target VCC
#define LED_GRN 5 // Target VCC
#define HFUSE 0x747C
#define LFUSE 0x646C
#define EFUSE 0x666E
// Define ATTiny series signatures
#define ATTINY13 0x9007 // L: 0x6A, H: 0xFF 8 pin
#define ATTINY24 0x910B // L: 0x62, H: 0xDF, E: 0xFF 14 pin
#define ATTINY25 0x9108 // L: 0x62, H: 0xDF, E: 0xFF 8 pin
#define ATTINY44 0x9207 // L: 0x62, H: 0xDF, E: 0xFFF 14 pin
#define ATTINY45 0x9206 // L: 0x62, H: 0xDF, E: 0xFF 8 pin
#define ATTINY84 0x930C // L: 0x62, H: 0xDF, E: 0xFFF 14 pin
#define ATTINY85 0x930B // L: 0x62, H: 0xDF, E: 0xFF 8 pin
void setup() {
pinMode(BUTTON, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(LED_GRN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED_RED, OUTPUT);
pinMode(VCC, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RST, OUTPUT);
pinMode(SDI, OUTPUT);
pinMode(SII, OUTPUT);
pinMode(SCI, OUTPUT);
pinMode(SDO, OUTPUT); // Configured as input when in programming mode
digitalWrite(RST, HIGH); // Level shifter is inverting, this shuts off 12V
Serial.begin(19200);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(LED_GRN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(LED_RED, LOW);
if (digitalRead(BUTTON) == LOW)
{
digitalWrite(LED_GRN, LOW);
digitalWrite(LED_RED, HIGH);
pinMode(SDO, OUTPUT); // Set SDO to output
digitalWrite(SDI, LOW);
digitalWrite(SII, LOW);
digitalWrite(SDO, LOW);
digitalWrite(RST, HIGH); // 12v Off
digitalWrite(VCC, HIGH); // Vcc On
delayMicroseconds(20);
digitalWrite(RST, LOW); // 12v On
delayMicroseconds(10);
pinMode(SDO, INPUT); // Set SDO to input
delayMicroseconds(300);
unsigned int sig = readSignature();
Serial.print("Signature is: ");
Serial.println(sig, HEX);
readFuses();
if (sig == ATTINY13) {
writeFuse(LFUSE, 0x6A);
writeFuse(HFUSE, 0xFF);
} else if (sig == ATTINY24 || sig == ATTINY44 || sig == ATTINY84 ||
sig == ATTINY25 || sig == ATTINY45 || sig == ATTINY85) {
writeFuse(LFUSE, 0x62);
writeFuse(HFUSE, 0xDF);
writeFuse(EFUSE, 0xFF);
}
readFuses();
digitalWrite(SCI, LOW);
digitalWrite(VCC, LOW); // Vcc Off
digitalWrite(RST, HIGH); // 12v Off
delay(1000);
}
}
byte shiftOut (byte val1, byte val2) {
int inBits = 0;
//Wait until SDO goes high
while (!digitalRead(SDO))
;
unsigned int dout = (unsigned int) val1 << 2;
unsigned int iout = (unsigned int) val2 << 2;
for (int ii = 10; ii >= 0; ii--) {
digitalWrite(SDI, !!(dout & (1 << ii)));
digitalWrite(SII, !!(iout & (1 << ii)));
inBits <<= 1; inBits |= digitalRead(SDO);
digitalWrite(SCI, HIGH);
digitalWrite(SCI, LOW);
}
return inBits >> 2;
}
void writeFuse (unsigned int fuse, byte val) {
shiftOut(0x40, 0x4C);
shiftOut( val, 0x2C);
shiftOut(0x00, (byte) (fuse >> 8));
shiftOut(0x00, (byte) fuse);
}
void readFuses () {
byte val;
shiftOut(0x04, 0x4C); // LFuse
shiftOut(0x00, 0x68);
val = shiftOut(0x00, 0x6C);
Serial.print("LFuse "); // this line may show up corrupted in some browsers it is a Serial.print("LFuse: ");
Serial.print(val, HEX);
shiftOut(0x04, 0x4C); // HFuse
shiftOut(0x00, 0x7A);
val = shiftOut(0x00, 0x7E);
Serial.print(", HFuse: ");
Serial.print(val, HEX);
shiftOut(0x04, 0x4C); // EFuse
shiftOut(0x00, 0x6A);
val = shiftOut(0x00, 0x6E);
Serial.print(", EFuse: ");
Serial.println(val, HEX);
}
unsigned int readSignature () {
unsigned int sig = 0;
byte val;
for (int ii = 1; ii < 3; ii++) {
shiftOut(0x08, 0x4C);
shiftOut( ii, 0x0C);
shiftOut(0x00, 0x68);
val = shiftOut(0x00, 0x6C);
sig = (sig << 8) + val;
}
return sig;
} davedarko
davedarko
Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.
I've set AVR clocks too slow before and had to slow AVRDUDE down. The -B option works wonders. There's an app note somewhere, but I vaguely remember something about keeping the period longer than 4 clock cycles. Or maybe it was 16... Anyway, you're just changing the fuse bits, so going infinitely slow doesn't hurt much.
Still, a HV programmer is a good thing to have because as Radomir points out, it gets you and extra 20% usable GPIO pins on the tiny-Tinies.
Are you sure? yes | no
Yeah, I wasn't sure what was wrong at all, until the fuse resetter showed me the previous fuse settings and after I put them into the fuse calculator. At this point I was all setup and didn't think of anything else. My usbasp gives me a warning that it can't set clock speeds and I need to update, so I'm not sure the -B option works... I don't know.
Are you sure? yes | no
Cool, now you can use that RST pin as GPIO too!
Are you sure? yes | no
Interesting that this fixes all of them :)
Could it be they sold them so cheaply because they were "faulty" devices?
Are you sure? yes | no
They were all set to 0x63 on the low fuse, making them run on 128kHz - that's something that my USBASP can't handle, as it seems :) I think with a slow SCLK it would have worked to recover them, not sure though.. anyway, I'm pretty happy that they're all fine and for the future I'm prepared :)
Not sure about the 'sold faulty', they might have... but then again they also work.
Are you sure? yes | no