-
1Step 1
Cannon code-
#include "Servo.h" // include the servo library
Servo armServo; // servo to raise the arm
Servo cannonServo; // servo to recoil cannon
// these constants won't change:
const int triggerSensor = 1; // the sensor is connected to analog pin 1
const int threshold = 36; // threshold value to decide when the sensor input triggers
const int servoPin1 = 9; // control pin for arm servo
const int servoPin2 = 6; // control pin for cannon servo
const int lasersightPin = 11; // control pin for laser sight
const int ledPin = 3; // control pin for cannon power up/down LED
const int ledPin1 = 12; // control pin for cannon firing LED
const int soundPin = 10; // control pin for sound board
const int powerPin = 2;
// these variables will change:
int sensorReading = 0; // variable to store the value read from the sensor pin
int ledState = LOW; // variable used to store the last LED status, to toggle the light
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // use the serial port
armServo.attach(servoPin1); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
cannonServo.attach(servoPin2); // attaches the servo on pin 6 to the servo object
pinMode(lasersightPin, OUTPUT); // sets the laser sight pin as an output
digitalWrite(lasersightPin, LOW); // turns off the laser sight pin
pinMode(soundPin, OUTPUT); // sets the sound pin as output
digitalWrite(soundPin, LOW); // turns off sound pin
digitalWrite(ledPin1, OUTPUT); // sets cannon firing LED pin as output
digitalWrite(ledPin1, LOW); // turns off the firing LED
digitalWrite(powerPin, OUTPUT); // sets the servo power pin as output
digitalWrite(powerPin, LOW); // turns off the servo power pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(powerPin, HIGH);
armServo.write(100);
cannonServo.write(63);
// read the sensor and store it in the variable sensorReading:
sensorReading = analogRead(triggerSensor);
// if the sensor reading is less than the threshold:
if (sensorReading <= threshold) {
digitalWrite(soundPin, HIGH); // turn the sound on
delay(10); // wait ten milliseconds
digitalWrite(soundPin, LOW); // turn the sound off
// fade in from min to max in increments of 1 point:
for(int fadeValue = 0 ; fadeValue <= 255; fadeValue +=3) {
// sets the value (range from 0 to 255):
analogWrite(ledPin, fadeValue);
// wait for 30 milliseconds to see the dimming effect
delay(30);
}
delay(3000);
digitalWrite(lasersightPin, HIGH); // turn on the laser sight
armServo.write(50); // raise cannon arm
cannonServo.write(125); // slide barrel forward
delay(3000);
digitalWrite(ledPin1, HIGH);
cannonServo.write(63);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(ledPin1, LOW);
delay(700);
cannonServo.write(125);
delay(3000);
digitalWrite(ledPin1, HIGH);
cannonServo.write(63);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(ledPin1, LOW);
delay(700);
cannonServo.write(125);
delay(3000);
digitalWrite(ledPin1, HIGH);
cannonServo.write(63);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(ledPin1, LOW);
delay(700);
cannonServo.write(125);
delay(3000);
digitalWrite(lasersightPin, LOW);
cannonServo.write(63);
armServo.write(100);
delay(3000);
// fade out from max to min in increments of 1 point:
for(int fadeValue = 255 ; fadeValue >= 0; fadeValue -=3) {
// sets the value (range from 0 to 255):
analogWrite(ledPin, fadeValue);
// wait for 30 milliseconds to see the dimming effect
delay(30);
}
digitalWrite(powerPin, LOW);
}
}
WaveShield code (courtesy of Adafruit)-
#include <FatReader.h>
#include <SdReader.h>
#include <avr/pgmspace.h>
#include "WaveUtil.h"
#include "WaveHC.h"
SdReader card; // This object holds the information for the card
FatVolume vol; // This holds the information for the partition on the card
FatReader root; // This holds the information for the filesystem on the card
FatReader f; // This holds the information for the file we're play
WaveHC wave; // This is the only wave (audio) object, since we will only play one at a time
#define DEBOUNCE 100 // button debouncer
// this handy function will return the number of bytes currently free in RAM, great for debugging!
int freeRam(void)
{
extern int __bss_end;
extern int *__brkval;
int free_memory;
if((int)__brkval == 0) {
free_memory = ((int)&free_memory) - ((int)&__bss_end);
}
else {
free_memory = ((int)&free_memory) - ((int)__brkval);
}
return free_memory;
}
void sdErrorCheck(void)
{
if (!card.errorCode()) return;
putstring("\n\rSD I/O error: ");
Serial.print(card.errorCode(), HEX);
putstring(", ");
Serial.println(card.errorData(), HEX);
while(1);
}
void setup() {
// set up serial port
Serial.begin(9600);
putstring_nl("WaveHC with 6 buttons");
putstring("Free RAM: "); // This can help with debugging, running out of RAM is bad
Serial.println(freeRam()); // if this is under 150 bytes it may spell trouble!
