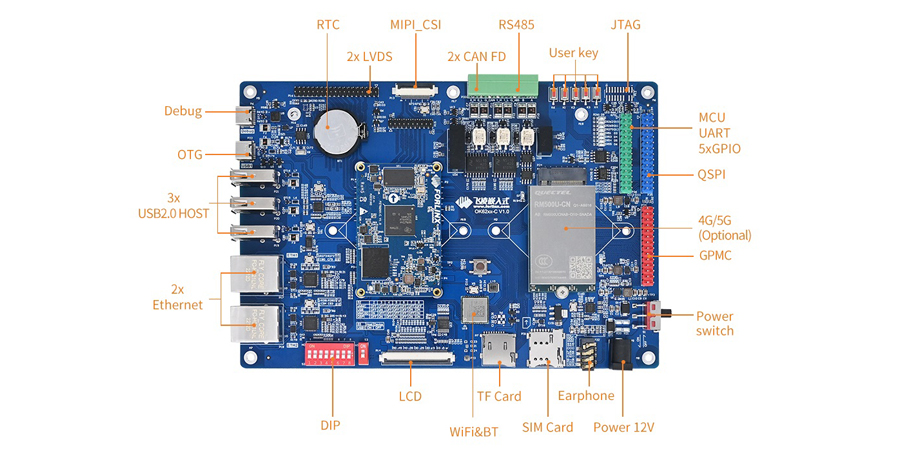
-
Guide to Porting and Configuring Nginx on OKMX6ULx Embedded Linux (Kernel 4.1.15)
5 days ago • 0 commentsNginx (engine x) is an open-source, high-performance Web server, reverse proxy server, load balancer, and HTTP cache server. It is characterized by low memory usage and strong concurrency ability. In fact, Nginx performs well in terms of concurrency among web servers of the same type. It is developed using the C programming language.
Nginx is specifically developed for performance optimization. Performance is an important consideration in its design. It focuses highly on efficiency in implementation and can withstand high-load tests, supporting up to 50,000 concurrent connections.
1. Compilation and Porting
1.1 Compile nginx-1.8 in Yocto
Execute the following commands for compilation:
$ DISTRO=fsl-imx-x11 MACHINE=imx6ull14x14evk source fsl-setup-release.sh -b build_x11 $ bitbake nginx
During the compilation process, the following errors appeared:
Solution:
Modify the build_x11/conf/bblayers.conf file and add the source code path of Nginx to the file. build_x11 is the installation and compilation path defined by yourself.
Modify the content as follows:
After adding, execute bitbake nginx again for compilation.
1.2 Package the Image
After compilation, go to the
build_x11/tmp/work/cortexa7hf-neon-poky-linux-gnueabi/nginx/1.8.1-r0/image
path to package the image.
$ cd tmp/work/cortexa7hf-neon-poky-linux-gnueabi/nginx/1.8.1-r0/image $ tar -cjvf nginx-1.8.1.tar.bz2 *
1.3 Transplant
Extract the image packaged in the previous step to the root path of the system.
tar -xvf nginx-1.8.1.tar.bz2 -C /
2. Test
2.1 Reverse Proxy
2.1.1 Tomcat Installation
① Install the JDK environment
Download address: Oracle JDK 8 Downloads
Download the following two files:
jdk-8u151-linux-arm32-vfp-hflt.tar.gz
and
jdk-8u151-linux-arm32-vfp-hflt-demos.tar.gz
Extract them to the development board:
Extract the above two compressed packages to /home/root/jdk1.8.0_151.
Modify the environment variables:
Add the following content at the end of the /etc/profile file:
JAVA_HOME=/home/root/jdk1.8.0_151 CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/rt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH export JAVA_HOME CLASSPATH PATH
Execute the following command to make the environment variables take effect immediately:
$ source /etc/profile
Verify whether the installation is successful:
Enter the following command to check the Java version:
$ java -version
② Install Tomcat
Download the source code: Tomcat 9.0 Downloads. Here, download version 9.0.108.
Extract the downloaded
apache-tomcat-9.0.108.tar.gz
to the
/home/root
path on the development board.
tar -xvf apache-tomcat-9.0.108.tar.gz -C /home/root
Start the Tomcat service:
cd /home/root/apache-tomcat-9.0.108/bin ./startup.sh
After starting, enter 192.168.1.13:8080 in the browser, and the Tomcat interface will be displayed.
2.1.2 Modify Nginx Configuration
Modify the /etc/nginx/nginx.conf file:
server { listen 80; server_name www.123.com; location / { proxy_pass http://192.168.1.13:8080/; index index.html index.htm; } }- listen: It indicates that the port 80 is monitored.
- server_name: The access domain name is defined here.
- proxy_pass: It is a proxy forwarding module. Its main function is to forward www.123.com requests to http://192.168.1.13:8080/.
Start the Nginx service:
mkdir /run/nginx nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Modify the hosts file in Windows:
Press Win + S, run Notepad as an administrator, open the hosts file under C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc, and add the mapping.
Test:
Enter www.123.com in the browser, and you can access the Tomcat interface via Nginx.
2.2 Load Balancing
1. Setup Service 8080:
Rename the above-mentioned apache-tomcat to apache-tomcat8080, and create a test file:
mv apache-tomcat-9.0.108/ apache-tomcat8080/ cd apache-tomcat8080/webapps mkdir test vi test.html
<!--apache8080--> <html> <body>welcome to service 8080</body> </html>
2. Setup...
Read more -
Guide to TFTP Flashing the File System on Forlinx Embedded RK3568 Development Board
5 days ago • 0 commentsThe test is conducted using the standard development environment of Linux 4.19.206 on the OK3568-C development board, which is equipped with the Rockchip RK3568 processor. It has a stable network foundation and can meet the transmission requirements of the TFTP protocol. During the testing, the TFTP server was deployed on the Ubuntu system. Ubuntu and the RK3568 development board were configured in the bridge mode (by leveraging the hardware advantage of the dual network interfaces on the development board, the network transmission latency can be reduced). The server address was set to 172.16.0.177.
Make sure to place the system images (boot.img and rootfs.img) in the TFTP server directory beforehand. Additionally, verify that there is a proper network connection between the development board and the server, as this is essential for the process to run smoothly.
Forlinx RK3568 SoM
1. Configuring U-Boot Environment Variables for Network Access
The Uboot environment configuration of the RK3568 development board is simple and intuitive. Coupled with the on-board Type - C Debug interface (which integrates a USB - to - serial chip, eliminating the need for an additional adapter), developers can quickly enter the Uboot command line through terminal tools (such as SecureCRT and Xshell) to complete the network parameter configuration.
Operation tips: The default baud rate of the Type - C Debug interface is 115200bps, with 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and no parity check. After connecting, restart the development board to enter the Uboot command line.
=> setenv ethaddr 22:51:a2:cc:47:2d # Set the Ethernet MAC address of the development board to ensure a unique network identity => setenv ipaddr 172.16.0.176 # Configure the static IP of the development board, which should be in the same network segment as the server => setenv gatewayip 172.16.0.218 # Set the gateway address to ensure cross - network segment communication (if needed) => setenv netmask 255.255.0.0 # Configure the subnet mask to match the LAN network segment planning => saveenv # Save the environment variables to the eMMC to prevent data loss after restart Saving Environment to ENV_BLK… Saving Environment to ENV_BLK... Writing to mmc(0)... done # Verify network connectivity: first ping the real machine, then ping the Ubuntu server => ping 172.16.0.77 # Test the network connectivity between the development board and the real machine ethernet@fe2a0000 Waiting for PHY auto negotiation to complete. done Using ethernet@fe2a0000 device host 172.16.0.77 is alive => ping 172.16.0.177 # Crucial step: verify the connectivity with the TFTP server (if it fails, check the VMware bridge mode or the network cable connection of the development board) Using ethernet@fe2a0000 device host 172.16.0.177 is alive => setenv serverip 172.16.0.177 # Specify the IP of the TFTP server, and subsequent transmissions will default to this address => saveenv Saving Environment to ENV_BLK... Writing to mmc(0)... done
Note: If pinging the server fails, you need to prioritize the following checks:
- Whether the VMware network is set to ''Bridge mode'';
- Whether the network cable connection of the development board is normal (it is recommended to use Category 5e or better network cables);
- Whether the TFTP port (default port 69) is blocked by the server firewall.
2. Querying the eMMC Partition Table
The Forlinx Embedded RK3568 development board offers multiple eMMC storage options of 8/16/32/64GB. In this test, the standard Linux partition plan is adopted. The complete partition structure can be viewed through the mmc part command to clarify the target partitions for the boot.img (boot image) and rootfs.img (file system image).
= > MMC part # List the partition table for eMMC device 0 (Partition Type: EFI) Partition Map for MMC device 0 -- Partition Type: EFI Part Start LBA End LBA Name Attributes Type GUID Partition GUID 1 0x00004000 0x00005fff "uboot" 0x00000000 0a100000-... b7030000-......
Read more -
One-click to Achieve Local TTS! Full Process of Deploying Piper Text-to-Speech Tool on OKMX8MP Development Board
12/10/2025 at 05:28 • 0 commentsIn IoT and edge computing projects, the demand for offline and localized text-to-speech (TTS) functionality is increasing. Piper, a fast and open-source neural network TTS engine, perfectly meets this demand.
Today, step by step instructions will be provided to deploy Piper on the Forlinx Embedded OKMX8MP development board and achieve high-quality local voice synthesis. This tutorial includes complete steps, code examples, and troubleshooting for common issues to help you get started easily!
Preparation
Required Files
piper_bin.tar (about 22.6 MB)
Piper executable files and core dependent libraries (e.g., libonnxruntime, libespeak-ng).
piper-voices_cut.tar (about 114.4 MB)
Trimmed Chinese and English voiceprint model libraries.
Development Environment
Forlinx OKMX8MP development board (with Linux system flashed).
Terminal access to the development board via SSH or serial port.
Tools for file transfer (e.g., USB drive, SCP).
Detailed Deployment Steps
Step 1: Deploy Piper Executable Files
1. Copy files to the development board
Copy piper_ok.tar to any directory on the development board (take /root as an example): # Assume the file has been copied to /run/media/sda1 via USB drive root@OK8MP:~# cp /run/media/sda1/piper_ok.tar ./ root@OK8MP:~# sync
2. Extract the files
Enter the working directory and extract the files. The -m parameterpreserves the file modification time.
root@OK8MP:~# tar -xvf piper_ok.tar -m
After extraction, the directory structure of piper is as follows:
piper/ ├── piper # Core executable file ├── lib*.so* # All dynamic link libraries required for running ├── espeak-ng-data/ # Voice data └── *.ort # ONNX-related model files
3. Perform a preliminary test
Try to run the piper program directly:
root@OK8MP:~/piper# ./piper # Expected error output: "Model file doesn't exist"
Note: It's normal to get an error at this point because no voiceprint models have been specified yet. This verifies that the program itself can run.
Step 2: Deploy the Voiceprint Model Library
1. Extract the voiceprint library
Extract piper-voices_cut.tar to the /opt directory, a common locationfor optional software.
root@OK8MP:/opt# tar -xvf /path/to/piper-voices_cut.tar -m
After extraction, you'll get Chinese voiceprint model files, forexample:
/opt/piper-voices_cut/medium_zh/zh_CN-huayan-medium.onnx.
2. Create a Chinese test text
Create a text file named zh_test.txt and write the content to beconverted.
# Use the cat command to quickly create a file root@OK8MP:~/piper# cat > zh_test.txt << EOF Welcome to use Forlinx Embedded OKMX8MP development board: This is a text-to-speech local test. EOF
Note: Ensure that the text file uses UTF-8 encoding to avoid Chinesecharacter garbling.
Step 3: Run Text-to-Speech and Play
1. Execute the conversion command
In the piper directory, execute the following command to convert thetext to an audio file zh_audio.mp3.
root@OK8MP:~/piper# ./piper \ -m /opt/piper-voices_cut/medium_zh/zh_CN-huayan-medium.onnx \ --output_file zh_audio.mp3 < zh_test.txt
Parameter description:
Successful output example:
[piper] [info] Loaded voice in 1.99 second(s) [piper] [info] Real-time factor: 0.61 (infer=1.72 sec, audio=2.82 sec) [piper] [info] Terminated piper
-m: Specify the voiceprint model file to be used.
--output_file: Specify the name of the output audio file.
< zh_test.txt: Redirect the input text from the file.
2. Play the audio file
Use the gst - play - 1.0 tool to play the generated audio.
root@OK8MP:~/piper# gst-play-1.0 ./zh_audio.mp3
Common Questions and Solutions (Q&A)
Question 1:
Error message: ''Model file doesn't exist''
Solution: Check if the path of the voiceprint model after the -m parameter is correct. Ensure that piper - voices_cut.tar has been successfully extracted to the /opt directory and the file permissions are normal.
Question 2:
Unable to directly input Chinese on the command - line or garbled characters...
Read more -
Rockchip RV1126B: The ''Performance Benchmark'' for Edge AI Vision Processing
12/08/2025 at 00:51 • 0 commentsThe emergence of the edge computing era has increased the demands on the AI processing capabilities of terminal devices. This is particularly true in AIoT sectors like intelligent security, industrial vision, and robotics. These applications require not only high-quality image processing capabilities but also efficient AI inference at the edge.
The RV1126B, a mid- to high-end AI vision processing SoC launched by Rockchip in May of this year, is specifically designed to meet this demand. The RV1126B is a significant upgrade to the RV1126 series, featuring 3TOPS of NPU computing power, a dedicated AI-ISP architecture, and comprehensive hardware-level security features. This makes it an ideal choice for intelligent upgrades across various industries.
Additionally, Forlinx Embedded is set to launch a new series of products that are designed and developed based on the RV1126B. Welcome to stay tuned for more updates!
AI Vision Processor with Comprehensive Upgrade in Chip Architecture Performance
As an upgraded version of the RV1126, the RV1126B has achieved significant breakthroughs in multiple key performance indicators.
This chip uses a quad-core Cortex-A53 CPU architecture, with performance more than twice that of chips in the same category, providing strong support for high-performance computing and multi - task processing. Working in tandem with the CPU is Rockchip's self-developed NPU. Its AI computing power has been increased from 2 TOPS to 3 TOPS, supporting weight sparsification, W4A16/W8A16 mixed-precision quantization, and Transformer optimization technology.
This means it can process AI tasks more efficiently and run large language models and multi-modal models with a parameter scale of less than 2B smoothly. The memory bandwidth has been increased from 2166MT/s to 3200MT/s, accelerating data access speed.
Four Core Technologies Build Differentiated Competitive Advantages
The core competitiveness of the RV1126B lies in four technological innovations, which make it stand out in the field of edge AI vision processing.
1. NPU Computing Power Strengths
The built-in 3TOPS NPU of the RV1126B supports INT4/INT8/INT16/FP16 mixed operations and can perform intelligent data processing, voice recognition, and image analysis. It supports deep-learning frameworks such as TensorFlow, TensorFlow Lite, Pytorch, Caffe, and Onnx, meeting the edge-computing AI application needs of most terminal devices.
2. AI-ISP and AOV 3.0
The RV1126B integrates a dedicated AI-ISP hardware, which breaks through the computing power bottleneck of traditional solutions.
Its core advantage is that the AI-ISP can run independently without occupying the resources of the general 3T computing power NPU. Combined with the AI Remosaic technology, it can achieve ''day-night dual-mode adaptation'', outputting ultra-high-definition images during the day and maintaining clear imaging under ultra-low illumination at night.
The AOV 3.0 technology features a low-power audio event wake-up function, enabling 24/7 all-weather audio-video monitoring and real-time detection of abnormal sound sources, including dog barks, broken glass, and gunshots. The device's power consumption is as low as about 1mW in standby mode, ensuring vigilance while being highly energy-efficient.
3. Video Processing Capability
The RV1126B integrates an intelligent encoding engine, supporting 8-megapixel 45FPS ultra-high-definition encoding.
Through the dynamic bit-rate optimization technology, it can save 50% of the bit-stream compared with the traditional CBR mode, doubling the recording time in the same storage space.
The chip also has hardware-level 6-DOF digital anti-shake, which can accurately identify and eliminate high-frequency jitter.
Its binocular/quad-camera panoramic dynamic stitching technology enables multi-camera stitching products to avoid image tearing and provides a super-wide-angle view.
4. Security Performance
The RV1126B chip has a built-in national-level...
Read more -
Master the Complete Process of Reading and Writing Files on Storage Devices at the U-Boot Stage of the RK3588 Development Board in 10 Minutes
11/27/2025 at 08:10 • 0 commentsThe Forlinx OK3588-C development board is built based on a flagship processor that utilizes an advanced 8nm manufacturing process and adopts a big.LITTLE architecture, featuring four Cortex-A76 cores and four Cortex-A55 cores. It not only features a triple-core NPU with 6 TOPS computing power and 8K ultra-high-definition processing capabilities, but also provides a stable and reliable hardware foundation for storage device debugging through rich hardware designs such as dual independent MMC controllers and multi-specification USB interfaces.
This article outlines standardized methods for accessing the contents of various storage devices (eMMC, TF cards, USB flash drives) during the U-Boot console stage of the RK3588 development board. While the initialization subsystems of various storage devices differ, unified read and write operations can be performed through the U-Boot console, making it ideal for development, debugging, and system verification scenarios.
I. Enter the U-Boot Console
The U-Boot for the Forlinx RK3588 development board has been extensively customized and optimized. By default, there is a reasonable boot delay configured. During the U-Boot startup process, you can interrupt this countdown and enter the interactive console by pressing the Spacebar or Ctrl + C before the automatic startup completes.
The operation interface and an example are as follows:
Hit key to stop autoboot('Spacebar'): 0 0:Exit to console 1:Reboot 2:Display type =>Prompt: If you fail to press the key in time, U - Boot will continuethe automatic startup (loading the kernel). You need to restart thedevelopment board and try again.
II. Reading and Writing Files on MMCDevices (EMMC/TF Cards)
The RK3588 development board features dual MMC controllers in its hardware, which correspond to the EMMC and TF card interfaces. It is fully compatible with the EMMC 5.1 specification and the SD 3.0 protocol. The board supports the HS400 high-speed transmission mode and allows for both 8-bit and 4-bit data bus widths. This design provides hardware support for the parallel operation of storage devices. Reading and writing files on MMC devices requires following a four-step process of ''identification → switching → querying → operating''.
The specific steps are as follows:
1. View MMC Controllers
Use the ''mmc list'' command to view the initialized MMC controllers (pre - defined by the device tree, usually 0 corresponds to EMMC and 1 corresponds to the TF card) and confirm whether the devices are recognized:
=> mmc list // View the currently initialized MMC controllers mmc@fe2c0000: 1 mmc@fe2e0000: 0 (eMMC)Device 'mmc@fe2c0000': seq 1 is in use by 'mmc@fe2c0000' mmc@fe2c0000: 1Device 'mmc@fe2e0000': seq 0 is in use by 'mmc@fe2e0000' mmc@fe2e0000: 0 =》
2. Switch MMC Devices
Use the''mmc dev <device number>''command to switch to the target device. The device number corresponds to the controller serial number queried in the previous step:
=> mmc dev 0 // Switch to EMMC switch to partitions #0, OK mmc0(part 0) is current device => mmc dev 1 // Switch to TF card switch to partitions #0, OK mmc0(part 0) is current device
3. View MMC Device Information
After switching the device, use the mmc info command to view the detailed device parameters (capacity, bus width, interface version, etc.).
Examples of EMMC and TF card information are as follows:
Example of EMMC device information:
=> mmc info //EMMC device information Device: mmc@fe2e0000 Manufacturer ID: 15 OEM: 100 Name: CJTD4 Timing Interface: HS400 Enhanced Strobe Tran Speed: 200000000 Rd Block Len: 512 MMC version 5.1 High Capacity: Yes Capacity: 58.2 GiB Bus Width: 8-bit DDR Erase Group Size: 512 KiB HC WP Group Size: 8 MiB User Capacity: 58.2 GiB WRREL Boot Capacity: 4 MiB ENH RPMB Capacity: 4 MiB ENH
Examples of TF card device information:
=> mmc info //TF device information Device: mmc@fe2c0000 Manufacturer ID: 3 OEM: 5344 Name: SL16G Timing...
Read more -
Implementation Scheme for I²C Operation during Linux 4.9 System Startup on T507 Platform
11/19/2025 at 02:54 • 0 comments1. Product Configuration
Product: T507
Hardware Configuration: v1.1
Software Configuration: Linux 4.9
2. Requirement Description
- The SoM needs to send an initialization sequence viaI²C.
- The registers of the temperature sensor need to be configured viaI²C.
3. Specific Implementation
- U-Boot Phase
In the U - Boot phase, it can be added to the board - levelinitialization file.
In the ft_board_setup function, there is some content for audio chipinitialization.
Specific Steps:
- Bus Initialization
① First, the pin functions need to be set.
Enable the bus.
② Switch the bus.
After switching the bus, all subsequent read and write operationswill be performed on this bus.
Suppose there are three I²C buses, numbered 3, 4, and 5, and theirnumbers in the U - Boot phase are 0, 1, and 2 respectively.
③ Perform i2c read/write operation according to chip timing.
④ The encapsulated functions of the system can also be used.
Specific Operations:
- Kernel Phase:
If it is just simple read and write operations, it does not need torely on the device tree.
Directly obtain the i2c adapter information in the entry function.The implementation of the write function is as follows.
Implementation of Writing a Function
static s32 aim955_i2c_write(struct i2c_adapter *client, unsigned short devID, unsigned char regadr, unsigned char regVal) { struct i2c_msg msg; s32 ret = -1; s32 retries = 0; static unsigned char cmdBuf[4]; memset(cmdBuf, 0x00, 4); cmdBuf[0x00] = regadr; cmdBuf[0x01] = regVal; msg.flags = !I2C_M_RD; msg.addr = devID; msg.len = 0x02; msg.buf = cmdBuf; while(retries < 5) { ret = i2c_transfer(client, &&msg, 1); if (ret == 1) { break; } else { retries++; } } if((retries >= 5)) { pr_err("write AIM error device ID %d regaddr = %d value = %d\n", devID, regadr, regVal); } return ret; }Examples:
aim955_i2c_write(client, 0x0C, 0x14, 0x10);
The parameter contains the bus information device address registeraddress register value.
11-14: Initialize the msg structure, fill in flag bits, deviceaddress, and register information
17-22: Send msg information through i2c_transfer function
Driver Examples:
#include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/i2c.h> #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/delay.h> #define DEVICE_ADDRESS 0x5d static struct i2c_board_info __initdata my_i2c_device = { I2C_BOARD_INFO("my_i2c_device", DEVICE_ADDRESS), }; static s32 aim955_i2c_write(struct i2c_adapter *client, unsigned short devID, unsigned char regadr, unsigned char regVal) { struct i2c_msg msg; s32 ret = -1; s32 retries = 0; static unsigned char cmdBuf[4]; memset(cmdBuf, 0x00, 4); cmdBuf[0x00] = regadr; cmdBuf[0x01] = regVal; msg.flags = !I2C_M_RD; msg.addr = devID; msg.len = 0x02; msg.buf = cmdBuf; while(retries < 5) { ret = i2c_transfer(client, &msg, 1); if (ret == 1) { break; } else { retries++; } } if((retries >= 5)) { pr_err("write AIM error device ID %d regaddr = %d value = %d\n", devID, regadr, regVal); } return ret; } static s32 aim955_i2c_read(struct i2c_adapter *client, unsigned short devID, unsigned char regadr, unsigned char *regVal) { struct i2c_msg msgs[2]; s32 ret=-1; s32 retries = 0; static unsigned char readAddr[4]; memset(readAddr, 0x00, 4); readAddr[0] = regadr; msgs[0].flags = !I2C_M_RD; msgs[0].addr = devID; msgs[0].len = 1; msgs[0].buf = readAddr; msgs[1].flags = I2C_M_RD; msgs[1].addr = devID; msgs[1].len = 1; msgs[1].buf = regVal; while(retries < 5) { ret = i2c_transfer(client, msgs, 2); if(ret == 2) { break; } else { retries++; } } if((retries >= 5)) { pr_err("read AIM error device ID %d regaddr = %d error!\n", devID, regadr); } return ret; } static void aim955_devInit(struct i2c_adapter *client) { unsigned char data_rec=0; int iloop = 0x00; //Each step of cgc, 955 configuration aim955_i2c_write(client, 0x0C, 0x01, 0x02); mdelay(4); aim955_i2c_write(client, 0x0C, 0x14, 0x10); mdelay(4); aim955_i2c_write(client, 0x0C, 0x87, 0x02); mdelay(4); aim955_i2c_write(client,...Read more -
Practical Guide: Connect and Configure an SPI Screen on the OK3568 Embedded Platform
11/14/2025 at 02:52 • 0 commentsThis article provides a detailed introduction on connecting and configuring an SPI screen in the Linux system, covering hardware wiring methods, steps for modifying the device tree, and driver adaptation techniques.
With the adaptation solution provided in this tutorial, the ST7735S screen can be quickly integrated with the Forlinx OK3568 development board, creating a cost - effective display solution for applications such as industrial control and portable devices.
If further expansion of functions is needed (such as touch control and backlight adjustment), additional development can be conducted based on this.
1. RK3568-spi Adaptation to 1.8-inch TFT Color Screen
Driver chip: : ST7735S
Resolution: 128×160, supporting 260,000 colors and 65K colors (16 - bit RGB565 format)
Interface Type: 4 - wire SPI (including CS/DC/RES/SCL/SDA pins), with independent backlight BL control
Operating Voltage: 3.3V (VCC pin, do not connect to 5V)
Communication Rate: Supports a maximum SPI clock of 50MHz
2. Hardware Connection
The connection relationship between the screen pins and the OK3568 must be strictly corresponding to ensure normal SPI communication and GPIO control.
The connection table is as follows:
Screen Pin Connected to OK3568 Function Description Notes VCC 3.3V power supply Core operating voltage of the screen Must be connected to 3.3V! Connecting to 5V will burn the chip. GND GND Power supply common ground Must be reliably grounded; otherwise, the display will be abnormal. BL 3.3V power supply Screen backlight control When not controlled by software, connect to 3.3V for constant lighting. CS spi0_cs0 SPI chip-select pin Selects the SPI slave device when at low level. DC GPIO3_A2 Data/command control pin Transmits data at high level and commands at low level. RES GPIO3_B3 Screen reset pin Pull low for reset during power-on and then pull high after completion. SCL spi0_clk SPI clock pin Provides a synchronous clock, up to 50MHz. SDA spi0_mosi SPI master-out slave-in pin Transmits screen commands and display data. 3. Device Tree Modification
diff --git a/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/OK3568-C-common.dtsi b/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/OK3568-C-common.dtsi index 31ffd6024..2274b26ec 100644 --- a/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/OK3568-C-common.dtsi +++ b/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/OK3568-C-common.dtsi @@ -673,7 +673,7 @@ rx_delay = <0x00>; phy-handle = <&rgmii_phy1>; - status = "okay"; + status = "disabled"; // Turn off the network port function, and the reset pin of &gmac1 conflicts with the pin of spi0 DC }; &mdio0 { @@ -1813,12 +1813,15 @@ pinctrl-names = "default", "high_speed"; pinctrl-0 = <&spi0m1_cs0 &spi0m1_pins>; pinctrl-1 = <&spi0m1_cs0 &spi0m1_pins_hs>; - status = "disabled"; + status = "okay"; spi@0 { - compatible = "rockchip,spidev"; + compatible = "sitronix,st7735r"; reg = <0>; + dc-gpios = <&gpio3 RK_PA2 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>; + reset-gpios = <&gpio3 RK_PB3 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>; spi-max-frequency = <50000000>; + rotation = <0>; }; };4. Kernel Driver Enable
CONFIG_FB_TFT=y CONFIG_FB_TFT_ST7735R=y
5. driver fb_st7735r.c Modification
diff --git a/drivers/staging/fbtft/fb_st7735r.c b/drivers/staging/fbtft/fb_st7735r.c index 9670a8989..e13625cc7 100644 --- a/drivers/staging/fbtft/fb_st7735r.c +++ b/drivers/staging/fbtft/fb_st7735r.c @@ -18,73 +18,49 @@ static const s16 default_init_sequence[] = { -1, MIPI_DCS_SOFT_RESET, - -2, 150, /* delay */ + -2, 10, -1, MIPI_DCS_EXIT_SLEEP_MODE, - -2, 500, /* delay */ + -2, 120, - /* FRMCTR1 - frame rate control: normal mode - * frame rate = fosc / (1 x 2 + 40) * (LINE + 2C + 2D) - */ - -1, 0xB1, 0x01, 0x2C, 0x2D, + -1, 0x11, + -2, 120, - /* FRMCTR2 - frame rate control: idle mode - * frame rate = fosc / (1 x 2 + 40) * (LINE + 2C + 2D) - */ + -1, 0xB1, 0x01, 0x2C, 0x2D, -1, 0xB2, 0x01, 0x2C, 0x2D, - - /* FRMCTR3 - frame rate control - partial mode - * dot inversion mode, line inversion mode - */ -1, 0xB3, 0x01, 0x2C, 0x2D, 0x01, 0x2C, 0x2D, - /*...Read more -
Common Interface Problems and Troubleshooting Ideas for AM62x Development Boards (2)
11/11/2025 at 02:24 • 0 commentsThe AM62x processor from Texas Instruments (TI) is a new-generation, high-performance, and low-power processor widely utilized in industrial control, human-machine interaction, and edge computing. Common issues encountered in the development of the OK62xx-C development board have been summarized, drawing significant interest from many friends.
This article lists systematic troubleshooting ideas and solutions for various interface problems that may arise during the development process.
![AM62x Development Boards]()
1. LVDS Problem
(1) Check whether the output mode of the LVDS display is consistent with the screen (VESA and JEIDA);
(2) Confirm whether the 100Ω resistors of each differential signal of the LVDS screen are soldered;
(3) Please incorporate a soft-start circuit for the LVDS power supply. Verify that the resistor at R247 is present to ensure Q3 turns on gradually, preventing the screen from pulling down VDD_5V;
(4) Measure whether the clock and data output are normal.
2. ENET Problem
(1) Confirm that the communication interface between the PHY chip and the MAC is consistent and that equal-length processing has been performed;
(2) Verify if the MDIO bus is properly pulled up and that the waveform appears normal; also, avoid splitting the MDIO wiring;
(3) Confirm whether the precision resistors meet the requirements;
(4) If the speed does not meet the requirements, check if each power supply and the reference ground are functioning properly;
(5) Detect whether the center tap of the network transformer is correct;
(6) Verify that the addresses of different PHY chips on the same bus do not conflict and are consistent with the software settings;
(7) Verify if the MDI data lines have been processed to equal lengths and if the impedance meets the specified requirements.
3. CAN Problem
(1) When there are multiple devices on the CAN bus, confirm whether there are 120Ω matching resistors at both ends of the devices;
(2) If the CAN devices cannot communicate, you can try to connect the reference grounds of the CAN devices to reduce common - mode interference.
4. UART Problem
(1) The serial port transceiver signals need to be cross - connected;
(2) Confirm whether the serial port tool configuration is correct, such as the baud rate.
(3) Measure whether the data output is normal.
5. RS485 Problem
(1) When there are multiple devices on the 485 bus, confirm whether there are 120Ω matching resistors at both ends of the devices;
(2) If the 485 devices cannot communicate, try to connect the reference grounds of the 485 devices to reduce common - mode interference;
(3) Since RS485 is a half - duplex transmission, some 485 chips require transceiver control signals. Confirm whether the chip driver has been added.
6. Audio Problem
(1) If the system cannot detect the audio chip, check whether the I2C bus communication is normal;
(2) If the chip can be mounted normally but there is no sound output, first check whether the I2S data waveform is output normally, and then check whether the audio output is normal.
7. PCIe Problem
(1) Confirm whether the PCIe device and the CPU use the same source clock and whether the frequency is correct;
(2) Detect whether there is an AC coupling capacitor for the PCIe transmission signal;
(3) Generally, an AC coupling capacitor has been added to the transmission signal at the PCIe device end, so there is no need to add another coupling capacitor at the receiving end.
8. GPIO Problem
When selecting a GPIO, confirm whether the signal is a Boot startup item pin. If so, do not use a pull-up or pull-down circuit when powering on, or a buffer chip needs to be added.
-
FET153-S SoM: Empowering PLC Intelligent Control Upgrade with Multi-core Performance and High Reliability
11/08/2025 at 06:56 • 0 commentsIn the era of Industry 4.0 and intelligent manufacturing, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) serve as the core equipment for industrial automation and are encountering various challenges in enhancing performance and fulfilling high-reliability standards. The FET153-S SoM, launched by Forlinx Embedded, offers a new solution for PLC equipment due to the inherent advantages of the T153 industrial processor, including multi-core heterogeneous computing, comprehensive interface coverage, and industrial reliability design.
Multi-core Heterogeneous Architecture
Solving the Contradiction Between Real-time Control and Efficient Computing in PLC
Traditional PLC main control primarily relies on single-core architecture, which can lead to computing power bottlenecks when handling complex logic controls, such as motor speed regulation and real-time sensor acquisition, as well as high-throughput data tasks like multi-port communication and equipment status monitoring.
The Allwinner T153 processor, used in Forlinx Embedded's FET153-S SoM, features a multi-core heterogeneous architecture consisting of a 4-core Cortex-A7 and an independent RISC-V E907. This design effectively addresses the dual requirements of programmable logic controllers (PLC).
The 4 x Cortex-A7 cores are responsible for the communication management, data storage, and complex algorithm operations of the PLC. For example, on the welding production line in automobile manufacturing, they can process the status data from multiple welding robots and the instructions from the upper-level computer, realizing real-time data analysis and response.
The RISC-V E907 core focuses on real-time control tasks, such as millisecond/microsecond-level logic operations, high-speed I/O point scanning, and interrupt handling in PLCs. In automated assembly line scenarios, strict synchronization between multiple sensors and actuators can be ensured, preventing declines in production rhythm or errors in product processing caused by delays in the scanning cycle.
Full-Scenario Interface Coverage
Meets the Complex Industrial Interconnection Needs of PLC
As the ''nerve center'' of the industrial field, PLCs need to connect various types of devices such as sensors, actuators, and Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs). Forlinx FET153-S SoM exposes all CPU pins through a stamp hole and LGA connector, allowing high-bandwidth communication and flexible expansion interfaces.
Industrial Network Integration: It includes 3 x Gigabit Ethernet ports (supporting RMII/RGMII) and 2 x CAN-FD interfaces, compatible with CAN 2.0A/B. This allows for "industrial switch-level" networking without the need for additional expansion chips. For instance, a power monitoring terminal can simultaneously connect smart meters, circuit breakers, and an upper-level computer.
Sensor and Actuator Connection: It features 24 x 12-bit GPADC, 30 x PWM channels, and 10 x UART channels, which can accurately collect analog signals such as temperature and pressure, as well as drive equipment like servo motors and frequency converters. In the photovoltaic inverter scenario, the GPADC can monitor the DC-side voltage in real-time, with a PWM output frequency ranging from 0 to 24MHz or 0 to 100MHz, ensuring efficient execution of the MPPT algorithm.
Display and Interaction Support: It integrates MIPI-DSI, LVDS, and RGB interfaces, supporting a maximum display resolution of 1920×1200@60fps, and can be adapted to industrial touch screens and HMI devices. Meanwhile, the 4-lane MIPI-CSI interface supports the access of dual cameras, providing a hardware foundation for machine vision inspection.
Industrial-grade Reliability
Stable Operation in Harsh and Complex Environments
In the harsh industrial environment, PLC needs to withstand multiple tests such as high and low temperature, vibration, electromagnetic interference and so on. The FET153-S SoM ensures long-term stable operation through the following...
Read more -
Porting of MobileNetV3 Model and Implementation of Handwritten Digit Recognition Based on OKMX8MP-C (Linux 5.4.70)
10/31/2025 at 01:19 • 0 commentsThis article details how to port and run the MobileNetV3 model on the Forlinx OKMX8MP-C embedded platform to achieve the function of handwritten digit recognition. From dataset import, model training and validation to TensorFlow Lite quantization and deployment, it fully demonstrates the usage process of the eIQ Portal tool. Through this case, readers can quickly learn how to implement edge inference of lightweight deep-learning models on an industrial-grade ARM platform.
1. Importing the Dataset
Before training the model, you need to prepare the dataset first. If you don't have a dataset, you can directly click ''Import dataset'' and select the dataset provided in the tool. (If you have your own dataset, you can click ''Create a blank project'' to directly import it.) As shown in the figure below.
This paper uses the dataset provided by the tool. Use the tool to load the dataset from TensorFlow, as shown below.
You can select the provided datasets from the drop - down menu in the upper - left corner. These are all datasets commonly used in TensorFlow. This paper uses the mnist dataset.
The mnist dataset has 60,000 handwritten digits as the training set and 10,000 handwritten digits as the validation set. In addition, there are three other datasets:
- cifar10: It contains color images of 10 classes, with 50,000 images as the training set and 10,000 images as the validation set.
- horses_or_humans: horses_or_humans: It has 2 classes, humans and horses. There are 1,027 images of humans and 1,027 images of horses respectively.
- tf_flowers: It has 5 classes, with a total of 3,670 images of all kinds of flowers.
Also, there is a ''Problem type'' drop - down menu in the upper - left corner, which represents the type of task. As shown below, this version of the tool only provides two types, one is image classification and the other is object detection. In the object detection task, there is only one dataset, coco/2017. This dataset can detect 80 types of object recognition, with 118,287 images as the training set, 5,000 images as the validation set, and 20,288 images as the test set.
After selecting the dataset, click the ''IMPORT'' button, select the save directory, and wait for the import. As shown in the figure below:
Select the save directory.
Wait for the dataset to be imported.
After the import is completed, you can view the mnist dataset. The left side shows the number of each image and the image labels. The right side shows each image in the dataset. You can view the detailed information by selecting an image.
2. Model Training
After importing the dataset, the next step is to select a model. As shown below, click the ''SELECT MODEL'' button in the figure.
The interface for selecting a model is as shown below. In this interface, three different options are shown on the left, and their functions are as follows:
- RESTORE MODEL: Load the model used last time.
- BASE MODELS: Select the provided base models.
- USER MODELS: Select the models you created.
On the right, models with different functions are shown, such as classification models, image segmentation models, and object detection models.
This paper uses the base model provided by eIQ Portal, so select ''BASE MODEL'' as shown in the figure below.
The figure below shows several base models provided by the tool. This paper uses the mobilenet_v3 model. The structures of different models can be viewed through the ''MODEL TOOL'' on the initial page.
After selecting the model, enter the model training stage. Its interface is as shown below. The left side shows the parameters to be adjusted during the training process, including the learning rate, Batchsize, and epochs, etc. It can be adjusted as needed. The right side can show relevant information such as the accuracy and loss value during the training process.
The parameters for this training are as shown below. After selection, click ''Start training''.
The training process is as shown below....
Read more -
How to Configure and Port Library Files via Buildroot on the RK3568 Platform
10/17/2025 at 02:53 • 0 commentsAs a high-performance industrial-grade chip, Rockchip RK3568 adopts a quad-core Cortex-A55 architecture and integrates a GPU and an NPU. It is widely used in edge computing and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Buildroot is a lightweight build tool designed specifically for embedded systems. It can quickly generate a customized Linux root file system through modular configuration. It is particularly suitable for the hardware features of RK3568, significantly improving development efficiency.
Operation method:
1. Switch to the path OK3568-linux-source/buildroot/output/OK3568/ and execute the command ''make menuconfig'';
2. Press the ''/'' key to open the search box and search for relevant library files by keywords. Take adding PYTHON3 as an example;
3. Select options from 1 to 3 according to the search results to jump to the corresponding configuration options. Please use the ''↑'' and ''↓'' keys to turn pages;
Select an option by pressing the ''Y'' key or toggle the selection state by pressing the ''Space'' key.
Choose whether to perform a complete installation according to the needs.
4. Keep selecting ''Exit'' until exit the graphical interface. When prompted to save the configuration, select ''yes'';
5. Recompile Buildroot. Execute the following command in the OK3568-linux-source directory:./build.sh buildroot
6. When prompted whether to overwrite the old.config configuration file, enter ''n''.
7. Rewrite the rootfs.ext2 image generated in OK3568-linux-source/buildroot/output/OK3568/images to the development board. In fact, the rootfs.img generated by a full compilation is created by directly renaming the rootfs.ext2 file. Therefore, using rootfs.ext2 for flashing has the same effect;
8. First, click on the device partition table, then select rootfs.ext2, and click to start the flashing process.
-
Implementation Scheme of Linux 4.14 OTA Upgrade Based on RAUC for OKMX8MM
10/16/2025 at 02:04 • 0 commentsThis document aims to provide an Over-The-Air (OTA) upgrade solution based on RAUC (Robust Auto-Update Controller), which is suitable for embedded Linux systems. RAUC is an open-source OTA framework developed by Pengutronix. It is specifically designed for industrial-grade devices and provides secure, reliable, and atomic firmware update capabilities. It can run on multiple platforms, including Linux, FreeRTOS, and bare-metal environments. OTA is a technology for remotely updating the firmware of embedded devices via wireless networks (such as Wi-Fi, 4G, 5G, etc.). It enables functions such as firmware updates, configuration pushes, and security patches without physically accessing the devices.
In this paper, the RAUC-V0.1 version (the official initial version) is taken as an example for deployment and verification on 8mm-linux4.14.78. Currently, RAUC has been updated to version V1.14. Other platforms can select appropriate versions for transplantation according to the kernel version, glib version, and openssl version. This transplantation only supports manual upgrades and manual partition switching. If necessary, automatic upgrades can be achieved by adding environment variables in U-Boot.
Other OTA upgrade tools: SWupdate
Configuration requirements
Note: Only the basic RAUC upgrade functions are described here. For example, streaming online updates are only supported in RAUC-v1.7 and above.
1. Kernel Version:
It has been verified that it can run on kernel versions above Linux 4.14. Lower versions have not been verified yet, but theoretically they can also be used. For kernel versions without systemd service, --disable-service needs to be specified when compiling the RAUC source code.
2. File System:
RAUC has no restrictions on the content of the file system. However, since an A/B system is implemented, the flash should have at least twice the capacity of the file system.
Deployment scheme
1. Install RAUC in the development environment.
~/work/project/rauc$ git clone https://github.com/rauc/rauc ~/work/project/rauc$ cd rauc ~/work/project/rauc$ git checkout v0.1 ~/work/project/rauc$ ./autogen.sh ~/work/project/rauc$ ./configure ~/work/project/rauc$ make
2. Install RAUC on the development board.
Note: Copy the json-glib and json-glib-native libraries to the cross-compiler for cross-compilation purposes
~/work/project/rauc$ git clone https://github.com/rauc/rauc ~/work/project/rauc$ cd rauc ~/work/project/rauc$ git checkout v0.1 ~/work/project/rauc$ ./autogen.sh ~/work/project/rauc$ ./configure --host=aarch64-poky-linux-gcc ~/work/project/rauc$ make
3. Key File
Manually generate a key in the development environment and put it in the source code of the file system. RAUC will verify whether the key of the image is consistent with that of the system when upgrading;
OK8MM-linux-sdk$ openssl genrsa -out autobuilder.key.pem 4096 OK8MM-linux-sdk$ openssl req -new -x509 -key autobuilder.key.pem -out \ autobuilder.cert.pem -days 365 -subj "/CN=AutoBuilder OTA \ Signing Authority/O=YourCompany/C=CN"
Place the generated autobuilder. cert. pem and autobuilder. key. pem key files under the filesystem/etc/rauc/.
4. bundle
Compile the configuration file of the upgrade package
Generate image check code: OK8MM-linux-sdk/images$ sha256sum ./rootfs.ext4de2f256064a0af797747c2b97505dc0b9f3df0de4f489eac731c23ae9ca9cc31
To create a manifest profile:
OK8MM-linux-sdk/bundle$ vim manifest [update] compatible=Forlinx_rauc_8m version=20250801 build=20250808 [image.rootfs] sha256=de2f256064a0af797747c2b97505dc0b9f3df0de4f489eac731c23ae9ca9cc31 size=24117248 filename=rootfs.ext4 Copy the upgrade image to the bundle directory: OK8MM-linux-sdk/bundle$ cp ../images/rootfs.ext4 ./
5. system.conf
The system. conf is the system configuration file of RAUC, which is responsible for configuring the storage, partition, and boot mode; it is the configuration file used in the upgrade process.
The path can be:/etc/rauc/system....
Read more -
Guide to Applying Real-Time Patches and Solving Problems on the T507 Platform Based on Linux 4.9
10/14/2025 at 03:40 • 0 commentsApplying Real-Time Patches
Each version of the kernel has a corresponding real-time patch.
The kernel version of T507 is 4.9.170, and here is the corresponding real-time patch version.
Download address: https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/projects/rt/4.9/older/
After obtaining the patch compressed package, extract it in the virtual machine:
tar -xzvf linux-4.4.206.tar.gz gunzip patch-4.4.206-rt190.patch.gz
Apply the patch under the kernel path.
Enter the kernel configuration menu.
Select the full preemption mode.
After the application is completed, compilation usually fails because the source code has been modified later, and there will be some parts that conflict with the official patch files. .rej files will be automatically generated at these locations.
Please manually add the modifications in these files to the source code. When adding, do not directly copy and paste.
For example, if the content in the patch file contains a variable a, but the context in the source code uses sunxi_a. Please unify these modifications with the existing source code and pay attention to these differences.
Solving Compilation Errors
1. The kernel source code of T507 is quite special. The zram part refers to the kernel of 5.10, so this part should be modified with reference to the real-time patch of 5.10;
2. During the compilation process, an error occurred regarding the driver of the 6256 wifi and Bluetooth chip. The error information at that time was not saved. The general meaning is that the actual parameters passed to one of the functions do not match the parameter types defined in the function;
The modifications are as follows:
diff --git a/linux-4.9/drivers/net/wireless/bcmdhd/dhd_pno.c b/linux-4.9/drivers/net/wireless/bcmdhd/dhd_pno.c old mode 100644 new mode 100755 index 8d2957fd8..52d491f21 --- a/linux-4.9/drivers/net/wireless/bcmdhd/dhd_pno.c +++ b/linux-4.9/drivers/net/wireless/bcmdhd/dhd_pno.c @@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ #ifdef PNO_SUPPORT #include #include - +#include #include #include @@ -3169,7 +3169,7 @@ exit: } mutex_unlock(&_pno_state->pno_mutex); exit_no_unlock: - if (waitqueue_active(&_pno_state->get_batch_done.wait)) + if (swait_active(&_pno_state->get_batch_done.wait)) complete(&_pno_state->get_batch_done); return err; } @@ -3948,7 +3948,7 @@ dhd_pno_event_handler(dhd_pub_t *dhd, wl_event_msg_t *event, void *event_data) { struct dhd_pno_batch_params *params_batch; params_batch = &_pno_state->pno_params_arr[INDEX_OF_BATCH_PARAMS].params_batch; - if (!waitqueue_active(&_pno_state->get_batch_done.wait)) { + if (!swait_active(&_pno_state->get_batch_done.wait)) { DHD_PNO(("%s : WLC_E_PFN_BEST_BATCHING\n", __FUNCTION__)); params_batch->get_batch.buf = NULL; params_batch->get_batch.bufsize = 0;The reason is that after applying the real-time patch, the interface used has been changed from waitqueue_active to swait_active, so an error regarding function parameter passing occurred.
3. The compilation script added to the kernel also needs to be modified.
The path in the above figure is the output path of the kernel driver module, which will be automatically created when compiling the kernel. If no modification is made, the compilation output will follow the path 4.9.170-rt129, but the path created by the compilation script is 4.9.170, so the compilation cannot pass.
4. After packaging into an image and running it on the board, the kernel keeps crashing, and the printed information is consistent with the content in the document provided by Allwinner.
(1)
(2)
5. When running the packaged image, the screen does not display.
The GPU driver module fails to load normally because the path of the startup script in init.d is incorrect.
The modifications are as follows:
By analogy, when loading other modules, please pay attention to the path changes.
Real-time performance after applying the patch.
-
Guide to OTA System Upgrade for Forlinx OKMX8MP-C Development Board on Linux 5.4.70
09/24/2025 at 02:53 • 0 commentsOTA is a method that enables lossless system upgrades for devices, allowing new features to be remotely deployed on products. The OTA upgrade package can not only be downloaded via the network but also used to upgrade the device after being downloaded to an SD card or a USB flash drive.
This article will introduce the specific implementation method of using OTA to upgrade the system on the Linux 5.4.70 system through the Forlinx Embedded OKMX8MP-C development board.
1. Environment Setup
1.1 Download the 22.04 Image of the Compilation Environment
Since RAUC version 1.6 is required, the 22.04 ISO image needs to be downloaded.
Download URL: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu-releases/22.04/
1.2 Modify the GCC Version of the Development Environment
1.2.1 Modify the apt Source
sudo gedit /etc/apt/sources.list
1.2.2 Add the Source at the End of the File
deb [arch=amd64] http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal main universe
1.2.3 Update the source
sudo apt update
1.2.4 Install GCC
sudo apt install gcc-7 g++-7
1.2.5 Back up the original GCC and G + +
sudo mv /usr/bin/gcc /usr/bin/gcc.bak sudo mv /usr/bin/g++ /usr/bin/g++.bak
1.2.6 Link to gcc-7
sudo ln -s /usr/bin/gcc-7 /usr/bin/gcc sudo ln -s /usr/bin/g++-7 /usr/bin/g++
1.2.7 Install and test
gcc --version g++ --version
GCC test run results:
G + + test run results:
1.3 Install the rauc tool
sudo apt install rauc
2. Source code configuration
2.1 EMMC partition
Need to modify the source code OK8MP-linux-fs/rootfs/etc/init.d/Init.sh
#! /bin/sh ## add forlinx user useradd -k /etc/skel -m -U forlinx -s /bin/bash passwd forlinx <<EOM forlinx forlinx EOM DEVICE="/dev/mmcblk2" # Create the partition fdisk $DEVICE <<EOF n p 3 13818240 13988608 t 3 c n p 4 13988609 30589000 w EOF # Refresh the partition table partprobe # Output partition information lsblk $DEVICE resize2fs /dev/mmcblk2p2 /usr/bin/fltest_runRefreshMatrix.sh ## delete Init.sh sed -i "s/\/etc\/init.d\/Init.sh//g" /etc/rc.local rm -f /etc/init.d/Init.sh sync
2.2 Decompression of rauc and dependent tools
(1)Decompress under liblz4.tar.bz2在/OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-fs/rootfs/usr/lib
tar -xvf liblz4.tar.bz2
(2)Decompress fw_setenv.tar.b z2 under /OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-fs/rootfs
tar -xvf fw_setenv.tar.bz2
(3)Decompress unsquashfs.tar.bz2 under /OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-fs/rootfs
tar -xvf unsquashfs.tar.bz2
(4)Decompress yocto-rauc-1.5.1.tar.bz2 under /OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-fs/rootfs
tar -xvf yocto-rauc-1.5.1.tar.bz2
2.3 Modifying the tool configuration
2.3.1 Modify the fw_env.config to specify the env base addr
/OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-fs/rootfs/etc/fw_env.config
gedit fw_env.config
Delete the original content and only add:
/dev/mmcblk2 0x400000 0x2000
2.3.2 Modify the rauc configuration file
/OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-fs/rootfs/etc/rauc/system.conf
gedit system.conf
Note: It is necessary to ensure that the compatibility is consistent with that in the upgrade package and that the partition contents are correct.
2.3.3 Modify the compilation script
forlinx@ubuntu:~/OK8MP-linux-sdk$ gedit tools/fakeroot.fs
This part of the script needs to be commented out:
2.3.4 Modify the mount configuration file
forlinx@ubuntu:~/OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-fs/rootfs/etc$ gedit fstab
Modify OK8MP-linux-fs/rootfs/etc/fstab as follows:
/dev/mmcblk2p3 /run/media/mmcblk2p3 auto defaults,sync,noauto 0 0 /dev/mmcblk2p4 /run/media/mmcblk2p4 auto defaults,sync,noauto 0 0
Note: The main purpose here is to prevent the service from automatically mounting the partition and causing the upgrade time partition to be already mounted.
3. Generate an upgrade package
3.1 Full compilation to obtain the required image
forlinx@ubuntu:~/OK8MP-linux-sdk$ . /opt/fsl-imx-xwayland/5.4-zeus/environment-set\up-aarch64-poky-linux forlinx@ubuntu:~/OK8MP-linux-sdk$...
Read more -
Tutorial on Creating and Configuring the psplash Boot Animation for the OK3588-C Embedded Linux System
09/13/2025 at 01:18 • 0 commentsIn the embedded Linux system of the RK3588 platform, the boot screen can not only enhance the user experience but also display brand logos or system status information. psplash is a lightweight boot screen program that can display static pictures or simple animations during system startup, providing intuitive feedback to users. This article will take the RK3588 as an example to introduce in detail how to create a boot animation from videos or pictures and configure psplash on the embedded device to achieve the display of a customized boot screen.
This method uses the psplash tool, which is a lightweight startup screen program commonly used in embedded Linux systems. Its main function is to display a graphical boot screen during system startup to provide user feedback, usually in the form of a brand logo or a progress bar.
Features:
- Lightweight: psplash is designed to be as small as possible to fit resource - constrained embedded devices.
- Graphical interface: It can display static images or simple animations, offering users a better visual experience during startup.
- Progress bar support: It can display a progress bar during the startup process to indicate the system loading status.
- Flexible configuration: Users can customize the boot image, progress bar color, display time, etc. through the configuration file.
The following is the operation method:
Picture Creation
Place the adapted files in the folder into the virtual machine for conversion.
Create a folder to save the project:
forlinx@ubuntu20:~$ mkdir -p psplash_logo/mp4_logo/
Then, put the video into the mp4_logo folder.
Download ffmpeg, which will be used later when processing the MP4 video:
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/psplash_logo/mp4_logo$ sudo apt-get update forlinx@ubuntu20:~/psplash_logo/mp4_logo$ sudo apt-get install ffmpeg
Create a new part0 folder to store the pictures that will be generated later:
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/psplash_logo/mp4_logo$ mkdir part0
Enter the following command for conversion:
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/psplash_logo/mp4_logo$ ffmpeg -i logo.mp4 -f image2 -r 7 part0/%04d.png
Now, take a look at the pictures in the part0 folder.
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/psplash_logo/mp4_logo$ ls part0/ 0001.png 0004.png 0007.png 0010.png 0013.png 0016.png 0019.png 0022.png 0025.png 0028.png 0031.png 0034.png 0037.png 0040.png 0043.png 0046.png 0049.png 0052.png 0002.png 0005.png 0008.png 0011.png 0014.png 0017.png 0020.png 0023.png 0026.png 0029.png 0032.png 0035.png 0038.png 0041.png 0044.png 0047.png 0050.png 0053.png 0003.png 0006.png 0009.png 0012.png 0015.png 0018.png 0021.png 0024.png 0027.png 0030.png 0033.png 0036.png 0039.png 0042.png 0045.png 0048.png 0051.png 0054.png
Convert Images to .h Files
Before converting to .h files, please check if the images match the screen resolution. When using psplash, the image resolution must be consistent with the screen resolution.
Use the following command:
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/psplash_logo/mp4_logo/part0$ file 0001.png 0001.png: PNG image data, 640 x 360, 8-bit/color RGB, non-interlaced
The current resolution is 640x360. Next, the conversion will be carried out.
Create a logo_h folder and inside it, create h, logo_1024x800, and master folders respectively:
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/psplash_logo$ mkdir logo_h forlinx@ubuntu20:~/psplash_logo/logo_h$ mkdir h logo_1280x800 master
Then, copy the previously generated PNG files into the master folder. The copying process is not demonstrated here.
Start resolution conversion after copy is complete:
Create the fix _ 1280x800.sh script in the master folder:
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/psplash_logo/logo_h/master$ vi fix_1280x800.sh /*File content*/ #!/bin/bash for img in *.png; do convert "$img" -resize 1280x800! "../logo_1280x800/$img" Done
Give executable permissions:
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/psplash_logo/logo_h/master$ chmod +x fix_1280x800.sh
After execution, the modified file is created at logo _ 1280x800.
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/psplash_logo/logo_h/logo_1280x800$...
Read more -
Configuration and Debugging of PCIe Endpoint (EP Mode) on OK3588-C Linux 5.10.66 Buildroot
09/09/2025 at 03:26 • 0 commentsWith the rapid development of high-performance embedded applications, the RK3588 processor has become the preferred platform for development boards and industrial applications due to its powerful multi-core computing power and rich peripheral interfaces. In the Linux 5.10.66 Buildroot system based on the Forlinx OK3588-C, the configuration and debugging of the PCIe Endpoint (EP) mode are crucial for achieving high-speed data transmission and device interconnection. This article will provide a detailed introduction on how to complete the kernel configuration, U-Boot settings, and performance testing of the EP device on the RK3588 development board, helping developers quickly set up an efficient and stable PCIe Endpoint environment.
The document testing is based on the RK3588 development board.
- During the testing, both the RC (Root Complex, host device) and the EP (Endpoint, peripheral device) are Linux devices (RK3588 development boards).
- This article focuses on describing the configuration and testing process of the EP device. For detailed configuration information, please refer to the document: Rockchip_Developer_Guide_PCIe_EP_Stardard_Card_CN.pdf.
- Software:Linux 5.10.66 4G+32G
Kernel version: OK3588 linux 5.10.66 version kernel (Android12 Linux ForlinxDesktop20.04 R5 release)
Uboot version: OK3588 protection encryption uboot (Android12 Linux ForlinxDesktop20.04 R4 release)
Hardware connection:
For the hardware connection, only one PCIe 3x4 lane male-to-male extension cable is required.
Software settings
Applying patches
To set the PCIe-EP mode on the 3588, Rockchip officially provides the configuration reference document and source code patches for the PCIe EP mode. The document is located in the docs directory.
Note:
1. The patch file is the basic configuration for the EP card. There is also an update package in the data package. The update package contains update patches based on the base patch, mainly for optimizing the base patch and fixing issues. First, apply the base patch, and then replace the corresponding files in the SDK with the files in the update package directory.
2. Both the patch directory and the source code directory contain necessary modifications. Users can choose to directly apply the patch file or replace the corresponding source code files, either method is acceptable.
(1) kernel
The kernel patch file is located at:
Rockchip_PCIe_EP_Stardard_Card_20231215\patch-kernel5.10\linux_base\Patch directory\kernel
Modify the kernel according to the patch file.
Modify the kernel according to the patch file.
Then replace the files under the kernel in the update package.
(2)uboot
The U-Boot patch file is located at:
\u-boot
After applying the patch, replace the files in the u-boot in the update package.
(3) rkbin
It is a bit cumbersome to use the patch method to modify the files under rkbin. Directly replace the source code files:
Rockchip_PCIe_EP_Stardard_Card_20231215\patch-kernel5.10\linux_base\Source code directory\rkbin
After replacing the files in the folder, replace the files in the update package to the corresponding positions.
The above configurations are required for both the EP card and the RC card.
General kernel configuration
The following configuration items need to be completed during the actual testing process to enable the functions of the EP card. It is recommended to make modifications according to the following configurations. If there are any objections, please refer to the Rockchip official document:
Rockchip_Developer_Guide_PCIe_EP_Stardard_Card_CN.pdf1. SRNS
In the SRNS mode, the Refclock uses its own internal clock. Set this option so that the RC card and the EP card each use their own 100M clock generators.
uboot
diff --git a/arch/arm/mach-rockchip/spl_PCIe_ep_boot.c b/arch/arm/mach-rockchip/spl_PCIe_ep_boot.c index 7a24a1d..f1ce41a 100755 --- a/arch/arm/mach-rockchip/spl_PCIe_ep_boot.c +++ b/arch/arm/mach-rockchip/spl_PCIe_ep_boot.c ...
Read more -
Edge Computing-Driven Intelligent Access Control Upgrade Solution: Application Analysis of FET3568-C SoM
09/03/2025 at 03:07 • 0 commentsEdge computing, as a new-type architecture that decentralizes computing power to the terminal, is widely empowering Internet of Things (IoT) applications in various industries, significantly enhancing the real-time performance and reliability of systems. In the typical scenario of access control systems, traditional solutions struggle to meet the requirements of high concurrency, high real-time performance, and high security in modern access scenarios due to limited local computing power, high network latency, and excessive reliance on the cloud. An intelligent access control system integrated with edge computing technology can greatly improve the response speed and system stability by completing identity verification and data processing on-site. It has become an important direction for industry upgrading.
1. Demand Upgrade Spurs Technological Innovation
As users' requirements for access management experience continue to increase, access control systems are no longer limited to traditional card-swiping and password verification. They are gradually evolving towards a more intelligent, flexible, and efficient direction. Here, list three main upgrade directions:
- (1) Intelligent identity recognition: If users expect seamless access, the system needs to support AI capabilities such as face recognition and voice interaction to enhance convenience while ensuring security;
- (2) System expansion and customization capabilities: Diverse requirements for the functions of access control systems are put forward in multiple business scenarios. Therefore, access control systems should have good scalability and be able to flexibly connect to various functional modules;
- (3) Fast-response experience: During peak hours in public places, the access control system must complete identity verification in a very short time to avoid delays and recognition errors.
2. RK3568 SoM Empowers Intelligent Access Control
To address the new challenges brought by new requirements, Forlinx Embedded recommends using the FET3568-C SoM as the main control solution for the edge-computing-based intelligent access control system. This platform has many advantages that can specifically improve the overall performance of the access control system:
(1) Powerful computing power for smooth AI inference:
The Forlinx Embedded FET3568-C SoM is equipped with the Rockchip RK3568 high-performance processor, which adopts a quad-core Cortex-A55 architecture with a maximum main frequency of 2.0GHz and has a built-in independent NPU with a computing power of 1TOPS; It can smoothly support edge AI applications such as lightweight face recognition and voice recognition, meeting the dual needs of real-time performance and accuracy of intelligent access control.
(2) Rich interfaces for flexible expansion:
The Forlinx Embedded FET3568-C SoM provides rich interfaces such as USB 3.0, GPIO, UART, I2C, and SPI, which can be widely connected to various recognition modules (such as face, fingerprint, iris, etc.) and sensor devices, facilitating system customization and secondary development by customers to meet the functional integration requirements of different scenarios;
(3) Large-memory configuration to ensure multi-task response:
The FET3568-C SoM has an on-board LPDDR4x running memory with a maximum option of 8GB and a storage option of 64GB eMMC, ensuring that the system can efficiently process multiple video streams and concurrent recognition tasks, greatly improving the recognition speed and system fluency and avoiding response delays caused by insufficient memory;
(4) Diverse system support:
In addition to the above-mentioned hardware advantages, Forlinx Embedded has also adapted multiple operating systems such as Linux, Android 11, Ubuntu, Debian 11, Linux-RT, and OpenHarmony for the FET3568-C SoM and ensured their stable operation through multiple tests to meet the needs of different users in different fields and scenarios;
3. Conclusion...
Read more -
Forlinx Embedded's FET-MX9596-C SoM: Achieving Performance, Real-time and Security Balance in Edge Computing
08/29/2025 at 06:24 • 0 commentsIn the current era of the deep integration of Industry 4.0 and AIoT, traditional single-core or even multi-core processors struggle to meet the complex requirements of high performance, real-time and security in the field of edge computing. To address this pain point, major chip companies have successively launched multi-core heterogeneous processors with both A-cores and M-cores. The NXP i.MX95xx series processor equipped on the newly released FET-MX9596-C SoM by Forlinx Embedded is a flagship multi-core heterogeneous chip. It integrates six Cortex-A55 cores, one Cortex-M7 core, and one Cortex-M33 core.
The advantages of this multi-core heterogeneous architecture are obvious. It enables hierarchical task processing via hardware isolation: the A55 core cluster handles Linux system-level computing, the M7 core focuses on real-time tasks like motion control, and the M33 core independently manages security encryption. In short, it combines “high performance, high real-time and high security”.
Analysis of Multi-core Heterogeneous Architecture
Achieving Hierarchical Task Processing through Hardware Isolation
Traditional embedded processors are often limited by the resource competition of homogeneous cores when facing complex application scenarios. The core advancement of the Forlinx Embedded FET-MX9596-C is its three-core heterogeneous architecture for physical quarantine, with each core fulfilling its designated role.
- Cortex-A55 Cluster: 6 high-performance cores @ 1.8GHz, responsible for running the Linux system, AI inference and processing complex algorithms;
- Cortex-M7 Core: An 800MHz real-time core dedicated to deterministic tasks such as motion control and sensor data collection;
- Cortex-M33 Core: A 333MHz security core that independently runs the encryption engine and security monitoring program.
This design is essentially a hardware-level functional decoupling. Through NXP's Energy Flex power management architecture, the three domains can be started and stopped independently. The real-time domain continuously monitors sensors, the security domain maintains the encryption state, and the application domain is only awakened when needed, reducing the system-level power consumption by at least 30%.
Breakthroughs in High-Performance Edge AI and Multimedia Processing
The high-performance of the FET-MX9596-C SoM comes from the A55 core cluster. Six Cortex-A55 cores share a 2MB L2 cache. Coupled with 8GB LPDDR4x memory, it can provide a bandwidth of up to 51.2GB/s, paving the way for edge AI computing.
Moreover, the inference speed of the integrated 2TOPS NPU in the processor is significantly improved, reaching 800MHz in normal mode and up to 1GHz in overclocking mode. The integrated image signal processor (ISP) and video processing unit (VPU) work together to provide excellent edge machine vision capabilities. Users can run advanced AI models on the NPU to achieve scene segmentation, real-time video enhancement and denoising, ensuring high-quality video images.
In addition, the new-generation ARM Mali-G310 GPU supports OpenGL ES3.2, Vulkan1.2 and OpenCL3.0, providing users with rich graphic experience and computing acceleration capabilities. The display controller can achieve two independent display output streams.
High Real-time
Hard Real-time Core Ensures Critical Tasks
High real-time is crucial in industrial scenarios. A timing deviation of more than 1ms in motion control may lead to product scrapping. In a vehicle system, a 1ms delay in brake signal processing may cause an accident. The Cortex-M7 core of the i.MX95xx series processor is designed for such scenarios. It is physically isolated from the A55 cluster. Even if the Linux system crashes, it can still ensure the stable operation of key communication interfaces, such as continuous communication on the CAN-FD bus, accurate output of PWM signals and uninterrupted ADC data collection.
On Forlinx Embedded's OK-MX9596-C development board,...
Read more -
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Ideas in the Development Process of the i.MX9352 SoM
08/29/2025 at 05:56 • 0 commentsAs a gold partner of NXP, Forlinx Embedded has launched several embedded main control products based on the i.MX series of application processors. In addition to the newly released i.MX95xx series of System on Modules (SoMs), the i.MX93xx series of SoMs—also part of the i.MX9 family—has been available on the market for many years and has gained recognition and preference from numerous customers.
Throughout the long-term technical support service process, Forlinx Embedded has compiled common issues and troubleshooting methods encountered by users developing the i.MX93xx series of products. This article aims to outline these experiences to help developers quickly identify problems and enhance the development efficiency.
General Troubleshooting Ideas
For troubleshooting the i.MX93xx series master control, follow these general steps for any abnormal functions:
1. Hardware Consistency Verification
- Ensure that the carrier board design is consistent with the schematic diagram. If the functional chip is replaced, the corresponding driver shall be transplanted;
- Check whether the power supply, reset, and clock of the functional chip are normal.
2. Cross-Test Positioning
- Determine the source of the problem by replacing the SoM or the carrier board.
3. Signal and Soldering Inspection
- Confirm that the pin levels are matched and the data signal output is normal.
- Check whether there are process problems such as cold soldering or bridging in the resistor and capacitor components.
4. Pin Multiplexing Configuration
- Verify whether the pin multiplexing settings are consistent with the functional requirements.
Common Issues and Solutions for Specific Modules
1. Non-startup Issue
- In addition to the power supply and reset, you need to confirm whether the PWR_EN signal is normal.
- Check whether the pull-up and pull-down resistors of the BOOT start pins on the carrier board are configured as required.
2. I2C Bus Issue
- Confirm whether a pull-up resistor is added to the I2C bus (open-drain output characteristic);
- Check whether there is an address conflict among devices in the same group;
- Measure the waveform: it should be at a high level in the idle state, and the waveform should meet the standard during data transmission;
- Adjust the resistance value of the pull-up resistor: if the rising edge is slow, reduce the resistance value; if the low level is too high, increase the resistance value;
- Use tools for detection:
i2cdetect -l # Detect the I2C bus groups i2cdetect -r -y 2 # Detect the devices on the second group of buses
3. SPI Communication Issue
- The MISO and MOSI of the SPI interface need to be connected correspondingly;
- Confirm that the chip-select signal (CS) is correctly connected;
- Verify whether the modes (such as CPOL and CPHA) of both communication parties are consistent;
- Measure whether the clock and data output are normal.
4. USB Interface Issue
- The USB_VBUS_3V3 signal must be 3.3V;
- Cross-connecting USB differential signal lines is strictly prohibited.
5. SDIO Interface Issue
- The pin level of the SD2 interface is related to the transmission speed. It is 3.3V by default and 1.8V in high-speed mode;
- The SDIO signal cannot have its pin level converted through a level-conversion chip;
- Check whether the SDIO bus has been treated for equal-length;
- Prioritize checking whether the clock output is normal.
6. LVDS Display Issue
- Confirm that the screen output mode (VESA/JEIDA) is consistent with the driver configuration.
7. Ethernet Network Issue
- Verify whether the PHY chip and the MAC interface mode (such as RGMII) are consistent and whether equal-length processing has been done;
- Check whether the pull-up resistor and the waveform of the MDIO bus are normal. Avoid bifurcated wiring;
- If the speed does not meet the requirements, you can check whether all power supplies and the reference ground are intact;
- Confirm that the...
-
29×40mm Ultra-Small SoM: 2-Second Quick Assembly & Rockchip RK3506J Processor
08/22/2025 at 03:55 • 0 commentsIn the field of embedded development, engineers are always pursuing a balance among performance, size, and reliability. FET3506J-C SoM, newly launched by Forlinx Embedded based on Rockchip RK3506J processor, has become the preferred solution for developers in fields such as industrial automation, new energy, consumer electronics, and smart medical care, thanks to its ultra-small size of 29mm×40mm, the design of board-to-board connectors for quick disassembly and assembly, and industrial-grade features.
Ultra-small Size of 29mm×40mm, An Ideal Choice for Compact Scenarios
The FET3506J-C SoM uses a compact design, with a size of only 29mm×40mm, which is significantly smaller than conventional SoMs. This breakthrough design comes from Forlinx Embedded's efficient use of the processor pins. Through the matrix IO design, 98 functional signals can be flexibly mapped on 32 physical pins. Any functional signal, such as UART, CAN-FD, JTAG, FSPI, etc., can be assigned to any pin through software configuration.
In space-constrained scenarios such as industrial handheld terminals and portable medical devices, the ultra-small SoM can be directly embedded in the device motherboard without the need for additional expansion board design. It can significantly improve the portability and market competitiveness of the products.
2mm Mating Height Board-to-board Connectors
a reliable guarantee behind the 2-second quick disassembly and assembly
The FET3506J-C SoM is physically connected to the carrier board through two 80-PIN board-to-board connectors with a mating height of only 2mm and a pin pitch of 0.5mm. This design brings two major core advantages: First, the board-to-board connectors allow for quick replacement of the SoM, greatly reducing the equipment maintenance cost; Second, the connectors have an anti-reverse-insertion design built-in to avoid hardware damage caused by misoperation. This design shows its unique value in scenarios that require regular maintenance, such as new energy vehicle charging piles and industrial control cabinets.
2 x CAN-FD
with ultra-stable communication performance
CAN-FD has become an indispensable bus interface in fields such as industrial automation, energy management, and smart transportation due to its higher data transmission rate and bandwidth utilization. The FET3506J-C SoM supports 2 x CAN-FD. According to actual tests, when the bus occupancy rate is 90%, whether it is single-channel or two-channel CAN-FD receiving/transmitting simultaneously, no frame loss will occur. Moreover, when the single-channel and two-channel are transmitting and receiving simultaneously at a 1:1 ratio and the bus occupancy rate is 87%, there is no frame loss or error frame. It is not difficult to see from the following test data that the CAN-FD interface of the FET3506J-C SoM has excellent communication performance.
No. Test Item Number Baud Rate Frame Capacity Note: Conclusion 1 Single-channel receiving only 1 Frame rate: 1M Extended ID frame 2800 frames per second Bus occupancy 90>#/td### Passed Data rate: 2M 2 Multi-channel receiving only 2 Frame rate: 1M Extended ID frame 2800 frames per second Bus occupancy 90>#/td### Passed Data rate: 2M 3 Single-channel sending only 1 Frame rate: 1M Extended ID frame 2800 frames per second Bus occupancy 90>#/td### Passed Data rate: 2M 4 Multi-channel sending only 2 Frame rate: 1M Extended ID frame 2800 frames per second Bus occupancy 90>#/td### Passed Data rate: 2M 5 Single-channel sending only 1 Frame rate: 1M Extended ID frame 2700 frames per second Bus occupancy 87>#/td### Passed Data rate: 2M 6 Multi-channel sending only 2 Frame rate: 1M Extended ID frame 2700 frames per second Bus occupancy 87>#/td### Passed Data rate: 2M Industrial-grade Features
The FET3506J-C SoM has undergone comprehensive and thorough reliability tests. The measured data shows that its power consumption is only 0.7W under full-load operation. Even without any heat dissipation measures, it can successfully pass the high-temperature...
Read more -
Forlinx OKMX8MP Linux 5.4.70 Porting Guide for Resistive Touchscreen Controller TSC2007
08/20/2025 at 03:17 • 0 commentsThis document provides a step-by-step guide for porting and calibrating the TSC2007 resistive touchscreen controller on the Forlinx OKMX8MP-C development board running Linux kernel 5.4.70.
- Purpose: Help developers enable and configure the TSC2007 driver so that resistive touchscreens can work properly on the OKMX8MP platform.
- Scope: Applicable to Forlinx OKMX8MP boards with Linux 5.4.70 SDK.
- Prerequisites: A working Linux build environment, basic knowledge of device tree modification, and hardware equipped with a TSC2007-based resistive touchscreen.
The TSC2007 is a low-power resistive touchscreen controller launched by Texas Instruments (TI). It adopts a 4-wire interface, integrates a 12-bit Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC), and features an I²C communication interface, supporting a wide voltage range from 1.2V to 3.6V.
1. Porting TSC2007 to the Kernel
Modify the Device Tree.
1.1 Device Tree Path:
forlinx@ubuntu: ~/work/$ vi OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/freescale/OK8MP-C.dts
Add the TSC2007 node under the i2c3 node:
[…] &i2c3 { clock-frequency =; pinctrl-names = "default"; pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_i2c3>; status = "okay"; touchscreen: tsc2007@48 { compatible = "ti,tsc2007"; reg =; pinctrl-names = "default"; pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_i2c4_gt928_io>; interrupt-parent = <&gpio1>; interrupts =; gpios = <&gpio1 0 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>; ti,x-plate-ohms =; linux,wakeup; status = "okay"; }; fusb302: typec-portc@22 { compatible = "fcs,fusb302"; reg =; pinctrl-names = "default"; pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_typec>; […]Note: The pins used here are those of the capacitive touchscreen GT928. In practice, the actual pins should be adapted according to the reserved pins on the carrier board.
1.2 Modify OK8MP-C_defconfig to include the TSC2007 driver in the build
If the Linux 5.4.70 kernel already contains the related driver, you only need to enable it in the configuration file and build it into the kernel.
Configuration file path:
forlinx@ubuntu: ~/work/$ vi OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-kernel/arch/arm64/configs/OK8MP-C_defconfig
Add the following configurations:
CONFIG_TOUCHSCREEN_TSC2007=y CONFIG_TOUCHSCREEN_TSC2007_IIO=y
1.3 Compile the source code and flash the board with the new image
2. Touchscreen Calibration
Note:
Sections 2.1 and 2.2 describe two different calibration methods.
2.1: After adding the driver in the source code and flashing, calibration is performed directly on the development board.
2.2: Calibration is added to the root filesystem source, and then flashed together with the image.
Either method can be used. If one does not work, try the other.
2.1 Resistive Touchscreen Calibration
2.1.1 Add Weston calibration support and reboot the board
Configuration file path:root@OK8MP:~# vi /etc/xdg/weston/weston.ini
Append the following content at the end of the file:
[…] [launcher] icon=/usr/share/weston/terminal.png path=/usr/bin/weston-terminal [libinput] touchscreen_calibrator=true
2.1.2 Run the calibration command in the terminal
root@OK8MP:~# weston-touch-calibrator "DPI-1" --debug -v
Note: DPI-1 is the node seen from the modetest command. For example, an LVDS screen would be shown as "LVDS-1".
The output is as follows:
could not load cursor 'dnd-move' could not load cursor 'dnd-copy' could not load cursor 'dnd-none' Configure calibrator window to size 800x480 Down[0] (0.156738, 0.210938) Finish[0] Conv[0] (0.150000, 0.100000) Down[1] (0.814209, 0.223633) Finish[1] Conv[1] (0.850000, 0.129167) Down[2] (0.202148, 0.802246) Finish[2] Conv[2] (0.200000, 0.800000) Down[3] (0.661865, 0.752197) Finish[3] got all touches Conv[3] (0.700000, 0.750000) calibration test error: -0.010711, 0.000734 Calibration values: 1.064632 0.002799 -0.017459 0.021535 1.182161 -0.152738
2.1.3 Copy the calibration results to the calibration file
Copy:1.064632 0.002799 -0.017459 0.021535 1.182161 -0.152738
Calibration file path:
/etc/udev/rules.d/ws-calibrate.rules...
Read more -
Efficient Deployment of Forlinx OK62xx-C Development Board Firmware on Linux via NFS and TFTP
08/13/2025 at 06:20 • 0 commentsOverview
This article introduces how to update the image over the network using NFS and TFTP on the OK62xx-C series development boards. Please refer to the document for the operations.
Application Scope
This article is mainly applicable to the Linux 6.1.33 operating system on the Forlinx OK62xx-C platform. Other platforms can also refer to it, but there will be differences between different platforms. Please make modifications according to the actual conditions.
1. Updating the Image over the Network using NFS and TFTP
NFS (Network File System) is a distributed file-sharing protocol that allows a computer to transparently access a remote file system over the network. It is commonly used to mount the root file system in embedded development.
1.1 NFS Service Setup
1). The method to set up an NFS server on Ubuntu is as follows:
Software Download and Installation
forlinx@ubuntu:~# sudo apt-get install nfs-kernel-server nfs-common portmap
Create an NFS Directory and Extract the File System (Take the rootfs.tar.bz2 file system as an example, and the current directory is the root directory)
forlinx@ubuntu:~# cd / forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo mkdir nfs_rootfs forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo tar -xvf rootfs.tar.bz2 -C /nfs_rootfs/
Modify the configuration file
forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo vim /etc/exports
Add the following configuration to the file:
/nfs_rootfs *(rw,sync,no_root_squash,no_subtree_check)
Restart profiles and services
forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo exportfs -rv forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo /etc/init.d/rpcbind restart forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo /etc/init.d/nfs-kernel-server restart
2) Verify the NFS server on the development board. After executing the following command, mount the NFS server to the /mnt directory of the development board:
root@imx6ulevk:~# mount -t nfs4 -o vers=4 192.168.0.57:/nfs_rootfs /mnt
After the successful mounting, check the /mnt directory, and you will see the file system that was just extracted.
root@imx6ulevk:~# ls /mnt/
Note: 192.168.0.57 is the IP address of the Ubuntu host of the NFS server. The network of Ubuntu needs to be set to the bridged mode and be in the same network segment as the development board. Copy the contents of /OK62xx - linux - fs/rootfs in the source code to /nfs_rootfs.
As shown in the figure:
Test NFS in the U-Boot stage of the development board.
Set the environment variables:
=> setenv ipaddr 172.16.0.141 //Development board ip => setenv serverip 172.16.0.142 //Server ip => nfs /home/forlinx/nfs_rootfs/bin/tar.tar //Download the file via NFS (absolute path here) link up on port 1, speed 1000, full duplex Using ethernet@8000000 device File transfer via NFS from server 172.16.0.141; our IP address is 172.16.0.142 Filename '/nfs_rootfs/bin/tar.tar'. Load address: 0x82000000 Loading: ################################################################# ############################## done Bytes transferred = 482272 (75be0 hex)
1.2 TFTP Service Setup
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) is a lightweight UDP - based file transfer protocol, mainly used for booting diskless devices or quickly transferring small files such as kernel images in embedded systems.
1)Install the server, client, and daemon process.
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt-get install tftp-hpa tftpd-hpa xinetd
2)Server configuration
First, create a tftpboot directory in the root directory and change its attributes to allow any user to read and write:
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ cd / forlinx@ubuntu:~ sudo mkdir nfs_rootfs forlinx@ubuntu:~$ sudo chmod 777 tftpboot
Then, enter the directory/etc/xinetd. d/, create a new file TFTP in it, and add the specified content to the TFTP file:
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ cd /etc/xinetd.d/ forlinx@ubuntu:~$ sudo vim tftp
Add the following to the TFTP file:
service tftp { disable = no 138 socket_type = dgram protocol = udp wait = yes user = root server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd server_args = -s /tftpboot -c per_source = 11 cps = 100 2 }Finally, modify the configuration...
Read more -
LLM + VLM Multimodal Visual Assistant Based on RK3576 SoM
08/02/2025 at 06:53 • 0 commentsIn areas like smart power, intelligent transportation, and industrial inspection, embedded devices act as essential "perception terminals" for collecting image information and performing intelligent analysis. Accurate image understanding is essential for enhancing the intelligent capabilities of various scenarios and ensuring the safe and efficient operation of both production and daily life. This involves identifying standardized operations and potential safety hazards in power inspection, interpreting the meanings of traffic signs and monitoring road conditions in traffic situations, as well as categorizing objects and identifying defects in industrial environments.
Traditional embedded solutions face limitations due to model architectures and computing power bottlenecks. These challenges result in issues such as inadequate recognition accuracy, slow response times, and high adaptation costs. Consequently, these solutions struggle to meet the intelligent requirements of precision, efficiency, and universality. In this context, Forlinx Embedded has developed a multimodal large model image understanding assistant based on the RK3576 SoM. It combines large language models (LLMs) and visual language models (VLMs) to create an "intelligent visual center" for embedded devices. This integration allows terminal devices to genuinely "understand" the complexities of the world around them.
FET3576-C SoM Multimodal Large Model Image Understanding Assistant
1. FET3576-C SoM Advantages
Forlinx Embedded´s FET3576-C System on Module (SoM) is developed based on the Rockchip RK3576 processor. This high-performance, low-power application processor is specifically designed by Rockchip for the AIoT and industrial markets. It features a combination of 4 ARM Cortex-A72 and 4 ARM Cortex-A53 high-performance cores, as well as a built-in Neural Processing Unit (NPU) that delivers impressive computing power of 6 TOPS. This capability enables the board to efficiently run large language models and multimodal models of various parameter scales, enhancing your AI applications.
2. Multimodal Large-Model Architecture
Forlinx Embedded’s multimodal large model seamlessly integrates a large language model (LLM) based on the Transformer architecture with a large visual language model (VLM). This combination forms a coherent multimodal system architecture that promotes efficient collaboration. The LLM and the visual model operate together within a unified framework, enabling a comprehensive understanding and effective response to complex tasks.
Core Architecture of the Multimodal Large Model
01 Visual Encoder: The Image "Translator"
Having a visual encoder is akin to giving an embedded terminal "eyes." It converts the original image into digital signals that machines can understand.
Consider the example of a photo featuring a power worker climbing a utility pole. The visual encoder will first extract key information from the image, such as the shape of the utility pole, the worker´s movements, and the background scenery. It then translates this visual content into a "universal language" that the embedded device can understand, which lays the groundwork for further analysis. Compared to traditional CNN models, Transformer-based visual encoders better capture long-distance dependencies, significantly enhancing target recognition accuracy in complex scenarios.
02 Projector: The Information "Converter"
As a "bridge" between vision and language, the projector further converts the image signals processed by the visual encoder into a format that the large language model can understand.
It is like a "converter" that can repackage and adjust the digital signals of the image, enabling the large language model to "understand" what the image is saying, thus paving the way for subsequent language understanding work. The multimodal large...
Read more -
Practical Tutorial: Running 32-Bit Applications on RK3568 Development Board
07/30/2025 at 01:13 • 0 commentsThe Rockchip RK3568 processor has established itself as a benchmark chip in the mid-range AIoT market, thanks to its well-balanced performance, power efficiency, and interface scalability, achieving remarkable market success since its launch. The RK3568 is a 64-bit processor, and the cross-compiler provided by the embedded system is also 64-bit. However, some users may need to run 32-bit applications on the RK3568 development board. This tutorial will provide a detailed walkthrough on how to use a 32-bit cross-compiler to compile 32-bit applications and ensure their seamless operation on the Forlinx Embedded RK3568 development board.
The following demonstrates the process using the gcc-linaro-7.5.0-2019.12-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf cross-compilation toolchain as an example.
1. Method Steps
(1) Kernel Configuration
The Forlinx Embedded RK3568 development board’s kernel is pre-configured with EL0 enabled by default, so no additional kernel configuration is required.
(2) 32-Bit Runtime Library Preparation
Since the system lacks 32-bit runtime libraries, the following steps are necessary:
- ① Package the lib directory from the libc folder in the cross-compilation toolchain. The specific path is:
gcc-linaro-7.5.0-2019.12-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libc - ② Manually create the /lib32 folder in the root directory of the Forlinx Embedded RK3568 development board.
- ③ Execute the following command to copy the packaged library files to the /lib32 directory on the development board as runtime libraries: cp ./* /lib32/ -rf
- ④ Add the environment variable to include /lib32 in the library search path: export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/lib32
- ⑤ Create a symbolic link: ln -s /lib32/ld-linux-armhf.so.3 /lib
(3) Application Testing
- ① Use the ld-linux-armhf.so.3 --list command instead of ldd to verify the required library files for the test program.
If all libraries are detected, proceed to execute the test program.
The test executable runs successfully.
- ② Check the test program in the development environment to confirm it is a 32-bit ELF format.
- ③ If manual library path specification is required, use the following command: /lib/ld-linux-armhf.so.3 --library-path /lib32 --list /home/forlinx/test
2. Key Considerations
(1) Glibc Version Compatibility
Ensure the glibc version in the cross-compilation toolchain matches the application’s requirements. Mismatched versions may cause runtime failures.
(2) Operational Accuracy
Double-check all commands during execution to avoid system issues on the development board due to misoperations.
(3) Development Environment Verification
Confirm proper configuration of the development environment, including installation of the cross-compilation toolchain and environment variable settings, before compiling and testing.
By following these steps, users can successfully run 32-bit applications on the Forlinx Embedded RK3568 development board, leveraging its high performance and low power consumption for diverse embedded development needs.
3. RK3568 Development Board Description
In the field of embedded development, the choice of development platform is critical to the success of a project. OK3568-C development board based on Rockchip RK3568 processor has become the first choice of many engineers because of its high performance, low power consumption and rich functional interfaces.
The RK3568 processor uses a quad-core 64-bit Cortex-A55 architecture with a main frequency of up to 2.0 GHz, and integrates Rockchip's self-developed NPU with 1 TOPS computing power. It also supports multi-format HD video decoding and multi-channel display output, meeting diverse application needs ranging from industrial control to intelligent security.
In addition to its powerful hardware capabilities, the Forlinx Embedded RK3568 development board offers extensive development tools and documentation, allowing engineers to effectively complete...
Read more - ① Package the lib directory from the libc folder in the cross-compilation toolchain. The specific path is:
-
From Beginner to Advanced: How to Choose the Rockchip RK Series SoM?
07/23/2025 at 01:54 • 0 commentsIn the fields of intelligent terminals, consumer electronics, industrial automation, edge AI, and the Internet of Things (IoT), Rockchip's RK series processors have won wide market recognition thanks to their adaptability to multiple scenarios, powerful multimedia processing capabilities, and mature ecological resources. As an important partner of Rockchip, Forlinx Embedded has launched multiple SoM products based on the RK series processors, which can meet the all-around needs from basic applications to complex AI scenarios.
Facing the three popular products, the FET3506J-S SoM, the FET3562J-C SoM, and the FET3576-C SoM, which cover different levels, how should engineers make a choice?
This article will analyze them from three dimensions: core configuration, functional features, and industry adaptability, to help you precisely identify the RK SoM solution that better suits your project requirements.
FET3506J-S SoM
The Forlinx Embedded FET3506J-S SoM is an option with significant price advantages. This industrial-grade SoM is built on the Rockchip RK3506J industrial-grade processor. With a tax-included price starting at just $14, it has become a star product in the entry-level market thanks to its high cost-effectiveness and stable industrial-grade quality.
1. Multi-core heterogeneous, flexible configuration
The design utilizes a 3×Cortex-A7 and 1×Cortex-M0 architecture, incorporating industrial-grade components throughout the entire board. This setup enables a single chip to manage complex tasks effectively: the Cortex-A7 handles the main control operations, while the Cortex-M0 is responsible for real-time I/O control. This dual architecture meets the requirements for both primary control and real-time performance in industrial control applications.
2. Ultra-low power consumption and rich interfaces
The measured power consumption of the FET3506J-S System on Module (SoM) at full load is only 0.7W, eliminating the need for any heat dissipation treatment. It can withstand high-temperature environment testing at +85°C while operating at full load. Additionally, it features a high-speed parallel bus interface known as DSMC. This low-cost, easy-to-develop communication bus supports high-speed connections between the FPGA and ARM, as well as master/slave configurations. Furthermore, it includes a configurable parallel data interface, FlexBUS, which can be used to connect ADC and DAC chips, DVP cameras, and QSPI LCD displays.
3. Applicable fields
FET3506J-S SoM is widely used in industrial automation, consumer electronics, intelligent medical treatment, power, new energy, communications and other industries and related applications. In addition, the competitive price advantage and complete after-sales technical support of Forlinx Embedded help your products come into the market quickly and walk in the forefront of the industry.
FET3562J-C SoM (A Lightweight yet All-Round AI Powerhouse)
When a project requires enhanced processing capabilities, improved multimedia performance, and moderate AI computing power, the Forlinx Embedded FET3562J-C SoM offers an exceptional balance. When a project requires enhanced processing capabilities, better multimedia performance, and moderate AI computing power, the Forlinx Embedded FET3562J-C SoM provides an excellent balance.
1. Powerful Quad-core + NPU
The FET3562J-C SoM is a high-performance, low-power consumption application processor specially designed for industrial automation and consumer electronic devices. It integrates 4 x ARM Cortex-A53 high-performance cores; an embedded 3D GPU to ensure full compatibility with OpenGL ES 1.1/2.0/3.2, OpenCL 2.0, and Vulkan 1.1; and a built-in NPU with a computing power of 1 TOPS, supporting mixed operations of INT4/INT8/INT16/FP16 data types, which can provide more options for your AI applications.
2. Powerful Multimedia and Expansion Capabilities
It supports H.264 encoding and...
Read more -
RK3588-based Intelligent Security Gateway Solution: Enabling Closed-loop Multi-channel Video AI Inference and Real-time Streaming
07/19/2025 at 05:46 • 0 commentsAgainst the backdrop of the accelerated development of smart cities and Industry 4.0, security monitoring systems are undergoing an intelligent upgrade from simply "seeing" to truly "understanding" what they observe. Especially in the fields of intelligent transportation, smart buildings, and public safety, real-time video analytics and rapid decision-making capabilities have become core requirements for ensuring operational efficiency.
In response to the dual challenges of real-time performance and intelligence posed by multi-channel video surveillance scenarios, Forlinx Embedded has launched an intelligent multi-channel security gateway solution based on the RK3588 SoM. Relying on the on-board video codec hardware acceleration unit (VPU) and neural network processing unit (NPU), it can achieve real-time encoding and decoding of multi-channel video data and inference of various AI models, thus establishing a full-process closed-loop from video collection to intelligent analysis.
1. Performance Analysis of FET3588-C SoM
Let's first take a look at the core configuration of the main control device. It is equipped with Rockchip's flagship RK3588 processor, which adopts a big-little core architecture of 4×Cortex-A76@2.4GHz + 4×Cortex-A55@1.8GHz, providing powerful power for multitasking. It has a built-in Rockchip self-developed triple-core NPU that can work collaboratively or independently, enabling flexible allocation of computing power to avoid redundancy.
The comprehensive computing power can reach 6 TOPS, offering abundant computing support for edge-side AI. It also incorporates the new-generation 48-megapixel ISP3.0, which can achieve effects such as lens shadow correction, 2D/3D noise reduction, sharpening and dehazing, fisheye correction, gamma correction, and wide-dynamic contrast enhancement, significantly improving the image quality.
In addition, it is fully equipped with a rich variety of high-speed data communication interfaces to meet the diverse needs of users.
2. System Data Flow
The FET3588-C SoM, multiple network cameras, and the PC are in a local area network formed by a switch. The FET3588-C SoM is responsible for the entire process of pulling and decoding the video streams input from the network cameras, conducting AI inference, and encoding and pushing the streams. The processed video streams are pushed to the designated streaming media server. The PC pulls and plays the corresponding videos from this streaming media server.
3. Highlights of the Solution
01. Efficient real-time video processing
The FET3588-C SoM adopts Rockchip's fourth-generation codec technology. In addition to supporting the mainstream 8K@60fps H.265 decoder and 8K@30fps H.264 decoder, it also supports the 8K@60fps VP9 decoder and 4K@60fps AV1 decoder.
Both video encoding/decoding and AI inference in the entire process rely on the SoM for codec processing. With multiple camera inputs, the decoding time for each frame of video data is about 15ms, and the inference time is about 30-200ms. Through frame-skipping operations, it can meet the requirement of real-time processing of multi-camera video data at around 20fps.
02. Real-time inference of multiple AI models
The FET3588-C SoM introduces INT4/INT8/INT16/FP16 mixed-precision operations, which improve the MAC utilization rate by over 28%. At the same time, it upgrades to the 2.0 RKNN TOOLkit2 suite, which has strong compatibility and can meet the edge-computing needs of most terminal devices.
This solution supports the deployment of multiple AI models to meet the requirements of different application scenarios. For example, one video stream can use an object detection model while another video stream uses a keypoint detection model. Currently, it supports YOLOv8 object detection models, keypoint detection models, and image segmentation models.
03. Flexible configuration through an external configuration file
Information such as the RTSP addresses...
Read more -
FreeRTOS Design Routine Based on i.MX9352 Development Board M Core
07/02/2025 at 06:22 • 0 commentsIn the embedded systems, the application of embedded real-time operating systems (RTOS) is becoming increasingly widespread. Using an RTOS can utilize CPU resources more reasonably and efficiently. As a lightweight and mature real-time operating system kernel, FreeRTOS has complete core functions, including task management, time management (such as delays and timers), synchronization mechanisms (semaphores, mutexes), inter-process communication (message queues), and so on. These features enable it to meet the needs of small and medium-sized embedded systems with relatively limited resources.
i.MX 9352 is a new generation of lightweight edge AI processor launched by NXP, which integrates 2 x Cortex-A55 cores and 1 x Cortex-M33 real-time core. Its architecture design fully reflects the balance between real-time and complex task processing capabilities. To help developers fully leverage the real-time capabilities of the i.MX 9352 M33 core, the FreeRTOS examples provided in the accompanying M-core SDK package are divided into two categories. One category introduces the features of FreeRTOS system components, such as semaphores, mutexes, and queues. The other category shows how to use peripheral interfaces in FreeRTOS. Examples from each of these two categories are selected for demonstration.
▊ Demo platform: Forlinx Embedded OK-MX9352-C Development Board
![Forlinx Embedded OK-MX9352-C Development Board]()
1. FreeRTOS-generic
The sample code of FreeRTOS features supported by the Forlinx Embedded OK-MX9352-C is as follows:
- freertos_event: Demonstration Routine for Task Event
- freertos_queue: Demonstration routine for implementing inter-task communication using queue messages
- freertos_mutex: Routine for using mutexes
- freertos_swtimer: Usage of software timers and their callbacks.
- freertos_tickless: Routine for delayed wake-up using LPTMR or wake-up by hardware interrupt.
- freertos_generic: Demonstration routine for the combined use of tasks, queues, software timers, tick hooks, and semaphores.
Since the FreeRTOS_generic routine uses many FreeRTOS features, let's focus on analyzing this routine.
(1)Software implementation
The content of the example program includes: task creation, queues, software timers, system tick clocks, semaphores, and exception handling. Specifically:
Task creation:
The main function creates three tasks: a queue sending task, a queue receiving task, and a semaphore task.
// Create the queue receiving task if (xTaskCreate(prvQueueReceiveTask, "Rx", configMINIMAL_STACK_SIZE + 166, NULL, mainQUEUE_RECEIVE_TASK_PRIORITY, NULL) != pdPASS) // Create the queue sending task if (xTaskCreate(prvQueueSendTask, "TX", configMINIMAL_STACK_SIZE + 166, NULL, mainQUEUE_SEND_TASK_PRIORITY, NULL) != pdPASS) // Create the semaphore task if (xTaskCreate(prvEventSemaphoreTask, "Sem", configMINIMAL_STACK_SIZE + 166, NULL, mainEVENT_SEMAPHORE_TASK_PRIORITY, NULL) != pdPASS)
Queues:
The queue sending task blocks for 200ms and then sends data to the queue. The queue receiving task blocks to read from the queue. If the data is read correctly, it prints the current number of received items in the queue.
// The queue sending task blocks for 200ms and then sends data to the queue static void prvQueueSendTask(void *pvParameters) { TickType_t xNextWakeTime; const uint32_t ulValueToSend = 100UL; xNextWakeTime = xTaskGetTickCount(); for (;;) { // The task blocks until the 200ms delay ends. vTaskDelayUntil(&xNextWakeTime, mainQUEUE_SEND_PERIOD_MS); // Send data to the queue. A blocking time of 0 means it will return immediately when the queue is full. xQueueSend(xQueue, &ulValueToSend, 0); } } //The queue receives the task, and the task is blocked to read the queue. If the data is read correctly, the number received by the queue at this time is printed. static void prvQueueReceiveTask(void *pvParameters) { uint32_t ulReceivedValue; for (;;) { //The task keeps blocking until data is read from the queue xQueueReceive(xQueue, &ulReceivedValue, portMAX_DELAY); //The queue data is...Read more -
Intelligent Lawn Mowing Robot Main Control Solution Based on RK3576
06/27/2025 at 03:02 • 0 commentsWith the rise of smart outdoor automation, intelligent lawn mowing robots are rapidly replacing traditional gasoline-powered mowers in Europe and America. To meet growing demands for autonomy, precision, and environmental performance, embedded system designers are turning to powerful platforms like the Rockchip RK3576. As a high-performance processor with built-in AI acceleration, the RK3576 offers an ideal main control solution for next-generation smart lawn mowers.
1. RK3576 SoM: A New and More Powerful Engine
The rising consumer demand for more functions in lawn mowing robots is creating an urgent need in the industry for intelligent and efficient technical solutions. As the core technological carrier of the intelligent wave, the Rockchip RK3576 processor, with its high-performance computing, high computing power, multi-sensor fusion, and low-power design, is expanding the technical boundaries of intelligent lawn mowing robots and driving the products to evolve towards greater precision, autonomy, and environmental friendliness.
The FET3576-C system on module(SoM) developed by Forlinx Embedded based on the Rockchip RK3576 chip uses advanced 8nm process technology. It integrates a quad-core Cortex-A72 (with a main frequency of 2.3GHz) and a quad-core Cortex-A53 (with a main frequency of 2.2GHz), and is equipped with a Mali-G52 MC3 graphics processing unit (GPU) and a neural network processing unit (NPU) with an independent computing power of 6TOPS, making it a more powerful engine for high-end lawn mowing robots.
2. Technological Innovation Driven by Powerful Performance
Using Forlinx Embedded's FET3576-C SoM, this powerful engine, as the main control device for the new-generation lawn mowing robots significantly enhances the functionality and performance. The technological innovation is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
(1) Core Computing Architecture
The FET3576-C SoM CPU features four Cortex-A72 cores and four Cortex-A53 cores. The big.LITTLE architecture enables it to support the concurrent execution of multiple tasks such as route planning, image acquisition, and mechanical control.
(2) AI Computing Acceleration System
The NPU built into the FET3576-C core board supports INT4/INT8/INT16/FP16/BF16/TF32 operations and multiple deep-learning frameworks like TensorFlow, Caffe, and Pytorch. With a computing power of 6TOPS, it can achieve accurate object recognition and detection, identify various obstacles in complex environments, and optimize lawn mowing route decisions.
(3) Realization of Intelligent Weeding System
The FET3576-C SoM constructs a complete functional closed-loop for intelligent mowing robots through diverse bus interfaces. Thanks to the FlexBus parallel bus (with a maximum clock of 100MHz and compatible with 2/4/8/16-bit transmission) and high-speed interfaces such as DSMC, CAN-FD, PCIe2.1, SATA3.0, and USB3.2, it can be flexibly adapted to multi-spectral camera arrays (connected via MIPI-CSI) and various actuators.
In terms of function realization, the AI vision algorithm uses camera data for accurate real-time obstacle identification; the decision-making layer uses AI models for dynamic path planning; the execution end controls the laser module or robotic arm through CAN/GPIO interfaces for millimeter-level precise operations. In addition, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth support remote setting of virtual boundaries and viewing of work logs via mobile phone apps.
3. Summary
Lawn mowing robots are transitioning from traditional tools to intelligent platforms, placing higher demands on the performance, stability, and AI capabilities of the main control system. The FET3576-C SoM, with its high-performance heterogeneous computing, powerful AI inference ability, and comprehensive system expansion interfaces, constructs an intelligent operation closed-loop from “perception-decision-execution”, providing solid technical support for intelligent lawn mowing robots and...
Read more -
How to Perform OTA Upgrade on the OKMX8MP-C Platform Based on Android 11 System
06/25/2025 at 02:27 • 0 commentsThe OTA (Over-The-Air Technology) upgrade system is a technical architecture that enables remote firmware updates for devices via wireless networks. It is mainly composed of a Bootloader program, a firmware transmission module, and a version management module. This system divides the device's storage space into a Bootloader area, an application area, and a download area to achieve the safe replacement of old and new firmware. It supports functions such as resume from breakpoint, encryption verification, and version rollback. Widely used in fields such as smartphones, IoT devices, and automotive electronics, it allows devices to complete function updates and security patch deployments without physical connections. This article describes the specific implementation method of using the OTA upgrade system on the OKMX8MP-Android 11 system.
Build the OTA upgrade package
1. Build a complete update package
Note: The following operations are based on the initial source code, that is, you start using the first version of the OTA function source code.
1.1 Enter the corresponding path of the source code:
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ cd imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source/ forlinx@ubuntu:~/imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source$
1.2 Configure environment
forlinx@ubuntu:~/imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source$ source env.sh forlinx@ubuntu:~/imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source$ source build/envsetup.sh forlinx@ubuntu:~/imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source$ lunch evk_8mp-userdebug ============================================ PLATFORM_VERSION_CODENAME=REL PLATFORM_VERSION=11 TARGET_PRODUCT=evk_8mp TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT=userdebug TARGET_BUILD_TYPE=release TARGET_ARCH=arm64 TARGET_ARCH_VARIANT=armv8-a TARGET_CPU_VARIANT=cortex-a53 TARGET_2ND_ARCH=arm TARGET_2ND_ARCH_VARIANT=armv7-a-neon TARGET_2ND_CPU_VARIANT=cortex-a9 HOST_ARCH=x86_64 HOST_2ND_ARCH=x86 HOST_OS=linux HOST_OS_EXTRA=Linux-5.4.0-150-generic-x86_64-Ubuntu-18.04.4-LTS HOST_CROSS_OS=windows HOST_CROSS_ARCH=x86 HOST_CROSS_2ND_ARCH=x86_64 HOST_BUILD_TYPE=release BUILD_ID=RQ1A.201205.003 OUT_DIR=out PRODUCT_SOONG_NAMESPACES=device/generic/goldfish device/generic/goldfish-opengl external/mesa3d vendor/nxp-opensource/imx/power hardware/google/pixel vendor/partner_gms hardware/google/camera vendor/nxp-opensource/imx/camera ============================================
1.3 Start compilation:
forlinx@ubuntu:~/imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source$ ./imx-make.sh kernel -j4 make: Entering directory '/home/forlinx/imx8mp/R3_6.28/OK8MP-android-source' /home/forlinx/imx8mp/R3_6.28/OK8MP-android-source/device/nxp/common/build/uboot.mk:74: *** shell env AARCH64_GCC_CROSS_COMPILE is not set. Stop. make: Leaving directory '/home/forlinx/imx8mp/R3_6.28/OK8MP-android-source' forlinx@ubuntu:~/imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source$ make otapackage -j4 ============================================ PLATFORM_VERSION_CODENAME=REL PLATFORM_VERSION=11 TARGET_PRODUCT=evk_8mp TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT=userdebug TARGET_BUILD_TYPE=release TARGET_ARCH=arm64 TARGET_ARCH_VARIANT=armv8-a TARGET_CPU_VARIANT=cortex-a53 TARGET_2ND_ARCH=arm TARGET_2ND_ARCH_VARIANT=armv7-a-neon TARGET_2ND_CPU_VARIANT=cortex-a9 HOST_ARCH=x86_64 HOST_2ND_ARCH=x86 HOST_OS=linux HOST_OS_EXTRA=Linux-5.4.0-150-generic-x86_64-Ubuntu-18.04.4-LTS HOST_CROSS_OS=windows HOST_CROSS_ARCH=x86 HOST_CROSS_2ND_ARCH=x86_64 HOST_BUILD_TYPE=release BUILD_ID=RQ1A.201205.003 OUT_DIR=out PRODUCT_SOONG_NAMESPACES=device/generic/goldfish device/generic/goldfish-opengl external/mesa3d vendor/nxp-opensource/imx/power hardware/google/pixel vendor/partner_gms hardware/google/camera vendor/nxp-opensource/imx/camera ============================================ [……] #### build completed successfully (13:07 (mm:ss)) ####
After compilation, the "evk _ 8mp-ota-" eng. Forlinx. zip "will be generated in the" out/target/product/evk _ 8mp/ "path, which is the compressed package required for OTA full upgrade.
forlinx@ubuntu:~/imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source$ cd out/target/product/evk_8mp/ forlinx@ubuntu:~/imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source/out/target/product/evk_8mp$...