// Set the output pins for the DAC control. This pins are defined in the library
pinMode(2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(4, OUTPUT);
pinMode(5, OUTPUT);
// pin13 LED
pinMode(13, OUTPUT);
// enable pull-up resistors on switch pins (analog inputs)
digitalWrite(14, HIGH);
digitalWrite(15, HIGH);
digitalWrite(16, HIGH);
digitalWrite(17, HIGH);
digitalWrite(18, HIGH);
digitalWrite(19, HIGH);
// if (!card.init(true)) { //play with 4 MHz spi if 8MHz isn't working for you
if (!card.init()) { //play with 8 MHz spi (default faster!)
putstring_nl("Card init. failed!"); // Something went wrong, lets print out why
sdErrorCheck();
while(1); // then 'halt' - do nothing!
}
// enable optimize read - some cards may timeout. Disable if you're having problems
card.partialBlockRead(true);
// Now we will look for a FAT partition!
uint8_t part;
for (part = 0; part < 5; part++) { // we have up to 5 slots to look in
if (vol.init(card, part))
break; // we found one, lets bail
}
if (part == 5) { // if we ended up not finding one :(
putstring_nl("No valid FAT partition!");
sdErrorCheck(); // Something went wrong, lets print out why
while(1); // then 'halt' - do nothing!
}
// Lets tell the user about what we found
putstring("Using partition ");
Serial.print(part, DEC);
putstring(", type is FAT");
Serial.println(vol.fatType(),DEC); // FAT16 or FAT32?
// Try to open the root directory
if (!root.openRoot(vol)) {
putstring_nl("Can't open root dir!"); // Something went wrong,
while(1); // then 'halt' - do nothing!
}
// Whew! We got past the tough parts.
putstring_nl("Ready!");
}
void loop() {
//putstring("."); // uncomment this to see if the loop isnt running
switch (check_switches()) {
case 1:
playcomplete("SOUND1.WAV");
break;
case 2:
playcomplete("SOUND2.WAV");
break;
case 3:
playcomplete("SOUND3.WAV");
break;
case 4:
playcomplete("SOUND4.WAV");
break;
case 5:
playcomplete("SOUND5.WAV");
break;
case 6:
playcomplete("SOUND6.WAV");
}
}
byte check_switches()
{
static byte previous[6];
static long time[6];
byte reading;
byte pressed;
byte index;
pressed = 0;
for (byte index = 0; index < 6; ++index) {
reading = digitalRead(14 + index);
if (reading == LOW && previous[index] == HIGH && millis() - time[index] > DEBOUNCE)
{
// switch pressed
time[index] = millis();
pressed = index + 1;
break;
}
previous[index] = reading;
}
// return switch number (1 - 6)
return (pressed);
}
// Plays a full file from beginning to end with no pause.
void playcomplete(char *name) {
// call our helper to find and play this name
playfile(name);
while (wave.isplaying) {
// do nothing while its playing
}
// now its done playing
}
void playfile(char *name) {
// see if the wave object is currently doing something
if (wave.isplaying) {// already playing something, so stop it!
wave.stop(); // stop it
}
// look in the root directory and open the file
if (!f.open(root, name)) {
putstring("Couldn't open file "); Serial.print(name); return;
}
// OK read the file and turn it into a wave object
if (!wave.create(f)) {
putstring_nl("Not a valid WAV"); return;
}
// ok time to play! start playback
wave.play();
}
-
2Step 2
Animatronic AVP Predator cannon
An animatronic display piece that is activated by an ultrasonic sensor
 jeromekelty
jeromekelty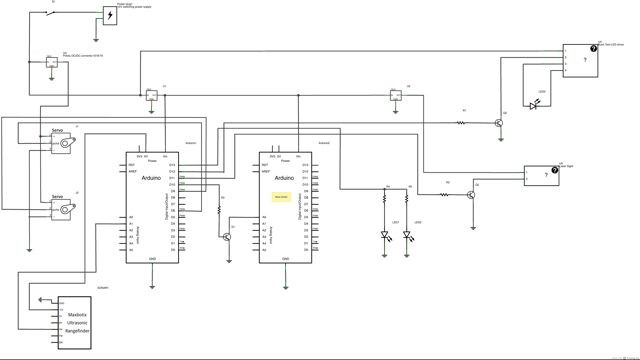
Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.