Read more -
Guide to Setting up TFTP, NFS, and SSH Network Services on the Forlinx OK-MX9352-C Platform Based on Linux
06/21/2025 at 07:29 • 0 commentsThis article describes how to set up common network services on the Forlinx OK-MX9352-C platform (running the Linux 6.1.36 operating system). Other platforms can also refer to it, but due to platform differences, please make adjustments according to the actual situation.
TFTP Service Setup
1. Server, Client Installation, and Daemons
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt-get install tftp-hpa tftpd-hpa xinetd
2.Server Configuration
First, create a tftpboot in the root directory and change the attributes to read and write for any user:
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ cd / forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo mkdir tftpboot forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo chmod 777 tftpboot
Then, go to the directory /etc/xinetd.d/ and create a new file tftp in it, adding the specified contents to the tftp file:
forlinx@ubuntu:/$ cd /etc/xinetd.d/ forlinx@ubuntu:/etc/xinetd.d$ sudo vim tftp
Add the following to the tftp text.
service tftp { disable = no 138 socket_type = dgram protocol = udp wait = yes user = root server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd server_args = -s /tftpboot -c per_source = 11 cps = 100 2 }Finally, modify the configuration file /etc/default/tftpd-hpa
forlinx@ubuntu:/etc/xinetd.d$ cd / forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo vim /etc/default/tftpd-hpa
Modify to
TFTP_USERNAME="tftp" TFTP_DIRECTORY="/tftpboot" TFTP_ADDRESS="0.0.0.0:69" TFTP_OPTI
Make sure to change TFTP_DIRECTORY to the path where the newly created tftpboot directory is located.
3.Services Restart
forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo /etc/init.d/xinetd reload forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo /etc/init.d/xinetd restart forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo /etc/init.d/tftpd-hpa restart
4.Server Test
To test this, create a new file in the /tftpboot folder
forlinx@ubuntu:/$ cd /tftpboot/ forlinx@ubuntu:/tftpboot$ sudo touch abc
Go to another folder
forlinx@ubuntu:/tftpboot$ cd /home/ forlinx@ubuntu:/home$ sudo tftp 192.168.2.57 //192.168.2.57 is the local IP. tftp> get abc tftp> quit forlinx@ubuntu:/home$ ls abc
If the server can be downloaded, it indicates that the server has been installed successfully. Once the development board is connected to the PC using an Ethernet cable, you can utilize TFTP to download files.
bootz ${loadaddr} - ${fdt_addr};NFS Service Setup
1. The method for setting up an NFS server on Ubuntu is as follows:
Software download and installation
forlinx@ubuntu:~# sudo apt-get install nfs-kernel-server nfs-common portmap
Create the NFS directory and extract the file system (using rootfs.tar.bz2 as an example, with the current directory as the root directory).
forlinx@ubuntu:~# cd / forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo mkdir nfs_rootfs forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo tar -xvf rootfs.tar.bz2 -C /nfs_rootfs/
Modify the configuration file
forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo vim /etc/exports
Add the following configuration to the file:
/nfs_rootfs *(rw,sync,no_root_squash,no_subtree_check)
Restart configuration files and services
forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo exportfs -rv forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo /etc/init.d/rpcbind restart forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo /etc/init.d/nfs-kernel-server restart
2. Verify the NFS server on the development board and mount the NFS server to the /mnt directory of the development board after executing the following command.
root@ok-mx93:~# mount -t nfs4 -o vers=4 192.168.0.57:/nfs_rootfs /mnt
After successful mounting, check the /mnt directory and you will see the file system you just extracted.
root@ok-mx93:~# ls /mnt/
Note: 192.168.0.57 is the IP of the NFS server host ubuntu, ubuntu's network needs to be set to bridge mode, and with the development board in the same network segment.
SSH Service Setup
1.SSH Installation
Install the SSH service by typing the following command in the Ubuntu (Linux host) terminal:
forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo apt-get install ssh
2.Enable SSH
forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo service ssh start
3.Check the status of the SSH service
forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo service ssh status ● ssh.service - OpenBSD Secure Shell server Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/ssh.service; enabled;...
Read more -
Solution | Forlinx Embedded’s AM62x SoM Drives Innovation in Microgrid Intelligence
06/18/2025 at 02:57 • 0 commentsDriven by the global goal of carbon neutrality, microgrid systems centered around distributed energy are becoming a crucial means for energy transformation. As the control center for local power generation, energy storage, and electricity loads, the microgrid coordination controller undertakes the core tasks of coordinating internal resources, ensuring stable operation of the system, and achieving economic optimization. Its reliability and performance directly affect the overall performance of the microgrid system and play a decisive role in the long-term operational economy of the system.
The FET6254-C Computer on Module developed by Forlinx Embedded based on the TI AM62x processor can provide strong support for the microgrid coordination controller with its multi-core collaborative processing capabilities, real-time response characteristics, and industrial-grade reliability, promoting efficient collaboration among distributed energy sources.
Key Role and Technical Challenges of Microgrid Coordination Controllers
The microgrid coordination controller is the core control device in a microgrid. It needs to monitor the operating status of equipment such as photovoltaics, wind power, energy storage, and charging piles in real-time, and formulate control strategies based on the goals of safety and economic optimization. Generally speaking, as the ''brain'' of the system, the microgrid coordination controller should have core functions such as high-speed data acquisition, seamless grid-connected and off-grid switching, power coordination control, frequency and voltage regulation control, and strategy execution.
Facing complex control tasks, traditional single-core processors are often inadequate. On one hand, they need to run the Linux system to achieve network communication, data processing, and human-machine interaction. On the other hand, they are required for real-time control, capable of completing grid-connected and off-grid switching and power adjustment within milliseconds. Meanwhile, the large number of microgrid devices and complex communication protocols pose strict requirements on interface resources.
FET6254-C SoM with Multi-core Heterogeneous Architecture Empowers Powerfully
To meet the technical requirements of microgrid coordination controllers, Forlinx Embedded recommends the FET6254-C SoM, which is designed and developed based on TI’s Sitara™ AM62x series of industrial-grade processors, as the main control solution. With its multi-core heterogeneous architecture and abundant interface resources, it can provide strong technical support for microgrid control.
1. Multi-core Heterogeneous Architecture for Both High-efficiency Computation and Real-time Control
The Forlinx Embedded FET6254-C SoM features a multi-core heterogeneous design of 4-core Cortex-A53 + Cortex-M4F, which can effectively integrate high-performance computing and real-time control. The 4-core Cortex-A53 with a main frequency of up to 1.4 GHz runs the Linux system and is used to handle complex algorithms, communication protocol stacks, and energy management strategies. The Cortex-M4F control core can independently run real-time tasks, dealing with millisecond-level controls such as grid-connected and off-grid switching, frequency regulation, and voltage regulation.
It is worth noting that the M4F core of AM62x can run independently, and its kernel startup and operation do not depend on the A53 kernel, ensuring the reliability of critical controls. This architectural design enables the coordination controller to handle management tasks and real-time control simultaneously, ensuring that it can switch to the off-grid mode within milliseconds in case of a power grid failure to guarantee the power supply for critical loads.
2. Abundant Interface Resources for Comprehensive Connection of Microgrid Devices
The microgrid coordination controller needs to connect various devices such as photovoltaic inverters, power conversion systems...
Read more -
Common Interface Problems and Troubleshooting Ideas of Forlinx Embedded AM62x Development Board (Phase 1)
06/13/2025 at 07:22 • 0 commentsAM62x processor, as a new generation of high-performance and low-power processor, has been widely used in industrial control, human-computer interaction, edge computation and other fields. OK62xx-C development board based on AM62x processor provides abundant hardware interface resources for developers. This article will provide systematic troubleshooting ideas and solutions for various interface problems that may be encountered in the development process to help developers quickly locate and solve problems.
![Common Interface Problems and Troubleshooting Ideas of Forlinx Embedded AM62x Development Board (Phase 1)]()
General Troubleshooting
In the process of hardware debugging, the systematic troubleshooting method can significantly improve the efficiency. The following is the general troubleshooting process:
Chip consistency verification:
First, make sure that the functional chip used is exactly the same as the reference design schematic. If the chip model is different, driver migration may be required, including modifying the device tree configuration and driver.
1. Basic signal checking:
For modules that fail feature verification, check in order:
- Whether the power supply voltage is within the allowable range;
- Check whether the reset signal timing meets the requirements;
- Check whether the frequency and amplitude of the clock signal are normal.
2. Cross Test:
By replacing either the System on Module (SoM) or the carrier board, quickly identify the source of the problem.
3. Signal integrity check:
- Measure whether the pin level is as expected;
- Check whether the data signal is output normally;
- Confirm whether the signal idle state is normal
4. Welding quality inspection:
- Check the welding problems, whether the resistance and capacitance devices have problems such as cold welding, continuous welding, missing welding, wrong welding, etc;
- Check the welding direction of the device to see if there is a problem that the pin 1 of the welded device does not correspond to the pin 1 of the carrier board.
5. Pin Multiplexing Checking:
Refer to the AM62x Technical Reference Manual to confirm whether the function multiplexing configuration of the used pins is correct. Pay special attention to the default functions of the pins related to startup.
Troubleshooting of System Failure to Start
Follow the steps below to troubleshoot the issue of system failure to start:
1. Key signal inspection:
- Measure the VCC3V3_SYS-PG (RD60) signal to ensure that the power supply is functioning properly;
- Check if all power rail voltages are within the allowable range;
- Verify whether the timing of the reset signal meets the requirements of the processor.
2. Start Configuration Check:
- Confirm that the GPMC bus related startup pins have been correctly pulled up and down in the carrier board design;
- Pay special attention to not affecting the startup configuration level when connecting external devices such as FPGA;
- Check the level status of the boot mode selection pin.
3. I2C bus conflict troubleshooting:
- RU50 and RU52 are I2C0 buses, and the SoM may have multiple devices mounted;
- Ensure that the bottom board does not float these pins, and other functions do not reuse I2C0;
- Check if the pull-up resistor on the I2C bus is normal.
4. Cross Test:
Replace the SoM or carrier board and confirm if it is an isolated issue.
Troubleshooting of I2C Interface Issues
Common problems and solutions of I2C bus:
1. Basic configuration check:
- Confirm that both SCL and SDA lines have pull-up resistors;
- Check if there are any conflicts in the addresses of devices mounted on the I2C bus within the same group.
2. Signal quality analysis:
- Measure whether the idle state is at a high level;
- Observe whether the waveform is complete and whether there is overshoot or ringing during data transmission;
- Use a logic analyzer to capture the complete communication process.
3. Impedance matching adjustment:
If the rising edge of the waveform is slow, the pull-up resistance value can be reduced;
If the low level is too high, the pull-up resistor value can be increased.
4. Diagnostic...
Read more -
How to Apply the Linux-RT Real-time Patch in the T113 Embedded System?
06/10/2025 at 07:17 • 0 commentsIn order to improve the response performance of the T113 embedded platform in real-time control scenarios, a PREEMPT-RT real-time patch (patch-5.4.61-rt37) needs to be applied to the Linux 5.4.61 kernel. It can optimizes the kernel scheduling mechanism and improves task response determinism, serving as a critical tool for embedded systems to achieve "soft real-time" or "firm real-time" performance.
Environmental Description
- Platform: Allwinner T113(OK113i)
- Kernel version: Linux 5.4.61
- Development environment: Based on OK113i Linux SDK (including kernel and buildroot)
- Goal: Integrate Linux-RT real-time patches into the kernel and validate real-time performance.
1. Download and extract the patch-5.4.61-rt37 patch
patch-5.4.61-rt37.patch.gz
The uname -a command reveals that the T113 platform runs Linux kernel version 5.4.61, which allows downloading the corresponding RT real-time patch from the official Linux-RT repository at:
Index of /pub/linux/kernel/projects/rt/5.4/older/2. Extract the downloaded patch-5.4.61-rt37.patch file and place the decompressed patch into the linux5.4 directory, as shown in the following project path:
3. Execute the following command in the linux5.4 directory to apply the patch to the kernel: How to Apply Kernel Patches with patch Command-CSDN Blog
4. Due to code discrepancies, the system will report numerous mismatches causing patch application failure. The following command can be used to identify failed patch files:
Then, according to the directory prompt, find the file that failed to enter the patch. Manually integrate it.
5. To enable the real-time system configuration in the kernel, open the menu configuration. The temporary .config file for the T113 is located in the OK113i-linux-sdk/out/kernel/build directory. Therefore, you need to run make menuconfig ARCH=arm in that directory.
The related configuration is as follows:
After completing the modification, save and exit.
Since the configuration file saved in OK113i-linux-sdk/out/kernel/build is only temporary, you need to copy the .config file to the kernel configuration directory:
OK113i-linux-sdk/kernel/linux-5.4/arch/arm/configs/, and rename it to sun8iw20p1smp_t113_auto_defconfig.
Then, perform a full kernel compilation based on this updated configuration.
Next Step: Add the rt-tests Tool in Buildroot
To add the rt-tests utility to Buildroot:
First, modify the Kconfig file located at OK113i-linux-sdk/kernel/linux-5.4/drivers/cpufreq/Kconfig to add the corresponding configuration option (checkbox).
Next, add the box selection in the figure in OK113i-linux-sdk/kernel/linux-5.4/init/Kconfig
After modification, switch to the path in the code box below to open the interface settings.
The relevant modification steps are shown in the figure below:
When the modification is complete, save and exit. Then compile under the current path.
After successful compilation, switch to the SDK path for full compilation.
After the compilation is successful, pack the image and burn it to the T113, and then describe below the relevant tests in the serial port terminal.
Real-time test: cyclictest-Zhihu (zhihu. com)
Input the following commands in the serial port terminal to test.
Plain Text copy the code.
1 2 cyclictest -l10000000 -m -n -t3 -p99 -i2000 -h100 // Or execute: cyclictest -t 5 -p 80 -n // Launches 5 threads at priority 80 with endless iteration.
Test data when no real-time patch is applied.
After comparison, it is found that the delay of T113 with linux-rt real-time patch is reduced to about 60 microseconds, while the maximum delay of T113 without linux-rt real-time patch is 9482 microseconds.
-
How to Build a Buildroot File System and Add System Tools on the OK3588-C Platform?
06/07/2025 at 06:12 • 0 commentsThis article takes the Forlinx OK3588-C development board platform as an example to explain how to use Buildroot to build a file system and add common system tools such as OpenCV. It is suitable for developers who need to customize embedded Linux systems.
1. Overview
This article applies to the Buildroot system of Linux 5.10.209. The purpose of this article is to show how to make customized modifications to Buildroot 209.
2. Operations
2.1 SDK Source Code Download and Decompression
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/3-3588-SDK_Kernel_5.10.209/1-Linux5.10.209+Qt5.15.10+Forlinx_Desktop22.04/OK3588-linux-source$ ls app build_secret_uboot.sh debian external output rkbin rtos ubuntu build_close.sh build.sh device kernel prebuilts rkflash.sh tools uefi buildroot common docs Makefile README.md rockdev u-boot yocto
2.2 Buildroot Compilation Available
To compile buildroot, delete or remove rootfs.ext4 from this directory (move to another directory or rename it)
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/3-3588-SDK_Kernel_5.10.209/1-Linux5.10.209+Qt5.15.10+Forlinx_Desktop22.04/OK3588-linux-source/prebuilts/forlinx/buildroot$ ls
rootfs.ext4
2.3 Compiling Default Configuration Items
To ensure compatibility with the previous default Buildroot configuration items (forlinx_ok3588_defconfig), re-compile by executing ./build.sh or ./build.sh buildroot.
During the build process, according to the configuration items in forlinx_ok3588_defconfig, the source code packages of software projects will be fetched from the server and placed in the /buildroot/package directory.
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/3-3588-SDK_Kernel_5.10.209/1-Linux5.10.209+Qt5.15.10+Forlinx_Desktop22.04/OK3588-linux-source/buildroot/package$
After the compilation is complete, a number of files are added and generated.
Generate files under buildroot/output/forlinx_ok3588/
>td >images
Table of Contents Usage Description build Store the intermediate and temporary files generated during the compilation process. If these files are deleted, the recompilation time will be very long. host Contains tools and binary files compiled for the build system host. Stores the finally generated firmware image files. rootfs.ext4 is the Buildroot system image and can be directly replaced. scripts Contains various script files used by Buildroot. Used for automated building, configuring the environment, or handling specific tasks. staging Contains header files, library files, and other development-related files of the target system. Required during the cross-compilation process. target Contains the complete content of the root file system (rootfs) on the target device. Only contains files required at runtime and does not include development-related header files or libraries. After compilation, it will be directly packaged into update.img.
Note: Many problems may occur during this process, such as the inability to obtain packages due to network timeouts, insufficient number of threads during compilation, insufficient memory, or insufficient swap partition. Non-software-source-code-related problems are generally considered from these aspects. Remember not to use sudo with root privileges.
2.4. Adding System Tools or Required Library Files to the Buildroot System
Here, take OpenCV4 as an example:
①. Enter the Buildroot directory and compile forlinx_ok3588_defconfig
make forlinx_ok3588_defconfig
②. Open the menuconfig graphical interface and select the projects need to be compiled.
make menuconfig ARCH=arm64
Read moreOptions Usage Target options Configure the architecture and hardware parameters of the target device. Build options Configure the build behavior of Buildroot. Toolchain Configure the cross-compilation toolchain System configuration Configure the cross-compilation toolchain. Kernel Configure the Linux kernel. Target packages Select the software packages to be installed on the target system. Filesystem images Configure the type of the generated file system image. Bootloaders Configure the bootloaders (e.g., U-Boot, GRUB). Host utilities Configure... -
5-Minute Guide to Network Service Setup with i.MX9352 and Linux 6.1
06/05/2025 at 07:29 • 0 commentsIn the technological wave of the ''Internet of Everything'', network services have become the core link connecting the physical world and the digital world. They not only endow terminal devices with the ability to ''communicate'', but also shape the development paradigm of intelligent devices.
This article will use the Forlinx Embedded OK-MX9352-C development board (equipped with the NXP i.MX9352 processor widely used in the industrial Internet of Things field) as a platform to introduce how to build common network services in the Linux 6.1.36 development environment. Engineers can refer to this article for operation.
![Learn to Build Network Services in 5 Minutes: A Practical Example with i.MX9352 + Linux 6.1]()
1. TFTP service setup
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) is a protocol in the TCP/IP protocol suite used for simple file transfer between clients and servers, and is commonly used for kernel debugging. In the process of embedded Linux development, kernel debugging is a fundamental and important part.
1.1 Server, Client Installation, and Daemons
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt-get install tftp-hpa tftpd-hpa xinetd
1.2 Server Configuration
First, create a tftpboot in the root directory and change the attributes to read and write for any user:
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ cd / forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo mkdir tftpboot forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo chmod 777 tftpboot
Then, go to the directory /etc/xinetd.d/ and create a new file tftp in it, adding the specified contents to the tftp file:
forlinx@ubuntu:/$ cd /etc/xinetd.d/ forlinx@ubuntu:/etc/xinetd.d$ sudo vim tftp
Add the following to the tftp text.
service tftp { disable = no 138 socket_type = dgram protocol = udp wait = yes user = root server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd server_args = -s /tftpboot -c per_source = 11 cps = 100 2 }Finally, modify the configuration file /etc/default/tftpd-hpa
forlinx@ubuntu:/etc/xinetd.d$ cd / forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo vim /etc/default/tftpd-hpa
Note that change the ''TFTP _ DIRECTORY'' to the path where you created the new tftpboot directory.
1.3 Services Restart
forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo /etc/init.d/xinetd reload forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo /etc/init.d/xinetd restart forlinx@ubuntu:/$ sudo /etc/init.d/tftpd-hpa restart
1.4 Server Test
To test it, create a new file in the/tftpboot folder:
forlinx@ubuntu:/$ cd /tftpboot/ forlinx@ubuntu:/tftpboot$ sudo touch abc
Go to another folder:
forlinx@ubuntu:/tftpboot$ cd /home/ forlinx@ubuntu:/home$ sudo tftp 192.168.2.57 //192.168.2.57 is the local IP tftp> get abc tftp> quit forlinx@ubuntu:/home$ ls abc
If the server can be downloaded, it indicates that the server has been installed successfully. Once the development board is connected to the PC using an Ethernet cable, you can utilize TFTP to download files.
bootz ${loadaddr}-${fdt_addr};2. NFS Service Setup
NFS (Network File System) allows file sharing between different machines and systems through the network. Through NFS, access remote shared directories just like accessing local disks.
2.1 The method for setting up an NFS server on Ubuntu is as follows:
Software download and installation
forlinx@ubuntu:~# sudo apt-get install nfs-kernel-server nfs-common portmap
Create the NFS directory and unzip the file system (for example, rootfs. tar. bz2 file system, the current directory is the root directory)
forlinx@ubuntu:~# cd / forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo mkdir nfs_rootfs forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo tar -xvf rootfs.tar.bz2 -C /nfs_rootfs/
Modify the configuration file
forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo vim /etc/exports
Add the following configuration to the file:
/nfs_rootfs *(rw,sync,no_root_squash,no_subtree_check)
Restart configuration files and services
forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo exportfs -rv forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo /etc/init.d/rpcbind restart forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo /etc/init.d/nfs-kernel-server restart
2.2 Validating the NFS Server on the i.MX9352 Development Board
Mount the NFS server to the board's/mnt directory after executing the following command
root@ok-mx93:~# mount -t nfs4 -o vers=4 192.168.0.57:/nfs_rootfs /mnt
After...
Read more -
Allwinner T507 Audio System: DMA Channel, Audio Hub Configuration and Test Guide
05/30/2025 at 05:51 • 0 commentsThis guide provides a concise overview of the audio system on the Allwinner T507 platform, covering the DMA transfer mechanism, Audio Hub configuration methods, and commonly used audio testing tools. It is intended to help developers quickly set up and validate audio functionality.
When a DMA channel sound card records or plays digital audio, it uses the DMA channel to transfer audio data between itself and RAM without CPU intervention to improve the data transfer rate and CPU utilization.
T507 Audio System
Audio codec, Audio Hub, DMIC, OWA(One Wire Audio)
Audio codec: Built-in module with digital-to-analog conversion to convert audio digital signals to analog signals.
Audio Hub: T507-specific module integrates basic audio input and output functions and special hardware mixing functions. The mixing function has three input terminals and 4 x I2S, which can complete the mixing of three channels of data. The mixed data is output through HDMI, I2S0, I2S2 and I2S3.
Audio Path Configuration
To view the current audio device node on the system:
root@forlinx:/# cat /proc/asound/cards 0 [audiocodec ]: audiocodec - audiocodec //codec corresponding card0 audiocodec 1 [sndahub ]: sndahub - sndahub //audio_hub corresponding card1 sndahub 2 [sndhdmi ]: sndhdmi - sndhdmi //hdmi corresponding card2 sndhdmi 3 [sndwm89603001a ]: sndwm8960_3-001 - sndwm8960.3-001a //8960 corresponding card3 sndwm8960.3-001a root@forlinx:/proc/asound# cat devices 0: [ 0] : control //device 0 16: [ 0- 0]: digital audio playback 24: [ 0- 0]: digital audio capture 32: [ 1] : control //device 1 33: : timer 48: [ 1- 0]: digital audio playback //APBIF_TXDIF0 play hub_device 0 49: [ 1- 1]: digital audio playback //APBIF_TXDIF1 play hub_device 1 50: [ 1- 2]: digital audio playback //APBIF_TXDIF2 play hub_device 2 56: [ 1- 0]: digital audio capture //APBIF0 play hub_device 0 57: [ 1- 1]: digital audio capture //APBIF1 play hub_device 1 58: [ 1- 2]: digital audio capture //APBIF2 play hub_device 2 64: [ 2] : control //device 2 80: [ 2- 0]: digital audio playback 96: [ 3] : control //device 3 112: [ 3- 0]: digital audio playback 120: [ 3- 0]: digital audio capture
Audio_hub Default Configuration
Default i2s3 configuration
root@forlinx:/# tinymix -D 1 Mixer name: 'sndahub' Number of controls: 26 ctl type num name value 0 ENUM 1 ahub audio format Function null 1 BOOL 1 I2S0IN Switch Off 2 BOOL 1 I2S0OUT Switch Off 3 BOOL 1 I2S1IN Switch Off 4 BOOL 1 I2S1OUT Switch On 5 BOOL 1 I2S2IN Switch Off 6 BOOL 1 I2S2OUT Switch Off 7 BOOL 1 I2S3IN Switch On 8 BOOL 1 I2S3OUT Switch On 9 BOOL 1 DAM0IN Switch Off 10 BOOL 1 DAM1IN Switch Off 11 BOOL 1 DAM0OUT Switch Off 12 BOOL 1 DAM1OUT Switch Off 13 ENUM 1 APBIF0 Src Select NONE 14 ENUM 1 APBIF1 Src Select I2S3_TXDIF 15 ENUM 1 APBIF2 Src Select NONE 16 ENUM 1 I2S0 Src Select NONE 17 ENUM 1 I2S1 Src Select APBIF_TXDIF0 18 ENUM 1 I2S2 Src Select NONE 19 ENUM 1 I2S3 Src Select APBIF_TXDIF1 20 ENUM 1 DAM0Chan0 Src Select NONE 21 ENUM 1 DAM0Chan1 Src Select NONE 22 ENUM 1 DAM0Chan2 Src Select NONE 23 ENUM 1 DAM1Chan0 Src Select NONE 24 ENUM 1 DAM1Chan1 Src Select NONE 25 ENUM 1 DAM1Chan2 Src Select NONE
I2s0 Recommended Configuration
tinymix -D 1 1 1 //Open input for i2s0 tinymix -D 1 2 1 //Open output for i2s0 tinymix -D 1 7 0 //Close i2s3 input tinymix -D 1 8 0 //Close i2s3 output tinymix -D 1 14 I2S0_TXDIF tinymix -D 1 16 APBIF_TXDIF1 tinymix -D 1 19 NONE
I2s2 Recommended Configuration
tinymix -D 1 1 1 //Open input for i2s2 tinymix -D 1 6 1 //Open output for i2s0 tinymix -D 1 7 0 //Close i2s3 input tinymix -D 1 8 0 //Close i2s3 output tinymix -D 1 14 I2S2_TXDIF tinymix -D 1 18 APBIF_TXDIF1 tinymix -D 1 19 NONE
The configuration of audio channels will affect the use of test routines:
Before conducting the playback test, please insert the prepared 3.5mm headphones into the HeadPhone interface. To play sound through...
Read more -
Allwinner T113 Linux 5.4 Boot Program Flow
05/27/2025 at 07:16 • 0 commentsThis document provides a detailed walkthrough of the Linux 5.4 boot process on the Allwinner T113 platform, covering the sequence from U-Boot parameter passing to the execution of the user-space init process. It explains how the kernel initializes, mounts the root filesystem, and transitions to user mode, highlighting key components like the kernel_init function and the /etc/inittab configuration file. This serves as a practical reference for developers looking to understand or customize the system's auto-start behavior on T113-based embedded systems.
Boot Steps
- Pass parameters by specifying U-Boot environment variables.
- The kernel starts init, obtains the first process, and switches to user mode.
- init starts system services and applications according to the configuration file.
When checking the U-Boot environment variables, it can be seen that when the boot method is specified by setargs_mmc, there is a parameter init=${init}, where ${init} refers to the environment variable init=/init.
init=/init setargs_mmc=setenv bootargs earlycon=${earlycon} clk_ignore_unused initcall_debug=${initcall_debug} console=${console} loglevel=${loglevel} root=${mmc_root} init=${init} partitions=${partitions} cma=${cma} snum=${snum} mac_addr=${eth0_mac} wifi_mac=${wifi_mac} bt_mac=${bt_mac} specialstr=${specialstr} gpt=1This indicates that the boot parameter configuration is already set during the U-Boot stage (on some platforms, a /linuxrc file is used).
After kernel initialization is complete, the init process runs with process ID 1 and serves as the parent process of all other processes. Other software also starts running concurrently. Switch to the init program running in user mode. The init program is configured through the /etc/inittab file.
The kernel source code in kernel/linux-5.4/init/main.c contains the kernel_init function. The process running this function is called the init process, which is process 1.
In the T113, kernel_init calls kernel_init_freeable, and kernel_init_freeable opens the console.
/* Open the /dev/console on the rootfs, this should never fail */ if (ksys_open((const char __user *) "/dev/console", O_RDWR, 0) < 0) pr_err("Warning: unable to open an initial console.\n"); (void) ksys_dup(0); (void) ksys_dup(0);Here, the /dev/console file is opened, and the file descriptor is duplicated twice, resulting in three file descriptors: 0, 1, and 2, which correspond to the standard input, standard output, and standard error, respectively. Process 1 opens these three file descriptors, so all processes spawned from process 1 inherit these file descriptors by default.
However, for the init process to transition from kernel mode to user mode, it must execute a user-space application. To run this application, it must first be located. To locate the application, the root filesystem must be mounted, since all applications reside within the filesystem. In the source code, it can be found that the init process mounts the root filesystem through the prepare_namespace function.
if (ksys_access((const char __user *) ramdisk_execute_command, 0) != 0) { ramdisk_execute_command = NULL; prepare_namespace(); }Next, U-Boot environment variables are used to pass parameters specifying the root filesystem partition and other related information. In U-Boot's cmdline parameters, init=/init indicates that the init program located in the root directory of the root filesystem is the 'init application,' which the kernel identifies and executes.
Identify the init program. if (ramdisk_execute_command) { ret = run_init_process(ramdisk_execute_command); if (!ret) return 0; pr_err("Failed to execute %s (error %d)\n", ramdisk_execute_command, ret); } Execute the init program. if (execute_command) { ret = run_init_process(execute_command); if (!ret) return 0; panic("Requested init %s failed (error %d).", execute_command, ret); }The init process transitions from a kernel-mode process to a user-mode process. The process ID remains unchanged...
Read more -
How to Modify Boot LOGO and Animation on OK3588-C Android 12 Development Board?
05/22/2025 at 03:39 • 0 commentsLearn how to modify the boot logo and boot animation on the OK3588-C Android 12 development board, powered by the Rockchip RK3588 SoM. This guide walks you through customizing startup visuals for your embedded device, including both ADB-based and source-level methods.
Modify the boot animation
Method:
1. To prepare a video, you need to select a video with the same resolution as the screen.
2. Copy the video to the development environment and convert it into a picture in PNG format.
(1) If ffmpeg is not installed in the development environment, you need to install ffmpeg first.
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work$ sudo apt-get update forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work$ sudo apt-get install ffmpeg
(2) Create a part0 directory to store the converted pictures.
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work$ mkdir part0
Enter the following command to convert:
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work$ ffmpeg -i animation.mp4 -f image2 -r 1 part0%02d.png
-r means 1 frame per second. If 2 frames are taken per second, the -r parameter can be changed to 2.
After the conversion is completed, there will be a generated picture in PNG format under the part0 directory.
3. Create a new desc. txt films
Picture properties 1920 (picture width) 1080 (picture height) 15 (display frames per second) Animation properties P (for play) 0 (infinite loop) 0 (the time interval to enter the phase) part 0 (image storage path) 4. Pack it into bootanimation.zip (only stored, not compressed)
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work$ zip -r -0 bootanimation.zip part0/ desc.txt
Alternative method:
Method 1: use ADB to replace directly
(1) Install adb in the development environment
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work$ sudo apt-get install adb
(2) Use the USB-type C cable to connect to the typeC0 interface of the board, and the PC end is identified in the virtual machine.
Check whether the connection is successful in the development environment summary.
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work$ adb devices
If the connection is successful, the device ID of the board is returned as follows:
Send the bootanimation. zip you just packed to the board.
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work$ adb root forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work$ adb remount forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work$ adb push bootanimation.zip /system/media
Sync Save
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work$ adb shell ok3588_c:/ $ sync
Method 2: Replace the boot animation in the source code
1. Replace the OK3588-android-source/device/rockchip/rk3588/ok3588 _ c/bootanimation. zip file in the source code with the packaged bootanimation. zip.Then re-compile and burn update. img files.
Modify the boot LOGO
Replace the logo. bmp and logo _ kernel. bmp in the OK 3588-android-source/kernel-5.10 directory.
Recompile after replacement.
Method for making bmp format picture:
Now take the 7-inch screen as an example. 1. Make a logo. jpg first. Note that the size should be the same as that of the 7-inch screen (1024 * 600). Otherwise, the picture position and effect may not be good;
2. Download the graphics conversion tool in the Ubuntu development environment
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work$ sudo apt-get install netpbmMake applicable pictures
Create a working directory
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work$ mkdir uboot-logo forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work$ cd uboot-logo
Copy the image to the uboot-logo directory and write the image conversion script.
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work/uboot-logo$ vi mkbmp.sh #!/bin/sh jpegtopnm $1 | ppmquant 31 | ppmtobmp -bpp 8 > $2
Give the script executable permission
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work/uboot-logo$ chmod +x mkbmp.sh
Use a script to convert to an image suitable for uboot
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/work/uboot-logo$ ./mkbmp.sh logo.jpg logo.bmp
A logo.bmp image is generated
-
FET-MA35-S2 Embedded SoM: Real-Time Industrial Dust Monitoring Solution with Multi-Sensor Integration
05/16/2025 at 03:57 • 0 commentsDust monitoring is a real-time online monitoring measure to prevent and control air pollution. Dust monitoring equipment can be used to monitor data such as particulate matter concentration, PM values, temperature, humidity, wind speed and direction in real time. Through real-time data monitoring and alarming, it is possible to promptly prevent and rectify dust pollution.
The FET-MA35-S2 embedded system-on-module, powered by the Nuvoton MA35 series processor, serves as the core of an advanced online dust monitoring solution. Designed for industrial applications, it supports real-time measurement of PM1.0, PM2.5, PM10, and environmental data through multi-sensor integration and stable communication interfaces.
System Composition:
The system consists of a data collector, sensors, a video monitoring system (optional), a wireless transmission system, a background data processing system, and an information monitoring management platform. The monitoring sub-station integrates multiple functions such as atmospheric PM1.0, PM2.5, and PM10 monitoring, environmental temperature and humidity monitoring, wind speed and direction monitoring, noise monitoring, and video monitoring (optional). The data platform is a networked platform with an Internet architecture, which has the functions of monitoring each sub-station, as well as various functions such as alarm processing, recording, querying, statistics, and report output of data. This system can also be linked with various pollution control devices to achieve the purpose of automatic control.
Application Advantages
- Industrial-grade design: It can operate stably in harsh outdoor environments.
- Multiple sensor interfaces: It supports the connection of various high-precision sensors to meet the multi-parameter monitoring needs for dust, environment, noise, etc.
- Real-time communication: It supports both wired and wireless communication technologies to ensure that the monitoring data can be transmitted to the monitoring center in a real-time and stable manner.
- Scalability: There are reserved interface resources, which facilitates subsequent function expansion and upgrades.
-
Quick Integration Solution for Local Applications in Buildroot on the Allwinner A40i Platform
05/15/2025 at 06:48 • 0 commentsIn embedded system development, quickly and seamlessly integrating proprietary applications into the Buildroot image is crucial for accelerating product iteration. Taking the Allwinner A40i platform as an example, this article walks you through the full process of creating a package directory, writing Config.in and .mk build scripts, and enabling your local application via the board-level defconfig.
Buildroot is essentially an automated build framework. Although build scripts for well-known open-source packages such as U-Boot and the Linux kernel are maintained by the community, you'll often need to add your own custom app_pkg packages to build and integrate your proprietary applications.
Buildroot offers a framework of functions and variable commands. Build scripts like app_pkg.mk, written using this framework, are parsed by the core script package/pkg-generic.mk, which integrates them into the main Buildroot Makefile. In the end, executing make all runs Buildroot's top-level Makefile and produces the target image.
package/pkg-generic.mk automatically handles routine tasks like downloading, extracting, and building dependencies by calling pkg-download.mk and pkg-utils.mk located in the same directory. Just follow the specified format to write the Makefile-style app_pkg.mk, filling in details such as the download URL, names of dependent libraries, and other package-specific build settings.
1. Run mkdir helloworld under the buildroot-201611/package/ directory to create a folder for helloworld.
2. In the demo_app directory, create the files Config.in and touch helloworld.mk. Note that the filenames are critical — helloworld.mk must be in lowercase and cannot be renamed, as the Buildroot framework follows specific naming conventions to process app packages. Therefore, when building projects in Buildroot, it is essential to adhere to the naming rules outlined in this article, or you may encounter various errors.
3. Modify the Config.in and helloworld.mk files.
Note:
Variables ending with _VERSION represent the source code version.
Variables ending with _SITE specify the source code downloading address.
Variables ending with _SITE_METHOD specify the method for downloading the source code.
Variables ending with _BUILD_CMDS are executed during the Buildroot framework compilation process. They are used to pass compilation and linking options to the source code's Makefile and to invoke the Makefile.
Variables ending with _INSTALL_TARGET_CMDS are executed after the compilation is complete, automating the installation process. They typically instruct Buildroot to copy the compiled binaries or libraries to the specified directory.
The most important part is $(eval $(generic-package)), which must not be omitted, or else the source code will not be compiled. This function expands the entire .mk build script into the Makefile under the buildroot/ directory, following the Buildroot framework, to generate the build targets.
Note that demo_app.mk does not replace the actual Makefile of the demo_app source code. It is simply an upper-level Makefile that tells Buildroot where to fetch the source code, how to extract the source, which compilation options to pass to the variables in the source code's Makefile, and where the compiled libraries and binaries should be installed in the root filesystem (rootfs). The specific step-by-step compilation of the demo_app source code relies on the Makefile within the demo_app source code itself.
The official website also has an English version of the documentation
https://buildroot.org/downloads/manual/manual.html#adding-packages. For a detailed explanation of the principles, you can refer to this document.
4. Create and modify/home/forlinx/helloworld/helloworld.c
5. Create and modify buildroot/package/app/helloworld/Makefile
6. Add the helloworld option in buildroot-201611/package/Config.in.
7. Add BR2_PACKAGE_HELLOWORLD=y in lichee/buildroot-201611/configs/sun8iw11p1_hf_defconfig....
Read more -
Forlinx MA35 Embedded SoM: Industrial IoT Gateway for Real-Time Elevator Monitoring & Predictive Maintenance
05/13/2025 at 08:12 • 0 commentsIn today’s rapidly evolving smart building and industrial automation landscape, real-time edge computing and monitoring have never been more critical. The Forlinx MA35 Embedded SoM is engineered precisely to meet these demands: featuring powerful processing capabilities, an extensive array of I/O interfaces, and dual 4G-to-cloud connectivity, it captures every aspect of elevator operation—from motion, leveling, and door status to environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and smoke.
With instant fault detection and immediate alerts, the MA35 cpu board empowers predictive maintenance, minimizes downtime, and ensures passenger safety around the clock.
As the nerve endings of the entire system, the intelligent IoT hardware for elevators is responsible for real-time monitoring of elevator operating status and analysis of its health status. It connects to the cloud platform through multiple network access channels, thus enabling multi-scenario applications for various user roles.
Function Features:
- It can collect signals of elevator up-and-down operation, stop signals, leveling signals, car door opening and closing signals, the floor where the elevator is located, elevator speed, and the single-run distance of the elevator.
- It can monitor elevator fault information in real-time (such as people trapped, elevator stuck on a floor, abnormal door operation, over-speeding at the top or bottom).
- It can store various types of elevator operation data, fault data, and elevator maintenance work information.
- It can transmit real-time elevator operation status data to the real-time elevator operation monitoring platform via the 4G wireless network, and can also report the data to the cloud platform simultaneously.
- It is equipped with more sensors to sense information such as temperature, humidity, and smoke inside the elevator. Once an abnormality is detected, an immediate alarm will be triggered.
Application Advantages
Small size and low power consumption: It uses LCC + LGA packaging and compact size. It has passed the rigorous industrial environment tests in Forlinx Embedded Laboratory to ensure the stability and reliability of the product.
Abundant peripheral resources: The SoM has as many as 260 pinsPin extended, which can support a variety of control interfaces and multiple wireless communication methods to meet the diverse communication needs of the elevator IoT system.
Convenient and easy to use: The SoM is equipped with the Linux 5.10.140 operating system. It also supports OTG and TF card batch programming methods, and single-step kernel updates, making product development and mass production more convenient.
-
Tutorial on Linux OTA Upgrade Process for Forlinx OK3568-C Development Board
05/10/2025 at 07:05 • 0 commentsThe two most commonly used programming systems for development boards are OTG and SD card programming systems. This article explains how to implement the OTA upgrade of the development board, thus solving the problem that the new features developed by customers cannot be immediately deployed to the products. OTA (Over-the-Air) is the technology of downloading over the air. OTA upgrade is the standard software upgrade method provided by the Android system. It has powerful functions and can upgrade the system without loss.
It mainly downloads the OTA upgrade package automatically via the network, such as WIFI, 3G/4G. It also supports upgrading by downloading the OTA upgrade package to the SD card/USB flash drive. The size of the OTA upgrade package can be freely packed according to requirements. This article mainly describes the OTA upgrade process, the process and technical details of the local upgrade program recovery executing the upgrade on the Rockchip platform RK3568.
Step 1: Create recovery.img
Note: (The default image of the development board already supports and has flashed the recovery.img file. You can skip this step.)
The source code path related to recovery:
buildroot/output/OK3568-recovery/build/recovery-develop
If the source code files in the above directory have been modified, the following operations need to be performed.
- 1. forlinx@ubuntu:~/OK3568-linux-source$ source envsetup.sh
- 2. Select the recovery configuration for a platform and enter 96
- 3. Recompile recovery and rkupdate
forlinx@ubuntu:~/OK3568-linux-source$ make recovery-dirclean && make recovery # Clear the compilation product and recompile it forlinx@ubuntu:~/OK3568-linux-source$ make rkupdate-dirclean && make rkupdate # Clear the compilation product and recompile it
If the source code files in the above directories have not been modified, directly execute the following operations:
forlinx@ubuntu:~/OK3568-linux-source$ ./build.sh recovery #Compile and generate recovery.img forlinx@ubuntu:~/OK3568-linux-source$ ./mkfirmware.sh #Copy the generated firmware to the rockdev/directory
Flash/OK3568-linux-source/buildroot/output/OK3568-recovery/images/recovery.img file.
Click the device partition table, check 9, select the recovery path, and click Execute.
Step 2: Create the upgrade image
How to verify the successful upgrade? First, a preliminary understanding of the boot.img file: it contains the device tree and the kernel. Therefore, appropriate modifications to either the device tree or the kernel can be made. In this example, the boot.img file is updated by making suitable changes to the device tree.
Modify the device tree file at /OK3568-linux-source/kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/OK3568-C-common.dtsi, and make the following changes to the forlinx_control node. By default, enable only HDMI output, and disable MIPI and LVDS outputs.
Modify the /OK3568-linux-source/tools/linux/Linux_Pack_Firmware/rockdev/package-file as needed. In this example, to update boot.img, other .img files are commented out. The file can be adjusted according to product update requirements.
In this example, a display-related modification in the device tree is used as an upgrade test. After modifying the device tree, recompile the kernel.
forlinx@ubuntu:~/OK3568-linux-source$ ./build.sh kernel #After modifying the device tree, recompile the kernel. forlinx@ubuntu:~/OK3568-linux-source$ ./build.sh updateimg #Package the upgrade firmware.
Note: If uboot or buildroot has been modified, execute the following commands before performing the packaging operation.
forlinx@ubuntu:~/OK3568-linux-source$ ./build.sh uboot #After modifying the device tree, recompile the kernel. forlinx@ubuntu:~/OK3568-linux-source$ ./build.sh buildroot #After modifying the device tree, recompile the kernel. forlinx@ubuntu:~/OK3568-linux-source$ ./build.sh updateimg #Package the upgrade firmware.
Note: If the compilation fails, it is due to the...
Read more -
Guide on Changing the Cross-Toolchain for T113S3/T113-i Buildroot
05/09/2025 at 03:47 • 0 commentsIf you’ve ever worked with the Allwinner T113 series, you know it’s a reliable choice for industrial control applications—but getting your toolchain set up just right can be tricky. In this quick guide, I’ll walk you through swapping out Buildroot’s cross-compiler for the T113-S3 and T113-i boards step by step, so you can compile faster and more reliably.
In a project, it may be necessary to change the file system toolchain to compile existing applications in batches.
At this time, the cross-toolchain for building Buildroot needs to be changed.
The main steps are as follows:
- 1. Place the cross-toolchain of the required version in the local project directory.
- 2. Configure the path of the relevant toolchain in Buildroot.
Here, the T113-I project with the change of the arm-gcc4.9 version toolchain is taken as an example for explanation:
Unzip the gcc-linux-arm-4.9 version to the dl/toolchain-external-arm-armm directory.
The detailed configuration is as follows:
Since the hardware floating-point compilation toolchain is provided by the customer, the configuration also needs to be changed.
After the above is completed, save and exit.
Delete the Buildroot directory generated in the previous out directory.
Re-compile.
During the compilation process, some tools may fail to compile or the compilation may get stuck. In this case, you can cancel the compilation of relevant items in the configuration file first.
If the following compilation problems occur, they are caused by the mismatch of kernel headers configuration. Set according to the error prompt. The 3.1.X configuration is ok.
If the compilation gets stuck at the opus module, find the corresponding configuration file and comment it out.
After the compilation is successful, write applications compiled by two different toolchains for testing.
The application compiled by the default 5.3.1 toolchain of T113-I is tested as follows:
Attach the configuration file of T113-I that has been debugged successfully.
-
FET-MA35-S2 SoM: A Multi-core Secure Industrial-grade Solution for EV Charging Pile TCU
04/30/2025 at 03:32 • 0 commentsCharging piles provide electrical energy for electric vehicles (EVs), converting grid power for fast and safe charging. As EVs become more popular, charging pile construction is increasingly important. TCU is the core control module of the charging pile, undertaking key functions such as charging process management, safety monitoring, data interaction, and billing control. As the hub connecting the vehicle, the grid, and the operation platform, the TCU effectively manages the charging process by integrating various functional modules.
TCU Core Functions:
Control & Communication
Supports multiple interfaces for real-time interaction with the vehicle’s BMS, charging modules, and cloud platforms.
Safety Protection
Real-time monitoring of equipment voltage, current, temperature, and other status, abnormal conditions trigger the protection mechanism and report fault codes; hardware support for secure encryption to protect payment and data privacy and security.
User Interaction
Display charging progress, cost, abnormal alarm information and other multi-mode interaction through LCD/HMI interface; record charging process data to provide data support for equipment maintenance and energy efficiency optimization.
As the "intelligent brain" of the charging pile, TCU must realise core functions such as charging control, data communication, safety monitoring, and human-machine interaction. With its high-performance multi-core heterogeneous architecture and rich interface design, the embedded FET-MA35-S2 SoM can be used as an ideal hardware platform for charging pile TCU.
1. Multi-Core Heterogeneous Architecture Architecture
Dual-core A35 + M4 collaborative control: It is equipped with 2 x 64-bit ARM Cortex-A35 (main frequency 800MHz) and 1 x Cortex-M4 (180MHz), running Linux system and real-time operating system respectively, and meeting the requirements of high efficiency and real-time control.
Application Scenario Adaptation: A35 kernel handles the main control logic of the charging pile (e.g., billing, communication protocol parsing), and M4 kernel monitors the voltage/current parameters in real time to ensure the safety of the charging process.
2. Interface Expansion
The SoM uses LCC + LGA packaging (48mm×40mm), with all 260 pins led out. It can support 17 x UART interfaces and the protocol conversion between RS232 and RS485. It can be directly connected to devices such as electric meters, barcode scanners, and card readers without the need for additional conversion chips. 2 x Gigabit Ethernet ports enable real-time data transmission between the charging pile and the cloud platform (such as charging status monitoring and remote operation and maintenance). 8 x ADC channels achieve accurate acquisition of voltage, current, and temperature, and cooperate with the dynamic PWM adjustment algorithm to prevent the device from overheating. 4 x CAN-FD interfaces meet the high-speed communication requirements with BMS, charging controllers, etc., ensuring the accurate matching of charging parameters.
3. Security & Reliability
Hardware-level security: It integrates Nuvoton's TSI (Trusted Security Island), TrustZone, secure boot, AES/SHA/ECC/RSA encryption accelerators, and a True Random Number Generator (TRNG) to ensure the security of key storage and communication data.
Industrial-grade reliability: It supports operation in a wide temperature range from -40°C to 85°C and has passed the EMC anti-interference test, making it adaptable to the harsh environments of outdoor charging piles.
4. Function Expansion
Multimedia interaction: It supports RGB display interfaces (with a maximum resolution of 1080P) and I2S audio interfaces, and can drive touch screens to implement user interface (UI) interaction and voice prompt functions.
Remote management: It supports OTA (Over-the-Air) upgrades and AI predictive maintenance through a 4G module or Ethernet.
![OK-MA35-S21 Single Board Computer by Forlinx front]()
![OK-MA35-S21 Single Board Computer by Forlinx back]()
In summary, the FET-MA35-S2 CPU module features...
Read more -
RK3568 Platform Network Service Setup and Network Boot: TFTP, NFS and U-Boot Configuration Details
04/25/2025 at 08:15 • 0 commentsLooking to harness the power of the RK3568 platform for your embedded systems? This comprehensive guide walks you through setting up essential network services including TFTP and NFS, as well as configuring U-Boot for seamless network booting. Whether you're developing Linux-based solutions or deploying ARM64 systems, mastering these configurations will optimize your RK3568 board’s performance and streamline your development process.
TFTP Service Setup
1. Server, Client , Installation, and Daemons
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt-get install tftp-hpa tftpd-hpa xinetd
2. Server Configuration
First, create a tftpboot in the root directory and change the attributes to read and write for any user:
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ cd / forlinx@ubuntu:~$ sudo mkdir tftpboot forlinx@ubuntu:~$ sudo chmod 777 tftpboot
Then, go to the directory /etc/xinetd.d/ and create a new file tftp in it, adding the specified contents to the tftp file:
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ cd /etc/xinetd.d/ forlinx@ubuntu:~$ sudo vim tftp
Add the following to the tftp text.
service tftp { disable = no 138 socket_type = dgram protocol = udp wait = yes user = root server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd server_args = -s /tftpboot -c per_source = 11 cps = 100 2 }Finally, modify the configuration file /etc/default/tftpd-hpa
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ sudo vim /etc/default/tftpd-hpa
Modify to
TFTP_USERNAME="tftp" TFTP_DIRECTORY="/tftpboot" TFTP_ADDRESS="0.0.0.0:69" TFTP_OPTIONS="--secure -l -c -s"
Make sure to change TFTP_DIRECTORY to the path where the newly created tftpboot directory is located.
3. Services Restart
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ sudo /etc/init.d/xinetd reload forlinx@ubuntu:~$ sudo /etc/init.d/xinetd restart forlinx@ubuntu:~$ sudo /etc/init.d/tftpd-hpa restart
4. Server Test
To test this, create a new file in the /tftpboot folder
forlinx@ubuntu:/tftpboot$ sudo touch abc
Go to another folder
forlinx@ubuntu:/tftpboot$ cd /home/ forlinx@ubuntu:/home$ sudo tftp 192.168.2.51 //192.168.2.51 is the local IP tftp> get abc tftp> quit forlinx@ubuntu:/home$ ls abc
If the server can be downloaded, it indicates that the server has been installed successfully. Once the development board is connected to the PC using an Ethernet cable, you can utilize TFTP to download files.
bootz ${loadaddr} - ${fdt_addr};NFS Service Setup
1. The method for setting up an NFS server on Ubuntu is as follows:
Software download and installation
forlinx@ubuntu:~# sudo apt-get install nfs-kernel-server nfs-common portmap
Create the NFS directory and extract the file system (using rootfs.tar.bz2 as an example, with the current directory as the root directory).
forlinx@ubuntu:~# cd / forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo mkdir nfs_rootfs forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo tar -xvf rootfs.tar.bz2 -C /nfs_rootfs/
Modify the configuration file
forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo vim /etc/exports
Add the following configuration to the file:
/nfs_rootfs *(rw,sync,no_root_squash,no_subtree_check)
Restart configuration files and services
forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo exportfs -rv forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo /etc/init.d/rpcbind restart forlinx@ubuntu:/# sudo /etc/init.d/nfs-kernel-server restart
2. Verify the NFS server on the development board (you need to make a file system supporting
NFS according to the application note), and execute the following command to mount the NFS server to the/mnt directory of the development board.
root@OK3568:~# mount -t nfs4 -o vers=4 192.168.0.57:/nfs_rootfs /mnt
After successful mounting, check the /mnt directory and you will see the file system you just extracted.
root@ OK3568:~# ls /mnt/
Note: 192.168.0.57 is the IP of the NFS server host ubuntu, ubuntu's network needs to be set to bridge mode, and with the development board in the same network 192.168.0.57
Boot via the network.
1. First, configure the kernel separately to enable NFS-related services.
Under the OK3568-linux-source/kernel directory:
make ARCH=arm64 menuconfig // Open the graphical configuration interface Enable the...
Read more -
Top 20 Must-Know Rockchip RK Commands to Double Your Dev Efficiency
04/23/2025 at 07:11 • 0 commentsRockchip is a leading AIoT SoC design and manufacturing enterprise, focusing on the R & D of intelligent application processors and peripheral supporting chips. As a strategic partner of Rockchip, Forlinx Embedded has launched multiple embedded main-control products based on Rockchip's RK3399, RK3568, RK3588, RK3576, RK3562, and RK3506 series processors. These products include SoMs, development boards, and industrial control computers, which have successfully helped thousands of enterprise customers quickly develop and implement their projects.
This article will systematically sort out the commonly used commands during the development process of Forlinx Embedded's RK platform main-control products, helping more developers quickly master the development methods of RK series chips.
01 View the CPU temperature
cat /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp
02 View CPU frequency (main frequency)
cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/cpuinfo_max_freq #View the maximum frequency the CPU can support cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_available_frequencies #View the current supported CPU frequencies (affected by the SoM temperature, the temperature control policy will change the list of supported frequencies) cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_cur_freq #View what frequency the current CPU is working at cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_available_governors #View all supported FM strategies for the current CPU cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_governor #View the current CPU applied FM policy #interactive:Dynamic FM mode #performance :High efficiency mode, CPU main frequency always supports the highest frequency in the list (subject to temperature control policy) #powersave:Power saving mode, CPU frequency always supports the lowest frequency in the list #userspace:User-defined mode # Usage: # echo userspace > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_governor # echo 1800000 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_setspeed #ondemand:Toggles between highest and lowest frequencies #conservative:Smooth adjustment frequency
03 Increase CPU Load
cat /dev/urandom | md5sum & # Run this command multiple times to the full CPU load.
04 View GPU usage
cat /sys/devices/platform/ff9a0000.gpu/devfreq/ff9a0000.gpu/load The path to the file after #platform needs to be checked to see what registers are mapped to the gpu of the current platform.
05 View GPIO occupancy status
cat /sys/kernel/debug/gpio
06 View all pinmux functions of the current system
cat /sys/kernel/debug/pinctrl/pinctrl-rockchip-pinctrl/pinmux-pins
07 Redefine shell window display size
resize
08 Remount the file system read-write attribute
mount -o rw,remount rootfs
09 Retrieve the current partition size of the file system
resize2fs /dev/mmcblk0p8
10 DDR current frequency acquisition and adjustable range
cat /sys/class/devfreq/dmc/cur_freq //Get current DDR frequency, adjustable value, capacity cat /sys/class/devfreq/dmc/available_frequencies //View DDR frequency adjustable values cat /proc/meminfo //Get DDR capacity //DDR tests the fixed frequency. If the cat output frequency is the input value, the fixed frequency is successful. Note that the setting value needs to obtain the adjustable value of DDR. echo userspace > /sys/class/devfreq/dmc/governor echo 856000000 > /sys/class/devfreq/dmc/userspace/set_freq cat cur_freq
11 View DDR Bandwidth Usage
cat /sys/devices/platform/dmc/devfreq/dmc/load
12 Gs treamer playback pictures
gst-launch-1.0 -v playbin delay=10000000000 uri="file:///home/test.jpg"
13 Clear VM Virtual machine loop partition occupancy 100>#/h2###
apt autoremove --purge snapd
14 Calculation method of GPIO number
Take GPIO4C6 as an example:
A-D corresponds to 1-4: A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4.
GPIOn_xy =n × 32 + (x-1) × 8 + y
GPIO4_C6=4 × 32 + (3-1) × 8 + 6 =15015 Calculation method for eMMC...
Read more -
Guide to RK3568 Android Application Porting and System Customization
04/19/2025 at 06:54 • 0 commentsApplication porting on Android devices is an important part of system development. Especially on embedded platforms like RK3568, pre-installing APK, system compilation, and permission management all require specific configurations and optimizations. This guide will provide a detailed introduction on how to complete Android application porting on the RK3568 platform, including key steps such as pre-installing and uninstalling APK and obtaining Root privileges, to help developers quickly adapt and customize the Android system.
Pre-installing Apps on the Android System
1. Adding an APK file: Take dogdog.apk as an example:
Add an Android.mk file under the "dogdog" folder and write the relevant content for the dogdog.apk file.
Add the Android. mk under the dogdog folder and write the dogdog. apk films.
Android.mk writing method:
LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir) include $(CLEAR_VARS) LOCAL_MODULE := dogdog LOCAL_SRC_FILES := dogdog.apk LOCAL_MODULE_CLASS := APPS LOCAL_MODULE_SUFFIX := .apk LOCAL_BUILT_MODULE_STEM := package.apk LOCAL_CERTIFICATE := platform LOCAL_DEX_PREOPT := false LOCAL_PRIVILEGED_MODULE := ture include $(BUILD_PREBUILT)
2. Adding an installation configuration
Modify/OK3568-android11-source/device/rockchip/rk356x/ok3568_r/ok3568_r.mk
Add dogdog \Compile again to generate update. img files, which can be flahsed and pre-installed apk normally.
Pre-installing Apps on the Android System
1. Delete the apk file
Delete the doggo file under/OK3568-android11-source/packages/apps/
2.Delete installation configuration
Mod/OK3568-android11-source/device/rockchip/rk356x/ok3568_r/ok3568_r.mk file
Delete dogdog \3.Delete the intermediate files generated by compilation
Delete /Ok3568-android11-source/out/target/product/ok3568_r/system/priv-app/ corresponding files
Compile again to generate the update. img file.
Android Getting Root Privileges
Location of references and test procedures:
1.The user debug version needs to be compiled.
2.Close selinux
Modify the configuration according to the red prompt:
Source code/device/rockchip/common/BoardConfig.mk
BOARD_MKBOOTIMG_ARGS := BOARD_PREBUILT_DTBOIMAGE ?= $(TARGET_DEVICE_DIR)/dtbo.img BOARD_ROCKCHIP_VIRTUAL_AB_ENABLE ?= false BOARD_SELINUX_ENFORCING ?= false
false is Close, true is Open.
3. Annotation User Group Permission Detection
Comment the following two lines.
Source code/system/extras/su/su.cpp
int main(int argc, char** argv) { //uid_t current_uid = getuid(); //if (current_uid != AID_ROOT && current_uid != AID_SHELL) error(1, 0, "not allowed"); // Handle -h and --help. ++argv;4. Grant root privileges to su files by default
(1)Source code/system/core/libcutils/fs_config.cpp
static const struct fs_path_config android_files[] = { …… // the following two files are INTENTIONALLY set-uid, but they // are NOT included on user builds. { 06755, AID_ROOT, AID_ROOT, 0, "system/xbin/procmem" }, { 06755, AID_ROOT, AID_ROOT, 0, "system/xbin/procmem" }, // the following files have enhanced capabilities and ARE included // in user builds.(2)Source code/frameworks/base/core/jni/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
static void DropCapabilitiesBoundingSet(fail_fn_t fail_fn) { /* for (int i = 0; prctl(PR_CAPBSET_READ, i, 0, 0, 0) >= 0; i++) {; if (prctl(PR_CAPBSET_DROP, i, 0, 0, 0) == -1) { if (errno == EINVAL) { ALOGE("prctl(PR_CAPBSET_DROP) failed with EINVAL. Please verify " ''your kernel is compiled with file capabilities support"); } else { fail_fn(CREATE_ERROR("prctl(PR_CAPBSET_DROP, %d) failed: %s", i, strerror(errno))); } } } */ }(3)Source code/kernel/security/commoncap.c
static int cap_prctl_drop(unsigned long cap) { struct cred *new; /* if (!ns_capable(current_user_ns(), CAP_SETPCAP)) return -EPERM; if (!cap_valid(cap)) return -EINVAL; */ new = prepare_creds(); if (!new) return -ENOMEM; cap_lower(new->cap_bset, cap); return commit_creds(new); }5.Complete compilation and flashing....
Read more -
Forlinx Embedded RK3576 System Fully Compatible with Linux, Android, and Desktop Systems
04/16/2025 at 08:04 • 0 commentsRecently, Forlinx Embedded officially released its new operating system, Forlinx Desktop 24.04, for the FET3576-C SoM. With this update, the FET3576-C is now fully compatible with Linux 6.1, Android 14, and Forlinx Desktop 24.04, demonstrating its outstanding versatility across various operating systems.
1. Multi-System Support to Meet Diverse Needs
The FET3576-C system on module(SoM) is developed based on the Rockchip RK3576 processor, which integrates 4 x high-performance ARM Cortex-A72 cores and 4 x ARM Cortex-A53 cores, along with a built-in 6 TOPS NPU for powerful AI computing capabilities.
Linux 6.1 system enables the Forlinx Embedded FET3576-C SoM to excel in open-source flexibility, stability, and efficiency. The Android 14 allows the Forlinx Embedded FET3576-C SoM to shine in fields such as smart mobile terminals and edge computing.
The newly released Forlinx Desktop 24.04 is deeply optimized for embedded devices, offering a more intuitive, user-friendly interface and a rich application ecosystem, supporting industrial control, smart home, digital multimedia, and more.
2. Rigorous Testing to Ensure Stable Operation
Forlinx Embedded understands the critical importance of stability for users, and has therefore conducted multiple rounds of testing on the FET3576-C SoM. These tests cover various aspects including hardware reliability, system stability, and performance, ensuring that the core board can operate reliably in a wide range of complex environments.
3. Wide Applications and Faster Time-to-Market
Thanks to its robust system compatibility and stability, the FET3576-C SoM shows strong potential across industries including industrial automation, AIoT, edge computing, smart terminals, and various digital multimedia applications. Whether it’s industrial control equipment requiring high computing power or smart home products demanding intelligent interaction, the FET3576-C delivers a compelling solution.
Additionally, Forlinx provides strong technical support to help clients accelerate product development, testing, and market launch.
In addition, Forlinx Embedded offers robust technical support services to help customers accelerate product development, testing, and time-to-market.
In summary, the deep compatibility of the Forlinx Embedded FET3576-C SoM with multiple operating systems not only maximizes its outstanding hardware performance but also delivers a smoother, smarter, and more secure user experience through system optimization and upgrades. For professional users in fields such as industrial automation, AIoT, edge computing, smart terminals, and various digital multimedia applications, the FET3576-C SoM is a reliable and trusted choice.
-
A Practical Guide to Porting and Interacting with AI Large Language Models from DeepSeek to Qwen
04/11/2025 at 05:11 • 0 commentsIn a previously published Technical Practice | A Complete Guide to Deploying the DeepSeek-R1 Large Language Model on the OK3588-C Development Board article, the porting and deployment of DeepSeek-R1 on Forlinx Embedded's OK3588-C development board were introduced, its effects were demonstrated, and performance evaluations were conducted. In this article, in-depth knowledge about DeepSeek-R1 will not only be continued to be shared but also porting methods on various platforms will be explored and more diverse interaction methods will be introduced to help better utilize large language models.
1. Porting Process
1.1 Deploying to the NPU Using RKLLM-Toolkit
RKLLM-Toolkit is a conversion and quantization tool specially developed by Rockchip for large language models (LLMs). It can convert trained models into the RKLLM format suitable for Rockchip platforms. This tool is optimized for large language models, enabling them to run efficiently on Rockchip's NPU (Neural Processing Unit). The deployment method mentioned in the previous article was NPU deployment through RKLLM-Toolkit. The specific method of operation is as follows:
(1) Download the RKLLM SDK:
First, download the RKLLM SDK package from GitHub and upload it to the virtual machine. SDK download link:
[GitHub-airockchip/rknn-llm]( https://github.com/airrockchip/rknn-llm)。
(2) Check the Python version:
Ensure that the installed SDK version is compatible with the target environment (currently only Python 3.8 or Python 3.10 is supported).
(3) Prepare the virtual machine environment:
Install therkllm-toolkitwheel in the virtual machine. The wheel package path is (rknn-llm-main\rkllm-toolkit).
pip install rkllm_toolkit-1.1.4-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl
(4) Download the model:
Select the DeepSeek-R1 model to be deployed.
git clone https://huggingface.co/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B
(5) Use the sample code for model conversion:
In the path rknn-llm-main\examples\DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B_Demo, use the sample code provided by RKLLM-Toolkit for model format conversion.
python generate_data_quant.py -m /path/to/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B python export_rkllm.py
(6) Compile the executable program:
Compile the sample code directly by running the build-linux.sh script under the deploy directory (replace the cross-compiler path with the actual path). This will generate a folder in the directory, which contains the executable file and other folders. Perform cross-compilation to generate the executable file.
Cross-compile to generate an executable file.
./build-linux.sh
(7) Deploy the model:
Copy the compiled _W8A8_ RK3588.rkllm file and the librkllmrt.so dynamic library file (path: rknn-llm-main\rkllm-runtime\Linux\librkllm_api\aarch64) together into the build_linux_aarch64_Release folder generated after compilation, and then upload this folder to the target board.
Next, add execution permissions to the llm_demofile in the build_linux_aarch64_Release folder on the target board and execute it.
chmod +x llm_demo ./llm_demo _W8A8_RK3588.rkllm 10000 10000
Demo 1
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages: After being deployed to the NPU, the large language model can run efficiently, with excellent performance and less CPU resource consumption.
Disadvantages: Compared with other methods, the deployment process is a bit more complex and requires a strong technical background and experience.
1.2 One-Click Deployment to the CPU Using Ollama
Ollama is an open-source local large language model (LLM) running framework that supports running various open-source LLM models (such as LLaMA, Falcon, etc.) in a local environment and provides cross-platform support (macOS, Windows, Linux).
With Ollama, users can easily deploy and run various large language models without relying on cloud services. Although Ollama supports rapid deployment, since DeepSeek-R1 has not been optimized for the RK3588 chip, it...
Read more -
A Detailed Guide to Porting EtherCAT on the Forlinx OKMX6ULx Platform
04/09/2025 at 06:04 • 0 commentsEtherCAT (Ethernet for Control Automation Technology) is a high-performance industrial Ethernet protocol, widely used in fields that require real-time performance, high synchronization accuracy, and efficient data transmission. This article introduces how to port EtherCAT on the Forlinx OKMX6ULx series platforms. This method is based on IGH EtherCAT, which is an open-source master protocol stack compliant with the EtherCAT international standard. It is specifically designed for the Linux system and supports efficient management and control of EtherCAT slave devices.
Its core features include:
- Open-source and low cost: Based on the LGPL license, it does not require dedicated hardware or licensing fees, making it suitable for rapid prototype verification.
- Real-time communication: Supports nanosecond - level synchronization accuracy and reduces transmission delay through Distributed Clock (DC) technology.
- Flexible topology: Supports any network topologies such as linear, tree, and star, and can connect up to 65,535 nodes at most.
1. Source Code Download
1.1 Select the 1.6 stable version for download. Other versions can be downloaded from the official GitLab.
https://gitlab.com/etherlab.org/ethercat/-/archive/stable-1.6/ethercat-stable-1.6.tar.gz
1.2 Copy it to the development environment provided by Forlinx and decompress it.
tar -xvf ethercat-stable-1.6.tar.gz cd ethercat-stable-1.6
2. Cross-porting
2.1 Execute the environment variables and run bootstrap to generate the configure file.
forlinx@ubuntu:~/111/ethercat-stable-1.6$ sudo -s forlinx@ubuntu:~/111/ethercat-stable-1.6$ . /opt/fsl-imx-x11/4.1.15-2.0.0/environment-setup-cortexa7hf-neon-poky-linux-gnueabi forlinx@ubuntu:~/111/ethercat-stable-1.6$./bootstrap
2.2 Execute configure to generate and compile the Makefile
forlinx@ubuntu:~/111/ethercat-stable-1.6$ ./configure --prefix=$PWD/__install --with-linux-dir=/home/forlinx/work/linux-4.1.15/ --enable-8139too=no --enable-generic=yes --host=arm-poky-linux-gnueabi forlinx@ubuntu:~/111/ethercat-stable-1.6$ make forlinx@ubuntu:~/111/ethercat-stable-1.6$ make install
Note: --with-linux-dir = The following path is the Linux source path
2.3 ethercat driver compilation
root@ubuntu:~/111/ethercat-stable-1.6# make modules
The driver has been generated.
root@ubuntu:~/111/ethercat-stable-1.6# find -name *.ko ./master/ec_master.ko ./devices/ec_generic.ko ./examples/mini/ec_mini.ko
3. Functions Test
3.1 Package and copy files to the development board
Ubuntu development environment:
root@ubuntu:~/111/ethercat-stable-1.6# cd __install/ root@ubuntu:~/111/ethercat-stable-1.6/__install# tar -cjvf ethercat.tar.bz2 *
Development Board
root@fl-imx6ull:~# tar -xvf /run/media/sda1/ethercat.tar.bz2 -C / root@fl-imx6ull:~# cp /run/media/sda1/ec_generic.ko /lib/modules/4.1.15-00076-g448d07c/ root@fl-imx6ull:~# cp /run/media/sda1/ec_master.ko /lib/modules/4.1.15-00076-g448d07c/ root@fl-imx6ull:~# sync
3.2 Add udev rule
root@fl-imx6ull:~# echo KERNEL==\"EtherCAT[0-9]*\", MODE=\"0664\" > /etc/udev/rules.d/99-EtherCAT.rules
3.3 View the network card mac
root@fl-imx6ull:~# ifconfig eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr E2:14:B0:1D:7C:CB inet addr:192.168.0.232 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::e014:b0ff:fe1d:7ccb%1996035792/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:4325 errors:0 dropped:267 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:71 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:1296750 (1.2 MiB) TX bytes:10368 (10.1 KiB) eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr D2:E1:14:B0:1D:7C inet addr:192.168.1.232 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0 UP BROADCAST MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B) lo Link encap:Local Loopback inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1%1996035792/128...
Read more -
How to Achieve Precise Motor Measurement on the TI AM6254 Platform Using eQEP
04/03/2025 at 03:24 • 0 commentsDescription
In today's era of booming industrial automation and intelligent robotics, high-precision positioning sensing technology has emerged as the core engine driving industrial transformation. As a new-generation motion control solution, eQEP (Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse) is widely used in fields such as servo motors, CNC machine tools, and intelligent robots, thanks to its sub-micron resolution, real-time signal decoding ability, and strong anti-interference characteristics. eQEP is specifically designed to process the signals from rotary encoders. By decoding two pulse signals (QEA and QEB) with a 90° phase difference output by the quadrature encoder and combining with the index signal (INDEX), it can achieve high-precision position, speed, and direction detection. Its core functions include a position counter, an edge capture unit, and a position comparison unit. It supports the quadrature clock mode and the direct counting mode, and is compatible with incremental or absolute photoelectric encoders, providing reliable technical support for complex trajectory tracking, dynamic response optimization, and stable operation in industrial environments.
Principle
EQEP_A and EQEP_B interfaces support two working modes. This article verifies the first one:
In the quadrature clock mode, counting is performed by detecting two square-wave signals with a 90° phase difference (i.e., a 1/4-cycle difference), so as to determine the rotation speed and direction of the working module (motor).
The EQEP_I interface is used for reset or event triggering.
The EQEP_S interface is used as a marker and is usually connected to a sensor to notify that the motor has reached a predefined position.
(The EQEP_I and EQEP_S ports were not tested.)
Timing diagram of the eQEP interface:
As can be seen from the timing diagram, the value of the counter changes by detecting the level changes at port A or port B. Whether it increases or decreases is determined by the order of the level changes at ports A and B detected by the interface.
For example:
When the initial states of QA and QB are both low, after QA first detects a rising edge and then QB detects a rising edge, the value of QDIR becomes high, and the corresponding counter will increase. When the initial state of QA is low and that of QB is high, after QA first detects a rising edge and then QB detects a falling edge, the value of QDIR becomes low, and the corresponding counter will decrease.
Based on the 6254 platform, the eQEP interface developed by TI can only be used to detect the input of peripheral modules. If motor control is required, other upper-layer application development is needed.
Hardware principle for implementation of detection:
Software simulation can also be achieved through the hardware principle. However, software simulation has requirements for time accuracy and may not reach the accuracy of the hardware interface.
Implementation Steps
3.1 Software Modification
1. Since the current SDK package of Forlinx does not support eQEP, the latest SDK10 needs to be downloaded from the official website. Then replace ti-eqep.c, Kconfig, and counter.h in SDK10.
Copy the ti-eqep.c and Kconfig files to the /drivers/counter/ directory of the kernel.
Copy the counter.h file to the /include/uapi/linux/ directory of the kernel.
2. Device tree modification:
Modify the K3-am62-main.dtsi device tree file and add the following:
Modify the OK62xx.dtsi device tree, reuse the corresponding pins, and add nodes.
Controllable GPIO interfaces:
3. Configure menuconfig
Device Drivers --->Counter support --->TI eQEP counter driver
4. Compile the kernel to generate new device tree files and modules
After compilation, the counter.ko and ti-eqep.ko files generated in the path OK62xx-linux-fs/rootfs/lib/modules/6.1.33/kernel/drivers/counter/ are the files we need.
Transfer the counter.ko and ti-eqep.ko files to the /lib/modules/6.1.33/kernel/drivers/counter/...
Read more -
SPI to Ethernet Communication on Forlinx OK-MX9352-C Board: W5500 Driver Setup & Debug Guide
03/28/2025 at 05:34 • 0 commentsThis article takes Forlinx Embedded’s OK-MX9352-C development board as an example to elaborate on how to adapt the network port module through the SPI interface to achieve Ethernet communication. The W5500 module, a high-performance SPI to 100Mbps Ethernet chip with up to 80Mbps data rate, suits embedded network needs.
Modules used:
Hardware Connection
Wiring between W5500 and OK-MX9352-C is in the table below.
Develop board pins
W5500 pins
LPSPI3_PCS0 SCS LPSPI3_SIN MISO LPSPI3_SOUT MOSI LPSPI3_SCK SCLK GPIO_IO04 INT GPIO_IO05 RST Among them, SCS is the chip-select signal, MISO is the master-in slave-out data line, MOSI is the master-out slave-in data line, SCLK is the clock signal, INT is the interrupt signal, and RST is the reset signal.
Software Configuration and Driver Debugging
1. Compilation Drive
First, add the relevant options to the kernel configuration
> Device Drivers > Network device support > Ethernet driver support ...... [*] WIZnet devicesWIZnet W5100 Ethernet support < > WIZnet W5300 Ethernet support WIZnet interface mode (Select interface mode in runtime) --->WIZnet W5100/W5200/W5500 Ethernet support for SPI mode ......
2. Devie Tree Modification
Add the relevant configuration of W5500 under SPI3 node.
&lpspi3 { fsl,spi-num-chipselects =; pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep"; pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_lpspi3>; pinctrl-1 = <&pinctrl_lpspi3>; cs-gpios = <&gpio2 8 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>; status = "okay"; ethernet: w5500@0 { compatible = "wiznet,w5500"; reg =; status = "okay"; pinctrl-names = "default"; pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_w5500>; interrupt-parent = <&gpio2>; interrupts =; spi-max-frequency =; }; };Multiplexed SPI
pinctrl_lpspi3: lpspi3grp { fsl,pins = < MX93_PAD_GPIO_IO08__GPIO2_IO08 0x3fe MX93_PAD_GPIO_IO09__LPSPI3_SIN 0x3fe MX93_PAD_GPIO_IO10__LPSPI3_SOUT 0x3fe MX93_PAD_GPIO_IO11__LPSPI3_SCK 0x3fe >; }; pinctrl_w5500: w5500grp { fsl,pins = < MX93_PAD_GPIO_IO04__GPIO2_IO04 0x31e //int MX93_PAD_GPIO_IO05__GPIO2_IO05 0x31e //rst >; };Since the W5500 driver uses software reset by default, it’s only necessary to ensure that the reset pin is in a pull-up state.
3. Compilation&Porting
Compile the device tree and drivers, including w5100.ko and w5100-SPI. Ko for W5500.
$ root@DESKTOP-GJ47EH8:/home/OKMX93-linux-sdk# ./build.sh kernel
After compiling, replace the device tree on the development board and place the driver in the directory where the system can find it.
$ root@ok-mx93:~# cp /run/media/boot-mmcblk1p1/OK-MX93-C.dtb /run/media/Boot-mmcblk0p1/ $ root@ok-mx93:~# cp /run/media/boot-mmcblk1p1/w5100.ko ./ $ root@ok-mx93:~# cp /run/media/boot-mmcblk1p1/w5100-spi.ko ./
4. Driver Loading
Execute the load driver command on the development board
root@ok-mx93:~# insmod w5100.ko root@ok-mx93:~# insmod w5100-spi.ko
The new eth2 network card can be seen through the ifconfig -a command, and the network card can be up normally.
root@ok-mx93:~# ifconfig -a ... eth2: flags=-28605 mtu 1500 inet 169.254.218.84 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 169.254.255.255 inet6 fe80::c4c5:86ff:fe12:9f9d prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20ether c6:c5:86:12:9f:9d txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 2115 bytes 340022 (332.0 KiB) RX errors 0 dropped 133 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 56 bytes 13927 (13.6 KiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 ... root@ok-mx93:~# ifconfig eth2 up root@ok-mx93:~# ifconfig ... eth2: flags=-28605 mtu 1500 inet 169.254.218.84 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 169.254.255.255 inet6 fe80::c4c5:86ff:fe12:9f9d prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20ether c6:c5:86:12:9f:9d txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 2430 bytes 398823 (389.4 KiB) RX errors 0 dropped 158 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 56 bytes 13927 (13.6 KiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 ...
5. Network Test
After the driver is loaded, IP can be set normally and the external network can be pinged.
root@ok-mx93:~# ifconfig eth2 172.20.2.167 root@ok-mx93:~# ifconfig ... eth2: flags=-28605 mtu 1500 inet 172.20.2.167...
Read more -
Achieving Fast Startup in the Industrial Automation Field with the Falcon Mode of Forlinx Embedded FET-MX9352-C Platform
03/26/2025 at 08:09 • 0 commentsFast startup is a key device performance indicator in today's rapidly evolving embedded systems. With the popularization of IoT, industrial control and in-vehicle electronics, higher requirements are placed on device response speed and startup time. Fast startup can not only enhance the user experience but also respond quickly in emergency situations, ensuring the stability and safety of the system. This article will introduce how to achieve fast startup to the interface after the system is powered on based on Forlinx Embedded's FET-MX9352-C platform.
Two Boot Modes of Bootloader
Bootloader is the first piece of software code to run after the system is powered on. It is responsible for loading the kernel image and detecting hardware and allocating resources. The Bootloader provides two boot modes: the default mode and the Falcon mode.
Default Boot Mode:
Boot Sequence: After the development board is powered on or reset, the BootROM (main program loader) stored in the CPU ROM is first executed.
Peripheral Initialization: The BootROM is responsible for basic peripheral initialization, such as phase-locked loop (PLL), clock configuration, memory initialization (SRAM), etc., to configure the system-on-chip (SoC).
Component Loading: After loading, the BootROM will find a boot device and load the bootloader image from this device. This image usually includes components such as U-Boot SPL, ATF, and U-Boot.
U-Boot SPL: As the first stage of the bootloader, SPL is the minimum code set suitable for SRAM. It is responsible for initializing hardware, such as the clock and memory controller, and configuring and initializing DRAM.
ATF and U-Boot: Subsequently, SPL loads ATF and U-Boot correctly into DRAM. ATF provides a reference trusted code library for the Armv8 architecture and implements a variety of ARM interface standards. U-Boot is the second-stage bootloader, which is responsible for loading and starting the kernel image and providing a command-line interface for interacting with the hardware.
Falcon Boot Mode
Feature: The Falcon mode is a feature in U-Boot that allows SPL to directly start the Linux kernel, thus skipping the loading and initialization process of U-Boot and achieving fast startup.
Advantage: By reducing the time spent in the bootloader, the Falcon mode significantly shortens the system startup time and improves the device's response speed.
Execution Process of Falcon Mode
The execution process of the Falcon mode is relatively simple and efficient, mainly including the following steps:
SPL Initialization: After the system is powered on or reset, the BootROM stored in the CPU ROM is first executed, and then SPL is loaded and run.
Hardware Initialization: SPL is responsible for initializing necessary hardware devices, such as the clock and memory controller, and configuring and initializing DRAM.
Kernel Loading and Startup: In the Falcon mode, SPL directly loads the Linux kernel into DRAM and jumps to the kernel entry address for execution. This process completely skips the loading and initialization steps of U-Boot.
System Startup: After the Linux kernel runs successfully, it takes over system control and completes the subsequent startup process.
Implementation of Falcon Mode
1.Reduce Bootloader Startup Time
The solution provided by NXP is implemented based on the Yocto BSP version 6.6.36, and the modified patches can be downloaded separately.
git clone https://github.com/nxp-imx-support/meta-imx-fastboot.git
u-boot patch
recipes-bsp/u-boot/files/0001-Enable-Fast-Boot-on-i.MX-8M-Family-and-i.MX-93.patch.
The main purpose of this patch is to add the logic of choosing to start UBOOT or the kernel during the SPL execution process. If any key is pressed during the boot process, it can prevent the automatic startup of the kernel, giving users the opportunity to enter the U-Boot command-line interface. If there is no key input, the system will continue the...
Read more -
OpenCV Porting on T507 Platform with Linux 4.19: A Deep Comparison Between Standalone Compilation and Buildroot Compilation
03/21/2025 at 06:21 • 0 commentsOpenCV is an open-source computer vision library that provides a rich set of image processing and computer vision algorithms, supporting multi-platform development. It can be used for various computer vision tasks such as image and video processing, feature extraction, object detection, image segmentation, pose estimation, and object recognition. There are two methods for porting OpenCV: standalone compilation and Buildroot compilation.
Standalone Compilation of OpenCV
Standalone compilation requires CMake, a cross-platform build system similar to the commonly used ./configure. Once configured, it generates a CMakeLists.txt file that defines the project's build rules.
1. Install CMake
2. Configuration
First, extract opencv-2.4.13.7.tar.gz, enter its directory, and run cmake-gui to open the configuration interface.
(1)Set the source code path and build output path (the output path must be created in advance);
(2)Click Configure and select Unix platform cross-compilation mode;
(3)Configure compiler settings.
(4)Configure compiler settings after configuration.
Enable TIFF support.
Disable CUDA (Compiling with CUDA fails; CUDA is for NVIDIA GPUs, which are not available on T507, so disabling it has no impact).
Select Grouped to configure the installation path in cmake.
Cancel GTK
Reconfigure and generate the build files.
3. Compilation
Before compiling, modify the CMakeLists.txt file to configure linker rules:
The goal is to configure the rules for the connector,
-lpthread: Links the libpthread.so library, which provides multithreading support
-lrt: links the librt.so library, which provides real-time extension-related functions
-lrt: links the librt.so library, which provides real-time extension-related functions
make compilation
4. Installation and Deployment
The installation path needs to be cleared before installation.
make install.
Generated test program.
Generated library.
There is also a part of the build path.
Package the above content and release it to the file system of the board.
5. Test
The program can be called to the library to run normally.
However, there are still some errors in the application processing.
Build root compile opencv
1. Enter the Graphical Interface
2. Select Compilation Parameters
Select opencv3 in the following path
Tick all the parameter items.
3. Save the .config file.
Go to the output path of the source package/OKT507-linux-sdk/out/t507/okt507/longan/buildroot,
Change the existing target file to any name and create a new target file
4. Standalone Compilation
Networking is required for the compilation process
Buildroot outputs the standalone compiled content to the previously created **target** directory. The contents can then be packaged and deployed to the **filesystem**.
5. Test
ZD-Atom provides an OpenCV Qt test program based on **i.MX6UL**, where the **.pro** file defines the application's dependencies.
These libraries are available in the files generated by the compilation.
Both methods have their pros and cons:
Standalone Compilation: Allows trying different source versions and offers more flexible parameter configuration, but the process is complex.
Buildroot Compilation: Enables easy deployment by simply extracting the generated files, but switching versions is inconvenient.
-
Forlinx Embedded Partners with Allwinner to Launch the Powerful T536 SoM
03/19/2025 at 05:22 • 0 commentsFET536-C SoM
FET536-C SoM is designed SoM based Allwinner on the newly released T536 industrial-grade processor. With a 1.6GHz quad-core Cortex-A55 CPU and a 64-bit Xuantie E907 RISC-V MCU, it delivers high computational efficiency. The board supports 2TOPS NPU, secure boot, full-path ECC, AMPRT, and other advanced features. Additionally, it offers a comprehensive set of connectivity interfaces, including USB, SDIO, UART, SPI CAN-FD, Ethernet, ADC, and LocalBus, meeting diverse application requirements.
Beyond its high cost-performance ratio, the entire board is built using industrial-grade components, making it an excellent choice for data concentrators, FTU, DTU Charging Piles, Transportation Robot, Industrial Controlsystems, and other key sectors that require cost-effective yet robust solutions.
Allwinner's New Generation High-Performance Chip
It integrates a powerful application core and an independent RISC-V MCU, supporting 2TOPS NPU, secure boot, full-path ECC, AMP, Linux-RT, LocalBus, and more. These features enhance edge machine learning applications.
Interface Rich Resources
AMP & Multi-core Heterogeneous
FET536-C incorporates a quad-core Cortex-A55 CPU and a 64-bit Xuantie E907 RISC-V MCU, supporting Linux RT, FreeRTOS, and bare-metal code. This combination ensures both high performance and real-time control capabilities.
NPU: 2TOPS Computing Power
Built-in neural processing unit (NPU) with computing power up to 2 TOPS provides Edge Computing powerful support for applications.
All Pins Are Exposed
Meets the diverse functional requirements of different products across various industries.
Supports parallel LocalBus
Supports parallel LocalBus with high data read/write speeds of 16-bit @100MHz or 32-bit @50MHz,ARMensuring convenient communication.
Security Features
ISP Greatly Improves Image Quality
Integrated ISP technology supports 8MP @30fps, WDR, and 3DNR, providing clear and accurate image data.
Continuously Updated User Documentation
Application Scenarios
With versatile functionality, it suits industries like data concentrators, DTU, EV charging, transportation, robotics, and industrial control. Forlinx Its performance, interfaces, reliability, and support ensure fast deployment and industry leadership.
-
FET3506J-S SoM: A High-performance Embedded Solution Designed for Global Industrial Applications
03/13/2025 at 05:06 • 0 commentsTo meet the demand for highly reliable embedded hardware in the global industrial sector, the FET3506J-S SoM stands out in numerous fields and becomes the ideal choice, thanks to its excellent technical features and proven stability.
It is equipped with the Rockchip RK3506J processor using triple-core Cortex-A7. After a series of comprehensive and strict reliability tests, it ensures stable operation in industrial environments and greatly reduces the risk of production interruption caused by hardware failures.
The processor is the core of the FET3506J-S System on Module. It uses the high-performance triple-core RK3506J, which is specially designed for intelligent industrial applications. When the SoM is running at full load, its power consumption is as low as 0.7W. It can withstand a high - temperature environment of +85°C without additional heat dissipation measures, demonstrating significant advantages in energy efficiency and heat dissipation. It is very suitable for industrial application scenarios with strict requirements on energy consumption and heat dissipation.
The SoM is equipped with a variety of peripheral interfaces, such as RMII, UART, CAN, Display, etc., which can meet the development needs of different application scenarios. Whether it is equipment communication in industrial automation, data transmission in transportation systems, or display output in consumer electronics, these interfaces can provide excellent support, facilitating developers to expand functions and integrate systems.
Its parallel bus interface DSMC provides strong support for low-cost and easily-developed FPGAs and high-speed communication. It supports master/slave modes and enables efficient data interaction.
Its configurable parallel data interface, FlexBUS, is also highly practical. It can be used to connect peripherals such as ADCs, DACs, DVP cameras, and Q LCD displays, further enhancing the SoM's functional diversity and application adaptability.
In addition, the RK3506J adopts a matrix IO design, allowing numerous functional signals to share limited pin interfaces. Moreover, any functional signal can be mapped to any pin interface through software configuration, supporting the mapping of 98 functional signals to 32 pin interfaces. This flexible pin configuration method provides greater freedom for product design. It enables rapid adjustment of the hardware layout according to specific application requirements, shortening the product R & D cycle and reducing development costs.
In terms of storage, Forlinx Embedded users are provided with in-depth storage driver optimization and an eMMC health diagnosis tool. This tool can monitor the status of storage devices in real-time, issue early warnings for potential failures, maximize the service life and reliability of storage devices, reduce product failures caused by exhausted storage life, and ensure data security and stable system operation.
In terms of software support, the FET3506J-S SoM is fully compatible with various software ecosystems such as Linux 6.1, LVGL 9.2, AMP architecture, and Linux RT, demonstrating strong software adaptability and a flexible system architecture. Whether it is to build a complex graphical user interface or achieve high-precision real-time control, it can handle them easily, fully meeting the diverse application needs from display to control and being widely applicable to various complex application scenarios.
FET3506J-S Computer on Module has advantages such as high performance, low power consumption, rich interfaces, flexible design, and strong software support. It is widely used in industries and related application fields such as industrial automation, consumer electronics, smart healthcare, power, new energy, and communication. Coupled with its competitive price and comprehensive after-sales technical support, it can help enterprises’ products be quickly launched into the market, gain an advantageous position in...
Read more -
Unboxing Quick View: NXP's First MPU FRDM Product-FRDM i.MX93 Dev Board
03/08/2025 at 08:53 • 0 commentsIn 2022, Forlinx Embedded globally launched the OK-MX9352-C development board equipped with the NXP i.MX 93 series processors. Over the past three years, this product has provided powerful intelligent main-control support for numerous customers with its excellent performance and high-level security.
Recently, NXP introduced the i.MX 93 series processors into the FRDM product line and launched the FRDM i.MX 93 development board. As the first FRDM board equipped with an i.MX MPU, it offers modular hardware, comprehensive software and tools, and a quick-start experience common to all FRDM development boards.
Forlinx Embedded got the FRDM i.MX 93 development board first. Here, I will give a quick unboxing review.
First Unboxing Experience: Small Size, Comprehensive Functions
Opening the FRDM i.MX 93 dev board's small package, you'll first notice its compact and delicate design. A rough ruler-measure shows its long side is only about 10.5 cm. Despite its small size, every component on the development board is carefully laid out to ensure comprehensive functions and stability.
In addition, the package also includes a quick-start guide, a list of accessories, and two USB 2.0 Type-A to Type-C cables.
i.MX 93 Processor:Balance between Performance and Power Consumption
The FRDM i.MX 93's core is the NXP i.MX93 processor, known for high-performance and low-power consumption. It integrates 2 x 1.7 GHz ARM Cortex-A55 multi-tasking cores and 1 x Cortex-M33 real-time core. It innovatively uses the ARM Ethos U-65 microNPU with 256 MACs/cycle and 0.5 TOPS computing power, enabling efficient, fast, and secure edge machine learning.
The Energy Flex architecture in i.MX 93 ensures high-efficiency complex-task processing and ultra-low standby power consumption, fitting IoT and industrial apps well.
Block Diagram of FRDM i.MX 93
IW612 Module: Connect to Multiple Wireless Networks
The FRDM i.MX 93 has an IW612 wireless module supporting 2.4/5 GHz Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5.4, and IEEE 802.15.4,etc. It enables easy connection to various wireless networks for smart homes, industrial IoT, etc.
The module has dedicated processors and memories for subsystems, allowing real-time independent protocol processing.
Internal Structure Block Diagram of IW612
Expansion Interfaces for Diverse Needs
The FRDM i.MX 93 provides a rich set of expansion interfaces, including GPIO, UART, I2C, SPI, etc.These interfaces can meet your needs for connecting various sensors, actuators, and peripherals. The flexibility of the development board allows it to adapt to multiple application scenarios, providing more possibilities for your project development.
Front
Back
Multimedia Performance: HDMI and MIPI Interfaces Available
For application scenarios requiring high-definition display, the FRDM i.MX 93 also performs excellently. The HDMI interface on the development board supports high-definition video output and can be connected to a monitor or TV to present delicate and clear pictures. This is undoubtedly a great plus for application scenarios such as industrial monitoring and home entertainment.
In addition, it is also equipped with a 4-channel MIPI-DSI interface and a 2-channel MIPI CSI-2 interface, which can easily achieve high-resolution display connection and high-resolution, high-frame-rate image capture, providing powerful multimedia processing capabilities.
Software and Tool Support: Greatly Accelerate the Development Cycle
To help developers get started faster, the FRDM i.MX 93 development board is also equipped with a comprehensive software and toolchain. It supports operating system environments (such as Yocto Linux and Debian Linux), as well as GoPoint for i.MX application processors and a rich set of application examples. These software and tools will greatly accelerate the development cycle and simplify the process from prototype to production.
GoPoint Tool Interface
It's pretty obvious that the...
Read more -
From eMMC to NAND: Software Optimization Strategies for Embedded System Storage
03/06/2025 at 02:44 • 0 commentsIn the embedded system development, as the core carrier of information interaction, the technical characteristics of the memory directly affect the system's performance and stability. However, when dealing with complex OS environments like Linux and Android, some struggle with understanding their storage mechanisms. Forlinx Embedded aims to overcome these hurdles by sharing storage knowledge to help build a comprehensive framework.
First, the media commonly used to store data in embedded scenarios can be divided into two categories:
Managed NAND: Mainly includes eMMC (embedded Multi - Media Card), TF cards, and SD cards, which have an internal storage management controller.
Raw NAND: Mainly based on NAND, without storage management functions, only containing simple IO logic control.
The figure above describes the relationship between NAND storage and eMMC storage. The NAND Controller refers to the CPU of the SoM, and NAND refers to the actual storage area. It can be seen that the difference between eMMC and NAND actually lies in whether the storage management control is inside the eMMC or in the CPU of the SoM. Storage management mainly includes the following functions: bad block management, ECC verification, wear leveling, data retention, address management and mapping, etc.
01 Related Concepts of Storage
Storage Types: SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC. In embedded systems, SLC and MLC are commonly used for low - capacity storage, while TLC is generally used for high-capacity storage.
SLC (Single-Level Cell) It has high speed, long lifespan, and high price, with a theoretical erase-write cycle of about 100,000 times.
MLC (Multi-Level Cell) It has relatively high speed, relatively long lifespan, and relatively high price, with a theoretical erase-write cycle of 3000-5000 times.
TLC (Trinary-Level Cell) It has low speed, short lifespan, and the lowest price, with a theoretical erase-write cycle of 1000-3000 times.
QLC (Quad-Level Cell) It can have a larger capacity and lower cost, but its P/E lifespan is shorter.
pSLC (pseudo SLC) It is based on MLC FLASH, but only stores 1 bit of data in each cell instead of 2 bits. Since it only stores 1 bit per cell like SLC but is not a real SLC, it is called pSLC.
According to the above principle, if MLC is used as pSLC, the storage space will be halved, and the lifespan can usually be increased to about 30,000 times.
P/E (Program/Erase Count) Erase-write lifespan, one of the two indicators of durability.
TBW (Total Bytes Written) Total write volume, which is the value used by manufacturers to define the warranty period. That is, after the write volume exceeds this value, the manufacturer will no longer provide warranty services. It is also one of the two indicators of durability.
FW (Firmware) Since the internal controller of eMMC is a software-programmable controller, it requires firmware. The corresponding firmware has been flashed into the eMMC before it leaves the storage manufacturer.
WA (Write amplification) Write amplification. It indicates how many times the actual physical data written is compared to the written data volume, i.e., the data volume written to the flash memory ÷ the data volume written by the main controller = write amplification.
GC(Garbage Collection) Garbage collection. The storage writing of NAND media is carried out page by page and erased block by block.
02 Differences Between eMMC and NAND
(1) Comparison Between eMMC and NAND
Read moreNAND eMMC Address Mapping Each time the CPU is mounted and read into memory, it is stored in NAND before being unloaded. Internal firmware management, using internal reservations Wear leveling, bad block management and garbage collection NAND and file system drivers running on the CPU Internal firmware management, firmware maintenance by storage manufacturer ECC error correction >td >Internal firmware management with hardware... -
A Step-by-Step Guide to Integrating AX210NGW Wi-Fi 6E With OK3576-C Development Board
02/28/2025 at 06:12 • 0 commentsIn the era of ubiquitous connectivity, wireless communication technology is an essential part of embedded systems. Wi-Fi modules, as a crucial link between devices and networks, require high performance and compatibility. Intel's AX210NGW Wi-Fi 6E module, a high-performance wireless network adapter, supports the latest Wi-Fi 6E standard and Bluetooth 5.3, offering excellent transmission speeds and compatibility, thus providing strong support for wireless connectivity in embedded systems.
AX210NGW Wi-Fi 6E Module
To meet the demand for high-performance embedded control applications, this article details how to adapt the AX210NGW Wi-Fi 6E module (hereinafter “the module”) on the Forlinx Embedded OK3576-C development board, enabling developers to quickly start and utilize its performance advantages.
Note: The Bluetooth function of the Wi-Fi module has not been adapted. This article only covers Wi-Fi adaptation.
![A Step-by-Step Guide to Integrating AX210NGW Wi-Fi 6E With OK3576-C development board]()
OK3576-C Development Board Interface Diagram
First, Wi-Fi module should be connected to the Forlinx OK3576-C development board. The Wi-Fi module uses an M.2 Key A + E interface, while the OK3576-C board lacks this interface. An M.2 to PCIe dual-band wireless network card adapter can be used for conversion.
Go to the kernel directory to start configuration:
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/3576$ cd kernel-6.1/ forlinx@ubuntu20:~/3576/kernel-6.1$ make menuconfig ARCH=arm64
Select in the following order:
Location: -> Device Drivers -> Network device support (NETDEVICES [=y]) -> Wireless LAN (WLAN [=y]) -> Intel devices (WLAN_VENDOR_INTEL [=y]) -> Intel Wireless WiFi Next Gen AGN-Wireless-N/Advanced-N/Ultimate-N (iwlwifi) (IWLWIFI [=m]) -> Intel Wireless WiFi MVM Firmware support (IWLMVM [=m])
Start to compile:
forlinx@ubuntu20:~/3576/kernel-6.1$ export CROSS_COMPILE=/home/forlinx/3576/prebuilts/gcc/linux-x86/aarch64/gcc-arm-10.3-2021.07-x86_64-aarch64-none-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-none-linux-gnu- forlinx@ubuntu20:~/3576/kernel-6.1$ export PATH=$PATH:/home/forlinx/3576/prebuilts/gcc/linux-x86/aarch64/gcc-arm-10.3-2021.07-x86_64-aarch64-none-linux-gnu/bin/ forlinx@ubuntu20:~/3576/kernel-6.1$ make ARCH=arm64 rk3576-evb1-v10-linux.img
Finally, copy the compiled module to the OK3576-C development board. Here, copy the module to the/root directory. Enter the kernel source path:
(1) drivers/net/wireless/intel/iwlwifi/iwlwifi.ko
(2) drivers/net/wireless/intel/iwlwifi/mvm/iwlmvm.ko
In addition, copy the Wi-Fi firmware and STA scripts to the/root directory for backup.
root@rk3576-buildroot:/root# ls firmware.zip fltest_wifi.sh iwlmvm.ko iwlwifi.ko
STA scripts can refer to the following contents, such as creating scripts by yourself, and remember to add executable permissions.
#!/bin/sh cnt1=`ps aux | grep hostapd | grep -v grep | wc -l` if [ "$cnt1" != "0" ];then killall hostapd > /dev/null fi ifconfig uap0 down function usage() { echo "Usage: -i-s-p" echo "eg: ./wifi.sh -i mlan0 -s bjforlinx -p 12345678 " echo "eg: ./wifi.sh -i mlan0 -s bjforlinx -p NONE " echo " -i : mlan0 or mlan1" echo " -s : wifi ssid" echo " -p : wifi password or NONE" } function parse_args() { while true; do case "$1" in -i ) wifi=$2;echo wifi $wifi;shift 2 ;; -s ) ssid=$2;echo ssid $ssid;shift 2 ;; -p ) pasw=$2;echo pasw $pasw;shift 2 ;; -h ) usage; exit 1 ;; * ) break ;; esac done } if [ $# != 6 ] then usage; exit 1; fi parse_args $@ if [ -e /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf ] then rm /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf fi echo \#PSK/TKIP >> /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf echo ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant >>/etc/wpa_supplicant.conf echo ctrl_interface_group=0 >>/etc/wpa_supplicant.conf echo update_config=1 >>/etc/wpa_supplicant.conf echo network={ >>/etc/wpa_supplicant.conf echo ssid=\"$ssid\" >>/etc/wpa_supplicant.conf echo scan_ssid=1 >>/etc/wpa_supplicant.conf if [ $pasw == NONE ] then echo key_mgmt=NONE >>/etc/wpa_supplicant.conf else echo psk=\"$pasw\" >>/etc/wpa_supplicant.conf echo key_mgmt=WPA-EAP WPA-PSK IEEE8021X...Read more -
NXP's FRDM i.MX93 Board Supercharges Industrial IoT
02/26/2025 at 03:49 • 0 commentsGet ready for a leap in Industrial IoT innovation! NXP has just dropped the FRDM i.MX93 Development Board – the first MPU-powered marvel in their FRDM series, a game-changer for edge computing.
This isn't just another dev board; it's a powerhouse packed into a compact design, engineered for the demands of the Industrial IoT frontier. Imagine smarter factories, more responsive infrastructure, and data insights at lightning speed – the i.MX93 is built to make it happen.
Here's why media tech pros should be paying attention:
- Brainpower at the Edge: Dual-core Cortex-A55 up to 1.7GHz + a dedicated Cortex-M33 real-time core + Ethos-U65 microNPU (0.5 TOPS, perfect balancing between performance and power efficiency). This board is serious about processing power for complex Linux systems and edge AI.
- Connectivity King: Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5.4, 802.15.4, Gigabit Ethernet, CAN, USB – you name it, it connects. Perfect for deploying across diverse industrial environments.
- Security Built-In: NXP EdgeLock security subsystem ensures your data is protected with hardware-level secure boot, encryption, and key management. Crucial for today's connected industrial world.
- Dev-Ready Ecosystem: Yocto & Debian Linux support, the GoPoint toolchain, and a suite of examples mean you can prototype and deploy faster.
The FRDM i.MX93 isn't just a board; it's a platform for a smarter, more connected industrial future. Want to dive deep into the tech specs and possibilities?
Check out the official NXP details here:
https://www.nxp.com/design/design-center/development-boards-and-designs/FRDM-IMX93#buy
https://www.nxp.com/document/guide/getting-started-with-frdm-imx93:GS-FRDM-IMX93
-
RK3576 with UFS Storage: In-depth Analysis of Performance Advantages and Read-Write Test Data
02/22/2025 at 01:13 • 0 commentsIn embedded storage field, UFS (Universal Flash Storage) is gradually emerging. UFS is a type of flash memory. Similar to eMMC, it integrates a control chip, accesses a standard interface, and undergoes standard packaging on the basis of NAND storage chips, thus forming a highly integrated storage chip. Due to its compact characteristics, UFS is widely used in embedded devices such as mobile phones and tablets. Moreover, since UFS far outperforms eMMC in terms of performance, it is often used in high-end products.
Advantages of UFS
1. Faster response speed for multitasking
Devices using UFS2.0. LVDS (Low-Voltage Differential Signaling) has a dedicated serial interface, allowing read and write operations to be carried out simultaneously. The CQ (Command) queue dynamically allocates tasks without waiting for the previous process to end. It’s like a car getting on the highway, with multiple lanes allowing high-speed and smooth travel. In contrast, mobile phones using EMMC must perform read and write operations separately, and the instructions are also packaged. In terms of speed, EMMC is already at a disadvantage, and it is naturally slower when performing multitasking. It likes traveling on an common two-lane road with speed limits.
2. Low latency, UFS has a 3-times faster response speed
When reading large-scale games and large-volume files, UFS2.0 takes less time. The time required to load a game is one-third of that of EMMC5.0. Correspondingly, when experiencing games, mobile phones with UFS2.0 have lower latency and smoother pictures.
3. Shorter loading time for photo thumbnails in the album
Taking the mobile phone album as an example, many people’s mobile phones are filled with hundreds or even thousands of photos. When you open the photo thumbnails in the album, you can clearly see the loading process. This is caused by the fact that the mobile phone cannot keep up with the refresh speed when reading photos from the flash memory. On a mobile phone with a good screen, the pictures will load smoothly as you scroll, while on a less-capable mobile phone, you can clearly feel the lag during loading.
4. Faster speed and lower power consumption
After the UFS chip improves its speed, it means that it takes less time to complete the same task. Higher efficiency means lower power consumption. When working simultaneously, the power consumption of UFS is 10% lower than that of eMMC, and it can save approximately 35% of power consumption in daily work.
UFS interface read-write performance test
RK3576 CPU also provides a UFS2.0 interface and an emmc5.1 interface.
FET3576-C SoM also reserves a UFS interface.
Refer to Rockchip’s official document “Rockchip_Developer_Guide_UFS_CN_V1.3.0” to conduct read-write tests on the UFS flash memory of OK3576-C.
Sequential write test
root@ok3576-buildroot:/# fio -filename=/dev /sda -direct=1 -iodepth
Read more
32 -thread -rw=write -bs=1024k -size=1G -numjobs=8 -runtime=180
-group_reporting -name=seq_100write_1024k
seq_100write_1024k: (g=0): rw=write, bs=(R) 1024KiB-1024KiB, (W) 1024KiB-1024KiB, (T)
1024KiB-1024KiB, ioengine=psync, iodepth=32
...
fio-3.34
Starting 8 threads
note: both iodepth >= 1 and synchronous I/O engine are selected, queue depth will be
capped at 1
note: both iodepth >= 1 and synchronous I/O engine are selected, queue depth will be
capped at 1
note: both iodepth >= 1 and synchronous I/O engine are selected, queue depth will be
capped at 1
note: both iodepth >= 1 and synchronous I/O engine are selected, queue depth will be
capped at 1
note: both iodepth >= 1 and synchronous I/O engine are selected, queue depth will be
capped at 1
note: both iodepth >= 1 and synchronous I/O engine are selected, queue depth will be
capped at 1
note: both iodepth >= 1 and synchronous I/O engine are selected, queue depth will be
capped at 1
note: both iodepth >= 1 and synchronous... -
A Comprehensive Guide to Deploying the DeepSeek-R1 Large Model on the Forlinx OK3588-C Development Board (Part 1)
02/20/2025 at 01:26 • 0 commentsDeepSeek, as a representative of AI Large Language Models, has attracted extensive attention in the global artificial intelligence field with its excellent reasoning ability and efficient text-generation technology. As the latest iteration of this series, DeepSeek-R1 has achieved breakthroughs in technological dimensions such as the leap in long-text processing efficiency, multi-modal expansion planning, and embedded adaptation.
RK3588, as the flagship chip launched by Rockchip, has become an ideal platform for embedded AI applications with its multi-core heterogeneous computing power and powerful CPU, GPU, and NPU performance. The in-depth integration of DeepSeek-R1 and the OK3588-C development board marks the extension of large AI models from the cloud to the edge. This collaborative model of "advanced algorithm + customized chip" not only meets key requirements such as real-time performance and privacy protection on the edge side but also builds a complete value chain from technology R & D to industrial empowerment, providing a reusable innovation paradigm for the intelligent transformation of various industries. Next, let's delve into how this process is specifically implemented.
01 Transplantation Process
(1) Download the DeepSeek-R1 Source Code
Download the DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B weight file from the official website of DeepSeek-R1 on the Ubuntu virtual machine.
(2) Install the Conversion Tool
Create a virtual environment on Ubuntu and install RKLLM-Toolkit to convert the DeepSeek-R1 large language model into the RKLLM model format and compile the executable program for board-side inference.
(3) Model Conversion
Use RKLLM-Toolkit to convert the model. RKLLM-Toolkit provides model conversion and quantization functions. As one of the core functions of RKLLM-Toolkit, it allows users to convert large language models in Hugging Face or GGUF format into RKLLM models, enabling the RKLLM models to be loaded and run on the Rockchip NPU.
(4) Compile the DeepSeek-R1 Program
Install the cross-compilation toolchain to compile the RKLLM Runtime executable file. This program includes all processes such as model initialization, model inference, callback function processing output, and model resource release.
(5) Model Deployment
Upload the compiled RKLLM model and executable file to the board for execution. Then, you can have a conversation with DeepSeek-R1 on the debugging serial port of the OK3588-C development board without an internet connection.
02 Demo
DeepSeek-R1 is a multi-functional artificial intelligence assistant that can provide efficient and comprehensive support in multiple fields. Even the local offline version can give accurate and practical suggestions based on its powerful data-processing ability and extensive knowledge repository, whether it's for daily information retrieval needs, maintenance guidance for professional equipment, solutions to complex mathematical problems, or assistance in completing programming tasks. It has become a reliable partner for users in exploring various fields.
(1) General Information Search
DeepSeek-R1 can quickly retrieve and provide accurate information. For example, when asked about "Forlinx Embedded Technology Co., Ltd.", DeepSeek-R1 can introduce the company's background, main business, product features, etc. in detail, helping users understand the company comprehensively.
(2) Maintenance Advice for Professional Equipment Problems
For professional equipment problems, DeepSeek-R1 can provide detailed fault analysis and solutions. For instance, regarding the problem of the PLC reporting error code E01, R1 analyzes the possible causes of the fault, such as power supply problems, wiring errors, or hardware failures, and provides corresponding solution steps to help users quickly troubleshoot the fault.
(3) Solving Math Problems
DeepSeek-R1 has excellent mathematical operation ability and is good at solving various mathematical problems. For example,...
Read more -
How to Compile and Run NPU Test Programs Based on rknn_yolov5_demo on RK3568?
02/13/2025 at 07:41 • 0 commentsWhen developing NPU (Neural Processing Unit) related applications on RK3568, compiling and running test programs is a crucial step. This article will take rknn_yolov5_demo as an example and guide through each step in detail.
1. Preparation: Locate the Compilation Script
Open external/rknpu2/examples/rknn_yolov5_demo/build-linux_RK3566_RK3568.sh
2. Key Configuration: Modify the Cross-Compilation Toolchain Path
After opening the build-linux_RK3566_RK3568.sh file, modify the GCC_COMPILER to the path of the cross-compilation toolchain and save the file.
3. Compile the rknn_yolov5_demo Program
In the terminal command window, navigate to the rknn_yolov5_demo folder:
cd external/rknpu2/examples/rknn_yolov5_demo/
Run the build-linux_RK3566_RK3568.sh script to compile the program:
./build-linux_RK3566_RK3568.sh
4. File Transfer: From Local to Development Board
Copy the contents of the install directory to the development board.
5. Navigate to the Correct Directory: Preparing to Run the Program
Navigate to the corresponding directory on the development board.
6. Set the Library File Path
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./lib
7. Run the Program to Identify Object Categories in the Image
The command format to run the program is: ./rknn_yolov5_demo
./rknn_yolov5_demo ./model/RK3566_RK3568/yolov5s-640-640.rknn ./model/bus.jpg
8. View the Results
Finally, copy the resulting image generated on the OK3568-C development board to local computer and view it. This way, the program's object recognition results in the image can be visually observed, the accuracy of the recognition can be checked, and the performance of the NPU test program can be evaluated.
By following these detailed steps, the rknn_yolov5_demo NPU test program on RK3568 can be successfully compiled and run. It is hoped that this article will be helpful for the development work.
-
NXP Unveils FRDM i.MX 93 Development Board to Accelerate Modern Industrial and Edge Intelligence Advancements
02/12/2025 at 06:22 • 0 commentsRecently, NXP Semiconductors introduced the FRDM i.MX 93 development board, the first development board in the FRDM series based on MPU. It is designed with a focus on low cost and compactness, featuring the NXP i.MX 93 series application processor. It aims to provide users with an efficient and reliable solution for developing modern industrial control and edge intelligence applications.
One of the key highlights of the FRDM i.MX 93 development board is its onboard IW612 module, which utilizes NXP’s Tri-Radio solution, integrating Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5.4, and 802.15.4 triple wireless communication technologies. It not only enhances the stability and speed of wireless communication but also provides developers with a wider range of connectivity options to meet the needs of various application scenarios.
In addition to its powerful wireless communication capabilities, the FRDM i.MX 93 development board is equipped with a rich set of hardware resources. HDMI display interface supports high-definition video output, greatly facilitating the development of multimedia applications. LPDDR4/LPDDR4X memory and eMMC storage ensure fast data processing and storage, further improving development efficiency. The board also features a power management integrated circuit (PMIC) and an EXPIO interface compatible with Raspberry Pi pin definitions, to meet the needs of developers in different application scenarios.
Front
Back
Moreover, the FRDM i.MX 93 development board supports GoPoint for i.MX Applications Processors. This feature helps developers quickly understand and apply the powerful functions of the i.MX processor through comprehensive demonstrations for various purposes, thereby accelerating product time-to-market. It serves as an ideal platform for beginners to learn and practice embedded development and is also a capable assistant for professional developers in prototyping and product development.
Click the link below to visit the NXP official website and learn more about the product information of the FRDM i.MX 93 development board.
https://www.nxp.com/document/guide/getting-started-with-frdm-imx93:GS-FRDM-IMX93
-
How to Boot the RK3562J on the M-Core?
02/08/2025 at 06:46 • 0 commentsFET3562J-C SoM based on Rockchip RK3562 series processor is a product designed for industrial automation and consumer electronics equipment. With its powerful functions and flexibility, it has attracted wide attention from customers in various industries since its launch. This article will introduce in detail how to start and test the MCU of RK3562J processor, and help engineers better understand this chip through practical operation steps.
RK3562J Processor Overview
RK3562J processor uses a 4*Cortex-A53@1.8GHz + Cortex-M0 @ 200MHz architecture. Among them, the four Cortex-A53 cores are the main cores responsible for handling complex operating system tasks and applications. In contrast, the Cortex-M0 cores serve as auxiliary cores running a bare-core system capable of fast response and control for tasks with high real-time requirements.
Preparations for Launching the M0 Core Firmware
At present, the M0 kernel firmware is not started by default on the embedded OK3562J-C development board. Therefore, we need to go through a series of steps to configure and start the M0 core. The following are the specific steps.
1.U-Boot Modification
In theory, we need to open the AMP (Asymmetric Multiprocessing) compilation macro, but because the U-Boot of the embedded OK3562J-C development board has been configured with the AMP function by default, the user does not need to modify any U-Boot.
2. Kernel Modification
(1) Toolkit Installation
First, we need to install the SCons toolkit for later compilation. It can be installed with the following command:
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt-get install scons
(2) Add AMP Device Tree Calls
OK3562J-C board has been added with a call to the AMP device tree. It's content can be viewed through the relevant configuration files.
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ cd /home/forlinx/work/OK3562-linux-source/ forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/OK3562-linux-source$ vi kernel-5.10/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/OK3562-C-common.dtsi +include "rk3562-amp.dtsi"
rk3562-amp.dtsi includes:
/ { /* Device description */ rockchip_amp: rockchip-amp { compatible = "rockchip,amp"; clocks = <&cru FCLK_BUS_CM0_CORE>, <&cru CLK_BUS_CM0_RTC>, <&cru PCLK_MAILBOX>, <&cru PCLK_INTC>, // <&cru SCLK_UART7>, <&cru PCLK_UART7>, <&cru PCLK_TIMER>, <&cru CLK_TIMER4>, <&cru CLK_TIMER5>; //pinctrl-names = "default"; //pinctrl-0 = <&uart7m1_xfer>; amp-cpu-aff-maskbits = /bits/ 64; amp-irqs = /bits/ 64 ; status = "okay"; }; /*Some reserved memory areas are defined */ reserved-memory { #address-cells =; #size-cells =; ranges; /* remote amp core address */ amp_shmem_reserved: amp-shmem@7800000 { reg =; no-map; }; rpmsg_reserved: rpmsg@7c00000 { reg =; no-map; }; rpmsg_dma_reserved: rpmsg-dma@8000000 { compatible = "shared-dma-pool"; reg =; no-map; }; /* mcu address */ mcu_reserved: mcu@8200000 { reg =; no-map; }; }; /* Implementing the Rockchip RPMsg function */ rpmsg: rpmsg@7c00000 { compatible = "rockchip,rpmsg"; mbox-names = "rpmsg-rx", "rpmsg-tx"; mboxes = <&mailbox 0 &mailbox 3>; rockchip,vdev-nums =; /* CPU3: link-id 0x03; MCU: link-id 0x04; */ rockchip,link-id =; reg =; memory-region = <&rpmsg_dma_reserved>; status = "okay"; }; };3. Generating Configuration Files
Next, we need to generate a configuration file for the M0 core firmware. In the RTOS source directory, generate the required configuration file by copying the default configuration file and running the SCons menu configuration interface. Although no additional configuration is required in this example, the user can configure it as needed.
forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/OK3562-linux-source$ cd rtos/bsp/rockchip/rk3562-32 forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/OK3562-linux-source/rtos/bsp/rockchip/rk3562-32$ cp board/rk3562_evb1_lp4x/defconfig .config forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/OK3562-linux-source/rtos/bsp/rockchip/rk3562-32$ scons --menuconfig
After opening the graphical configuration interface, you can exit directly without configuration.
If there are other functional requirements, you can exit and save...
Read more -
Forlinx Embedded T527 SoM Adapted to Forlinx Desktop 22.04
01/22/2025 at 08:29 • 0 commentsForlinx Embedded Systems has recently adapted the FET527N-C SoM for the latest Forlinx Desktop 22.04 operating system, bringing significant improvements to user experience. Users can now enjoy smoother, more stable operations and take advantage of the rich features and innovative characteristics of Forlinx Desktop 22.04 to enhance work efficiency and application compatibility.
OK527N-C Development Board Running Forlinx Desktop 22.04
1. Dual Empowerment of System and Hardware
Forlinx FET527N-C SoM is equipped with Allwinner’s T527N processor, which integrates 8 x high-performance ARM Cortex-A55 cores, along with 1 RISC-V core and 1 x DSP core, providing 2 x TOPS of NPU computing power to support complex applications and AI requirements.
Forlinx Desktop 22.04 optimizes the kernel and resource management strategies to fully unleash the hardware’s potential, closely integrating with the FET527N-C SoM. This combination offers users a smoother and more efficient experience in handling large data and complex algorithms.
2. Easy to Use & Efficient Development
On Forlinx Desktop 22.04, APT (Advanced Package Tool) is used as the software package management tool, providing powerful functions for searching, installing, upgrading, and deleting packages, making operations simpler and development more efficient.
3. Stable Supply
Forlinx FET527N-C SoM has 10 to 15 years' longevity, ensuring that users receive stable hardware support over the long term.
-
3.1s Fast Startup! Deploying LVGL on the i.MX93 Series Development Board to Create a More Efficient GUI
01/20/2025 at 01:47 • 0 commentsRecently, to improve user efficiency and satisfaction, Forlinx Embedded has developed an easy-to-use and lightweight UI based on the NXP i.MX93 series processor.
By adjusting the boot sequence during the U-Boot stage, the SPL (Secondary Program Loader) is configured to directly boot the Linux kernel, achieving fast startup. This approach completely bypasses the loading and initialization of U-Boot, significantly reducing the time spent in the bootloader. As a result, the boot time has been reduced to just 3.1 seconds.
Additionally, the OK-MX9352-C development board has successfully integrated LVGL v8.3, enhancing the interface’s aesthetics and sophistication. This improvement provides customers with more options for UI design.
LVGL (Light and Versatile Graphics Library) is a free and open-source graphics library specifically designed for embedded systems. Renowned for its lightweight, efficiency, and ease of use, LVGL supports multiple screen resolutions and hardware configurations. It offers a rich set of GUI components, enabling developers to easily create beautiful and powerful user interfaces. Click on the image below to visit the LVGL official website:
Recently, Forlinx Embedded successfully ported LVGL v8.3 to the OK-MX9352-C development board based on the NXP i.MX93 series processor, which not only realizes a beautiful and delicate interface but also dramatically improves the start-up speed, which can be completed in just 3.1 seconds.
Below, we will demonstrate the practical runtime performance of LVGL v8.3 on the OK-MX9352-C development board through the Ebike Screen Demo.
LVGL v8.3 Case Study: Ebike Screen
On the OK-MX9352-C development board, ForlinxTech Embedded ported an Ebike Screen Demo to simulate the user interface of an electric-assisted bicycle screen. It fully leverages LVGL's components and features to showcase a visually appealing and practical dashboard.
01 Custom Background Image
The demo utilizes a custom-drawn background image, which not only enhances aesthetics but is also seamlessly embedded into the interface using LVGL's image processing capabilities, making the entire dashboard look more appealing.
02 Flexible Application of Basic Components
The demo employs fundamental components such as buttons and page switching, providing rich interactive functionality. Users can click buttons to switch between different pages and view various information. The flexible application of these components makes the interface more intuitive and user-friendly.
03 Rich Information Display
Ebike Screen Demo showcases a variety of information, including speed, battery level, time, map, and settings. This information is clearly presented on the screen using LVGL's chart and text components, allowing users to easily grasp the current status of the electric-assisted bicycle at a glance.
Through the Ebike Screen Demo, we can observe the advantages of LVGL running on the OK-MX9352-C development board: fast startup, feature-rich functionality, and an aesthetically pleasing interface. This makes it an excellent choice for developers seeking lightweight, easy-to-integrate GUI solutions.
By providing rapid startup, intuitive operation, and timely feedback, it helps users get started quickly and accomplish tasks efficiently. Additionally, lightweight design reduces resource consumption, improves startup and runtime performance, and enhances product competitiveness.
Looking ahead, LVGL's graphical interface is expected to become more diverse and intelligent. Forlinx Embedded will continue to adapt more products with LVGL, bringing richer and more efficient interaction experiences to embedded devices. Stay tuned for more updates!
-
NXP i.MX8MP Platform Porting Driver Tutorial
01/16/2025 at 07:18 • 0 commentsThis tutorial will take the example of writing and porting a driver called Hello Driver and explain the complete process from code writing to driver testing in detail. This process teaches you how to create, configure, compile, and load custom drivers on the i.MX8MP platform.
Step 1: Create the drive directory and files
1.1 Go to the source code directory
Before we start writing the driver, we first need to enter the directory where the Linux kernel source code is located. Open a terminal and enter the following command to navigate to the driver's folder in your Linux kernel source directory.
cd /home/forlinx/work/OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-kernel/drivers
1.2 Create a new Hello directory
After entering the drivers folder, we create a new directory called hello to store the files related to the hello driver.
mkdir hello cd hello
1.3 Write the Hello driver source code:
create the hello.c file using a text editor (e.g. vi) and enter the following code:
#include #include static int hello_init(void) { printk(KERN_ALERT "Hello world\n"); return 0; } static void hello_exit(void) { printk(KERN_ALERT "Goodbye world\n"); } module_init(hello_init); module_exit(hello_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");Meaning of the demo program: Print Hello World when the insmod driver is mounted, and Goodbye World when the rmmod driver is unmounted.
Step 2: Configure Kconfig and Makefile
2.1 Create Kconfig:
Create a new Kconfig file in the hello directory to define the configuration options of the driver.
forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-kernel/drivers/hello$ vi Kconfig
Write the following in the Kconfig file:
config HAVE_HELLO tristate "hello driver" help This hello driver is just to show how to develop driver process. This driver can also be built as a module. If so, the module will be called. default y
Indicates that if CONFIG_HAVE_HELLO is enabled in the kernel trimming configuration file, the hello drivers menu will be displayed and compiled into the kernel by default:
y:Compile into the kernel
m:Compile as a module.ko file
n:Indicates no compilation, not enabled.
2.2 Create Makefile:
Create a new Makefile in the hello directory and specify the compilation rules.
forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-kernel/drivers/hello$ vi Makefile
Write the following in the Makefile file:
obj-$(CONFIG_HAVE_HELLO) += hello.o
Note: The name of the macro definition should be the same as that in Kconfig. Add the name of the file that needs to be compiled. Because the kernel automatically adds the prefix CONFIG, we also need to add CONFIG _ in front of the name here. Indicates that the file specified by the compilation rule is a hello. c when the CONFIG _ HAVE _ HELLO is enabled.
2.3 Modify file permissions:
Ensure that the hello. C, Kconfig, and Makefile files have executable permissions.
forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-kernel/drivers/hello$ chmod 777 hello.c forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-kernel/drivers/hello$ chmod 777 Kconfig forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/OK8MP-linux-sdk/OK8MP-linux-kernel/drivers/hello$ chmod 777 Makefile
Step 3: Integrate into the kernel build system
3.1 Edit the top-level kconfig:
In the kconfig file in the drivers directory, add a configuration reference to the hello directory.
Write the following in the Kconfig file:
source "drivers/counter/Kconfig" source "drivers/mxc/Kconfig" source "drivers/hello/Kconfig" //Add the configuration file parsing of the hello folder before the endmenu endmenu
In this way, the configuration system will parse the Kconfig under the hello folder according to this configuration.
3.2 Edit the top-level Makefile:
In the Makefile in the drivers directory, add the conditions for compiling the hello driver.
Write the following in the Makefile file:
obj-$(CONFIG_COUNTER) +=...
Read more -
Forlinx Embedded i.MX8M Mini SoM Now Fully Compatible With Linux 6.1 System
01/10/2025 at 08:50 • 0 commentsForlinx Embedded FETMX8MM-C SoM now supports the Linux 6.1 system. This upgrade not only enriches the system’s function but also significantly enhances memory performance through a new BSP (Board Support Package).
Based on the NXP i.MX8M Mini processor, Forlinx Embedded FETMX8MM-C SoM features 4 x high-performance Cortex-A53 cores and 1 x real-time Cortex-M4 core, delivering high performance, computational power, and a smooth system operation speed. Linux 6.1 system introduces several new features, including enhanced hardware acceleration, optimized power management, and improved system security and stability. These enhancements make the FETMX8MM-C SoM perform exceptionally well in data processing, power consumption control, and data security.
FETMX8MM-C platform has various built-in command line tools available to users, As follows:
root@okmx8mm:~# uname -a Linux okmx8mm 6.1.36 #19 SMP PREEMPT Wed Oct 9 18:15:14 CST 2024 aarch64 GNU/Linux
The highlight of this upgrade is the significant boost in memory bandwidth. Thanks to the new BSP, the FETMX8MM-C’s memory read bandwidth has surged to approximately 2170 MB/s, while the write bandwidth has reached about 1030 MB/s—almost doubling compared to previous versions.
This means that when handling large data sets, high-definition video, or complex algorithms, the SoM can provide smoother and more efficient performance, significantly enhancing the user experience.
Addtionally, the FETMX8MM-C SoM is equipped with a rich set of peripheral interfaces, such as MIPI-CSI, MIPI-DSI, USB, and PCIe, offering users great flexibility for expansion.
It is worth noting that the i.MX8M Mini processor on the FETMX8MM-C SoM benefits from NXP’s long-term supply commitment, ensuring at least 15 years of stable supply, providing users with reliable assurance for long-term usage.
In summary, with the support of the Linux 6.1 system, the Forlinx Embedded FETMX8MM-C SoM not only sees a substantial increase in memory bandwidth but also gains more comprehensive system functionality, making it an ideal choice for high-performance embedded application development.
-
Real-time Application Solution for RISC-V Core on Forlinx Embedded T113-i Development Board
01/08/2025 at 02:35 • 0 commentsAs market demands for embedded devices continue to rise, there is an increasing number of master control solutions that integrate embedded processors and real-time processors to better balance performance and efficiency. In these solutions, the real-time core handles high-real-time tasks, while the A-core processes complex tasks, and real-time data exchange between the two cores is required. However, in data transmission, traditional serial interfaces, although cost-effective, have relatively slow transmission speeds. On the other hand, parallel interfaces offer faster speeds but come at a higher cost. Therefore, multi-core heterogeneous processors on a single chip have become an ideal choice to meet these demands.
RISC-V, as an open-source instruction set architecture, provides strong support for real-time processing scenarios due to its simplicity, consistency, scalability, and high compilation efficiency. Combining the A-core with the RISC-V core as a single-chip multi-core heterogeneous solution effectively leverages the advantages of RISC-V, achieving a harmonious combination of high performance and high real-time performance.
This article takes the OK113i-S development board as an example to introduce the resources and application cases of the RISC-V core.
1. RISC-V Core on OK113i-S Development Board
Forlinx Embedded OK113i-S development board is a cost-effective development board based on the Allwinner T113-i industrial-grade processor. It integrates a dual-core Cortex-A7 CPU, a 64-bit XuanTie C906 RISC-V core, and a DSP, providing efficient computing capabilities and high cost-effectiveness. Particularly noteworthy is its built-in RISC-V core, which, as an ultra-high-efficiency real-time processor, can reach a peak frequency of 1008MHz. It is equipped with a standard memory management unit, enabling smooth operation of RTOS systems or bare-metal programs, further enhancing application flexibility.
1.1 Characteristics of the RISC-V Core
- (1) Maximum frequency of up to 1008MHz;
- (2) 32KB instruction cache;
- (3) 32KB data cache;
- (4) Capable of running in large-capacity DDR…
1.2 Interface Resources of the RISC-V Core
Function
Description
GPIO output
GPIO output (e.g., controlling relays, etc.)
GPIO Input Interrupt
Captures important signals
I2C
Supports data transmission as a host; can connect to various slaves (e.g., RTC chips, EEPROMs, etc.)
SPI
Supports SPI master mode; supports both interrupt and DMA modes
UART
Supports SPI master mode; supports both interrupt and DMA modes
Inter-core Communication
Supports communication between the A-core and RISC-V core; small data transmission via RPMsg and large data transmission via RPBuf
DDR Operation
Supports RISC-V programs running on large-capacity DDR (available space: 35M+)
HTIMER
Supports general-purpose timers (us level) and high-precision timers (ns level)
PWM
Supports PWM output with different periods and duty cycles
GPADC
Supports general-purpose 12-bit ADC sampling
OS
Supports general-purpose 12-bit ADC sampling
2. Application Examples
2.1 SPI Data Sending and Receiving
This case involves an SPI loopback test, where the MOSI and MISO pins of the SPI are shorted to perform data transmission and reception.
(1) Function Introduction
(2) Achievement of Results
Both the SPI transmission and reception FIFOs have a capacity of 64 bytes. In the underlying HAL library program, an interrupt method is used when the data length is less than 64 bytes, while a DMA mode is employed when the FIFO is greater than or equal to 64 bytes.
Interrupt Method Transmission Effect:
DMA Method Transmission Effect:
In the DMA transmission mode, the SPI speed defaults to 5M bit/s. In this example, the average transmission speed is 580.43KB/s, equivalent to 4.6M bit/s, close to the theoretical value.
2.2 Inter-core Communication RPBuf
RPBuf is a high-bandwidth data transmission framework implemented by Allwinner based on RPMsg. RPMsg is an inter-core communication mechanism based on shared...
Read more -
How to Enhance Real-Time Performance of Linux 6.1 Kernel on OK-MX9352-C by Applying Real-Time Patches
01/03/2025 at 06:12 • 0 commentsAs we all know, the Linux system is a non-real-time system based on time-slice scheduling, and its real-time performance is difficult to meet the timing requirements of industrial applications. Therefore, in many scenarios, the Linux operating system cannot be used. Of course, this limitation has been improved. Currently, the Linux community has added many versions of real-time patches. By applying these real-time patches to the Linux kernel, its real-time performance can be significantly enhanced.
1. Download the patch
Download the real-time patch corresponding to the Linux version. We need to download the real-time patch for Linux 4.1.15.
Index of /pub/linux/kernel/projects/rt/6.1/
The kernel version we are using is Linux 6.1.36. Find a similar patch in the “older” section: patches-6.1.33-rt11.tar.gz.
2. Type into the kernel
unpack patches-6.1.33-rt11.tar.gz to the sdk path, which is the upper layer of the kernel source code.
$ ls OKMX93-linux-fs OKMX93-linux-kernel appsrc build.sh environment-setup-aarch64-toolchain extra images patches patches-6.1.33-rt11.tar.gz tools
Since more than 200 patches are in the extracted patch, use a script in the kernel directory to merge the patches.
$ cd OKMX93-linux-kernel
The script reads as follows:
#!/bin/sh cat ../patches/series | while read line do patch -p1 < ../patches/$line done
After executing this script, compile the kernel
make Image -j16
3. Test real-time
3.1 cross-compiling cyctest
git clone git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/utils/rt-tests/rt-tests.git cd rt-tests/ git checkout -b v1.0 origin/stable/v1.0
Modify Makefile
#CC?=$(CROSS_COMPILE)gcc #AR?=$(CROSS_COMPILE)ar
Compile
make
3.2 cyclictest test method
Load the compiled cyclictest onto the board and increase its executable permissions, you can use the cyclictest command to carry out real-time performance testing of the Linux kernel, the test command is:
root@fl-imx6ull:~# ./cyclictest -t8 -p 80 -n -i 10000 -l 10000
Specific parameters can be used as a reference:
-p
--prio = thread with PRIO ordinal 0
The priority usage method for the highest priority thread is: -p 90 / --prio=90
-m
--mlockall thread priority is 0
Lock current and future memory allocation
-c
--clock=CLOCK Counter. Every time interval of the thread is reached, the counter is increased by 1.
Select clock cyclictest -C 1 0 = CLOCK _ MONOTONIC (default) 1 = CLOCK _ REALTIME
-i
--interval=INTV
Basic thread interval, default is 1000 (unit is us)
-l
--loops=LOOPS
The number of cycles, which is 0 (infinite) by default, can be combined with the number of -I intervals to roughly calculate the time of the entire test, for example, -I 1000-l 1000000, the total cycle time is 1000 * 1000000 = 1000000000 us = 1000s, so it is roughly more than 16 minutes
-n
--nanosleep
Use clock_nanosleep
-h
--histogram=US
Draw a histogram of the delay on a standard output device after execution (many threads have the same permissions) US is the maximum trace time limit.
-q
--quiet
The -q parameter prints no information at runtime, only a summary on exit, which in combination with the -h HISTNUM parameter prints HISTNUM line statistics and a general summary on exit.
-f
--ftrace
The ftrace function traces (usually used with -b, in fact -b is usually used without -f)
-b
--breaktrace=USEC
Sends a stop trace when the delay exceeds the value specified by the USEC. USEC, in milliseconds (us)
Run Result Meaning:
T:0
Serial number is 0
P:0
Thread priority is 0
C:1000
Counter. Every time interval of the thread is reached, the counter is increased by 1.
I: 1000
Time interval is 1000 microseconds (us)
Min:
Minimum Delay (us)
Act:
Last Delay (us)
Avg:
Everyrage Delay (us)
Max:
Maximum Delay (us)
3.3 Testing unpatched kernels
First Test
root@ok-mx93:~# ./cyclictest -t8 -p 80 -n -i 10000 -l 10000 # /dev/cpu_dma_latency set to 0us policy: fifo: loadavg: 0.04 0.04 0.04 1/127 996 T: 0 ( 917) P:80 I:10000 C: 10000 Min: 5 Act: 7 Avg: 7 Max: 65 T: 1 ( 918) P:80 I:10500 C: 9533 Min: 5 Act: 8...
Read more -
How to Easily Install and Use Node-RED on iMX6UL Series Processors?
12/27/2024 at 05:08 • 0 commentsWith the rapid development of Internet of Things (IoT) technology, efficient and stable development platforms have become key to driving project success. iMX6UL series processors, with high performance, low power consumption, and compact size, have become the ideal choice for many IoT applications. Combined with the Linux 4.1.15 operating system, we provide developers with a complete technical solution designed to help you easily install and use Node-RED on the iMX6UL series, thereby accelerating the development of IoT projects.
Node-RED is a flow-based flashing tool that offers a browser-based flow editor. Users can create automation tasks and applications by dragging and dropping nodes and connecting them. It features a rich library of nodes, supports various protocol conversions, and allows users to create custom nodes to extend functionality. It is particularly suitable for building and deploying IoT applications, enabling easy integration of various hardware devices and sensors.
Installation Steps:
1. Install Node.js
Node.js is the foundational environment for running Node-RED. Here are the detailed installation steps:
1.1 Download the source code:
Download link: https://registry.npmmirror.com/binary.html?path=node/v11.1.0/
Version:node-v11.1.0-linux-armv7l.tar.gz
1.2 Copy the file:
Copy the downloaded source package to the iMX6UL development board and extract it:
$ cp /run/media/sda1/node-v11.1.0-linux-armv7l.tar.gz ./ $ tar -xvf node-v11.1.0-linux-armv7l.tar.gz $ mv node-v11.1.0-linux-armv7l nodejs
1.3 Create symbolic links:
To facilitate global access, create symbolic links for Node.js and npm:
$ ln -s /home/root/nodejs/bin/node /usr/bin/ $ ln -s /home/root/nodejs/bin/npm /usr/bin/
1.4 Check the version:
Verify if Node.js and npm are installed successfully:
node -v npm -v
If the version numbers are printed, the environment setup is correct.
Otherwise, please set the executable permissions and check again.
chmod 777 nodejs/bin/*
chmod 777 nodejs/bin/*
2. Install Node-RED
2.1 Install Node-RED:
Ensure the development board can access the internet normally, then enter the following command to install Node-RED:
npm install -g --unsafe-perm node-red
If you encounter the following error:
please execute:
npm config set strict-ssl false
Then try the installation again.
npm install -g --unsafe-perm node-red
If it gets stuck at this point:
please execute:
npm install -g node-gyp
Then try the installation again.
npm install -g --unsafe-perm node-red
2.2 Install pm2:
pm2 is a powerful process management tool for Node.js applications, which can help you better manage the Node-RED service. The installation command is as follows:
npm install -g pm2
2.3 Set a symbolic link:
For ease of use, you can create a symbolic link for pm2 (path subject to actual conditions).
ln -s /home/root/nodejs/bin/pm2 /usr/bin
2.4 Manage and start Node-RED:
Use pm2 to start the Node-RED service and set it to start automatically on boot:
pm2 start /home/root/nodejs/bin/node-red -- -v pm2 save pm2 startup
Use Node-RED
After installation, you can access the Node-RED user interface via a browser at http://:1880. Node-RED provides a rich library of nodes, supporting functions such as data acquisition, device control, event handling, etc. By dragging and connecting nodes, you can easily build complex IoT application flows.
Notes:
- This technical solution is primarily applicable to the Forlinx MCU FETMX6ULL and FETMX6UL platforms with the Linux 4.1.15 operating system. For other platforms, please refer to the corresponding documentation for modification;
- If you encounter any issues during installation, please check network connectivity, file permissions, and other settings;
- Node-RED's node library is continuously updated, so it is recommended to regularly visit the official website for the latest nodes and examples.
Conclusion
With this technical solution, developers...
Read more -
How to Port BOA to the FET-MX9352-C Platform on Linux 6.1.36?
12/26/2024 at 02:11 • 1 commentIn the management and interaction of embedded devices, the application based on Web mode has become the mainstream. This kind of server not only occupies small resources and runs efficiently, but also can dynamically generate page content according to actual needs. For users, they can realize the remote management, status monitoring and function control of embedded devices only through the commonly used Web browser, without installing additional software or complex configuration.
BOA is a lightweight, efficient, and embedded Web server known for its minimal resource consumption and straightforward configuration. It is particularly suited for devices with limited memory and processing capabilities, providing essential Web functionalities. This article describes how to port the boa server on the FET-MX9352-C platform.
How to Compile Source Code?
Download address:
1. Install dependent libraries
sudo apt-get install bison flex
Unzip the source code in Ubuntu
$ tar xvf boa-0.94.14rc21.tar cd boa-0.94.14rc21/
Modify the boa source code
Modify src/compat.h
find
#define TIMEZONE_OFFSET(foo) foo##->tm_gmtoff
Modify to
#define TIMEZONE_OFFSET(foo) (foo)->tm_gmtoff
Otherwise, an error occurs:
util.c:100:1: error: pasting "t" and "->" does not give a valid preprocessing token make: *** [util.o]
error 1
Modify src/log.c
find
if (dup2(error_log, STDERR_FILENO) == -1) { DIE("unable to dup2 the error log"); }Modify to
/*if (dup2(error_log, STDERR_FILENO) == -1) { DIE("unable to dup2 the error log"); }*/Otherwise, an error occurs:
log.c:73 unable to dup2 the error log:bad file descriptor
Modify src/boa.c
find
if (passwdbuf == NULL) { DIE(”getpwuid”); } if (initgroups(passwdbuf->pw_name, passwdbuf->pw_gid) == -1) { DIE(”initgroups”); }Modify to
#if 0 if (passwdbuf == NULL) { DIE(”getpwuid”); } if (initgroups(passwdbuf->pw_name, passwdbuf->pw_gid) == -1) { DIE(”initgroups”); } #endifOtherwise, an error occurs: boa.c:211 - getpwuid: No such file or directory
Set environment variables and compile
. /opt/fsl-imx-xwayland/6.1-mickledore/environment-setup-armv8a-poky-linux ./configure --host=arm-linux make aarch64-poky-linux-strip src/boa
At this point, the boa has been cross-compiled
Expected file path examples/boa. conf and SRC/boa
2. Modify boa.conf
vi boa.conf
(1) Group modification
Modify Group nogroup
to Group root
(2) User modification
Modify User nobody
to User root
(3) Modify DocumentRoot
DocumentRoot /var/www
(4) Modify ScriptAlias
ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ /usr/lib/cgi-bin/
(5) ServerName settings
Modify #ServerName www.your.org.here
ServerName www.your.org.here
Otherwise, an error will occur “gethostbyname::No such file or directory
3. Compile the test file
Unzip the source code in Ubuntu
tar xvf cgi_app.tar.gz cd cgi_app/
Clean up the files
make clean
Set environment variables and compile
. /opt/fsl-imx-xwayland/6.1-mickledore/environment-setup-armv8a-poky-linux $CC -o app.cgi cgi_app.c cJSON/cJSON.c
Generate app.cgi
4.Arrange to the development board
To create the directory, enter the following command on the development board.
mkdir /usr/lib/cgi-bin mkdir /var/www mkdir /etc/boa
mkdir /usr/lib/cgi-bin/ Table of ContentsPut app.cgi in the /usr/lib/cgi-bin/ directory
Put index.html, xmlhttpreq.js to /var/www/ folder
Put boa.conf in the/etc/boa/directory
Place boa in the/usr/bin/directory
Place the mime. Types in the/etc/directory
Modify permissions
chown root:root /var/www/* chown root:root /usr/lib/cgi-bin/app.cgi chmod o+x /usr/lib/cgi-bin/app.cgi chmod o+r /usr/lib/cgi-bin/app.cgi
Turn off the original network services
Because 9352 self-started lighttpd services, ps aux | grep http can see his process ID. To disable the startup of the Lighttpd service, vi /lib/systemd/system/lighttpd.service change line 8 and 9 to
#ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/lighttpd...
Read more -
Balancing Low Cost and High Performance, Forlinx Embedded Releases the i.MX8MPL SoM
12/21/2024 at 07:31 • 0 commentsTo effectively meet the basic application needs and project cost reduction requirements of more customers. Forlinx Embedded is now launching the FETMX8MPL-C SoM. Compared to the FETMX8MP-C SoM, which has been successfully introduced to the market previously, the FETMX8MPL-C SoM has been cleverly streamlined in terms of hardware configuration.
As is well known, not all application scenarios require high-performance hardware configurations, such as the Video Processing Unit (VPU), Neural Network Processing Unit (NPU), Image Signal Processing Unit (ISP), and high-performance digital signal processor (HiFi-4DSP). Therefore, to effectively meet the basic application needs and project cost reduction requirements of more customers, the FETMX8MPL-C has streamlined these chip units while retaining core processing capabilities and mainstream functional interfaces, thereby achieving effective cost control.
At the same time, the FETMX8MPL-C SoM is software and hardware compatible with the already released FETMX8MP-C SoM. This not only ensures that the FETMX8MPL-C SoM can be easily integrated into customers' existing systems but also significantly enhances the stability and reliability of the product during use. However, it should be noted that the FETMX8MPL-C SoM currently only supports Linux5.4.70 system.
Folinx Embedded Embedded FETMX8MPL-C SoM with a configuration of 2GB + 16GB will be available for immediate sale starting December 13th, while the 1GB + 8GB configuration will be released on January 15th, 2025.
Stay tuned!
-
Forlinx Embedded Launches New FET-MA35-S2 SoM Based on Nuvoton MA35D1
12/18/2024 at 06:04 • 0 commentsNuvoton's NuMicro® MA35D1 series microprocessors have become the engineers' trusted choice for high-end industrial control, edge IoT gateway, and HMI applications due to their high-performance multi-core heterogeneous design, reliable security mechanisms, rich communication interfaces, excellent HMI application,s, and extensive ecosystem support.
Now, Forlinx Embedded and Nuvoton have partnered to launch the FET-MA35-S2 SoM, aiming to provide engineers with a more efficient and convenient development experience!
FET-MA35-S2 SoM is designed and developed based on Nuvoton's MA35D1 series high-performance multi-core heterogeneous processor. It integrates 2 x 64-bit ARM® CortexARM Cortex-A35 cores, with a clock frequency of up to 800 MHz, and 1 x single ARM Cortex-M4 core running at 180 MHz.
FET-MA35-S2 SoM uses a compact LCC+LGA packaging, measuring 48mm × 40mm and featuring 260 pins. These pins expose the CPU's full functions, including 4 x CAN-FD interfaces, 17 x UART serial communication interfaces, 2 x Ethernet interfaces, and 8 x ADC interfaces, ensuring high flexibility and scalability, so as to meet the actual needs of different fields and products for diverse functions.
Additionally, FET-MA35-S2 SoM has passed rigorous industrial environment testing at Forlinx Embedded's lab, ensuring exceptional stability in applications and a reliable foundation for user project success.
MA35D1 processor is equipped with multiple advanced security mechanisms, including Nuvoton's TSI (Trusted Secure Island) independent security hardware module, TrustZone technology, secure boot, tamper detection, built-in AES, SHA, ECC, RSA, and SM2/3/4 encryption/decryption accelerators, and a true random number generator (TRNG). Additionally, it includes key storage and one-time programmable (OTP) memory. All security-related operations are performed within the TSI, effectively protecting sensitive and high-value data.
FET-MA35-S2 SoM is a highly resourceful and versatile product suitable for a wide range of applications in industries such as Charging Piles, Industrial Control, Edge Gateway, New Energy, Electricity, Fire Alarm etc. Combined with Forlinx Embedded's robust technical support capabilities, it accelerates your product's time-to-market, keeping you at the forefront of the industry.
OK-MA35-S21 Development Board, accompanying the Nuvoton MA35 series SoM, integrates a diverse array of functional interfaces, offering users great flexibility and convenience. These interfaces and resources enable users to more easily evaluate the product's performance, stability, and usability, accelerating functional verification and prototype design. Moreover, OK-MA35-S21 development board provides user-friendly development environment and comprehensive support documents, including detailed hardware manuals, example code libraries, and abundant online resources. This significantly reduces the development threshold and shortens the product development cycle, It lays a solid solutions foundation for the rapid introduction of high-quality and high-performance solutions embedded systems.
![OK-MA35-S21 Development Board font]()
![OK-MA35-S21 Development Board back]()
-
How to Compile and Use fw_printenv in the OKMX6UL Series Linux 4.1.15 System
12/12/2024 at 06:46 • 0 commentsfw _ printenv is a tool for reading the U-boot environment variable. It provides the configuration information stored in the U-boot environment variable to the Linux system. These environment variables are typically used to configure and control the boot loading process, such as boot commands, kernel parameters, device tree file paths, and more.
This article shows how to use fw_printenv on OKMX6UL boards, mainly for Forlinx OKMX6UL with Linux 4.1.15. Other platforms can also reference this guide, but adjustments may be required.
1. Compile the fw_printenv Tool
Execute the following commands under the U-boot source code path, and then the tool will be generated under tools/env.
$ . /opt/fsl-imx-x11/4.1.15-2.0.0/environment-setup-cortexa7hf-neon-poky-linux-gnueabi $ make env
If you encounter the following error:
...... In file included from tools/env/aes.c:1:0: tools/env/../../lib/aes.c:28:20: fatal error: string.h: No such file or directory compilation terminated. scripts/Makefile.host:111: recipe for target 'tools/env/aes.o' failed make[1]: *** [tools/env/aes.o] Error 1 Makefile:1372: recipe for target 'env' failed make: *** [env] Error 2
Then modify the uboot top-level Makefile to comment out CC
#CC = $(CROSS_COMPILE)gcc
Then compile
$ make env
Compile to generate the following two files under the tools/env/ path:
- fw_printenv
- fw_env.config
fw_printenv used for reading and writing environment variables
fw_env.config used to describe the partition, address, etc. where the variable is located.2. Configuration File
modify the fw_env.config file under tools/env in the uboot source directory according to the mtd partition, the location and size of the UBOOT environment variables, etc. See the instructions in the fw_env.config file and the /tools/env/README file for specific modifications.
Device offset, Env size, and Flash sector size should correspond to the three macro definitions in the include/configs/xxxx. H files in the uboot source directory.
- CONFIG_ENV_OFFSET
- CONFIG_ENV_SIZE
- CONFIG_ENV_SECT_SIZE
Note: The following is based on the 2024 image, and it is recommended to double-check the exact address in uboot.
(1) OKMX6ULL
The header file for the OKMX6ULL-S and OKMX6ULL-C series is include/configs/mx6ullevk.h, which is configured as follows:
#define CONFIG_ENV_SIZE SZ_8K #if defined(CONFIG_ENV_IS_IN_MMC) #define CONFIG_ENV_OFFSET (12 * SZ_64K) #elif defined(CONFIG_ENV_IS_IN_SPI_FLASH) #define CONFIG_ENV_OFFSET (768 * 1024) #define CONFIG_ENV_SECT_SIZE (64 * 1024) #define CONFIG_ENV_SPI_BUS CONFIG_SF_DEFAULT_BUS #define CONFIG_ENV_SPI_CS CONFIG_SF_DEFAULT_CS #define CONFIG_ENV_SPI_MODE CONFIG_SF_DEFAULT_MODE #define CONFIG_ENV_SPI_MAX_HZ CONFIG_SF_DEFAULT_SPEED #elif defined(CONFIG_SYS_BOOT_NAND) #undef CONFIG_ENV_SIZE #define CONFIG_ENV_OFFSET (0x6 << 20) /* 60 -> 06 */ #define CONFIG_ENV_SECT_SIZE (128 << 10) #define CONFIG_ENV_SIZE CONFIG_ENV_SECT_SIZE #elif defined(CONFIG_SYS_BOOT_NAND_1G) #undef CONFIG_ENV_SIZE #define CONFIG_ENV_OFFSET (0xa << 20) #define CONFIG_ENV_SECT_SIZE (256 << 10) #define CONFIG_ENV_SIZE CONFIG_ENV_SECT_SIZE #endif
Some of the macros used above can be found in the./include/Linux/sizes. h.
#define SZ_8K 0x00002000 #define SZ_16K 0x00004000 #define SZ_32K 0x00008000 #define SZ_64K 0x00010000 ......
It follows that:
CONFIG_ENV_OFFSET CONFIG_ENV_SIZE CONFIG_ENV_SECT_SIZE EMMC 0x80000 0x2000 / 256 Nand 0x600000 0x20000 0x20000 1G Nand 0xA00000 0x40000 0x40000 Therefore, the configuration files for each version of the SoM are as follows:
emmc
...... # Block device example /dev/mmcblk1 0x80000 0x2000 ......
256 nand
...... # NAND example /dev/mtd2 0x00000 0x20000 0x20000 1 ......
1G nand
...... # NAND example /dev/mtd2 0x00000 0x40000 0x40000 1 ......
(2) OKMX6UL
OKMX6UL-C Environment Variables
#define CONFIG_ENV_SIZE SZ_8K #if defined(CONFIG_ENV_IS_IN_MMC) #define CONFIG_ENV_OFFSET (8 * SZ_64K) #elif defined(CONFIG_ENV_IS_IN_SPI_FLASH) ...
Read more -
OKMX6UL Development Board Debian Filesystem Creation Process (Including Tool Installation, Configuration, and Burning)
12/07/2024 at 03:29 • 0 commentsThis article describes how to create a Debian filesystem for the OKMX6UL series development boards, primarily applicable to the Forlinx OKMX6UL series with the Linux 4.1.15 operating system. Other platforms can refer to this guide, but there will be differences between platforms, which need to be modified to suit the actual use.
Note: Operate under the root user by default.
1. Qemu and Debootstrap Installation
Since a Debian file system is built on Ubuntu apt- these two tools can be installed directly using the apt-get command. The commands are as follows:
sudo apt-get install binfmt-support qemu qemu-user-static debootstrap
2. Extracting Debian File System
Use the debootstrap command to extract the file system. Execute the following command to retrieve the file system from the Debian download source:
mkdir /home/forlinx/debian sudo debootstrap --arch=armhf --foreign buster root https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/debian/
Explanation of command parameters:
arch specifies the CPU architecture
buster is the Debian version number. Currently, the latest version is 10
foreign: This parameter needs to be specified when the architecture is different from the host’s, used only for the initial unpacking
root: The folder where the filesystem will be stored
https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/debian/ is the download source.
The extraction process takes a relatively long time, approximately 10 minutes. Please be patient. Once successful, the Linux directory structure can be seen. If the extraction fails, please try a few more times or change the network:
3. Improving the File System
To improve the filesystem, the qemu is required. Since it is operating on an X86 virtual machine, the ARM filesystem can not be improved directly. Therefore, qemu is used to simulate an ARM environment.
a.To copy qemu-arm-static into the newly built base system, use the following command:
cd root sudo cp /usr/bin/qemu-arm-static usr/bin cd ..
b.Initialize the file system.
Execute the following command:
sudo DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive DEBCONF_NONINTERACTIVE_SEEN=true LC_ALL=C LANGUAGE=C LANG=C chroot root debootstrap/debootstrap --second-stage
c.Use the chroot root command to initialize file system
chroot root
d.Use the command to create the following
echo "proc /proc proc defaults 0 0" >> etc/fstab mkdir -p usr/share/man/man1/ mknod dev/console c 5 1
e.Download Source Update
Use the command vi /etc/apt/sources.list to open the source.list file and replace the contents with the following.
deb http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian stable main contrib non-free #deb-src http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian stable main contrib non-free deb http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian stable-updates main contrib non-free #deb-src http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian stable-updates main contrib non-free #deb http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian stable-proposed-updates main contrib non-free #deb-src http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian stable-proposed-updates main contrib non-free
Then save and exit, and use the command apt-get update to update the download source. When the update download source reports an error, the date command can be provided to modify the system time to solve the problem.
apt-get update
f.Use the command apt-get install vim to install some necessary software
apt-get install vim apt-get install sudo apt-get install dpkg apt-get install bzip2 apt-get install net-tools apt-get install ntpdate apt-get install gcc
g.Create a new user with the command adduser forlinx, then enter the password
adduser forlinx
h.Set the root password, use the command passwd root, and set the password to forlinx.
passwd root
i.To set up Ethernet, enter the following command:
vi /etc/network/interfaces
As follows:
#/etc/network/interfaces -- configuration file for ifup(8), ifdown(8) #The loopback interface auto lo iface lo inet loopback #Wireless interfaces iface wlan0 inet dhcp wireless_mode managed wireless_essid any wpa-driver...
Read more -
Forlinx Embedded FET3576-C SoM Successfully Adapted to Android 14
12/04/2024 at 05:43 • 0 commentsAt the RKDC2024 event held in March, Forlinx Embedded's FET3576-C SoM made a grand debut as the industry's first showcase solution for the Rockchip RK3576 processor. Subsequently, the product was successfully mass-produced and shipped in June, consistently and reliably supplying customers, earning high recognition from numerous partners.
FET3576-C SoM previously provided the Linux 6.1.57 system. To meet the needs of more customers, Forlinx Embedded has recently successfully adapted the Android 14 system to it—a deep combination of the SoM's excellent hardware performance with Android 14, which will bring a smoother, more open, and intelligent experience.
1. High-Performance Processor and Efficient System Architecture
(1)RK3576 Processor Support
FET3576-C SoM is equipped with the Rockchip RK3576 processor, featuring a high-performance combination of ARM Cortex-A72 and Cortex-A53 cores, ensuring smooth system performance in handling complex tasks. Android 14 operating system optimizes the basic architecture and significantly improves resource efficiency. The combination of this optimization and the system makes the device more fluent when running large applications or multitasking.
(2)Efficient NPU and AI Optimization
6TOPS high-performance NPU built into FET3576-C complements the AI acceleration features of Android 14, enabling quick responses and precise processing in areas such as voice recognition, image recognition, and deep learning algorithms, offering users a more intelligent experience.
2. Memory Management and Storage Optimization
(1)Large-Capacity Memory and Efficient Management
FET3576-C SoM supports up to 4GB LPDDR4 memory, combined with Android 14's efficient memory management mechanism, effectively reducing memory fragmentation and speeding up application startup and system response, even under resource-constrained conditions.
(2)Fast Storage and Data Security
32GB eMMC provides ample storage space, while Android 14's storage optimization technology further enhances data read and write speeds and strengthens data protection measures to ensure user data security and privacy.
3. Interface Optimization and Visual Enjoyment
(1)High-Definition Display and Multi-Screen Display
FET3576-C SoM supports various display interfaces including HDMI and MIPI DSI, capable of driving high-resolution displays and using AI for image intelligent repair. Combined with Android 14's UI optimization, it delivers more detailed and clear visual experiences. The multi-screen display feature further enhances flexibility in multimedia processing and multitasking.
(2)Intelligent Interaction and User Experience
Android 14 has undergone comprehensive upgrades in user interface and interaction design, coupled with the powerful computing power of the FET3576-C SoM, making touch responses more sensitive, and voice assistants and gesture recognition more accurate, providing a more natural and smooth interaction experience for users.
4. Security and Privacy Protection
FET3576-C SoM features the RK Firewall technology, which can achieve true hardware resource isolation. This, combined with hardware-level security isolation and management, effectively prevents attacks by malicious software.
Additionally, Android 14 further enhances privacy protection functions, providing stricter permission management and data encryption measures.
The in-depth adaptation of the Forlinx Embedded FET3576-C SoM with the Android 14 operating system not only significantly improves the excellent performance of the SoM hardware but also brings users a smoother, smarter, and safer using experience through system optimization and upgrading. Forlinx Embedded FET3576-C SoM is a reliable choice for professional users in industrial, AIoT, edge computing, smart mobile terminals and a wide range of other digital multimedia-related applications.
-
Steps to Use .NET on the Forlinx OKMX6UL Series Development Board (Linux4.1.15)
12/02/2024 at 02:29 • 0 commentsIn this era of everything interconnected, embedded development is becoming increasingly popular. .NET, a powerful and cross-platform development framework introduced by Microsoft, is gradually making its mark in the embedded field as well.
So how to use.NET on Forlinx OKMX6UL series development board to make your embedded development journey more colorful!
1. Scope and Preparation
This article primarily targets the Folinx OKMX6UL series development boards, with Linux4.1.15. Other platforms can also refer to this it, but may need to make appropriate adjustments according to the actual circumstances.
2. .NET Installation
(1) Download the .NET compressed package from the official website.
https://dotnet.microsoft.com/en-us/download/dotnet/6.0
For 32-bit processors, please download the arm32 compressed package;
For 64-bit processors, please download the arm64 compressed package;
Note: The following instructions are based on .NET V6.0.415 as an example.
(2) Extract the Compressed Package
Extract the compressed package to the root user directory
mkdir /home/root/.dotnet tar -xvf dotnet-sdk-6.0.415-linux-arm.tar.gz -C /home/root/.dotnet
After decompression, the following file is obtained.
root@fl-imx6ull:~# ls .dotnet/ LICENSE.txt dotnet packs sdk-manifests templates ThirdPartyNotices.txt host sdk shared
(3) Configure Environment Variables
To make the system recognize the .NET commands,please configure the environment variables.
vi /etc/profile
Add:
export DOTNET_ROOT=$HOME/.dotnet export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/.dotnet:$HOME/.dotnet/tools
Re-run/etc/profile to validate the environment variable
root@fl-imx6ull:~# source /etc/profile
Check environment variables
root@fl-imx6ull:~# export export DOTNET_ROOT="/home/root/.dotnet" ...... export PATH="/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/sbin:/sbin:/home/root/.dotnet:/home/root/.dotnet/tools" ......
3. .NET Usage in Practice
Check the Version
First, you can view the version of .NET and related information by using the command dotnet --info.
root@fl-imx6ull:~# dotnet --info .NET SDK (reflecting any global.json): Version: 6.0.415 Commit: 6963d2d1e0 Runtime Environment: OS Name: Linux OS Version: OS Platform: Linux RID: linux-arm Base Path: /home/root/.dotnet/sdk/6.0.415/ global.json file: Not found Host: Version: 6.0.23 Architecture: arm Commit: e0f0de876a .NET SDKs installed: 6.0.415 [/home/root/.dotnet/sdk] .NET runtimes installed: Microsoft.AspNetCore.App 6.0.23 [/home/root/.dotnet/shared/Microsoft.AspNetCore.App] Microsoft.NETCore.App 6.0.23 [/home/root/.dotnet/shared/Microsoft.NETCore.App] Download .NET: https://aka.ms/dotnet-download Learn about .NET Runtimes and SDKs: https://aka.ms/dotnet/runtimes-sdk-info
First Test Application
Create a.NET project
root@fl-imx6ull:~# dotnet new console -o sample1 The template "Console App" was created successfully. Processing post-creation actions... Running 'dotnet restore' on /home/root/sample1/sample1.csproj... Determining projects to restore... Restored /home/root/sample1/sample1.csproj (in 1.81 sec). Restore succeeded.
You can see the following files under the sample 1 path.
root@fl-imx6ull:~# ls sample1/ Program.cs obj sample1.csproj
Among them, the source code is stored in the Program. CS.
root@fl-imx6ull:~/sample1# cat Program.cs // See https://aka.ms/new-console-template for more information Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!");This part is written in C.
Running
root@fl-imx6ull:~# cd sample1/ root@fl-imx6ull:~/sample1# dotnet run Hello, World!
Compile the Application
Create a project
root@fl-imx6ull:~# dotnet new console -o sample1
Compilation
root@fl-imx6ull:~/sample1# dotnet build MSBuild version 17.3.2+561848881 for .NET Determining projects to restore... All projects are up-to-date for restore. sample1 -> /home/root/sample1/bin/Debug/net6.0/sample1.dll Build succeeded. 0 Warning(s) 0 Error(s) Time Elapsed 00:00:27.31
Generate after compilation
...
Read more -
OKMX8MP-C GDB Remote Debugging Skills
11/27/2024 at 03:27 • 0 commentsIn the field of embedded development, debugging is a critical step to ensure the stable operation of a program. For developers using the OKMX8MP-C development board, mastering GDB remote debugging techniques can significantly enhance development efficiency. GDB, short for The GNU Project Debugger, is a comprehensive debugging tool under Linux. GDB supports a variety of debugging methods, including setting breakpoints, single-step execution, printing variables, observing variables, examining registers, and viewing the call stack.
In Linux environment software development, GDB is the primary debugging tool used to debug C and C++ programs. OKMX8MP-C's 5.4.70 version comes with default support for gdbserver, and our provided development environment also supports gdb by default. Next, will detail how to perform GDB remote debugging on the OKMX8MP-C.
1. Preparation Before Compilation
Before performing GDB debugging, it is essential to ensure that the application has been correctly compiled and includes debugging information. This can be achieved by adding the -g option during compilation. For example:
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ $CC -g test_bug.c -o test_bug
This command will compile the test_bug.c source file and generate an executable file test_bug with debugging information included. This way, GDB can accurately locate the corresponding positions in the source code during subsequent debugging processes.
After compilation, the generated executable file needs to be copied to the development board. This is typically achieved via serial port, network, or other file transfer methods. In this example, we assume that the test_bug file has been copied to the / directory on the development board.
2. Development Board IP and Starting gdbserver Settings
Next, you need to set the IP address on the development board and start the gdbserver service. The specific steps are as follows:
Set the IP Address:
Use the ifconfig command to set the IP address for the development board. For example:
ifconfig eth0 172.16.0.109
Here, the development board's IP address is set to 172.16.0.109
Start gdbserver on the development board, specifying the listening port number and the program to be debugged. For example:
gdbserver 172.16.0.109:2345 /test_bug
This command will start gdbserver and listen on port 2345 for connection requests from the GDB client.
root@OK8MP:~# ifconfig eth0 172.16.0.109 root@OK8MP:~# gdbserver 172.16.0.109:2345 test_bug Process /home/root/test_bug created; pid = 1356 Listening on port 2345
On the virtual machine or host, set an IP address within the same network segment as the development board and use the ping command to test connectivity with the development board.
Ensure successful pinging of the development board's IP address, which is a prerequisite for remote debugging.
3. Starting the GDB Client and Connecting to the Development Board
Start the GDB client:
On the virtual machine or host, use the aarch64-poky-linux-gdb command to start the GDB client and specify the program to be debugged. For example:
forlinx@ubuntu:~/ aarch64-poky-linux-gdb test_bug GNU gdb (GDB) 8.3.1 Copyright (C) 2019 Free Software Foundation, Inc. License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it. There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law. Type "show copying" and "show warranty" for details. This GDB was configured as "--host=x86_64-pokysdk-linux --target=aarch64-poky-linux". Type "show configuration" for configuration details. For bug reporting instructions, please see: http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/bugs/ Find the GDB manual and other documentation resources online at: http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/documentation/ For help, type "help". Type "apropos word" to search for commands related to "word"... Reading symbols from test_bug... (gdb)
Connect to the board:
In the GDB client, use the target remote command to connect to gdbserver...
Read more -
Empowering Smart Motion Control Systems with FET6254-C SoM
11/22/2024 at 06:19 • 0 commentsSmart motion control systems are an important branch in the field of automation, primarily used for real-time control and management of mechanical motion components such as position, torque, speed, and acceleration. They can achieve precise control of industrial robotic arms, conveyor belts, automated assembly lines, and other equipment, aiming to improve production efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and ensure production safety.
It integrates precise feedback, advanced sensing, high-performance control, and seamless connectivity technologies, enabling high-precision, low-latency automated control, which is of great significance in modern production and daily life.
The system requires processing large amounts of sensor data, executing complex motion algorithms, and responding in real-time to external commands, thus placing high demands on the system’s main control. Here,it is recommend to use the Forlinx Embedded FET6254-C SoM as the main control device for smart motion control systems.
Designed and developed based on the TI Sitara™ AM62x series processors, the Forlinx Embedded FET6254-C SoM, with its unique advantages of multi-core heterogeneous architecture, rich interface resources, and high-performance processing capabilities, provides an ideal main control solution for smart motion control systems.
![Empowering Smart Motion Control Systems with FET6254-C SoM]()
1. High-Performance Main Control, More Efficient
As the core of the system, the FET6254-C SoM is responsible for data processing, algorithm operation, and command issuance. The quad-core Cortex-A53 + Cortex-M4F multi-core heterogeneous architecture ensures the efficient combination of high-performance computing and real-time control.
It can not only achieve high-precision planning and real-time adjustment of motion trajectories, ensuring the accuracy and stability of equipment motion, but also quickly process sensor data, implement complex motion algorithms, and fault diagnosis, enhancing the system’s intelligence level.
2. Rich Functional Interfaces, More Versatile
Forlinx Embedded FET6254-C SoM extends all the capabilities of the processor, making it more versatile in expansion. Through interfaces such as I2C, SPI, it can connect various sensors (such as position sensors, speed sensors, force sensors) to collect real-time device status information; using PWM, GPIO, etc., it directly controls actuators such as motor drivers and solenoid valves to achieve precise motion control.
It is worth noting that the FET6254-C SoM natively supports 3 CAN-FD channels, with a maximum transmission speed of up to 5Mbps, enabling high-speed and stable access to industrial network systems via CAN-FD and other communication interfaces, providing functional support for industrial automation and vehicle applications.
Additionally, the FET6254-C SoM supports TI processor’s unique General Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC) interface, with high data read/write speeds of up to 100MB/s, multi-channel chip selects, more flexible configuration, and multiple methods to connect with peripherals, enabling communication with a wide range of external devices.
3. Outstanding Human-Machine Interaction Capabilities
FET6254-C SoM boasts excellent display capabilities, supporting dual-screen independent display and three-screen display, combined with an intuitive operation interface, making it easy for operators to monitor device status, adjust parameters, and issue commands.
Based on the FET6254-C SoM, smart motion control systems provide strong technical support to the field of industrial automation with their high precision, efficiency, real-time capabilities, and scalability. These systems not only enhance production efficiency and reduce energy consumption but also elevate the intelligence level of production lines, providing strong support for enterprises’ transformation and upgrading.
-
FET527N-C SoM Adapted for Android 13
11/20/2024 at 05:19 • 0 commentsForlinx's Embedded FET527N-C system on module(SoM) has successfully been adapted for Android 13, offering users an enhanced experience with the new system.
So, what are the outstanding advantages of the FET527N-C SoM running Android 13?
1. Performance and Compatibility Enhancement
FET527N-C SoM is equipped with Allwinner's high-performance T527 series processor, featuring 8 ARM Cortex-A55 cores, an integrated RISC-V core, and a DSP core working together to provide excellent processing power and energy efficiency. The adaptation of Android 13 further enhances the board's compatibility.
2. Rich Application Ecosystem
Android 13 boasts a vast application ecosystem support. Whether it's entertainment software, office tools, industrial products, or applications in other fields, almost all can find suitable development components. After adapting Android 13, users of the FET527N-C SoM can enjoy these diverse applications, meeting various needs.
3. Improved Fluency and Stability
Through deep optimization and adaptation, Android 13 runs more smoothly on the FET527N-C SoM, reducing lags and delays. Additionally, Android 13 enhances security and privacy protection, providing solid security for user data.
4. Hardware Acceleration Features
Android 13 supports more hardware acceleration features, making the FET527N-C SoM excel in image processing and video encoding. Coupled with its powerful performance and rich interface features, it delivers better functional performance.
5. User Customization Experience
The ease of use and personalized settings of Android 13 allow users to customize based on their needs, enabling better empowerment for HMI. Whether in industrial control, power, transportation, or medical industries, it makes machines smarter and more efficient in interacting with humans.
6. Quality Selection and Stable Supply
Additionally, the FET527N-C SoM undergoes comprehensive optimization in material selection, from memory to power management chips and every resistor-capacitor component, enhancing product safety and competitiveness. FET527N-C SoM has a 10 to 15-year life cycle, providing continuous supply assurance for your products.
In summary, the combination of Forlinx's FET527N-C SoM and Android 13 brings new development opportunities to the embedded device field. This integration not only enhances the board's performance and compatibility but also provides users with a richer and smoother experience. In the future, Forlinx will continue to focus on technological innovation and product development, offering more high-quality solutions for various industries.
-
OK6254-C Development Board LVDS Screen Replacement Logo Solution
11/13/2024 at 06:46 • 0 commentsLVDS Screen Logo Display Optimization
The LVDS display's driver, panel-lvds, is compiled as a module by default. During boot, module-type drivers are loaded later, causing the LVDS display to initialize later, and it takes around 20 seconds for the desktop to appear on the LVDS screen.
To initialize the LVDS display earlier, you need to compile the LVDS driver into the kernel, allowing it to initialize earlier.
The main modification can be made by compiling panel-lids.c directly into the kernel in the OK6254-C_defconfig file.
OK6254-linux-sdk/OK6254-linux-kernel/arch/arm64/configs/OK6254-C_defconfig CONFIG_DRM_PANEL_LVDS=y
And then carry out full compilation and flashing. Start after burning, LVDS will display the penguin logo about 10 seconds after starting. Here is how to replace the penguin logo with other logos.
Replace Penguin Logo With Custom Logo
First, find the location of the penguin logo as follows:
The penguin logo image used on the TI AM6254 platform is called logo _ ti _ clut224.ppm. Here's how to replace the image with a custom logo.
Note: The logo resolution cannot exceed the resolution of the LVDS screen, and the background color should be black. Take 1280x800 as an example. Here is a 1280x800 resolution picture made by the drawing software under windows, preferably in PNG format. If it is a picture in other formats, please convert it to PNG format first and then perform the following operations. (myilogo.png)
Put it anywhere on the virtual machine, and convert it to the format needed, with the following command:
pngtopnm mylogo.png > my_linux_logo.pnm pnmquant 224 my_linux_logo.pnm > my_linux_logo_224.pnm pnmtoplainpnm my_linux_logo_224.pnm > my_linux_logo_224.ppm
After converting the image to ppm format, copy the resulting image in ppm format to the path where the penguin logo is located. Then we convert the image in ppm format to a.c file, where we use the pnmtologo tool under the path (if you report a permission error, add sudo before the command).
./pnmtologo -t clut224 -n logo_ti_clut224 -o logo_ti_clut224.c my_linux_logo_224.ppm
Realize logo centered display
1. Modify the fb_show_logo_line function in source code /driver/video/fbdev/core/fbmem.c.
//image.dx=0; //image.dy=y; image.width=logo->width; image.height=logo->height; image.dx = (info->var.xres / 2) - (image.width / 2); image.dy = (info->var.yres / 2) - (image.height / 2);
Description:
The image. dx and image. dy variables are used to set the top-left corner of the image on the screen. The info-> var.xres and info-> var.yres variables represent the horizontal and vertical resolution of the screen, respectively. The image.width and image.height variables represent the width and height of the flag image, respectively. image. dx is calculated to center the image horizontally on the screen by subtracting half the image's width from half the screen's width. image. dy is calculated to vertically center the image on the screen by subtracting half the height of the image from half the height of the screen. Overall, this code centers the logo image horizontally and vertically on the screen.
2. Modify the source code/driver/video/fbdev/core/fbcon.c中的fbcon_prepare_logo() function.
After logo_height = fb_prepare_logo(info, ops->rotate); add the following line of code
logo_height += (info->var.yres / 2) - (logo_height / 2);
Now you can compile and burn it. If you are only in the debug phase, you can compile the kernel separately and replace the Image. It can also be fully compiled and then burned.
Note: If the logo is not centered or not displayed, check whether the LCD screen has been turned off, otherwise the resolution of the LCD screen will prevail.
Common issues 1
Image has more than 224 colors Use ppmquant(1) to reduce the number of colors
Solutions
ppmquant 224 logo_ti_clut224.ppm > logo_ti_clut224_224.ppm
Common issues 2
logo_ti_clut224.ppm: Binary PNM is not supported ...
Read more -
T113 Buildroot Cross-compilation Toolchain Replacement Methods
11/08/2024 at 06:51 • 0 commentsCross-compilation Toolchain Location:
OK113i-linux-sdk/out/t113_i/ ok113i/longan/buildroot/host/bin/arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc
Before executing the method below, please delete the out directory and decompress the cross-compilation tool chain in the lower path of the source code./buildroot/buildroot-201902/dl/toolchain-external-linaro-arm/gcc-linaro-7.3.1-2018.05-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf.tar.xz
1. Modify mkcmd.sh and mkcommon.sh according to the patch modification method in the figure.
2. Go back to the sdk path and execute the following command:
forlinx@ubuntu:~/shuishui/OK113i-linux-sdk$ ./build.sh config
It is modified to emmc or NAND version according to the actual board configuration.
3. Next, execute the following command to enter the configuration of buildroot.
Enter toolchain
Modify the relevant options as shown in the figure below:
Enter target options
Because hard-float is needed, the highlighted part in the diagram needs to be modified to EABIhf.
Save and exit after setting.
Enter the following path to compile.
./build.sh
Full compilation may require an error with an environment variable, resulting in a failure to compile.
If this problem occurs, execute the following instructions and compile the buildroot.
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=""
In the middle of compiling buildroot, you may encounter an error as shown in the following figure.
If these errors are encountered, you can find the corresponding source code and compile it through the tools in the decompressed cross-compilation chain. Subsequently, place the compiled executable file in the bin path and the library file in the lib path. Finally, continue executing ./build.sh until compilation is successful. After compiling successfully, return to the SDK path, perform full compilation build. sh, and then pack the image.
Next, write a test program to verify whether the cross-compilation chain can be successfully replaced. Here, you need to compare the program compiled with the original compilation chain with the program cross-compiled with the current compilation chain.
The part highlighted in the diagram is a program compiled using our original cross-compilation chain. It can be observed that it does not run normally. "Test" is a program compiled using the tools from the replaced cross-compilation chain, which runs normally. Additionally, the relevant information of the two programs can be determined using the ''strings'' tool.
-
FET113i-S SoM Now Supports RISC-V, Offering a Superior Cost-Effective Solution
11/07/2024 at 07:09 • 0 commentsFET113i-S is an industrial-grade SoM designed by Forlinx Embedded based on Allwinner T113-i processor. With excellent stability and ultra-high cost performance, FET113i-S SoM has gained wide attention from customers. As a multi-core heterogeneous architecture chip with an A7 core, a RISC-V core, and a DSP core, Allwinner Technology recently released the RISC-V core (XuanTie C906) details for the T113-i, and Forlinx embedded quickly adapted to this development.
1. What is RISC-V?
RISC-V is an open-source instruction set architecture (ISA) based on the principles of Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC). It was first introduced by the University of California, Berkeley in 2010 and has since gained significant attention and support from academia and industry worldwide. RISC-V architecture, characterized by its openness, simplicity, and scalability, is emerging as a formidable force in the global semiconductor industry.
2. What Are the Advantages of the T113-i's Risc-v?
High Efficiency and Low Power Consumption
RISC-V architecture follows the principles of reduced instruction set computer, which simplifies the hardware design, improves the execution efficiency and reduces the development cost. The RISC-V cores in the T113-i processor can efficiently perform a wide range of computational tasks while maintaining low power consumption, making it ideal for resource-constrained edge computing environments.
Modularity and Scalability
RISC-V architecture is designed with simplicity and modularity in mind, allowing different instruction set extensions to be chosen based on requirements. RISC-V core in the T113-i processor supports multiple standardized extension instruction sets, such as M (integer multiplication and division), A (atomic operations), and F/D/Q (single/double/quad-precision floating-point operations), enabling flexible combination and addition according to specific application scenarios.
Open Standard and No Licensing Fees
RISC-V is open source, allowing anyone to use and extend it for free, without licensing fees. This greatly promotes technology sharing and innovation, reducing product development costs.
Real-Time Performance
In the T113-i, the A7 core, RISC-V core, and DSP core can run simultaneously, realizing multi-core heterogeneous computing. This design enhances overall system performance and meets diverse application requirements. The RISC-V core, in particular, can accommodate applications with high real-time requirements, ensuring rapid response and processing of real-time data.
3. A Quality Choice for Cost Reduction
Forlinx Embedded FET113i-S SoM, with completed RISC-V core adaptation, is highly competitive in price. Its industrial-grade quality enables it to handle more complex application scenarios, while its comprehensive peripheral interface resources make it both powerful and user-friendly.
FET113i-S SoM's clear advantages, combined with Folinx Embedded's stable supply chain and robust technical support, ensure swift project implementation and market primacy for customers.
-
Introduction to the PWM Capture Function of the Rockchip RK3562 Platform and Application Cases
11/01/2024 at 06:53 • 0 commentsDescription
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is very common in embedded systems. It provides a method for generating pulse periodic wave-forms for motor control or can function as a digital-to-analog converter with some external components.
RK3562 supports 16 interrupt-driven on-chip PWM channels and offers capture mode with the following features:
- Measurement of high/low polarity effective periods of input waveforms;
- Generation of a single interrupt when the input waveform polarity changes;
- 32-bit high polarity capture register
- 32-bit low polarity capture register
- 32-bit current value register
- Capture results can be stored in an 8-depth FIFO FIFO data can be read by CPU or DMA
- Channel 3 supports a 32-bit power key capture mode
- Supports switching IO between channel 3 and channels 0/1/2
- Supports input pulse counters
- Supports input filters to eliminate noise
The capture mode of the RK3562 uses the PWM channel clock to measure the high/low effective periods of the PWM channel input waveforms and generates interrupts when the polarity of the input waveform changes. It can also capture the pulse counts of the input waveform, which can be used to measure waveform information such as duty cycle and frequency.
Application Scenario
PWM capture is a technique used to measure the cycle, frequency, and duty cycle of external signals. In the power sector, real-time data acquisition is essential for analyzing and monitoring grid power due to the normal fluctuations in grid frequency. The PWM capture technology can be utilized to detect grid frequency in real-time.
This article will use a signal generator to produce square waves of specific frequencies to simulate signal input in real application scenarios and provide a simple demonstration of the PWM capture function of the RK3562.
Cases
Development Board Model: OK3562-C + FET3562J-C
Forlinx Material Version: OK3562-C_Linux 5.10.198_User Manual_R1
Development Board System: Linux 5.10.198 (CPU0, 1, 2) + RT-Thread (CPU3)
Hardware Preparation:
One set of OK3562-C development board
One signal generator
Several Dupont wires
Software Preparation:
Please contact Forlinx to get it!
Source Code Compilation:
Extract the source code and enter the OK3562-linux-source directory
Execute ./build.sh defconfig:forlinx_ok3562_linux_rtos_defconfig to change the compilation configuration to run Linux on 3 CPUs and RT-Thread on 1 CPU in AMP mode;
Execute ./build.sh for a full compilation and wait for the process to complete;
The compiled update.img image is saved in the rockdev directory.
Testing Steps:
1. Follow the user manual in the software materials to burn the image. After burning, power on the device; RT-Thread will print the following:
2. Execute fl_pwmcap to enable PWM capture functionality and start detecting the input signals. Successful startup will appear as shown below:
3. Turn on the signal generator and change the output mode to continuous pulse waveform, with a frequency set to 10 kHz and a duty cycle of 90%.
After enabling the output of the signal generator, the board will start printing the measured period and duty cycle (the 89% duty cycle is due to the program's calculation not preserving decimal points, causing some errors).
Change the duty cycle of the signal generator to 30%, and the board output will reflect this change to 30%.
Change the frequency of the signal generator to 500 kHz and duty cycle to 75%, and continue observing the board output:
-
Forlinx iMX93 Development Board Achieves Routing Functionality: Bridge Setup, 4G Forwarding, and Device Configuration
10/26/2024 at 06:31 • 0 commentsRouting is a core component of device networking, responsible for intelligent data packet forwarding, ensuring efficient communication and internet access. It also assigns IP addresses to devices connected via the network interface, ensuring stable and secure connections. Below is a guide on how to implement routing functionality on the Forlinx i.MX93 platform.
1. Bridge Building
1.1 Busybox Compilation and Brctl Tool Loading
There is no brctl tool in the busybox of the 93 development board, so it needs to be recompiled. If the busybox of the board has the brctl tool, this step can be ignored.
Down load busybox-1.35 source code, website: https://busybox.net/
Unzip it on the 93 development environment and execute make menuconfig to configure.
forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/busybox$ tar -xvf busybox-1.35.0.tar.bz2 forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/busybox$ cd busybox-1.35.0/ forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/busybox/busybox-1.35.0$ . /opt/fsl-imx-xwayland/5.15-kirkstone/environment-setup-armv8a-poky-linux forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/busybox/busybox-1.35.0$ make menuconfig
Select Setting-->[*] Don't use /usr
In this way, it will be installed to the directory specified by itself (default./_ install). This option must be selected, otherwise busybox will be installed under/usr of the original system after make install, which will overwrite the original commands of the system. After selecting this, make install will generate the _ install directory under the busybox directory, which contains the busybox and the link pointing to it.
Add cross-compilation path (it can be set according to your own requirements):
Setting-->--- Build Options(arch64-poky-linux-) Cross compiler prefix (/opt/fsl-imx-xwayland/5.15-kirkstone/sysroots/armv8a-poky-linux) Path to sysroot (-O2 -pipe -g -feliminate-unused-debug-types) Additional CFLAGS (-Wl,-O1 -Wl,--hash-style=gnu -Wl,--as-needed -Wl,-z,relro,-z,now) Additional LDFLAGS
Select brctl tool
Networking Utilities --->[*] brctl (4.7 kb)
Modify and then compile
forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/busybox/busybox-1.35.0$ make forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/busybox/busybox-1.35.0$ make install
Copy the generated busybox command to the development board/home/root path
1.2 Kernel Source Code Modification
forlinx@ubuntu:~/work/ok-mx93/OKMX93-linux-sdk/OKMX93-linux-kernel$ vi drivers/net/ethernet/stmicro/stmmac/dwmac4_core.c (478 line) /* if (hw->promisc) { netdev_err(dev, “Adding VLAN in promisc mode not supported\n"); return -EPERM; }*/ (533 line) /* if (hw->promisc) { netdev_err(dev, "Deleting VLAN in promisc mode not supported\n"); return -EPERM; }*/Save and recompile the kernel after modification, generate Image and update the kernel
1.3 Building a Bridge With Brctl
root@ok-mx93:~# ./busybox brctl addbr br0 //Create bridge device br0 root@ok-mx93:~# ./busybox brctl stp br0 off //Turn off the STP root@ok-mx93:~# ./busybox brctl addif br0 eth0 //Add eth0 to the bridge root@ok-mx93:~# ./busybox brctl addif br0 eth1 //Add eth1 to the bridge root@ok-mx93:~# ifconfig br0 192.168.0.10 up configure br0 ip and start it
2. 4G for Network Forwarding
2.1 4G Dial-up
If there is command service, you need to delete it and restart.
root@ok-mx93:~# rm /usr/sbin/connmand root@ok-mx93:~# sync root@ok-mx93:~# reboot root@ok-mx93:~# fltest_quectel.sh root@ok-mx93:~# ifconfig eth0 up root@ok-mx93:~# ifconfig eth1 up
Note: The network port will be closed in the 93 dial-up script. If it is not necessary, you can comment out the command to close the network port in the script.
2.2 Route Priority Adjustment
Checking with ''route -n'' reveals that the priorities of eth0 and eth1 are higher than 4G. At this point, 4G cannot access the Internet, so it is necessary to adjust the priorities to avoid affecting the 4G network.
root@ok-mx93:~# route -n Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1 0.0.0.0...
Read more -
Ideas and Methods for Adjusting Touchscreen on the iMX6ULL Platform
10/23/2024 at 03:24 • 0 commentsThe touchscreen driver usually employs the input subsystem driver framework, so the application layer interface must adhere to the interfaces of the input framework.
By entering ls -l /dev/input in the command line, you can see the current input devices available.
root@freescale ~$ ls -l /dev/input/ total 0 crw - r----- 1 root root 13, 64 Jan 1 00:17 event0 crw - r----- 1 root root 13, 65 Jan 1 00:17 event1 crw - r----- 1 root root 13, 66 Jan 1 00:17 event2 crw - r----- 1 root root 13, 63 Jan 1 00:17 mice Lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 6 Jan 1 00:18 ts0 -> event2 Lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 6 Jan 1 00:18 ts2 -> event1 root@freescale ~$
View Touch Original Data
When there is an issue with the touch function, you can determine whether the problem lies in the driver layer or the application layer by checking the raw data. There are several methods to view the raw data:
1. cat /dev/event2
Directly using cat on the touch event will output garbled characters when you touch the screen.
2. hexdump
$ hexdump -d /dev/input/event0
0000000 15989 00000 18969 00004 00004 00004 00001 00009 # Other events 0000010 15989 00000 18969 00004 00001 00272 00001 00000 # BTN_MOUSE,press 0000020 15989 00000 18969 00004 00003 00000 16333 00000 # ABS_X 0000030 15989 00000 18969 00004 00003 00001 09599 00000 # ABS_Y 0000040 15989 00000 18969 00004 00000 00000 00000 00000 # Synchronous events 0000050 15989 00000 49415 00005 00004 00004 00001 00009 # Other events 0000060 15989 00000 49415 00005 00001 00272 00000 00000 # BTN_MOUSE,release 0000070 15989 00000 49415 00005 00000 00000 00000 00000 # Synchronous events
The fourth, third, and second-to-last lines correspond to type, code, and value, which are all defined in linux/input.h. The event types for input devices in Linux are:
#define EV_SYN 0x00 // Synchronous events
#define EV_KEY 0x01 // Key events
#define EV_REL 0x02 // Relative coordinates
#define EV_REL 0x03 // Absolute coordinates
#define EV_MSC 0x04 // Other eventsType is the event type, where 3 is the EV _ ABS = 0x03 and 0 is the EV _ SYN = 0x00 (as a separator of events).
The value of code depends on the event type. If the type is EV _ ABS, the value of code 0 is ABS _ X and the value of code 1 is ABS _ Y.
Then, the value represents the measurement under the premises of type and code. For example, if the type is EV_ABS and the code is 0 (which corresponds to ABS_X), then the value represents the absolute X-axis position of the touch point.
For example, if the type is EV_KEY, the code 272 corresponds to BTN_MOUSE, and code 330 corresponds to BTN_TOUCH; a value of 1 indicates a press, while a value of 0 indicates a release. For instance, if the type is EV_ABS and the code is 24 (which corresponds to ABS_PRESSURE), a value of 1 indicates that the screen is being pressed, while a value of 0 indicates it is released.
The tests show that the coordinate values generated by the touchscreen touch events have a range of X: 016384 and Y: 09600, and this touchscreen does not upload ABS_PRESSURE.
3. ts_print / ts_print_raw
The difference between the two is that ts _ print prints the data after tslib processing, while ts _ print _ raw prints the data before tslib processing.
4. evtest
Evtest can not only print original, but it also allows you to see the event types.
Driving Layer Processing Idea
1. Find the corresponding driver in the kernel source code by checking the device information.
You can look for the corresponding string in the kernel source code;
2. To locate the touch reporting position, you can search for the string ABS in the corresponding driver.
The image above shows the touch driver for a resistive screen.
3. Add print statements for further processing.
Application Layer Processing
1. Use tools like ts_test to check if tslib is receiving data.
2. Change the version of tslib.
Capacitive Screen
In theory, capacitive screens do not require touch calibration; however, if they are not calibrated, there...
Read more -
How Forlinx Embedded Board Handles Vibration
10/18/2024 at 03:08 • 0 commentsIn practical applications, embedded boards are often subjected to various vibrations, which may come from device operation, vehicle movement, or external environmental disturbances. The impact of vibration on boards cannot be ignored, as it can cause loose connectors, damage to structural components, and even lead to functional instability and performance degradation.
Forlinx Embedded has three R&D labs: the Physical Environment Lab, the Electromagnetic Compatibility Lab, and the Stability Lab. These labs conduct 10 major test items, each designed to simulate extreme conditions that products might encounter in real-world applications, ensuring they can operate stably in complex environments.
To ensure the stability and reliability of embedded boards in vibrational environments, professional vibration testing becomes crucial. Forlinx's physical lab is equipped with an advanced vibration testing system that provides accurate test data during the design phase.
In the vibration tests, Forlinx precisely sets vibration parameters such as frequency range, amplitude, and acceleration according to the standards of specific application scenarios. The vibration table simulates real-world vibration environments.
During the test, the embedded board is securely placed on the vibration table, and high-precision sensors continuously monitor the vibration waveforms to ensure they strictly comply with the preset parameters. The test also pays close attention to any resonance or abnormal occurrences. Additionally, Forlinx closely monitors the real-time operation status of the board to comprehensively assess its stability and reliability under vibration.
After testing, Forlinx's test engineers conduct detailed visual inspections, structural verifications, and functional performance tests on the board. For specific user scenarios, supplementary mechanical shock and impact tests may also be required to further verify the durability and practicality of the board design.
Through these scientific and rigorous testing methods, we ensure that the embedded board can exhibit outstanding performance and rock-solid stability even when facing vibration challenges, providing strong technical support for various electronic devices.
-
Network Configuration Guide for Router Based on NXP 104x Platform
10/16/2024 at 06:38 • 0 commentsConfiguring a Bridge for LAN Ports
1. Create/etc/systemd/network/br0.netdev
[NetDev] //A section identifier indicating that the following configuration information belongs to a network device definition.
Name=br0 //Specifies the name of the network device to be "br0".
Kind=bridge //# Specifies the device type as a bridge, used to connect multiple network devices for network communication.2. Create/etc/systemd/network/br0.network
[Match] //Indicates that the following content is for matching device conditions.
Name=br0 //Specifies the device name to match as "br0". The following configuration will apply to the device named "br0".
KernelCommandLine=!root=/dev/nfs
//Specifies the kernel command line condition for the device, preventing accidental boot to an NFS root file system.
[Network]
Address=192.168.3.1/243. Create the Port Configuration Files:
touch /etc/systemd/network/fm1-mac2.network
touch /etc/systemd/network/fm1-mac4.network
touch /etc/systemd/network/fm1-mac5.network
touch /etc/systemd/network/fm1-mac6.network
touch /etc/systemd/network/fm1-mac9.network
touch /etc/systemd/network/fm1-mac10.networkEnter the following content, taking fm1-mac2.network as an example:
Name=fm1-mac2 The attribute differs, must correspond to the filename.
[Match]
Name=fm1-mac2
KernelCommandLine=!root=/dev/nfs
[Network]
Bridge=br0Enable 5G Dial-Up on Boot
1. Add 5G Autostart:
At the end of the /root/.forlinx file, add the following content:
sleep 10 //Prevents this service from starting before some dependent services.
/root/Net_Tools/quectel-CMPossible Reasons for Dial-Up Failure:
SIM card inserted incorrectly, SIM card is out of credit.
IoT card is locked, need to add APN (cmnet: Mobile; 3gnet: Unicom; ctnet: Telecom).
The board has a 4/5G switching dial switch.
Install and Configure udhcpd Service
1. Install udhcpd Service:
apt-get update //May fail due to reasons: the board itself has no network, DNS not set, RTC clock not updated.
apt-get install udhcpdOther Solutions for Source Update Failure:
(1) https://blog.csdn.net/Chaowanq/article/details/121559709 apt command certificate error.
(2) https://blog.csdn.net/zhushixia1989/article/details/104550890 GLib-CRITICAL **: g_strchomp: assertion ‘string != NULL’ failed
(3) https://blog.csdn.net/downanddusk/article/details/126334776 kali-rolling InRelease‘ is not signed
2. Configure udhcpd Service:
Open /etc/udhcpd.conf
and modify the /etc/udhcpd.conf configuration file to customize the IP pool, gateway, DNS, interface, etc.
Here, I allocate IP range 192.168.3.20 — 192.168.3.254, interface as br0.
Modify /etc/default/udhcpd to enable it.
DHCPD_ENABLED=“yes”.
After configuration, start the service: systemctl start udhcpd.service.
Restart the service: systemctl restart udhcpd.service.
Enable the service at boot: systemctl enable udhcpd.service.
Check the service status: systemctl status udhcpd.service.
Set Network Node usb0 Forwarding Rules
1. Set Forwarding Rules:
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o usb0 -j MASQUERADE(Ensure the -o parameter interface is confirmed correctly.)
2. Save Forwarding Rules:
netfilter-persistent save
netfilter-persistent reload-t nat: Specifies the table to operate on as the nat table. The nat table is used for network address convert.
-A POSTROUTING: -A indicates that a rule is being appended to the end of the chain, and in this case, the chain being appended is the POSTROUTING chain. Rules in the POSTROUTING chain are handled when a packet is about to leave a network interface.
-o usb0: The -o option specifies which network interface the packets will be sent out from. In this example, usb0 is the designated network interface (usually a USB network adapter).
-j MASQUERADE: The -j jump to target action, here is MASQUERADE, which means enabling IP masquerading, replacing the source...
Read more -
3D Scanner System Solution Based on FET3576-C Embedded Board
10/10/2024 at 05:30 • 0 comments3D scanning, an integrated technology of optics, mechanics, electronics, and computing, captures 3D coordinates and color information of object surfaces through non-contact measurement, generating high-precision 3D models. In game development, 3D scanners have significantly enhanced the realism and detail richness of game scenes, characters, and objects.
The production team of the popular game "Black Myth: Wukong" spent a year using 3D scanning to create precise 3D models of real Buddhist statues, temples, and rocks across China. These models not only provide rich materials and inspiration for game designers but also ensure the authenticity and detail richness of game scenes. By capturing real-world 3D data, every detail in the game accurately reproduces historical features, enhancing the game's cultural depth and artistic value.
Not only in the gaming field, but 3D scanning systems, with their high precision, non-contact measurement, and digitization characteristics, can also contribute to the preservation and restoration of cultural relics. The fire at Notre-Dame Cathedral in 2019 attracted global attention. Prior to this, Notre-Dame Cathedral had already undergone comprehensive data recording using 3D scanning technology. This allows experts to use this data to carry out precise repair work after the fire. In addition, it can also be widely used in surveying and mapping engineering, industrial manufacturing, architectural design, education and scientific research and many other industries.
The 3D scanner, as the core component, is responsible for data acquisition and conversion. It consists of a probe, lens, and camera. The probe collects surface patterns without contact, the lens adjusts the probe position and viewing angle, and the camera converts captured images into digital signals for further processing like denoising, stitching, and optimization.
Hardware implementation faces several challenges:
- Complex data processing: Limited by onsite conditions during data collection, processing can be complex, requiring extended post-processing like noise removal and mesh reconstruction, demanding high-performance hardware.
- Compatibility issues: Incompatible hardware and software designs for point cloud data processing across different manufacturers hinder resource sharing and conversion, increasing learning and technical difficulties for users.
- Environmental sensitivity: Lasers and optical systems are sensitive to temperature changes, requiring frequent calibration and affecting efficiency. External factors like temperature, humidity, and vibration can also impact measurement accuracy, necessitating strict environmental control.
- High cost: The hardware cost of 3D scanners is often high, potentially leading to increased product prices and affecting market competitiveness.
Forlinx Embedded recommends using the FET3576-C embedded board as the main controller for 3D scanners. Based on the RK3576 processor, the FET3576-C is a high-performance, low-power, feature-rich, cost-effective solution tailored for AIoT and industrial markets. It integrates four ARM Cortex-A72 and four ARM Cortex-A53 high-performance cores, with a 6TOPS powerful NPU supporting various operations and deep learning frameworks.
(1)Versatile Interfaces
With GPIO, UART, SPI, and other communication interfaces, the FET3576-C precisely controls scanning parameters (e.g., scanning speed, resolution) and sensor states (e.g., laser emitter, camera shutter), enhancing scanning efficiency and quality
(2)Data Processing Hub
As the system's ''brain,'' the FET3576-C processes raw data like laser point clouds and images, ensuring accurate and complete 3D models through filtering, denoising, registration, and fusion.
(3)Intelligent Optimization
6TOPS NPU enables intelligent analysis of scanned data, automatically identifying and optimizing issues like flaws and holes in models, further...
Read more -
Application of FETMX6ULL-C Embedded Board in Energy Consumption Monitoring Gateway Products
09/30/2024 at 03:41 • 0 comments1. Product Background
The energy consumption monitoring and management system relies on information technologies such as computer networks, wireless communication, and metering collection. This system targets energy mediums such as electricity and water, establishing an energy consumption monitoring center for enterprises, industrial parks, and other energy-consuming units. It enables real-time collection, measurement, and analytical calculation of electricity and water usage, reflecting dynamic data changes and storing historical data for querying, thus achieving digital, networked, and visualized energy and energy-saving management. It helps factory managers understand energy costs, manages control in real time, improves management efficiency, reduces operating costs, and achieves scientific energy use and energy conservation.
Energy consumption monitoring systems have wide applications, including hospitals, residential communities, schools, industrial factories, office buildings, and commercial complexes.
2. Product Features
The energy consumption monitoring system consists of three components: the metering layer, information management layer, and application management layer. The metering terminals include electricity, water, and gas meters, while the gateway collects data from these meters. The system provides statistical analysis, presenting intuitive data visualization to management staff, allowing them to understand real energy consumption data, automatically analyze high energy consumption points, and provide energy-saving solutions for refined management.
Functions of the Energy Consumption Monitoring System
- Real-time Monitoring: Continuously monitors the usage of all users within the system, providing real-time data feedback on energy consumption.
- Data Analysis: Detailed recording and analysis of electrical usage in each circuit, displayed in tabular format, with the ability to switch to bar charts, line graphs, and other intuitive formats for comparison.
- Data Statistics: Offers comprehensive classified and detailed energy consumption statistics reports, allowing users to print daily, monthly, seasonal, and annual electricity consumption statistics at any time.
- Fault Alarm: The system issues voice alerts when there is an unexpected change in electricity load, with alarm messages sent to relevant personnel via SMS.
- Automatic Energy-saving Report Generation: Staff can review real energy consumption data for public buildings, automatically analyze high energy points, and propose energy-saving solutions for refined building management.
3. Product Design Challenges
Hardware Compatibility and Standardization: The energy consumption monitoring gateway needs to connect multiple types of sensors and metering devices from various manufacturers, using different communication protocols and data formats. Therefore, the gateway’s hardware design must consider broad compatibility and standardized interfaces for seamless device connections.
Stability and Reliability: The monitoring gateway operates 24/7, requiring high stability and reliability in hardware design, including the selection of high-quality components, proper heat dissipation design, and effective fault detection and recovery mechanisms.
Scalability and Maintainability: As technology advances and demands increase, the monitoring gateway may need to expand its functionality or interfaces. Therefore, hardware design must account for future scalability and ensure easy addition of new functions or devices. Good maintainability is essential for quick recovery in case of issues.
Power Consumption and Cost: Since the gateway typically runs continuously, power consumption is a critical factor. Hardware design needs to optimize for lower power usage while reducing costs without sacrificing performance, including the selection of low-power components, optimizing power management, and implementing energy-saving strategies.
4....
Read more -
Compilation Method for Rockchip Driver
09/27/2024 at 01:57 • 0 commentsCompile the driver to the kernel:
Create the hello folder for the kernel driver source code, add the hello. c and Makefile file, modify the parent directory/kernel/drivers/Makefile file, and execute the full compilation operation.
Modify as follows:
/hello/Makefile is:obj-y += hello.o
/kernel/drivers/Makefile; add the following code:obj-y += hello
Compile the driver as a module:
Method 1:
Create the hello folder for the kernel driver source code, add the hello. c and Makefile file, modify the parent directory/kernel/drivers/Makefile file, and execute the full compilation operation.
Modify as follows:
/hello/Makefile is:obj-m += hello.o
/kernel/drivers/Makefile; add the following code:obj-y += hello
If wanting to compile the driver but not wanting to perform a full compile operation that takes too much time, the following method can be chosen.
Method 2:
Create a hello folder in the kernel driver source code, add the hello. c and Makefile file, modify the parent directory/kernel/drivers/Makefile file, modify the/kernel/Makefile file to add the architecture and cross-compiler, and execute the make modules command.
Modify as follows:
/hello/Makefile is:obj-m += hello.o
/kernel/drivers/Makefile; add the following code:obj-y += hello
/kernel/Makefile, add the following code:
ARCH?= arm64
CROSS_COMPILE?=
$(srctree)/../prebuilts/gcc/linux-x86/aarch64/gcc-linaro-6.3.1-2017.05-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-linux-gnu-
Advantages: When executing the make modules command, only the modules will be compiled, and the compilation time will be shortened.
Disadvantages: The driver source code needs to be added to the kernel, which is not easy to find and modify. In addition, the make modules command will determine that the source code is configured as a module and will be compiled.
Issues encountered:
Solution: The kernel top-level Makefile file specifies the architecture and cross-compiler.
Method 3:
Create a folder named "hello" at any path, and add the files ''hello.c'' and ''Makefile''. In the ''/hello/Makefile'', add the architecture and cross-compiler. Then, execute the ''make'' command in the directory where ''hello.c'' is located.
/hello/Makefile to write the following code.
Advantages: Execute the make command, and only hello. C driver files will be compiled separately.
Issues encountered:
Solution: The kernel top-level Makefile file specifies the architecture and cross-compiler.
Appendix:
hello.c #include #include MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); static int hello_init(void) { printk(KERN_ALERT "Hello World enter\n"); return 0; } static void hello_exit(void) { printk(KERN_ALERT "Hello World exit\n"); } module_init(hello_init); module_exit(hello_exit); MODULE_DESCRIPTION("A Sample Hello World Module"); MODULE_ALIAS("A Sample module"); -
Stability Testing: The Key to Ensuring Long-lasting and Stable Operation of Smart Devices
09/21/2024 at 07:33 • 0 commentsIn the modern era of intelligence, embedded circuit boards are the core components that support the stable operation of various smart devices, making their performance and reliability crucial. However, prolonged operation, frequent power cycles, or restarts may lead to occasional anomalies due to aging, electrical parameters reaching critical values, or unreasonable software logic design. These anomalies can cause devices to fail to start or reboot normally, significantly reducing reliability and stability. Stability testing has become an essential step to validate the reliability of devices during prolonged operation, multiple power cycles, and restarts.
Forlinx Embedded has three R&D laboratories: the Physical Environment Lab, the Electromagnetic Compatibility Lab, and the Stability Lab, which host multiple testing projects to simulate various extreme conditions in real-world applications, ensuring products can operate stably. The Stability Lab specifically focuses on verifying the reliability of embedded circuit boards during prolonged operation and multiple power cycles. Stability testing is primarily divided into cold start testing and hot start testing.
Cold start testing examines the power cycling process of the device over a specific period, typically conducting up to 10,000 tests. Before the test, Forlinx's testing engineers set reasonable startup and cooling times based on the actual device conditions and use a programmable power supply along with automated testing software to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
Hot start testing involves executing reboot commands while keeping the device powered on, conducting 1,500 tests. During each test, engineers check various interfaces, including WiFi, 4G, USB, TF cards, and network interfaces, to ensure they function correctly during device restarts. To ensure traceability, testing engineers record daily testing counts and interface statuses, maintaining comprehensive experimental logs.
The results of the stability tests on embedded circuit boards provide valuable insights for improving product reliability. Cold start testing verifies whether the device's power circuit stability meets design requirements, while hot start testing checks the normalcy of the operating system's shutdown and startup processes, including the correctness of the shutdown and startup logic. Engineers use these test results to make targeted improvements in design and quality, continually enhancing product reliability.
Additionally, stability testing is a crucial assessment method for determining whether a product can meet its design lifecycle. It ensures that embedded circuit boards operate consistently throughout their lifecycle, providing users with lasting and reliable service.
In conclusion, stability testing of embedded circuit boards is a key factor in ensuring the long-term stable operation of smart devices. Through rigorous testing processes and precise result analysis, we can not only promptly identify and resolve issues but also provide robust support for continuous product improvement and optimization.
-
Hardware Implementation Scheme of Intelligent Weeding Robot Based on FET3588J-C SoM
09/21/2024 at 02:10 • 0 comments1. Introduction to Weeding Robots
In the agricultural sector, traditional weeding methods are not only inefficient and costly but can also lead to environmental pollution. With advancements in technology, intelligent weeding robots have emerged as important tools in modern agriculture. This intelligent weeding robot employs advanced machine vision and artificial intelligence technologies to precisely identify weeds and crops, enabling automated and intelligent weeding operations. This significantly enhances agricultural productivity while protecting the ecological environment.
2. Product Features
- Precision Identification: Equipped with a high-performance image recognition system, it accurately differentiates between weeds and crops, ensuring precise weeding, avoiding crop damage, and improving weeding efficiency.
- Autonomous Navigation: The built-in advanced navigation system autonomously plans the work path, adapting to different shapes and sizes of fields to ensure comprehensive coverage without leaving any blind spots.
- Eco-Friendly and Energy-Efficient: Powered by batteries with zero emissions, it reduces reliance on chemical herbicides, decreasing chemical residues in agricultural products and protecting soil and the environment.
- Intelligent Learning: Capable of self-learning and optimization, it adjusts strategies based on the working environment to enhance weeding effectiveness and reduce energy consumption.
3. Product Design Challenges
- High-Performance Requirements: Weeding operations require the main control system to have high processing power and computational speed to support real-time image processing and complex algorithms. High performance often comes with high power consumption, challenging the robot’s endurance.
- High-Temperature Stability: Outdoor environments are variable, requiring the main control system to have strong environmental adaptability to withstand dust, moisture, high temperatures, and other harsh conditions, ensuring long-term stable operation.
- Machine Learning Capabilities: Improving the control system's recognition and decision-making abilities through machine learning involves complex issues such as data collection, model training, and optimization.
- Diverse Interfaces: The main control system should offer a variety of interfaces to support different types of sensors and communication modules.
4. Folinx Implementation Solution
To address these challenges, Forlinx's embedded FET3588J-C platform provides powerful hardware support for the intelligent weeding robot, featuring the following significant advantages:
- High Performance: The combination of a quad-core Cortex-A76 and a quad-core Cortex-A55 processor ensures strong performance under high load while achieving low power consumption during low load, meeting the dual demands of performance and power efficiency for intelligent weeding robots.
- Image Processing Capability: FET3588J-C supports a 48-megapixel ISP3.0 and various image processing functions, significantly enhancing image capture quality and providing robust support for precise weed and crop identification.
- Rich Interface Resources: Provides various interface resources to connect different sensors and expansion devices, meeting the diverse application needs of intelligent weeding robots.
- Powerful AI Capabilities: With a built-in NPU providing up to 6 TOPS of computing power, the robot gains substantial AI learning and edge computing capabilities, enabling it to intelligently handle various weeding tasks.
- Product Stability: Rigorous environmental temperature and stress testing ensures stable operation in complex environments, providing reliable performance assurance for the intelligent weeding robot.
In summary, Forlinx's FET3588J-C, as a hardware implementation solution for intelligent weeding robots, offers exceptional performance, rich interface resources, powerful AI computing capabilities, and overall...
Read more -
Smart Assistance and AI Visualization Gateway Solution for Power Substations Based on RK3576
09/13/2024 at 02:28 • 0 commentsAmidst the ongoing reforms in the power industry, the intelligent management of key electrical infrastructure such as substations and distribution rooms has become a crucial driver for ensuring the safe, economical, and efficient operation of power grids.
With the growing demand for electricity and the accelerating process of urbanization, the number of power substations has surged, with widespread distribution and complex environmental conditions. This presents unprecedented challenges to the stability, reliability, and safety of power systems.
Traditional monitoring systems for power rooms face significant limitations: independent operation of subsystems, severe information silos, and consequently low overall monitoring efficiency. This fragmented management approach not only increases operation and maintenance costs but also hampers rapid response to emergencies, with insufficient capability for early warning of potential risks. These issues severely constrain the intelligent upgrading and efficient operation of power grids.
To address these problems, the Smart Assistance and AI Visualization Gateway for power substations has emerged.
Designed specifically for power scenarios such as substations and distribution rooms, this innovative solution integrates LCD screens with advanced AI technology, enabling comprehensive visualization, monitoring, and management of on-site parameters. This intelligent gateway can monitor real-time information from multiple dimensions, including transformer status, switch gear operation, environmental temperature and humidity, air conditioning and fan status, lighting systems, smoke detection, access control, and video surveillance, creating a comprehensive and multidimensional monitoring network for power substations.
By intelligently analyzing real-time data collected from various sensors and accurately comparing it with preset thresholds, the intelligent gateway can quickly identify and respond to anomalies, providing features such as automatic alarms, remote control, and fault prediction. This significantly enhances the safety protection level and emergency response capability of power substations. Furthermore, its powerful data integration and analysis capabilities offer robust data support for operational decision-making, facilitating the refined and intelligent transformation of maintenance management.
1. Client Requirements
Through communication with the client, Forlinx Embedded has identified the following requirements for the main control unit of the Smart Assistance and AI Visualization Gateway project for power substations:
(1) The gateway's core CPU should use an ARM architecture with at least 4 cores and a clock speed of no less than 1GHz;
(2) The gateway should include a video processing module for video stream processing and AI analysis, with computing power of no less than 3 TOPS;
(3) The gateway should have at least 2GB of memory and 8GB of storage capacity;
(4) The gateway should use a Linux kernel operating system;
(5) The gateway should include at least 4 RS485 ports, with selectable serial port speeds of 9600bps, 19200bps, and 115200bps;
(6) The gateway should support Ethernet interfaces with adaptive rates of 100/1000Mbps.
2. Main Control Selection: RK3576 Processor
Based on the actual project requirements, the client has chosen the Rockchip RK3576 processor as the main control unit for the Smart Assistance and AI Visualization Gateway for power substations. Based on the actual project requirements, the client has chosen the Rockchip RK3576 processor as the main control unit for the Smart Assistance and AI Visualization Gateway for power substations.
In terms of performance, the RK3576 processor features 4 x Cortex-A72 and 4 x Cortex-A53 high-performance cores, with a maximum clock speed of 2.3GHz and an integrated 6 TOPS NPU. This provides robust performance support for the Smart Assistance and AI Visualization Gateway for power substations and ample...
Read more -
Guide to Sleep and RTC Alarm Wakeup on the Forlinx OK113i-S Development Board
09/11/2024 at 05:53 • 0 commentsSystem sleep and wake technology is a crucial aspect of power management. Firstly, it allows the system to reduce power consumption to the lowest level when idle by putting external devices, internal IP of the chip, and clocks into a low-power state or completely shut off the power state, thereby greatly extending the product's runtime. Secondly, when users need the system to run, it can quickly recover power, clocks, internal IP of the chip, and the working state of external devices to ensure that the user's experience is not interrupted.
Forlinx T113 supports two types of sleep modes: freeze and mem. These two methods can be operated through the/sys/power/state file node, and the user can trigger the corresponding sleep state by writing freeze or mem to the file node. Before hibernation, the system configures the wakeup source. Once the system enters the sleep state, it can be awakened by these wake-up sources, such as keys, RTC, etc., when needed. This design allows users to choose when and how to wake up the system quickly according to their needs, achieving a balance between power consumption minimization and fast recovery. This mechanism enables the system to greatly reduce power consumption in the sleep state, while retaining the convenience of the user to use the system quickly after waking up.
Here's how to enter sleep mode and wake up the system using the RTC on the Forlinx Embedded OK113i-S development board.
Two Sleep Modes:
freeze: Freezes I/O devices, placing them into a low-power state, and puts the processor into an idle state. It offers the quickest wake-up time, but consumes more power than other methods. Measured current with only serial port connected and 5V power supply: Approximately 0.112A
mem: Suspend-to-RAM, where the computer stores current runtime state data in memory and shuts down the hard drive, external devices, etc., entering a wait state. At this time, the memory still needs power to maintain its data, but the whole machine consumes very little power. When recovering, the computer reads data from memory, returns to the state before suspension, and recovers quickly. Measured current with only serial port connected and 5V power supply: approximately 0.076A
1. cat /sys/power/state shows the supported modes.
2. cat /sys/power/state shows the supported modes.
3. cat /sys/power/state shows the supported modes.
RTC Alarm Wakeup
Tips: Note that the internal RTC needs to be used here; external RTCs do not support wakeup functionality, and we will mention this later.
Enter the kernel configuration:
Follow the instructions in the diagram to select the wake-up function.
After completing the configuration, save it, then modify the device tree file to enable the internal RTC.
Compile after saving:
After the compilation is successful, it is packaged into an image. After the programming is completed, we test it at the serial port terminal.
Enter the serial port terminal for test:
echo''+15''> /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm
This sets a 15-second timer, which can be adjusted as needed. After executing this command, it will take effect. If the system goes into sleep after 15 seconds, it will not trigger a wake-up. (Note: This requires using the internal RTC; external RTC does not support wake-up functionality.)echo mem > /sys/power/state (The two commands need to be entered closely together; a long interval between them will make them ineffective.)
(It should be noted here that when the internal RTC is not opened, the default external RTC node is rtc0. After modification, the external RTC device node will be changed to rtc1.)
3. cat /sys/power/state shows the supported modes.
RTC Alarm Wakeup
Tips: Note that the internal RTC needs to be used here; external RTCs do not support wakeup functionality, and it will be mentioned later.
Enter the kernel configuration:
Follow the instructions in the diagram to select the wake-up function.
After completing...
Read more -
Stunning Product: Rockchip RK3568 SoM is Here
09/09/2024 at 08:31 • 0 commentsIn this era of rapid technological advancement, an amazing product — RK3568 System on Module (SoM) has emerged.
✨It is equipped with Rockchip’s new — generation AIoT processor RK3568, which is a 64 — bit quad — core Cortex — A55 System on Chip (SoC) based on the advanced 22nm process technology. The built — in Neural Processing Unit (NPU) has a processing performance of up to 1TOPS.
Network models based on a series of frameworks such as TensorFlow, MXNet, PyTorch, and Caffe can be easily converted, and it also supports RKNN — Toolkit. At a running speed of up to 2.0GHz, it still maintains excellent low — power performance.
🎯In terms of graphics processing, the 38.4GFLOPS 800MHz GPU Mali — G52 performs outstandingly.
🎥The video codec capabilities are extremely powerful. It supports 4K resolution H.264, H.265, VP9 and other formats of high — definition hard decoding. It can support the decoding of multiple video sources simultaneously and also supports HDR10 with excellent color and dynamic range performance. At the same time, it supports H.264 and H.265 format hardware encoding at 1080p60fps and can adjust the dynamic bit rate, frame rate and resolution.
📺There are various display interfaces, including HDMI (up to 4K output), LVDS, MIPI — DSI, RGB, eDP, etc., which can support three — screen synchronous / asynchronous playback. It is perfectly suitable for fields such as PDAs, cash registers, multi — screen advertising machines, karaoke machines, electronic bus stop signs, and self — service machines.
🖥Multiple high — speed interfaces make it even more powerful, including 2 USB3.0, 2 PCIE3.0, 3 SATA3.0, 2 1000Mbps Ethernet (GMAC), 3 CAN — FD, and 10 UART.
🛡After undergoing harsh ambient temperature tests, stress tests and long — term running tests, the FET3568 — C SoM has been proved to be robust and reliable. It is widely used in multiple fields such as medical, industrial, transportation, cloud terminal, streaming media, security, AI application, and energy management.
Whether you are looking for high — performance, multi — interface or stable and reliable devices, Rockchip RK3568 SoM will be your ideal choice. Come and explore its infinite possibilities!
-
Advantages of Using FETA40i-C in Laser Coding Machines
09/07/2024 at 06:21 • 0 comments1. Introduction to Laser Coding Machines:
Laser coding machines use high-energy lasers focused directly on the surface of objects to induce physical and chemical changes, creating markings.
As the laser beam's focus moves systematically across the marking surface, controlling the laser's activation allows for the creation of specific marking patterns on the object's surface.
Laser marking offers advantages such as non-contact marking, high speed, minimal pollution, no consumable loss, and clear, permanent identification. These benefits give it a competitive edge, leading to its gradual replacement of traditional ink-jet coders.
2. Structure of Laser Coding Machines:
A laser coding machine primarily consists of the following components:
- Control System: The core component responsible for editing and processing marking content, generating marking data, transmitting it to the galvo system and laser system, and handling external input.
- Laser System: Responsible for generating and transmitting the laser to the galvo system.
- Galvo System: Quickly and precisely rotates mirrors to alter the laser beam's path, focusing it into a spot on the marking surface.
- Power Supply System: Provides power to the entire laser marking machine, including the controller, laser, and galvo system.
- Conveyor Mechanism: Moves items to be marked and uses speed measurement devices to monitor real-time item movement, feeding this data back to the control system.
3. ARM+FPGA-Based Control System Design:
ARM processor manages the human-machine interface, complex data processing, and communication, while the FPGA handles the reception, storage, conversion of marking data, and controls the marking equipment.
The marking control is managed by the marking card, with real-time performance mainly relying on the FPGA. ARM SoM is used for interface display and higher-level computation.
4. Folinx Solution
Forlinx Embedded recommends the FETA40i-C SoM as the ARM platform for laser coding machines, offering notable advantages: Notable advantages:
- High Performance Processing: The A40i platform, with its 1.2GHz high frequency, rapidly processes complex coding tasks. In laser coding machines, a high-performance processor ensures speed, precision, and efficiency in coding, with the A40i's high frequency reducing response time, enhancing productivity.
- Excellent Display Capabilities: A40i platform supports multiple display interfaces, making the coding interface more intuitive and visually appealing. A clear and user-friendly interface is crucial for operators, who can more easily view and edit coding content via a large screen, improving work efficiency.
- Robust Communication Capabilities: A40i features dual Ethernet ports and a 4G communication module, supporting various communication methods. This allows easy data transfer and communication with other devices, meeting the networking needs of modern industrial production, and facilitating future interface upgrades.
- Extensive External Expansion Interfaces: A40i platform offers numerous native external expansion interfaces, including 8 x serial ports and 3 x USB. These provide ample connection options for external devices, enabling easy integration and interaction with various peripherals.
- Industrial-Grade Stability and Reliability: A40i is an industrial-grade CPU known for its stable and reliable quality. Stability and reliability are critical in laser coding machines, ensuring long-term stable operation in harsh industrial environments, reducing failure rates, and extending equipment lifespan.
In summary, Forlinx Embedded A40i platform offers numerous advantages as the hardware control platform for laser coding machines, meeting the high-performance, high-stability, and high-reliability demands of modern industrial production
-
Guide to Adding Python3-pip Package in OK3568 Buildroot
09/05/2024 at 09:09 • 0 commentsOK3568 4.19.232 buildroot adds python3-pip installation package.
1. Modify buildroot/package/Config.in to add python-pip/Config.in.
2. Download python-pip and extract the compressed package to the buildroot/package directory.
3. Modify the defconfig file used by buildroot. Execute make menuconfig in the buildroot/output/OK3568 directory to select python3 and python-pip.
After modification, save the modified .config file to buildroot/configs/OK3568_defconfig. Then, perform a full compilation. During the compilation, the downloading, compilation, and installation of pip-related packages will be visible, indicating success.
Burn the compiled file system to the development board to enable pip commands.
4. Possible compilation errors and solutions:
a. Possible compilation errors and solutions:
Solution:
Re-create a soft link from OK3568-linux-source/buildroot/output/OK3568/host/bin/python to python3.
cd buildroot/output/OK3568/host/bin
rm python
ln -s ln -s python3 pythonAfter re-establishing the soft link, recompile. Use ls -l python to check if the soft link is successful.
b. SSL error when using pip install on the development board:
Solution:
Delete the python-related files in OK3568-linux-source/buildroot/output/OK3568/build/ and recompile.
This is because pip installation depends on SSL, and if the full compilation in step 1 was done using python2 for SSL compilation,
pip requires python3. So, after re-linking to python3, recompile the python-related files.
rm buildroot/output/OK3568/build/python-* -rf
./build.sh buildrootAfter compilation, burn and verify the file system. Opencv-python related tests can then be performed.
-
Using SPI for Interfacing with Digital RTD Temperature Sensors on the RK3562J Platform
08/29/2024 at 02:58 • 0 commentsThe MAX31865 is a simple and easy-to-use thermistor-to-digital output converter, optimized for platinum resistance temperature detectors (RTD). External resistors set the sensitivity of the RTD, while a high-precision Δ-Σ ADC converts the ratio of the RTD resistance to the reference resistance into a digital output. The MAX31865 input has overvoltage protection of up to ±45V and provides configurable detection for RTD and cable open-circuit and short-circuit conditions. It is suitable for a wide range of high-precision temperature devices in medical, industrial, temperature computation, satellite, meteorological, resistance measurement, and other applications.
The latest OK3562J-C single board computer from Forlinx Embedded has reserved the SPI2 interface, located on the P8 pin header:
SPI2_CLK_M0,
SPI2_CSN0_M0,
SPI2_MOSI_M0,
SPI2_MISO_M0.
This article will introduce how to use SPI2 on the OK3562J-C development board to interface with the MAX31865 (digital RTD temperature sensor) chip.
1. Modification Approach
The approach to adding an SPI device is as follows:
Add a description in the device tree → Corresponding device driver in the device tree description → Add the device driver to the kernel.
2. Modification Method
(1) The MAX31865 module supports 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire connection methods. The 3-wire connection method is utilized here, which is a compromise requiring one less wire than the 4-wire method. To compensate for the voltage drop across the leads, the voltage between (RTDIN+ and RTDIN-) will be reduced by the voltage between FORCE+ and RTDIN+. Sampling at the input is achieved using FORCE2. If the cable resistance has good consistency, it can eliminate errors introduced by the cable resistance.
Before wiring, the module needs to be soldered to configure it in a 3-wire mode as shown in the diagram below.
(2) Add the relevant descriptions for the MAX31865 in the device tree. Since we are using a 3-wire connection, we need to add the maxim,3-wire parameter.
3. Compiling the Driver as a Module
(1) Create a folder named max31865 under the /drivers directory in the kernel source, and add the max31865.c and Makefile files.
(2) Modify the parent directory /kernel/drivers/Makefile, and perform a full compilation operation. The modifications are as follows:
The content is: /drivers/max31865/Makefile:
obj-m += max31865.o
Add the following code to /kernel/drivers/Makefile:
obj-y += max31865
Then execute the ./build.sh kernel script to compile the kernel, which will generate the .ko module in the /drivers/max31865 directory.
(3) Copy max31865.ko to the OK3562J-C development board and execute insmod max31865.ko to load the module.
4. Test
Use a 22Ω resistor to simulate the platinum resistance and run the following command to check the raw ADC value:
cat /sys/bus/iio/devices/iio:device2/in_temp_raw
The ADC value for the 22Ω resistor should be observed as 1655. Comparing this with the values in the chip manual indicates that this is normal, corresponding to a temperature of approximately -190℃.
At this point, the new MAX31865 (digital RTD temperature sensor) device has been successfully added, and applications can be developed based on the raw ADC values to correspond to the measured temperature.
The above is the method of using SPI2 to mount MAX31865 (digital RTD temperature sensor) device on OK3562J-C development board. It is hoped that this will be helpful for project development.
-
Calling All Embedded Engineers! Be the First One to Review Forlinx Products!
08/28/2024 at 06:17 • 0 comments![Forlinx Embedded scheduled to attend electronica 2024 in Munich, Germany]()
Welcome to the Forlinx Product Review Program. At Forlinx, we offer a range of single board computers (SBCs) powered by NXP, TI, Rockchip, and Allwinner. As curious and passionate members of the embedded community, we believe many of YOU want to get hands-on with these products, test them out and share your real experience with the community.
So whether you're a professional or an enthusiastic hobbyist, if you have a strong presence in the embedded community, we want to hear from you.
Who We're Looking For
Engineers with a solid social media presence or active community involvement in embedded systems.
What You'll Do
Review our SBCs, share your feedback on your social media channel, and engage with the embedded engineers.
How to Join: Email us at rongyi@forlinx.com with
- Your name and address
- The product you'd like to review
- A brief introduction explaining why you’re the perfect fit
- Links to your social media channels/website/technical articles
Apply NOW and make your mark!
-
A Porting Solution for a 8-Channel Output LVDS Display on the 8MP Platform with Android 11
08/23/2024 at 03:18 • 0 commentsFor example, porting 8-channel output LVDS display with a resolution of 1024x768, a clock of 65MHz, and a refresh rate of 76.
Kernel Stage Modifications
1. Modify screen parameters in device tree
vi vendor/nxp-opensource/kernel_imx/arch/arm64/boot/dts/freescale/OK8MP-C.dts
Locate the lvds0_panel node and update the screen parameters and clock settings:
These settings include screen resolution, front and back porch, and clock. The system calculates the refresh rate based on these variables, so accuracy is crucial. Small deviations are allowed, but they should not be excessive. The calculation formula is as follows:
clock-frequency= fframe*(hfront+hback+hsync+xres)*(vfront+vback+vsync+yres)
Eg.:65000000=76*(34+20+1024+2)*(4+10+768+5)
2. Remove clock limitations in U-Boot stage
vi vendor/nxp-opensource/kernel_imx/drivers/gpu/drm/imx/imx8mp-ldb.c
Comment out the relevant restriction.
3. Calculate the clock and modify it according to the actual situation of the ported screen
(1) vi vendor/nxp-opensource/kernel_imx/drivers/clk/imx/clk-imx8mp.c
Locate imx8mp_videopll_tbl and add a 910 clock as an example:
Parameters to set: rate, mdiv, pdiv, sdiv, kdiv.
- rate = 910,000,000 (calculated as 65,000,000 × 7 × 2, which is clock-frequency × 14).
- mdiv = 152
- pdiv = 2
- sdiv = 1
- kdiv = 0 (default value)
Calculation formula:
Fout = (M*Fin)/(P*2 S)
Fin = 24 (known value, used directly), Fout = 910, and MPS are all unknown and must be derived independently.
So:910 = (M*24)/(P*2S) -->910 = (152*24)/(2*21)
(2)vi vendor/nxp-opensource/kernel_imx/arch/arm64/boot/dts/freescale/imx8mp.dtsi
Locate the clock node and change the clock from 1039 500 000 to 910 000 000:
4. Recompile and flash after the above modifications
U-Boot Stage Modifications
The steps to modify the uboot stage are basically the same as the kernel stage, both require changing the device tree and adding clocks.
1. Modify screen parameters in device Tree
vi vendor/nxp-opensource/uboot-imx/arch/arm/dts/OK8MP-C.dts
Locate the lvds0_panel node and update the screen parameters and clock settings:
2. Calculate the clock and modify it according to the actual situation of the ported screen.
(1)vi vendor/nxp-opensource/uboot-imx/arch/arm/mach-imx/imx8m/clock_imx8mm.c
Locate imx8mm_fracpll_tbl and add a 910 clock:
(2)Locate VIDEO_PLL_RATE, then modiffy the value from 1,039,500,000 to 910,000,000:
3. Modify U-Boot environment variables
vi vendor/nxp-opensource/uboot-imx/include/configs/OK8MP-C_android.h
Locate CONFIG_EXTRA_ENV_SETTINGS, and modify video_mipi and video_hdmi to ''off''.
4. Recompile and flash
-
RK3562J Technical Share | First Experience with Bare-Metal Interrupt Nesting in AMP Dual-System Setup
08/21/2024 at 07:08 • 0 commentsMulticore heterogeneous systems are computing systems that allow different cores within the same SoC chip to independently run different platforms. By properly allocating processor cores and peripheral resources, a single SoC chip can simultaneously run Linux and real-time operating systems (RTOS), meeting the demands for system functionality, hardware diversity, and real-time performance, while also offering excellent cost-effectiveness and product compactness.
1. Rockchip Multicore Heterogeneous System
Rockchip's multicore heterogeneous system solution includes:
Operating Platforms:
Linux provides the standard Linux Kernel;RTOS offers the open-source RT-Thread;Bare-metal supports a bare-metal development library based on the RK HAL hardware abstraction layer. Users can also adapt other RTOS based on RK HAL.
Processor Cores:
It supports homogeneous ARM Cortex-A cores running independently within the SoC, as well as heterogeneous ARM Cortex-M or RISC-V cores. The system allocates tasks to the most suitable core, enhancing performance and efficiency.
Currently, Rockchip's multicore heterogeneous system uses an unsupervised AMP (Asymmetric Multiprocessing) approach. It does not use virtualization management, which allows for faster interrupt response in real-time systems, meeting stringent real-time requirements in industries such as power and industrial control.
2. RK3562J Processor Cores and AMP Support
Processor Cores:
AMP Support:
3. Interrupt Nesting Mechanism
Interrupt nesting is an effective interrupt handling mechanism that allows the system to respond to and process interrupts based on their priority, ensuring that critical tasks are handled in a timely manner. It features high real-time performance, flexibility, and quick response. However, traditional Linux systems do not support interrupt nesting to simplify design, improve system stability, reduce resource contention and deadlock risks, and enhance compatibility and maintainability. While Linux performs well in many application scenarios, it struggles with high real-time applications.
4. Case Study
Development Board Model: OK3562J-C
Documentation Version: OK3562-C_Linux 5.10.198_User Documentation_R1
Testing Approach:
Use two GPIO, GPIO4B1 set as output and GPIO0B0 set as input with falling edge trigger.
Physically short GPIO4B1 and GPIO0B0.
Use Timer4 to generate a timer interrupt every second, and in the interrupt handler, control GPIO4B1 to create a falling edge and delay. If the print statement in GPIO0B0's interrupt handler appears, it indicates successful interrupt preemption.
Testing Steps:
(1) Write the test program fltest_irq_preempt.c to enable TIMER4 and GPIO0B0 interrupts and configure GPIO0B0 for falling edge trigger. In the timer interrupt handler, toggle GPIO4B1 to trigger GPIO0B0's interrupt and print a message in GPIO0B0's interrupt handler to indicate the interrupt;
(2) Modify the interrupt routing to bind TIMER4 and GPIO0 interrupts to CPU3, and set TIMER4's interrupt priority higher than GPIO0B0;
(3) Recompile the image and flash it to the development board;
(4) Enable AMP in the uboot menu and reboot the OK3562J-C development board. The RTOS debug serial port will display related information:
Press the tab key to print out all the current commands:
Then the command is registered successfully.
Execute the fl_irq_test command, and you will see:
GPIO0B0's interrupt preempts the TIMER4 interrupt.
Swap their priorities, recompile and flash again, and it will be observed that GPIO0B0's interrupt is handled after the TIMER4 interrupt ends, without preemption.
-
Forlinx FET62xx-C Enhances Performance of Ultrasonic Testing Instruments
08/16/2024 at 02:33 • 0 commentsIntroduction to Ultrasonic Testing Instruments
Ultrasonic testing instruments are portable, non-destructive testing devices that use ultrasonic technology to quickly, conveniently, and accurately detect, locate, and assess various internal defects (such as cracks, porosity, and inclusions) in workpieces. These instruments are suitable for both laboratory environments and field use, and are widely used in industries including, but not limited to, boilers, pressure vessels, aerospace, power, oil, chemical, marine oil, pipelines, defense, shipbuilding, automotive, machinery manufacturing, metallurgy, and metalworking.
Ultrasonic flaw detectors work on the principle that ultrasound waves are strongly reflected when they pass through the interface of tissues with different acoustic impedances. When ultrasonic waves encounter defects or interfaces, they reflect, and the testing instrument identifies and locates these defects by receiving and processing the reflected waves.
Product Features
- High Precision Detection: Capable of accurately detecting minute internal defects such as cracks and porosity, providing detailed information and location of defects.
- Portable Design: Typically designed to be lightweight and easy to carry, enabling quick field inspections.
- Versatility: Many ultrasonic testing instruments offer advanced features such as automatic calibration, automatic display of defect echo positions, and automatic recording of the inspection process.
- User-Friendly: Equipped with intuitive user interfaces and displays, simplifying operation while providing detailed inspection reports and data storage capabilities.
- Strong Adaptability: Capable of meeting the demands of different industries and materials by changing probes and adjusting settings to meet specific testing requirements.
Design Requirements
- Processing Power and Real-Time Performance: Ultrasonic testing instruments need to process large amounts of ultrasonic signal data quickly, requiring the main control platform to have strong processing capabilities. The processing must also meet real-time requirements to ensure accuracy and efficiency of the testing.
- Interface Richness and Compatibility: The instrument may need to connect and exchange data with various peripherals and sensors, necessitating a control platform with extensive interface support and good compatibility to adapt to devices from different manufacturers and models.
- Power Consumption and Heat Dissipation: Given that ultrasonic testing instruments often operate continuously for extended periods, power consumption and heat dissipation are key design considerations. The control platform must minimize power consumption to reduce heat generation and improve device endurance.
- Cost Considerations: Cost is a critical factor in the design of ultrasonic testing instruments. The choice and design of the control platform need to balance performance and functionality with cost-effectiveness to ensure market competitiveness.
Forlinx Embedded FET62xx-C is highly suitable as a hardware development platform for ultrasonic testing instruments, featuring:
1. High-Performance Processor: FET62xx-C SoM uses the TI Sitara™ AM62x series industrial-grade processors with an Arm Cortex A53 architecture, operating at up to 1.4GHz. This high-performance processor ensures speed and accuracy in data processing, image analysis, and real-time feedback, enhancing the overall performance of the testing instrument.
2. Extensive Interface Support: It integrates a wide range of interfaces, including 2 x TSN-supported Gigabit Ethernet ports, USB 2.0, LVDS, RGB parallel, UART, OSPI, CAN-FD, Camera, and Audio. These interfaces provide seamless connectivity with various peripherals and sensors, offering greater expandability and application possibilities for the ultrasonic testing instrument.
3. Flexible Processor Options: It is compatible with the full AM62x processor series, offering...
Read more -
OKMX8MP-C Development Board AI Project Implementation: YOLO Environment Setup
08/14/2024 at 01:10 • 0 commentsThis project is based on the Forlinx Embedded OKMX8MP-C development board, which has a virtual machine ported. It is necessary to install the required packages on the development board and ensure that the board is connected to the network.
01 Logging into the OKMX8MP-C Development Board
Connect the Type-C cable to the Debug port and select eMMC as the boot mode (i.e., set mode selection switch 2 to “on” and all others to “off”). After booting, log in using the root account.
02 Modifying the pip Source
To speed up the installation process, it is necessary to modify the pip source:
mkdir ~/.pip
vim ~/.pip/pip.confAdd the followings:
[global]
trusted-host=mirrors.aliyun.com
index-url=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/03 Installing the Python venv Environment
First, install the python3-venv package:
apt install python3-venv
Once installed successfully, create a directory named yolo (or any name of choice) and enter this directory to set up the Python 3 environment:
Create the yolo directory (the directory name can be taken by yourself), and enter the directory to install the python3 environment:
cd ~
mkdir yolo
cd yolo
python3 -m venv venvExecute the following figure:
Activate the Python 3 venv environment:
source venv/bin/activate
If activation is successful, it will display the following:
04 Installing Ultralytics
Ultralytics YOLOv8 is based on cutting-edge deep learning and computer vision technologies, offering unparalleled performance in speed and accuracy. Its streamlined design makes it suitable for various applications and easily adaptable to different hardware platforms, from edge devices to cloud API.
To install it, use the following command:
pip3 install ultralytics
Be patient while the installation completes:
Once the installation is successful:
05 Testing the Installation
Use the following command to test the setup. The image link in source can be replaced with another link:
During this process, the model and image will be downloaded, so patience is required.
After successful execution, the results will be generated in the runs/detect/predict* directory. The results can be copied to a Windows computer using the scp command. In the cmd terminal, execute the following command:
scp root@192.168.123.18:/root/yolo/runs/detect/predict/8f.jpg E:\\
If the output can be recognized, it indicates that the YOLO environment is functioning correctly.
It is the process of setting up the YOLO environment on the Forlinx Embedded OKMX8MP-C development board. Hope it is useful.
-
MIPI-CSI Debugging for RK3576 Processor — Channel Analysis
08/10/2024 at 03:18 • 0 commentsMIPI-CSI is a common camera interface in embedded systems or mobile devices, enabling high-speed image data transfer. The latest OK3576-C development board from Forlinx Embedded offers a wealth of resource interfaces, including support for 5 x CSI-2 , meaning it can support up to five camera inputs simultaneously.
This article introduces the Camera path of RK3576 processor and how to configure different output formats of MIPI-CSI camera through OK3576-C development board.
01. RK3576 Camera Channels
If there is only one camera access, turn on only rkispx_vir0 . Please note:
- vicap and isp do not have a direct correspondence;
- The relationships between different vir0/vir1 channels are essentially the same hardware being multiplexed, with the same effect. When using multiple cameras, configure them using 0, 1, 2, etc., as much as possible.
The hardware channel diagram is as follows:
There is one dcphy interface and two dphy interfaces. The connection paths are as follows:
Single Camera (connected to one dphy):
sensor0->csi2_dphy0->mipi1_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds1(sditf)->rkisp_vir0
Dual Cameras (connected to two dphys)
sensor0->csi2_dphy0->mipi1_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds1(sditf)->rkisp_vir0
sensor1->csi2_dphy3->mipi3_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds3(sditf)->rkisp_vir1Three Cameras (connected to dcphy and two dphys)
sensor0->csi2_dcphy0->mipi0_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds(sditf)->rkisp_vir0
sensor1->csi2_dphy0->mipi1_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds1(sditf)->rkisp_vir1
sensor2->csi2_dphy3->mipi3_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds3(sditf)->rkisp_vir2Five Cameras (connected to dcphy and two split dphys)
sensor0->csi2_dcphy0->mipi0_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds(sditf)->rkisp_vir0
sensor1->csi2_dphy1->mipi1_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds1(sditf)->rkisp_vir1
sensor2->csi2_dphy2->mipi2_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds2(sditf)->rkisp_vir2
sensor3->csi2_dphy4->mipi3_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds3(sditf)->rkisp_vir3
sensor4->csi2_dphy5->mipi4_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds4(sditf)->rkisp_vir4Camera Channel Connection Diagram:
(Note: For RGB data input, it is also necessary to connect to rkisp_virx)
02. Sensor Link Scenarios for Different Platforms
yuv422/rgb888 input
There are three common scenarios for yuv422/rgb888 input:
- Cameras with Built-in isp or External isp. Enter yuv422 format;
- HDMI to MIPI CSI Input. Common chips like rk628d/f,lt6911xxx, etc., typically convert yuv422, but rgb888 format is also possible;
- Multiple ahd and serdes. A single mipi port can support up to four virtual channels. For these scenarios, an isp is not required, and the connection only needs to go to cif. Thus, the link is:
sensor->csi2_dphyX->mipiX_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvdsX rkcif_mipi_lvdsx_sditf
The isp node can be disabled. The X varies depending on the platform and hardware connections.
The node used for capturing images is the first video node corresponding to rkcif_mipi_lvdsX. This can be viewed using media-ctl to check the topology. For example, on the OK3576-C development board with an OV5645 camera, it is mounted on the media1 node.
root@ok3576-buildroot:/# media-ctl -p -d /dev/media1 Media controller API version 6.1.57 driver rkcif model rkcif-mipi-lvds1 serial bus info platform:rkcif-mipi-lvds1 hw revision 0x0 driver version 6.1.57 Device topology - entity 1: stream_cif_mipi_id0 (1 pad, 11 links) type Node subtype V4L flags 0 device node name /dev/video11 pad0: Sink <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":1 [ENABLED] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":2 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":3 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":4 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":5 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":6 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":7 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":8 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":9 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":10 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":11 [] - entity 5: stream_cif_mipi_id1 (1 pad, 11 links) type Node subtype V4L flags 0 device node name /dev/video12 pad0: Sink <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":1 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":2 [ENABLED] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":3 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":4 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":5 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":6 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":7 []...
Read more -
MIPI-CSI Debugging for RK3576 Processor — Channel Analysis
08/09/2024 at 03:48 • 0 commentsMIPI-CSI is a common camera interface in embedded systems or mobile devices, enabling high-speed image data transfer. The latest OK3576-C development board from Forlinx Embedded offers a wealth of resource interfaces, including support for 5 x CSI-2 , meaning it can support up to five camera inputs simultaneously.
This article introduces the Camera path of RK3576 processor and how to configure different output formats of MIPI-CSI camera through OK3576-C development board.
01. RK3576 Camera Channels
If there is only one camera access, turn on only rkispx_vir0 . Please note:
- vicap and isp do not have a direct correspondence;
- The relationships between different vir0/vir1 channels are essentially the same hardware being multiplexed, with the same effect. When using multiple cameras, configure them using 0, 1, 2, etc., as much as possible.
The hardware channel diagram is as follows:
There is one dcphy interface and two dphy interfaces. The connection paths are as follows:
Single Camera (connected to one dphy):
sensor0->csi2_dphy0->mipi1_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds1(sditf)->rkisp_vir0
Dual Cameras (connected to two dphys)
sensor0->csi2_dphy0->mipi1_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds1(sditf)->rkisp_vir0
sensor1->csi2_dphy3->mipi3_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds3(sditf)->rkisp_vir1Three Cameras (connected to dcphy and two dphys)
sensor0->csi2_dcphy0->mipi0_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds(sditf)->rkisp_vir0
sensor1->csi2_dphy0->mipi1_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds1(sditf)->rkisp_vir1
sensor2->csi2_dphy3->mipi3_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds3(sditf)->rkisp_vir2Five Cameras (connected to dcphy and two split dphys)
sensor0->csi2_dcphy0->mipi0_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds(sditf)->rkisp_vir0
sensor1->csi2_dphy1->mipi1_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds1(sditf)->rkisp_vir1
sensor2->csi2_dphy2->mipi2_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds2(sditf)->rkisp_vir2
sensor3->csi2_dphy4->mipi3_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds3(sditf)->rkisp_vir3
sensor4->csi2_dphy5->mipi4_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds4(sditf)->rkisp_vir4Camera Channel Connection Diagram:
(Note: For RGB data input, it is also necessary to connect to rkisp_virx)
02. Sensor Link Scenarios for Different Platforms
yuv422/rgb888 input
There are three common scenarios for yuv422/rgb888 input:
- Cameras with Built-in isp or External isp. Enter yuv422 format;
- HDMI to MIPI CSI Input. Common chips like rk628d/f,lt6911xxx, etc., typically convert yuv422, but rgb888 format is also possible;
- Multiple ahd and serdes. A single mipi port can support up to four virtual channels. For these scenarios, an isp is not required, and the connection only needs to go to cif. Thus, the link is:
sensor->csi2_dphyX->mipiX_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvdsX rkcif_mipi_lvdsx_sditf
The isp node can be disabled. The X varies depending on the platform and hardware connections.
The node used for capturing images is the first video node corresponding to rkcif_mipi_lvdsX. This can be viewed using media-ctl to check the topology. For example, on the OK3576-C development board with an OV5645 camera, it is mounted on the media1 node.
root@ok3576-buildroot:/# media-ctl -p -d /dev/media1 Media controller API version 6.1.57 driver rkcif model rkcif-mipi-lvds1 serial bus info platform:rkcif-mipi-lvds1 hw revision 0x0 driver version 6.1.57 Device topology - entity 1: stream_cif_mipi_id0 (1 pad, 11 links) type Node subtype V4L flags 0 device node name /dev/video11 pad0: Sink <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":1 [ENABLED] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":2 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":3 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":4 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":5 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":6 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":7 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":8 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":9 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":10 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":11 [] - entity 5: stream_cif_mipi_id1 (1 pad, 11 links) type Node subtype V4L flags 0 device node name /dev/video12 pad0: Sink <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":1 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":2 [ENABLED] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":3 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":4 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":5 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":6 [] <- "rockchip-mipi-csi2":7...
Read more -
Exploring Embedded Board Stability in Harsh Environments
08/09/2024 at 03:18 • 0 commentsDriven by modern technology, embedded boards have become integral to various aspects of life, from power supply and transportation to precision medical devices. Their stable operation is crucial for the smooth functioning of society. However, devices in these critical areas often operate under extreme temperature conditions, demanding high levels of stability from embedded boards. Therefore, performance testing under high and low temperatures is essential.
Forlinx Embedded understands this need and has equipped its physical environment laboratory with three advanced high-low temperature testing devices. These devices have a broad temperature control range, from -60°C to +150°C. Forlinx conducts stability tests on embedded boards for up to 48 hours within this extreme temperature range. This step is crucial for validating the board's stability and reliability in various environments, ensuring fault-free operation in real-world applications.
To comprehensively assess board performance, Forlinx also offers customized tests based on client requirements, including temperature variation tests, constant temperature and humidity tests, and cyclic humidity tests. These tests simulate working conditions under different temperatures and humidity levels to ensure high stability in variable environments.
Why Are High and Low Temperature Tests for Embedded Boards So Critical?
The increasing use of embedded boards in sectors such as power, transportation, and healthcare means these devices often need to operate in extreme climates. Whether in a hot desert or a cold polar region, embedded boards must operate reliably to prevent system failures and potential safety hazards.
In high temperatures, electronic components on embedded boards risk performance degradation, slow response, or even damage. In low temperatures, components might fail to start due to condensation or freezing. To mitigate these issues, Forlinx incorporates several preventive measures in board design, including careful layout and thermal management to minimize the impact of temperature on its performance.
In low-temperature environments, special attention is given to waterproofing, moisture-proofing, and condensation prevention to ensure reliable operation under harsh conditions.
During testing, Forlinx ensures that boards run stably for 24 hours in both low and high-temperature environments to mimic extreme scenarios. Comprehensive performance testing and reliability assessments are conducted to identify and resolve potential issues, guaranteeing outstanding stability and adaptability in real applications.
Through rigorous testing and optimization, Forlinx Embedded is dedicated to providing solutions for embedded boards that perform reliably in various extreme environments, contributing to the stability of critical industries.
-
NXP i.MX6 Series Processors Listed in Longevity Program, with Forlinx SoM Longevity Extended Accordingly
08/08/2024 at 02:00 • 0 commentsRecently, NXP (NXP Semiconductors) i.MX 6 series processors have been added to its "NXP's Product Longevity Program", which extends the lifecycle of different processor models by 10 to 15 years, ensuring long-term stable supply and maintenance.
(The purpose of NXP's Product Longevity Program is to provide stable chip supply for customers' embedded products. The NXP's Product Longevity Program for specific products means ''NXP will at least support this product for a specified period,'' and in special cases, the supply duration can be extended.)
As a gold partner of NXP, Forlinx Embedded has launched 7 SoM products based on 4 processors from the i.MX 6 series, with various temperature ranges and connector types, offering more flexible options for customers. These products are currently widely used in fields such as artificial intelligence, industrial IoT, energy storage, smart transportation, medical equipment, charging stations, consumer electronics, and HMI, and have gained the trust of thousands of customers.
Thanks to NXP's Product Longevity Program, the supply lifecycle of Forlinx Embedded's i.MX 6 series SoMs has also been further extended, providing customers with more durable and stable product support.
i.MX6UltraLite (NXP's Product Longevity Program Until 2035)
Folinx Embedded FETMX6UL-C SoM
Designed based on the NXP i.MX6UltraLite processor with Cortex-A7 architecture and a clock frequency of 528MHz. It uses two sets of high-quality 80Pin board-to-board connectors. Rigorous temperature range testing ensures stable operation in environments from -40℃ to +85℃, supporting up to 8 x UART, 2 x Ethernet, and 2 x CAN industrial bus interfaces. It is available in industrial and commercial versions, providing users with more options.
i.MX 6Quad(NXP's Product Longevity Program Until 2035)
Folinx Embedded FETMX6Q-C SoM
Designed based on the NXP quad-core ARM Cortex-A9 processor with a clock frequency of 1GHz and 12-layer PCB gold-plated technology. The overall board size is only 40mm x 70mm and features four 1.5mm high connectors with up to 320 pins, exposing all processor function pins. It comes with rich carrier board resources, including Gigabit Ethernet, CAN-bus, camera, Wi-Fi & Bluetooth, as well as MIPI, MLB, EIM BUS, and other CPU-specific functions.
Folinx Embedded FETMX6Q-S SoM
Also based on the NXP i.MX 6Quad processor, this version uses 8-layer PCB gold-plated technology with better electrical characteristics and anti-interference properties. The board has 220 pins (55*4) and measures 60mm x 60mm, offering a square structure design for easier carrier board layout.
i.MX 6DualLite (NXP's Product Longevity Program Until 2035)
Folinx Embedded FETMX6DL-C SoM
Designed based on the NXP dual-core ARM Cortex-A9 i.MX6DualLite processor with a clock frequency of 1GHz and 12-layer PCB gold-plated technology. The board is compact at 40mm x 70mm, featuring optimized fixed holes and anti-misplug design, with four 1.5mm high connectors and up to 320 pins, exposing all processor function pins. It comes with abundant carrier board resources, including Gigabit Ethernet, CAN-bus, camera, Wi-Fi & Bluetooth.
Folinx Embedded FETMX6DL-S SoM
Also based on the NXP i.MX6DualLite processor, this board uses 8-layer PCB gold-plated technology. The stamp hole connection method provides better electrical characteristics and anti-interference properties. This SoM is a minimal system with an integrated LCD interface, eliminating the need for a carrier board and enabling immediate startup and debugging, reducing development difficulty. FETMX6DL-S SoM is available in industrial and commercial versions for more options.
i.MX6ULL
Note: i.MX6ULL processor was released in 2016 with a 15-year supply period, and its product longevity has not yet been extended.
Folinx Embedded FETMX6ULL-C SoM
Developed based on the NXP i.MX6ULL processor, using the low-power ARM Cortex-A7 architecture,...
Read more -
Flashing Systems | OTG Flashing and MASKROM Mode for OK3568-C Single Board Computer
08/02/2024 at 02:26 • 0 comments1. OTG Driver Installation
Tool: OK3568-C ForlinxDesktop User Profile\ForlinxDesktop\Tool\DriverAssitant_v5.11.zip
Extract the above path file to any directory and run it with administrator privileges
Open DriverInstall.exe
Click "Driver Installation"
2. OTG Full Flashing Test
Path: OK3568-C ForlinxDesktop User Profile\ForlinxDesktop\Tool\RKDevTool_Release.zip
It is a development tool provided by Rockchip, before using it, unzip it to a full English path, connect the development board and the host computer with a Type-C cable, press and hold the recovery key of the development board and don't release it, then press the reset key to reset the system, about two seconds after releasing the recovery key. There will be prompts on the Rockchip development tool :
loader device found
Note:
The condition for recognition is that the development board is powered up and the recover key is in the pressed state.
Theoretically, Rockchip development tools have no requirements for the unzip directory. However, some users have feedback that the unzip directory should be in full English. If the tool doesn't match the following figure, please consider unzipping it in an English directory.
Note: Pay attention to two points during OTG programming:
1. Link the OTG line.
2. If OTG is multiplexed with the USB 3.0, it is necessary to modify the dial switch, as shown in the following figure:
Open the RKDevTool
Click the "Upgrade Firmware" tab, click the "Firmware" button to select the full upgrade image update.img.
If the key operation fails, the board will start normally, and the tool interface displays Found One ADB Device. In this case, you can click the “switch” button of the tool to enter loader mode.
3. OTG Step Programming Test
In the development phase, it is very time-consuming to flash all of them every time, so here is the method of using OTG flashing tool to flash in separate partitions.
Note:
The condition for recognition is that the development board is powered up and the recover key is in the pressed state.
First, after OK3568-Forlinx Desktop-release is compiled, a separate partition image can be found in the rockdev directory
Take separate programming boot.img (including device tree and startup logo) as an example to demonstrate the programming method. Use the Type-C cable to connect the development board to the host. Press and hold the recover key and do not release it. Then press the reset key to reset the system. Release the recover key after about two seconds. The system will prompt to discover the loader device.
Click the "Dev Partition" button to automatically read the partition address. There will be a prompt that some partitions cannot be read. Click OK.
Click the right test area of the partition to select the partition mirror, and check the partition.
Click the "Run" button will automatically flash and restart.
Other partitions have been detected on the right but are not displayed in the list on the left, and when you need to flash the partition, you need to right-click on the left and select "Select Add Item", just enter the partition, click "Read Partition Table" again, and the software will automatically assign the partition address.
Introduction to MASKROM mode
If Loader mode is inaccessible (loader problem, etc.), press and hold the BOOT key, then press the reset key to enter maskrom mode for flashing.
At this time, the system will prompt the discovery of a maskrom device. The flashing process is consistent with the loader mode, so it is best to use an update.img flashing.
Note: Don't click "Device Partition Table" in maskrom mode, it is invalid.
-
Comprehensive Guide to Android OTA Updates on the iMX8MP Platform
08/01/2024 at 03:12 • 0 commentsOTA Description
OTA, short for Over-the-Air Technology, refers to the process in Android systems where mobile devices download and install updates directly via wireless networks (such as WiFi, 3G/4G/5G) from remote servers, without needing to connect to a computer, simplifying the upgrade process and enhancing user experience.
Advantages of OTA
The advantages of OTA (Over-the-Air) updates in the Android ecosystem are significant and well-appreciated. The primary reason for their popularity is the convenience and speed – users can upgrade their devices without connecting to a computer, simply by being on a network, which saves a considerable amount of time and effort. Simultaneously, OTA updates efficiently and automatically detect new versions and notify users, ensuring that their devices always operate on the latest, most secure system or applications. This not only simplifies the process of manually searching for and installing updates but also reduces the security risks associated with outdated versions. Consequently, OTA updates are vital for enhancing user experience, lowering operational costs, and ensuring the security of devices.
How to implement Android OTA upgrade in imx8mp platform?
Build the OTA upgrade package
1. Build the target file
Enter the related path:
forlinx@ubuntu:~$ cd imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source/ forlinx@ubuntu:~/imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source$
Configure the environment:
forlinx@ubuntu:~/imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source$ source env.sh forlinx@ubuntu:~/imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source$ source build/envsetup.sh forlinx@ubuntu:~/imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source$ lunch evk_8mp-userdebug ============================================ PLATFORM_VERSION_CODENAME=REL PLATFORM_VERSION=11 TARGET_PRODUCT=evk_8mp TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT=userdebug TARGET_BUILD_TYPE=release TARGET_ARCH=arm64 TARGET_ARCH_VARIANT=armv8-a TARGET_CPU_VARIANT=cortex-a53 TARGET_2ND_ARCH=arm TARGET_2ND_ARCH_VARIANT=armv7-a-neon TARGET_2ND_CPU_VARIANT=cortex-a9 HOST_ARCH=x86_64 HOST_2ND_ARCH=x86 HOST_OS=linux HOST_OS_EXTRA=Linux-5.4.0-150-generic-x86_64-Ubuntu-18.04.4-LTS HOST_CROSS_OS=windows HOST_CROSS_ARCH=x86 HOST_CROSS_2ND_ARCH=x86_64 HOST_BUILD_TYPE=release BUILD_ID=RQ1A.201205.003 OUT_DIR=out PRODUCT_SOONG_NAMESPACES=device/generic/goldfish device/generic/goldfish-opengl external/mesa3d vendor/nxp-opensource/imx/power hardware/google/pixel vendor/partner_gms hardware/google/camera vendor/nxp-opensource/imx/camera ============================================
Start compiling:
forlinx@ubuntu:~/imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source$ ./imx-make.sh bootloader kernel -j4 make: Entering directory '/home/forlinx/imx8mp/R3_6.28/OK8MP-android-source' /home/forlinx/imx8mp/R3_6.28/OK8MP-android-source/device/nxp/common/build/uboot.mk:74: *** shell env AARCH64_GCC_CROSS_COMPILE is not set. Stop. make: Leaving directory '/home/forlinx/imx8mp/R3_6.28/OK8MP-android-source' forlinx@ubuntu:~/imx8mp/OK8MP-android-source$ make target-files-package -j4 ============================================ PLATFORM_VERSION_CODENAME=REL PLATFORM_VERSION=11 TARGET_PRODUCT=evk_8mp TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT=userdebug TARGET_BUILD_TYPE=release TARGET_ARCH=arm64 TARGET_ARCH_VARIANT=armv8-a TARGET_CPU_VARIANT=cortex-a53 TARGET_2ND_ARCH=arm TARGET_2ND_ARCH_VARIANT=armv7-a-neon TARGET_2ND_CPU_VARIANT=cortex-a9 HOST_ARCH=x86_64 HOST_2ND_ARCH=x86 HOST_OS=linux HOST_OS_EXTRA=Linux-5.4.0-150-generic-x86_64-Ubuntu-18.04.4-LTS HOST_CROSS_OS=windows HOST_CROSS_ARCH=x86 HOST_CROSS_2ND_ARCH=x86_64 HOST_BUILD_TYPE=release BUILD_ID=RQ1A.201205.003 OUT_DIR=out PRODUCT_SOONG_NAMESPACES=device/generic/goldfish device/generic/goldfish-opengl external/mesa3d vendor/nxp-opensource/imx/power hardware/google/pixel vendor/partner_gms hardware/google/camera vendor/nxp-opensource/imx/camera ============================================ [……] #### build completed successfully (13:07 (mm:ss)) ####
After the compilation is completed, it will generate "evk_8mp-/target_files-eng.forlinx.zip" under the path
"out/target/product/evk_8mp/obj/PACKAGING/target_files_intermediates/".target_files-eng.forlinx.zip"...
Read more -
Advantages of FET3588J-C SoM in UAV Hyperspectral Imager Application
07/27/2024 at 02:51 • 0 commentsProduct Background
With the rapid development and widespread application of drone technology, drone-mounted hyperspectral imaging systems integrating drone platforms with high-precision spectral imaging technology are gradually gaining attention. The drone-mounted hyperspectral imaging system can measure spectral information of plants, water bodies, soil, etc., in real-time and generate spectral images.
By analyzing these images, it is possible to establish relationships with the physicochemical properties of plants and use the data for research on plant classification and growth conditions. Additionally, it has applications in geological and mineral resource exploration, forest pest and disease monitoring, meteorological studies, and other industry fields.
Product Features
- Hyperspectral resolution: Capable of capturing hundreds of continuous and narrow spectral bands, enabling detailed spectral characterization of surface materials.
- High spatial resolution: Combined with the flexibility and stability of the drone platform, this enables high-resolution imaging of ground targets.
- Intelligent data processing: Integrates advanced image processing algorithms and spectral analysis software, supporting rapid processing and interpretation of data.
- Portability and ease of use: The equipment is lightweight and portable, making it easy to mount on drone platforms, while the user interface is user-friendly, simplifying operation for users.
- Broader application scenarios: Suitable for environmental monitoring, agricultural surveys, geological exploration and other fields, meeting the needs of different users.
Product Requirements:
1. Compact carrier board design: Considering the weight and space constraints of the drone, the accompanying imaging device needs to be designed as compactly as possible. The carrier board design should be compact, effectively utilizing every inch of space while ensuring that all key components can be securely installed.
The size of the SoM should also be strictly controlled to fit the compact carrier board layout, without sacrificing its performance.
2. High compression ratio image compression algorithm: The product should incorporate a proprietary high compression ratio image compression algorithm to optimize the storage and transmission efficiency of image data. The algorithm needs to fully leverage the computational power of the SoM to ensure that excessive performance loss does not occur during image compression. The compression algorithm should minimize file size while maintaining image quality to accommodate the limited data transmission bandwidth and storage space of drones.
3. High-quality product stability: Given the complexity of the product application environment, such as extreme weather and mechanical vibrations, the requirements for product quality and stability are extremely high. All components and materials shall be of industrial grade or higher quality to ensure proper operation in a variety of harsh environments. Products shall be subjected to rigorous tests for shock, impact and weather resistance to verify their reliability in complex application environments.
Based on the product characteristics, Forlinx Embedded recommends using the FET3588J-C system on module(SoM) as the hardware design solution for the product.
Solution Features:
1. Strong performance support
High-performance processor: FET3588-C is based on Rockchip's new flagship RK3588 processor, which adopts an 8nm manufacturing process and integrates a quad-core Cortex-A76+quad-core Cortex-A55 architecture with a clock speed up to 2.4GHz, ensuring strong data processing capabilities for drones during hyperspectral imaging.
Powerful computing power: The built-in NPU provides 6 TOPS computing power, which makes it possible for artificial intelligence to be applied in UAV hyperspectral imaging, such as automatic target recognition, real-time analysis, etc.
2. Excellent image processing capabilities...
Read more -
Four Advantages Detailed Analysis of Forlinx Embedded FET3576-C System on Module
07/23/2024 at 06:52 • 0 commentsTo fully meet the growing demand in the AIoT market for high-performance, high-computing-power, and low-power main controllers, Forlinx Embedded has recently launched the FET3576-C System on Module, designed based on the Rockchip RK3576 processor. It features excellent image and video processing capabilities, a rich array of interfaces and expansion options, low power consumption, and a wide range of application scenarios. This article delves into the distinctive benefits of the Forlinx Embedded FET3576-C SoM from four key aspects.
Advantages: 6TOPS computing power NPU, enabling AI applications
Forlinx Embedded FET3576-C SoM has a built-in 6TOPS super arithmetic NPU with excellent deep learning processing capability. It supports INT4/ INT8/ INT16/ FP16/ BF16/ TF32 operation. It supports dual-core working together or independently so that it can flexibly allocate computational resources according to the needs when dealing with complex deep learning tasks. It can also maintain high efficiency and stability when dealing with multiple deep-learning tasks.
FET3576-C SoM also supports TensorFlow, Caffe, Tflite, Pytorch, Onnx NN, Android NN and other deep learning frameworks. Developers can easily deploy existing deep learning models to the SoM and conduct rapid development and optimization. This broad compatibility not only lowers the development threshold, but also accelerates the promotion and adoption of deep learning applications.
Advantages: Firewall achieves true hardware resource isolation
The FET3576-C SoM with RK3576 processor supports RK Firewall technology, ensuring hardware resource isolation for access management between host devices, peripherals, and memory areas.
Access Control Policy - RK Firewall allows configuring policies to control which devices or system components access hardware resources. It includes IP address filtering, port control, and specific application access permissions. Combined with the AMP system, it efficiently manages access policies for diverse systems.
Hardware Resource Mapping and Monitoring - RK Firewall maps the hardware resources in the system, including memory areas, I/O devices, and network interfaces. By monitoring access to these resources, RK Firewall can track in real-time which devices or components are attempting to access specific resources.
Access Control Decision - When a device or component attempts to access hardware resources, RK Firewall will evaluate the access against predefined access control policies. If the access request complies with the policy requirements, access will be granted; otherwise, it will be denied.
Isolation Enforcement - For hardware resources identified as requiring isolation, RK Firewall will implement isolation measures to ensure that they can only be accessed by authorized devices or components.
In summary, RK Firewall achieves effective isolation and management of hardware resources by setting access control policies, monitoring hardware resource access, performing permission checks, and implementing isolation measures. These measures not only enhance system security but also ensure system stability and reliability.
Advantages: Ultra clear display + AI intelligent repair
With its powerful multimedia processing capability, FET3576-C SoM provides users with excellent visual experience. It supports H.264/H.265 codecs for smooth HD video playback in various scenarios, while offering five display interfaces (HDMI/eDP, MIPI DSI, Parallel, EBC, DP) to ensure compatibility with diverse devices.
FET3576-C SoM notably supports triple-screen display functionality, enabling simultaneous display of different content on three screens, significantly enhancing multitasking efficiency.
In addition, its 4K @ 120Hz ultra-clear display and super-resolution function not only brings excellent picture quality enjoyment, but also intelligently repairs blurred images, improves video frame rate, and brings users a clearer and smoother visual...
Read more -
Building and Configuring Debian File System on iMX6ULL Platform
07/19/2024 at 05:47 • 0 commentsNote: Operate under the root user by default.
1. Qemu and Debootstrap Installation
Since a Debian file system is built on Ubuntu, these two tools can be installed directly using the apt-get command. The commands are as follows:
sudo apt-get install binfmt-support qemu qemu-user-static debootstrap
2. Extracting Debian File System
Use the debootstrap command to extract the file system. Execute the following command to retrieve the file system from the Debian mirror:
mkdir /home/forlinx/debian sudo debootstrap --arch=armhf --foreign buster root https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/debian/
Explanation of command parameters:
arch:Specify CPU architecture
buster:Debian version (currently 10)
foreign:Use when initializing unpacking in a different architecture than the host
root:The folder where the file system is stored
https: // mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn / debian /:Download source
Extraction may take around 10 minutes. Please be patient. Successful extraction reveals the Linux directory tree. If extraction fails, try multiple attempts or switch networks.
3. Perfecting the File System
Since the operation is conducted on an X86 virtual machine, QEMU needs to be used to simulate an ARM environment to improve the file system.
a.To copy qemu-arm-static into the newly built base system, use the following command:
cd root sudo cp /usr/bin/qemu-arm-static usr/bin cd ..
b.Initialize the file system.
Execute the following command:
sudo DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive DEBCONF_NONINTERACTIVE_SEEN=true LC_ALL=C LANGUAGE=C LANG=C chroot root debootstrap/debootstrap --second-stage
c.Use the chroot root command to initialize file system
chroot root
d.Use the command to create the following
echo "proc /proc proc defaults 0 0" >> etc/fstab mkdir -p usr/share/man/man1/ mknod dev/console c 5 1
e.To update the download sources, use the command vi /etc/apt/sources.list to open the source.list file and replace the contents with the following:
deb http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian stable main contrib non-free #deb-src http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian stable main contrib non-free deb http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian stable-updates main contrib non-free #deb-src http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian stable-updates main contrib non-free #deb http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian stable-proposed-updates main contrib non-free #deb-src http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian stable-proposed-updates main contrib non-free
Then save and exit. Use the command apt-get update to update the source. If updating the download source reports an error,use the date command to modify the system time to solve the problem.
f.Use the command apt-get install vim to install some necessary software
apt-get install vim apt-get install sudo apt-get install dpkg apt-get install bzip2 apt-get install net-tools apt-get install ntpdate
g.Create a new user with the command adduser forlinx, then enter the password
adduser forlinx
h.Set the root password, use the command passwd root, and set the password to forlinx.
passwd root
i.To set up Ethernet, enter the following command:
vi /etc/network/interfaces
As follows:
#/etc/network/interfaces -- configuration file for ifup(8), ifdown(8) #The loopback interface auto lo iface lo inet loopback #Wireless interfaces iface wlan0 inet dhcp wireless_mode managed wireless_essid any wpa-driver wext wpa-conf /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf iface atml0 inet dhcp #Wired or wireless interfaces auto eth0 #iface eth0 inet dhcp #iface eth1 inet dhcp iface eth0 inet static address 192.168.0.232 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 192.168.0.1 broadcast 192.168.0.255 auto eth1 iface eth1 inet static address 192.168.1.232 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 192.168.1.1 broadcast 192.168.1.255 #Ethernet/RNDIS gadget (g_ether) #... or on host side, usbnet and random hwaddr iface usb0 inet static address 192.168.7.2 netmask 255.255.255.0 network 192.168.7.0 gateway 192.168.7.1 #Bluetooth networking iface...
Read more -
Forlinx FET3568-C SoM: The Efficient and Intelligent Main Control Choice for Vending Machines
07/16/2024 at 07:49 • 0 comments1. Product Description
Vending machines, combining modern technology with the idea of convenient shopping, have become essential in our lives. It breaks through the constraints of time and space, providing us with round-the-clock uninterrupted product purchasing services. Whether in busy transportation hubs or quiet residential areas, you can always find its presence.
2. Components:
- Body Compartment: Made from high-strength, corrosion-resistant metal materials to ensure the stability and durability of the vending machine. The warehouse's interior is well-designed and can be adjusted according to the size of the goods to maximize the use of storage space.
- Payment System: Integrated with multiple payment methods including coins, bills, card swiping, and mobile payments, satisfying various consumer payment needs.
- Display and operation: HD touchscreen shows product information and purchase process, simplifying steps to enhance user experience.
- Product Delivery System: Uses precise mechanics and sensors for accurate, fast delivery to the outlet after payment.
- Communication Management System: Enables real-time monitoring, sales data analysis, and remote fault diagnosis and repair of vending machines via wireless network.
Business Logic Topology
The vending machine's main control system acts as its operational core, akin to its "brain", overseeing and coordinating each module's functions. With the ongoing development of IoT, big data, and AI, automation has become an inevitable trend in the vending machine industry. This has led to new demands for the main control systems, focusing on:
- Core Controller: It is essential to choose a stable, reliable, and high-performance core controller to ensure the overall logic control and data processing capabilities of vending machines.
- Device Stability: It requires 24/7 uninterrupted operation, necessitating high stability and durability in both hardware and software. Specifically, the software system should have fault self-check and automatic recovery capabilities.
- Scalability and Compatibility: To meet various scenarios and demands, the main control system of vending machines needs to be scalable. As products evolve, the main control system should be compatible with new hardware and software standards.
- Payment Security: As payment methods diversify, ensuring the security of the payment process has become increasingly important. Vending machines need to guard against various security threats, such as data breaches and fraudulent activities.
- AI Integration: Vending machines need to have intelligent recognition capabilities and data analysis abilities to recommend products based on users' purchasing preferences.
FET3568-C system on module(SoM) from Forlinx Embedded Systems offers high performance, low power consumption, and rich functionality, making it ideal for vending machines for these reasons:
- Powerful Performance: FET3568-C SoM is based on the Rockchip RK3568 processor, which features a quad-core 64-bit Cortex-A55 architecture with a clock speed of up to 2.0GHz. It supports lightweight edge AI computing and delivers strong computational and processing capabilities. Such performance meets the high demands of logic control and data processing for vending machine control systems, ensuring efficient and stable operation of the vending machines.
- Rich Interfaces and Expandability: The FET3568-C SoM offers 3 x PCIe slots, 4 x USB ports, 3 x SATA3.0 controllers, and 2 x Gigabit Ethernet ports. It supports 5 x display interfaces including HDMI2.0, eDP, LVDS, RGB Parallel, and MIPI-DSI, with up to three simultaneous display outputs. These interfaces provide great convenience for expanding the functionality of vending machines, enabling customized development to meet various scenarios and requirements.
- Multi-OS Support: FET3568-C SoM supports multiple operating systems including Linux, Android 11, Ubuntu, and Debian 11. This...
-
AM6254 Embedded Platform: Optimization Scheme for Shortening U-boot Boot Time
07/12/2024 at 08:06 • 0 commentsIntroduction to the U-Boot boot process
U-Boot Boot Process Stage 1
Main process Partial Hardware Initialization -> Load Full U-Boot into RAM -> Jump to Stage 2 Entry for Execution.
Files Used Mainly in Stage 1 (Non-Open Source Scenario):
- start.S (Hardware Initialization, watchdog, interrupts, clock configurations)
- lowlevel_init.S (RAM (DDR) initialization, U-Boot code loading, stack setup, BSS clearing, jump to U-Boot Stage 2
U-Boot Boot Process Stage 2
Stage 2 involves further hardware initialization by U-Boot, configuring command line parameters and environment variables, and transitioning to the kernel.
The main documents used are:
- board.c file: Typically, our own files are located in the board/forlinx/ directory.
- main.c file: Located in the common directory
Main function
Some of the more important initialisation functions are as follows:
1.''setup_mon_len'' function: Set the ''gd'' structure's ''mon_len'' member variable, representing the length of the entire code;
2.''initf_malloc'' function: Sets the ''gd '' structure's member variables related to ''malloc'';
3.''board_early_init_f''function;
4.To initialize the IO configuration of the serial port, defined in the board/freescale/mx6ull_toto/mx6ull_toto.cfile;
5.''timer_init'' function: Initialize the kernel timer to provide clock ticks for U-Boot, defined in the ''arch/arm/imxcommon/timer.c''file;
6.''get_clocks'' function: Retrieve the clock for the SD card peripheral (sdhc_clk), defined in the arch/arm/imxcommon/speed.c file;
7.''init_baud_rate'' function: Initialize the baud rate, defined in the ''common/board_f.c'' file.
8.''serial_init'' function: Initialize serial communication settings, defined in the''drivers/serial/serial.c''file;
9.''console_init_f'' function: Initialize the console, defined in the ''common/console.c'' file;
10.''display_options'' function: Print U-Boot version information and compilation details, defined in the lib/display_options.c file;
11.''print_cpuinfo'' function: To display CPU information and the main clock frequency, defined in the arch/arm/imx-common/cpu.c file;
12.''show_board_info'' function: Print development board information, defined in the common/board _ info.c file;
13.''init_func_i2c'' function: To initialize I2C;
14.''announce_dram_init'' function: This function is simple, it outputs the string "DRAM:";
15.''dram_init'' function: Doesn't actually initialize DDR but rather sets the value of gd->ram_size.
Current U-boot startup print information
U-Boot SPL 2021.01-gd1345267-dirty (Jul 08 2023 - 08:00:49 +0800) SYSFW ABI: 3.1 (firmware rev 0x0015 '21.5.1--w2022.07-am62x (Terrifi') am625_init: board_init_f done(counter=1) SPL initial stack usage: 13768 bytes i2c_write: error waiting for data ACK (status=0x116) i2c_write: error waiting for data ACK (status=0x116) Auth Success! normal mode am625_init: spl_boot_device: devstat = 0x1843 bootmedia = 0x9 bootindex = 0 Trying to boot from MMC1 am625_init: spl_boot_device: devstat = 0x1843 bootmedia = 0x9 bootindex = 0 Loading Environment from MMC... MMC: block number 0x3500 exceeds max(0x2000) *** Warning - !read failed, using default environment am625_init: spl_boot_device: devstat = 0x1843 bootmedia = 0x9 bootindex = 0 am625_init: spl_boot_device: devstat = 0x1843 bootmedia = 0x9 bootindex = 0 init_env from device 9 not supported! Starting ATF on ARM64 core... NOTICE: BL31: v2.5(release):v0.6-6-gd489c56b NOTICE: BL31: Built : 15:08:18, Jun 26 2023 U-Boot SPL 2021.01-gd1345267-dirty (Jul 08 2023 - 08:00:56 +0800) SYSFW ABI: 3.1 (firmware rev 0x0015 '21.5.1--w2022.07-am62x (Terrifi') am625_init: board_init_f done am625_init: spl_boot_device: devstat = 0x1843 bootmedia = 0x9 bootindex = 0 Trying to boot from MMC1 am625_init: spl_boot_device: devstat = 0x1843 bootmedia = 0x9 bootindex = 0 U-Boot 2021.01-gd1345267-dirty (Jul 08 2023 - 08:00:56 +0800) SoC: AM62X SR1.0 Model: Forlinx OK62xx-C board DRAM: 2 GiB MMC: mmc@fa10000: 0, mmc@fa00000: 1 Loading Environment...
Read more -
RTC Operations on i.MX6ULL Embedded Platform
07/05/2024 at 00:46 • 0 comments1. RTC Description
1.1 What's RTC?
RTC (Real Time Clock): It is an electronic device that functions like a clock to output real-world time. RTC Overview: The RTC is a 32-bit timer that increments every second, functioning like a clock. Date and time can be modified by adjusting the timer value.
To ensure that the RTC time is not lost during power outages, a small battery is usually connected separately to provide power to the RTC. Once the small battery is removed, the RTC will lose the time after a power outage.
However, the time in the lower right corner of the computer and the time seen with date under Linux are not RTC time. During system operation, a high-precision register on the chip serves as the system time reference. To avoid drift over extended system operation and prevent time loss after power failure, each time the system starts up, it retrieves the time from the RTC to set as the system time.
1.2 Difference Between Internal and External RTC
External RTC advantages:
Low power consumption
Minimal deviation
Therefore, an external RTC (Real-Time Clock) is generally used.
2. Unix Time Stamp
Unix timestamp is defined as the number of seconds elapsed since 00:00:00 coordinated Universal Time (UTC) on January 1, 1970, excluding leap seconds.
The timestamp is stored in a seconds counter, which is a 32-bit/64-bit integer variable.
The timestamp is stored in a 32-bit/64-bit integer seconds counter, uniform globally across all time zones, with local times derived from applying offsets to this counter.
3. Common operation
3.1 Date
The "date" command can read/write the current system time and also display the time zone. Common operations:
View time:
Before changing the timezone
root@fl-imx6ull:~# date
Thu Sep 21 04:43:03 UTC 2017
After changing the timezone
root@fl-imx6ull:~# date
Thu Sep 21 12:43:50 HKT 2017View timezone
Before changing the timezone
root@fl-imx6ull:~# date -R
Fri, 26 Apr 2019 19:07:20 +0000
After changing the timezone
root@fl-imx6ull:~# date -R
Thu, 21 Sep 2017 12:45:37 +0800Set time:
root@fl-imx6ull:~# date -s "20240531 12:00:00"
Fri May 31 12:00:00 UTC 20243.2 Timezone modification
The time zone file is/etc/localtime. When the time zone needs to be modified, only the corresponding time zone file needs to be linked to/etc/localtime.
root@fl-imx6ull:~# rm /etc/localtime
root@fl-imx6ull:~# ln -s /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Hong_Kong /etc/localtime3.3 hwclock
Read RTC time
root@fl-imx6ull:~# hwclock -r
Thu Sep 21 04:47:03 2017 0.000000 secondsWrite in time
hwclock -w
root@fl-imx6ull:~# date
Thu Sep 21 12:50:41 HKT 2017
root@fl-imx6ull:~# hwclock -w
root@fl-imx6ull:~# hwclock -r
Thu Sep 21 12:51:36 2017 0.000000 seconds
hwclock -wu
root@fl-imx6ull:~# date
Thu Sep 21 12:52:51 HKT 2017
root@fl-imx6ull:~# hwclock -wu
root@fl-imx6ull:~# hwclock -r
Thu Sep 21 04:52:56 2017 0.000000 secondsNote: If UTC is enabled and the time zone is modified, hwclock -wu should be usedSync system time to RTC
hwclock --systohc
Sync RTC time to system
hwclock --hctosys
4. Sync RTC to system
At system startup, the RTC time is read and used as the system time. Using the example of the imx6ull processor, after powering on, the operations related to RTC are as follows:
There are the followings in the /etc/rcS.d/S55bootmisc.sh:
#
# This is as good a place as any for a sanity check
#
# Set the system clock from hardware clock
# If the timestamp is more recent than the current time,
# use the timestamp instead.
test -x /etc/init.d/hwclock.sh && /etc/init.d/hwclock.sh start
if test -e /etc/timestamp
then
SYSTEMDATE=`date -u +%4Y%2m%2d%2H%2M%2S`
read TIMESTAMP < /etc/timestamp
if [ ${TIMESTAMP} -gt $SYSTEMDATE ]; then
# format the timestamp as date expects it (2m2d2H2M4Y.2S)
TS_YR=${TIMESTAMP%??????????}
TS_SEC=${TIMESTAMP#????????????}
TS_FIRST12=${TIMESTAMP%??}
TS_MIDDLE8=${TS_FIRST12#????}
date -u ${TS_MIDDLE8}${TS_YR}.${TS_SEC}
test -x /etc/init.d/hwclock.sh && /etc/init.d/hwclock.sh stop
fi
fiThe main functions of this part...
Read more -
Fast Pesticide Residue Detection Solution Based on Forlinx FET3568-C SoM
07/03/2024 at 03:09 • 0 commentsFast Pesticide Residue Detector: Efficient and convenient device for rapid analysis of pesticide residue in fruits and vegetables. It accurately measures pesticide residue in agricultural products, ensuring food safety and dietary health. It is widely used in industrial and commercial administration, vegetable wholesale markets, supermarkets, shopping malls and other fields.
Hardware Technology Implementation Features
- High Sensitivity and Accuracy: The detector employs advanced detection technology, capable of detecting very low concentrations of pesticide residues, ensuring precise and sensitive test results.
- Fast Detection and High Throughput: Utilizing advanced electronic and optoelectronic systems, the pesticide residue detector provides quick and accurate test results, enhancing detection efficiency. Some models also handle large sample volumes, further enhancing their high-throughput detection advantage.
- Automation and User-friendliness: It uses automated control technology to perform testing processes such as sample introduction, detection, and cleaning automatically, reducing manual operation time and errors. User-Friendly Interface: Its intuitive design simplifies operation, requiring minimal specialized skills.
- Versatility and Wide Applicability: In addition to pesticide residue detection, some pesticide residue analyzers also offer multiple detection methods to meet various pesticide testing needs. This makes the instrument valuable across various fields such as agricultural product quality and food safety.
With food safety concerns increasingly prominent, pesticide residue detection has become a crucial step in ensuring food quality and safety. Traditional pesticide analyzers are often limited by processing capabilities and power consumption, hindering rapid and accurate detection demands. Forlinx Embedded recommends the FET3568-C SoM as the solution.
FET3568-C is a high-performance, low-power processor, particularly suitable for embedded devices and IoT applications. In pesticide residue analyzers, the FET3568-C platform provides robust support for efficient operation with its outstanding computational power and power management capabilities.
- With powerful computing power. The powerful CPU cores can process large volumes of data to finish the pesticide residue detection and analysis within a short time. This is crucial for scenarios requiring real-time detection and output of results, effectively enhancing detection efficiency.
- Excellent power consumption control In the pesticide residue analyzer, low power consumption means extended battery life, which is crucial for users who need to conduct long-term detection in fields or laboratories. Additionally, low power consumption helps reduce device heat generation, thereby enhancing device stability and reliability.
- Rich peripheral interfaces such as UART, SPI, I2C, etc., facilitate communication with various sensors and external devices. In the pesticide residue analyzer, these interfaces can connect key components such as photodetectors and sensors, enabling rapid data acquisition and transmission. Additionally, the RK3568 supports various storage media, making it convenient for users to save and export test data.
- In addition to hardware performance improvements, the FET3568-C also enables software optimization for pesticide residue analyzers. Based on the powerful computing capabilities of RK3568, the analyzer can run more complex algorithms and models, thereby improving detection accuracy and precision. Additionally, the RK3568 supports various operating systems and programming environments, providing developers with flexible development options.
Rockchip's RK3568 significantly enhances the performance and reliability of pesticide residue analyzers. Its powerful computing capabilities, excellent power management, and rich peripheral interfaces enable pesticide residue analyzers to better meet the demands for rapid and accurate...
Read more -
Forlinx FET3588J-C: Hardware Solution Customized for Marine Instrument Panel Technology
06/28/2024 at 03:46 • 0 commentsMarine instrument panels are critical display and monitoring devices on ships, crucial for ensuring maritime safety, efficiency, and comfort. Real-time monitoring of vital ship information such as position, speed, heading, and engine status through marine instrument panels enables prompt adjustments and decision-making. They not only enhance the precision and reliability of ship operations but also help reduce accident risks, ensuring safe navigation. Moreover, the digital and intelligent design of marine instrument panels allows crew members to manage and control ships more efficiently, improving operational efficiency. They are key tools for ship operation and management.
With the continuous advancement of maritime technology, there is an increasing demand for intelligence and digitization in modern ships. As a core component for ship information display and monitoring, the performance and stability of marine instrument panels are crucial to meet modern maritime needs for information display, data monitoring, and navigation safety. Specific objectives include:
- Providing a clear and intuitive instrument display interface enables crew members to quickly access navigation information.
- Facilitating compatibility with various data interfaces enables seamless data transmission with onboard sensors and equipment.
- Ensuring that instrument panels can operate stably in harsh maritime environments, with high resistance to interference and waterproof performance, is essential.
Based on the above characteristics, the hardware platform of modern marine instrument panels should possess the following features:
- High-performance processor: Ensures fast response and accurate display of navigation information, equipped with powerful data processing and graphic rendering capabilities.
- Rich Data Interfaces: Integrated with multiple data interfaces such as display ports, serial ports, Ethernet ports, USB ports, etc., enabling seamless connection with various sensors and devices onboard ships for easy data display, real-time acquisition, and transmission.
- Reliability Design: The hardware itself demands high quality and stability to ensure long-term reliable operation in harsh maritime environments.
Based on a modern marine instrument screen hardware platform, Forlinx Embedded recommends FET3588J-C as the hardware development solution.
Product Characteristics
- High-performance processor: Quad-core 64-bit Cortex-A72 + quad-core Cortex-A55 architecture with integrated 6 TOPS NPU for enhanced AI learning and edge computing capabilities in diverse operational scenarios.
- Rich Display Interfaces: Offers multiple interfaces such as HDMI, eDP, DP, MIPI-DSI, supporting various display types including up to 8K output, meeting diverse requirements for maritime instrumentation screens. At the same time, it supports four-screen display function, which enables the crew to monitor multiple important parameters at the same time and improve work efficiency.
- High-efficiency Graphics Processing: Integrates ARM Mali-G610 MP4 quad-core GPU, fully compatible with OpenGLES 1.1, 2.0, and 3.2, OpenCL up to 2.2, and Vulkan 1.2. Enables maritime instrumentation screens to efficiently handle complex graphic tasks such as real-time rendering and 3D map display, enhancing user operational experience.
- Versatile Peripheral Interfaces: Features include dual Gigabit Ethernet, USB 3.1, PCIe 3.0, and 10 UART ports, enhancing data speed and efficiency. This strengthens maritime instrumentation screen functionality, meets navigation needs, and ensures stable data transmission and efficient device communication.
- Robust and Reliable Performance: The RK3588J platform meets industrial-grade temperature range standards and has undergone rigorous testing to provide stable performance support for high-end applications. During maritime navigation, stable and reliable instrumentation screens are crucial for ensuring the safety of vessels....
-
FAQ about the Forlinx i.MX6ULL Embedded Development Board
06/26/2024 at 02:39 • 0 comments▊ IP Settings
(1)Set a default static IP;
(2)Set a temporary static IP ( it is disabled after power cycling).
1. Static IP settings
(1) Open /etc/network/interfaces and modify the configuration vi /etc/network/interfaces
As follows, configure eth0 as static and eth1 as dynamic:
(2) DNS settings
Open rc.local with the command vi /etc/rc.local and add the following to it:
echo "nameserver 8.8.8.8" > /etc/resolv.conf
(3) Block information update&restart
sync
reboot
2. Temporary network settings
Alternatively, the commands can be used temporarily to set the IP and gateway. However, please note that this method's configuration will be lost after a restart.
ifconfig eth0 172.16.0.171//Set eth0 static IP
route add default gw 172.16.0.1 //Set gateway
echo ''nameserver 8.8.8.8'' > /etc/resolv.conf //Set DNS▊ Adding Startup Auto-run Content
1. Adding the following to the startup script
Enter vi /etc/rc.local
As an example of booting with the output ''hello world,'' add the following content:
Note: Add the startup auto-run content before exit 0;
2. Adding startup auto-run items
To create a startup auto-run item in the /etc/rc5.d/ directory
vi /etc/rc5.d/S99test.sh
As follows:
#!/bin/bash
echo "helloworld!"
chmod 777 /etc/rc5.d/S99test.sh
S99 indicates the startup priority as 99, which can be adjusted by the user based on demand.
3. Power-on self-starting 4G dialing method
Previously it was mentioned that startup applications can be directly added to /etc/rc.local. However, 4G slightly differs from other applications because it uses a separate 4G module that requires initialization time. Based on practical tests, the 4G module takes 3-5 seconds after startup to function properly. Therefore, before initiating 4G dialing, a delay of 3-5 seconds is necessary. Modify as follows:
vi /etc/rc.local
Add the following:
Note: The delay time cannot be less than 3s.
▊ WiFi
1. Static IP Settings (WiFi)
WiFi login script: /usr/bin/fltest_cmd_wifi.sh
The second-to-last line of the script assigns a dynamic IP to wlan0. If there is a need to set a static IP, it can be done as follows:
2. Power-on self-starting settings (WiFi)
Also put the WiFi script in the/etc/rc.local.
In this case, it is necessary to add an ''&'' symbol at the end to run the script in the background. Otherwise, it might block and prevent access to the file system.
▊ Boot
1. SSH connection failure
(1) When SSH cannot connect, check if ping is possible. If ping fails, it could be due to network issues. The computer and the device should be on the same subnet. The default IP for eth0 is 192.168.0.232. Users can directly connect them or connect both to the same router. Then, set a 192.168.0 subnet IP on the computer;
(2) If ping is successful, first confirm whether the factory image can connect normally. If the factory image can connect normally, check what services are starting up at boot causing the issue; ensure that services starting at boot are backgrounded. Failure to do so may cause process blocking, preventing SSH login. Consider reflashing the factory image if necessary;
(3) Ensure that the board's IP address is being pinged. This can be tested by unplugging the Ethernet cable and then pinging from the computer.
-
Forlinx Launched FET3576 System on Module powered by the Rockchip RK3576 processor!
06/24/2024 at 06:04 • 0 commentsForlinx Launched FET3576 System on Module powered by the Rockchip RK3576 processor!
FET3576-C system on module(SoM) is powered by the Rockchip RK3576 processor. This high-performance, low-power, feature-rich application processor is tailored for the AIoT and industrial markets. With 4 x ARM Cortex-A72 and 4 x ARM Cortex-A53 cores, plus a built-in 6TOPS NPU, it enhances your AI applications. Featuring board-to-board connection design for easy setup, it’s rigorously tested in Forlinx’s lab for stability in industrial conditions. With a 10 to 15-year life-cycle, ensure continuous supply.
Rockchip RK3576 SoM Features:
• 8nm processing technology;
• 4x 100-pin board-to-board connectors to maximize processor performance;
• Compatible design with FET3588-C;
• Firewall supports device access control and priority management;
• H.265 decoding up to 8K resolution;
• Multiple display interfaces: HDMI/eDP, MIPI DSI, Parallel, EBC, DP;
• Supports three displays working together with different content;
• Various high-speed peripherals: PCIe 2.1, USB 3.2, CAN-FD, etc.
-
The Design Insight of A Peritoneal Dialysis Machine Based on Forlinx T113 SoM
06/21/2024 at 06:24 • 0 commentsProduct Description
The peritoneal dialysis machine is an advanced medical device designed for performing peritoneal dialysis, a treatment for acute and chronic renal failure. This process involves infusing dialysate into the patient's abdominal cavity, where the peritoneum serves as a semipermeable membrane to exchange solutes and fluids, effectively removing metabolic waste and toxins while correcting fluid and electrolyte imbalances. The device comprises a main unit, control unit, and heater, available in both powered and gravity-driven models.
This technology significantly enhances the quality of life for patients, allowing them to connect the peritoneal dialysis catheter to an automated machine before sleep. The machine performs dialysis treatments overnight, typically for 8 to 10 hours. In the morning, patients can disconnect the catheter and continue their daily activities seamlessly.
Hardware Key Components
- Central Control Unit: Manages the operation and data processing of the device. Modern systems feature intelligent controls that monitor and record real-time parameters, such as infusion volume, dwell time, drainage time, outflow volume, and dialysate temperature.
- Heater: Ensures the dialysate is warmed to the optimal temperature, improving efficiency and patient comfort.
- Power Unit: Facilitates the delivery and drainage of dialysate to and from the patient's peritoneal cavity.
- Sensors and Monitoring System: Utilizes various sensors to ensure real-time monitoring and safety of the dialysis process.
- User Interface: Provides an intuitive platform for setting parameters, monitoring status, and receiving alerts.
Main Challenges in Hardware Design
- Precise Control and Monitoring: Demands accurate control and monitoring of parameters like temperature, pressure, and flow rate, requiring high hardware accuracy and stability.
- Portability and Compact Design: Essential for home-based dialysis, necessitating a balance between size, weight, and performance.
- Safety and Reliability: Critical for medical equipment, requiring thorough consideration of electrical and mechanical safety, and prevention of cross-contamination.
- Cost-effectiveness: Balancing performance, safety, and reliability with reduced hardware costs to alleviate patient financial burdens and enhance market competitiveness.
Recommended Hardware Platform: Forlinx T113 SoM
The T113 SoM stands out as a highly competitive solution for addressing the hardware challenges of peritoneal dialysis machines. Here are five reasons for its recommendation:
- High-Performance Computing: Integrates dual-core Cortex-A7 CPU, 64-bit XuanTie C906 RISC-V DSP with clock speeds up to 1.2GHz, providing robust computing power for precise control and real-time monitoring.
- Extensive Connectivity: Offers diverse connectivity options (USB, SDIO, UART, SPI, CAN, Ethernet) for flexible data exchange and communication, enhancing compatibility and future upgrade potential.
- Multimedia Support: Capable of decoding and encoding multiple formats with various display and audio interfaces, improving the user interface and feedback experience.
- Stable and Reliable Performance: Undergoes rigorous testing for environmental stress and long-term stability, ensuring consistent operation and high patient satisfaction.
- Cost-effective: Features compact, low-power consumption design ideal for portable devices, with competitive pricing to reduce overall machine costs and ease patient financial burdens.
In conclusion, the T113 SoM's combination of high performance, rich connectivity, multimedia support, compact size, and reliable operation makes it an excellent core hardware solution for peritoneal dialysis machines. It effectively addresses the need for control, monitoring, and user experience while reducing costs and enhancing market competitiveness.
-
Setup Linux Wake-On-LAN on RK3568 Platform
06/19/2024 at 06:58 • 0 comments1. GPIO Wake-up
The supported system sleep modes can be viewed with cat /sys/power/state.
To achieve functionality similar to the 6ul, use the "wake-up" function in ''gpio-keys.c''. Add a GPIO node specifying the wake-up GPIO pin. During sleep, a message indicates only GPIO0 supports wake-up; testing confirmed only GPIO0 can wake up.
cat /proc/interrupts indicates that the interrupt for key1 has been successfully registered.
Testing has been conducted to verify that both freeze and mem modes can wake up.
2. Network Wake-up
Firstly, NIC support for Wake-on-LAN is required. Use the ethtool tool to check NIC information. The default setting for wake-on is ''d'', which means network wake-up is disabled. The ''supports Wake-on'' option is ''ug'', where ''u'' allows any unicast data and ''g'' allows magic packets. The wake-on can be set to ''ug'' for eth0 using the following command: ''ethtool -s eth0 wol ug''.
Test for u:
echo freeze > /sys/power/state//Enter freeze sleep mode
Waking up can be achieved by pinging the IP of this network port in any local area network.
Test for g:
ethtool -s eth0 wol g//Set wake-on to g
At this point, the ping fails, but the mac can be specified through the wol to wake up.
Testing revealed that Wake-On-LAN is only possible in freeze mode. Observations showed that after entering mem mode, the network LED does not light up; whereas, in freeze mode, the network LED continues to blink normally. This indicates that the PHY (physical layer) is not functioning in mem mode, and therefore, it cannot trigger an interrupt for wake-up.
It is also possible that this interrupt pin is connected to gpio3 _ A2.
-
FET3576-C SoM Release, Powering AIoT Applications
06/18/2024 at 02:33 • 0 commentsTo fully meet the growing demand in the AIoT market for high performance, robust computing power, and low power consumption, Forlinx Embedded presents the all-new FET3576-C SoM, developed based on the Rockchip RK3576 processor!
Integrated with 4 x ARM Cortex-A72 and 4 x ARM Cortex-A53 high-performance cores, featuring a built-in 6 TOPS powerful NPU, the FET3576-C SoM empowers your AI applications. With a board-to-board connection design and plug-and-play capability, it facilitates easy installation and maintenance for your products.
The product undergoes rigorous testing at Forlinx Embedded Laboratory ensuring stability and reliability for your products. With a 10-15 year life-cycle, it assures continuous supply.
FET3576-C SoM release marks a new milestone in the collaboration between Forlinx Embedded and Rockchip. As we enter the era of mobile intelligence, we are committed to working together to provide customers with excellent products and high-quality services.
01 Eight-core High-performance Chip with Advanced Video Decoding Capabilities
RK3576 is a high-performance, low-power application processor designed by Rockchip specifically for the AIoT market. It features four ARM Cortex-A72 cores and four ARM Cortex-A53 high-performance cores, along with a built-in 6TOPS powerful NPU for advanced computing tasks. Additionally, it includes an embedded 3D GPU, a dedicated 2D hardware engine with MMU, and H.265 hardware decoding, supporting up to 8K resolution for enhanced display performance.
02 Firewall Achieves True Hardware Resource Isolation
RK Firewall for managing access rights from master to slave devices and memory areas for true hardware resource isolation
03 Supercharge Your AI Applications With 6TOPS Computing Power NPU!
RK3576 processor is equipped with a powerful 6TOPS NPU, supporting INT4/INT8/INT16/FP16/BF16/TF32 operations. It can operate in dual-core collaboration or independently, facilitating multitasking and parallel processing across various scenarios. It supports multiple deep learning frameworks such as TensorFlow, Caffe, Tflite, Pytorch, Onnx NN, and Android NN.
04 Ultra-HD Display + AI Intelligent Repair
RK3576 processor supports high-definition H.264 and H.265 encoding/decoding, and features five display interfaces: HDMI/eDP, MIPI DSI, Parallel, EBC, and DP. It enables triple-display setups, 4K@120Hz Ultra HD display, and super-resolution capabilities. Intelligent image restoration enhances blurry images and improves video frame rates, meeting diverse display requirements across multiple scenarios.
05 FlexBus New Parallel Bus Interface
FlexBus features a flexible parallel bus interface capable of simulating irregular or standard protocols, supporting 2/4/8/16-bit data parallel transmission at clock speeds up to 100MHz. Additionally, it includes a rich array of bus communication interfaces such as DSMC, CAN-FD, PCIe 2.1, SATA 3.0, USB 3.2, SAI, I2C, I3C, and UART.
06 Continuously Updated User Profile
Comprehensive resources including carrier board schematics ensure simplified development and streamlined production processes for you.
07 Wide Range of Industry Applications
Forlinx Embedded FET3576-C SoM is versatile across industrial, AIoT, edge computing, and smart mobile terminals. With Forlinx's robust technical support services, accelerate your product's time-to-market and seize the lead in your industry.
Carrier Board
![Rockchip RK3576 Development Board]()
OK3576-C Development Board
To minimize your development workload, we can provide starter kits that can be used as complete development platforms for evaluation and application development.
Read more
OK3576-C Single Board Computer by Forlinx is powered by Rockchip RK3576 processor, featuring 4x ARM Cortex-A72@2.3GHz + 4x Cortex-M53@2.2GHz, 2GB/4GB LPDDR4 RAM, and a 6TOPS NPU. It employs 4 100-pin board-to-board connectors to easily access all processor function pins, offering seamless functionality and ease of customization, and supports Linux... -
Basic Knowledge of Video Codec Technology From Video Formats to Frame Formats
06/12/2024 at 00:50 • 0 commentsBasic Knowledge of Video Codec Technology From Video Formats to Frame Formats
Video Package Format
MP4, AVI, and MKV are all suffixes for local video files and are used in Windows to indicate which application the operating system should use to open them. In the streaming media world, these are known as ''video encapsulation formats'' because, in addition to the audio and video streams, they also contain some ancillary information and a way of organizing the video and audio. The user experience of videos in different formats on different platforms varies largely due to the differences brought by the organization of audio and video. A video format is an identifier given to a video file by video playback software to be able to play the video file. In short, the video format specifies the communication protocol with the player.
The "video packaging format" is a "packaging" of the encoded video and audio with playback-related protocol data.
The "video protocol" is for web streaming media, and some articles will classify the "video protocol" as a "video encapsulation format". Both "video protocol" and "video encapsulation format" carry audiovisual content and metadata, as well as other information required by the protocol/format. Taking FFMpeg as an example, it does not distinguish between video formats and video protocols; however, with GStreamer, you may need to specify the "video protocol", but it does not distinguish the "video encapsulation format".
Video streaming
In terms of video streams, you must have heard terms like ''h264 stream,'' ''yuv stream,'' ''encoded stream,'' ''decoded stream,'' ''raw stream,'' ''raw stream,'' ''compressed stream,'' or ''uncompressed stream'' and so on in your daily life. In general, when mentioning "video streams," there are only two forms:
1. Encoded streams (such as h264, yuv);
2. Raw streams (whether compressed or uncompressed).
Uncompressed stream data, when decoded, is referred to as ''raw stream.'' One can imagine a video as being composed of a series of continuous ''images'' over time, and because the internal ''images'' of the video are in the ''YUV'' format, it is often also referred to as a ''YUV stream.''
Stream data that has been compressed by compression algorithms is referred to as ''encoded stream,'' and due to the prevalence of the H.264 compression/encoding algorithm, it is also commonly known as ''H.264 stream.''
Summary: "H.264 stream," "encoded stream," and "compressed stream" refer to the compressed/encoded video streams, while "YUV stream," "decoded stream," and "uncompressed stream" denote the video streams that have not been compressed/encoded. ''Raw stream'' is a term with ambiguity, dependent on context, which can refer to either the former or the latter.
In daily life, the vast majority of video files we encounter are encoded/compressed, and in network transmission scenarios, the majority are also encoded/compressed. During video playback, viewers see a decoded video stream frame by frame converted to RGB.
Encoding/compression is a very important technology in the field of streaming media: the process from an H264 bitstream to a YUV stream is called decoding, and the reverse is called encoding.
Frame format
In the field of streaming media, "streaming" is important, and the basic element of "frames" is equally important. The reason is that for video encoding/compression, its core is to encode a series of temporally continuous frame data into as small a space as possible; whereas for video decoding, it is to try to restore a series of encoded/compressed frame data to its original state as much as possible.
Coding/compression algorithms that can be recovered by 100% are called lossless compression and vice versa are called lossy compression.
"A "frame" can be associated with an "image" that we normally see, except that the images we normally encounter are in RGB format, whereas video frames are usually in YUV format.
With the maximum compression rate achieved,...
Read more -
Application of Forlinx FETMX8MP-C SoM in ECG Monitor
06/05/2024 at 07:13 • 0 commentsECG monitor is a kind of medical equipment that is used to monitor and record human ECG in real-time. It can continuously observe the electrical activity of the heart through the display, providing doctors with reliable and valuable indicators of cardiac activity, thus guiding real-time management. ECG monitor has a wide range of applications in the medical field, especially for patients with abnormal ECG activity, such as acute myocardial infarction, various arrhythmias, etc., which plays an important role in auxiliary diagnosis.
Application Scenario
ECG monitor is widely used in various places of the hospital, such as ICU, CCU, operating room, ward and so on. It is suitable for critically ill patients or patients with certain risks after operation, as well as patients who need to monitor ECG signals continuously for a long time. By using an electrocardiogram monitor, doctors can promptly detect abnormalities in patients' physiological indicators, thereby taking appropriate treatment measures to ensure the patients' safety.
Features:
1. Accurate monitoring:The electrocardiogram monitor can real-time monitor the patient's cardiac signals, collect the weak signals of cardiac electrical activity through electrodes attached to the patient's body, and display them on the screen after internal circuit processing. In addition to cardiac signals, an electrocardiogram monitor can also simultaneously monitor other physiological parameters such as respiration, blood pressure, blood oxygen saturation, etc., providing doctors with comprehensive physiological information.
2. Alarm function: The electrocardiogram monitor has an alarm function, which can be set with different alarm thresholds according to the patient's condition and the doctor's requirements. When the monitored parameters exceed the set values, the monitor will emit audio and visual alarms to promptly remind medical staff to take action.
3. Data recording and analysis: The electrocardiogram monitor can automatically record the patient's cardiac data and generate electrocardiograms for analysis. Doctors can analyze the electrocardiogram to understand the patient's cardiac condition, providing a basis for subsequent diagnosis and treatment.
4. Stable operational capability: The electrocardiogram monitor can effectively shield interference factors such as electromyographic signals and electromagnetic signals, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of cardiac data. It can continuously monitor patients' physiological parameters for 24 hours, assisting doctors in promptly detecting changes in the patient's condition.
Folinx Solutions
As an important equipment in the medical field, ECG monitor plays a vital role in monitoring the physiological parameters of patients continuously, stably and accurately. In order to meet the high performance, high stability, multi-function and other requirements of modern medical ECG monitor, for product development, we recommend the embedded FETMX8MP-C SoM based on NXP i.MX8MPlus processor as the development platform of ECG monitor.
Technical Features:
- High performance: The CPU is a 1.6GHz quad-core 64-bit Cortex-A53 architecture with a Neural Processing Unit (NPU) running up to 2.3TOPS.
- Network Interface: The SoM natively supports 2 Gigabit network interfaces, which makes data transmission and interaction with external medical information systems (LIS/HIS) efficient and stable.
- Display and Expansion Interface: It also supports screen interfaces such as LVDS and HDMI, which can meet the display needs in different scenarios, such as dual-screen simultaneous display or heterodyne display, and the highest resolution of HDMI can be reached4K. In addition, communication interfaces support USB 3.0, PCIE Gen 3, SDIO, CAN FD, etc. to connect to various sensors or medical devices.
- Industrial-grade design and stability: The whole board adopts industrial-grade design and undergoes the stringent 7x24 hours continuous...
-
A Comprehensive Guide to Screen Porting for the Forlinx Embedded 8M Series
05/30/2024 at 06:35 • 0 commentsAs the embedded industry continues to evolve, the need for efficient and reliable screen integration has become increasingly important. Whether you’re working with MIPI or LVDS displays, understanding the nuances of screen porting can make all the difference in delivering a seamless user experience.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive into the key considerations and best practices for screen porting, covering both MIPI and LVDS transitions. By the end of this article, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of screen integration and ensure a successful project.
MIPI Screen Porting: The Initialization Sequence Unraveled One of the most critical aspects of MIPI screen porting is the initialization sequence. Most MIPI displays require a specific set of initialization commands to function properly. Analyzing the initialization sequence provided by the screen manufacturer and translating it into the appropriate driver format is a crucial first step.
Our experts delve into the various formats of initialization sequences, guiding you through integrating them into your Uboot and kernel drivers. Understanding the structure and logic behind these sequences allows you to seamlessly port your MIPI screens, ensuring a smooth startup and optimal display performance.
Navigating the LVDS Landscape: Clocks, Registers, and Calculations LVDS screen porting presents its own set of challenges, with a focus on accurate clock configurations and intricate register settings. Whether you’re working with single-channel, dual-channel, single-hex, or dual-hex LVDS displays, the nuances of these parameters can make or break your integration efforts.
In this section, we delve into the step-by-step process of calculating the appropriate clock frequencies, modifying the necessary registers, and ensuring a successful LVDS screen porting. From the Uboot to the kernel stage, we provide you with the tools and knowledge to tackle even the most complex LVDS scenarios.
Bridging the Gap: Migrating from MIPI to LVDS For those facing the task of transitioning from MIPI to LVDS displays, this guide offers a comprehensive roadmap. We explore the Uboot-level configurations, kernel-stage modifications, and the all-important parameter adjustments required to seamlessly migrate your screen technology.
By understanding the intricacies of both MIPI and LVDS displays, you’ll be equipped to navigate the challenges of cross-platform integration, ensuring a smooth and efficient transition for your embedded system.
Embark on Your Screen Porting Journey with Confidence Mastering the art of screen porting is essential for embedded system developers who strive to deliver exceptional user experiences. This comprehensive guide equips you with the knowledge and strategies to tackle the complexities of MIPI and LVDS screen integration, empowering you to tackle even the most daunting screen porting challenges with confidence.
Ready to take your embedded system to new heights? Dive into the insights and best practices outlined in this article and revolutionize your screen porting process today.
A Comprehensive Guide to Screen Porting for the Forlinx Embedded 8M Series
-
Presenting the OK3588-C Development Board Featuring the Rockchip RK3588
05/28/2024 at 06:57 • 0 commentsIntroduction:
In March of this year, I attended the Embedded World Exhibition, which focuses on embedded systems. During my visit, I explored the Forlinx booth. Forlinx is renowned for developing System on Modules (SoMs) and Evaluation Boards for industrial PCs. I previously acquired an evaluation board from Forlinx last year. This year, I am excited to present the new Forlinx OK3588-C board in this video.
Presenting the OK3588-C Development Board (featuring a Rockchip RK3588)
Today, we will explore the Forlinx OK3588-C board. Allow me to switch off the camera and transition to the desktop view.
Here, I have the hardware manual for the OK3588 board. If you require this hardware manual or the necessary SDKs to develop software for this board, please contact Forlinx, and they will provide you with the required resources.
SoM Appearance Diagram:
The evaluation board comprises two primary components. Firstly, this is the physical appearance. Here, we have the System on Module (SoM) mounted on a carrier board, which connects all peripherals to the SoM.
Let's begin by examining the System on Module. This module includes the Rockchip RK3588 main processor, two DRAM ICs, and eMMC storage for non-volatile data. Various components on the module generate the required voltages for the chip's operation. The Rockchip RK3588 is a robust processor.
RK3588 Description:
Displayed here is a block diagram of the RK3588. It features a dual-cluster core configuration. One cluster consists of a quad-core Cortex-A76 processor clocked at 2.6 GHz, and the second cluster includes a quad-core Cortex-A55 processor, clocked at either 1.5 or 1.8 GHz. This setup allows for power-saving capabilities by disabling the A76 cores when full performance is not required.
Another notable feature is the high-performance Neural Processing Unit (NPU), which is advantageous for tasks related to artificial intelligence and machine learning. In the future, I hope to demonstrate the NPU's capabilities.
The chip also includes a multimedia processor supporting various video decoders, even up to 8K resolution, and an embedded Mali-G GPU. For external memory interfaces, it has two eMMC controllers and support for LPDDR4 and LPDDR5. Additionally, it includes standard system peripherals, such as USB OTG 3.1, PCIe interfaces, Gigabit Ethernet, GPIO, SPI, and I²C.
Development Board Interface Description:
The carrier board includes numerous peripherals. There is a 12V power supply, a power switch, a reset switch, up to five camera connectors, microphone and speaker connectors, USB 2.0 host, and two USB 3.1 OTG ports. These USB ports can function as either hosts or devices. It also features two HDMI ports (one input and one output), a real-time clock with a battery, eDP ports, ADC connectors, an SD card slot, a fan connector, and M.2 slots for Wi-Fi and cellular cards.
The board also includes two full-size PCIe connectors, user buttons, CAN interfaces, an RS485 interface, a USB-to-serial adapter, and two Gigabit Ethernet ports. The overall setup is impressive.
Operation:
Let's power on the board. I have also connected a PCIe card to a free slot. Before proceeding, let's open the serial terminal to monitor the output.
The board is booting, and the kernel is starting successfully. Currently, we are running a minimal BusyBox root file system. In a future video, I will demonstrate how to build a custom Linux for this board. For now, this setup is sufficient.
We are running kernel version 5.10.66, built for ARM64 architecture. The board has eight processors, consisting of different Cortex-A cores. The available memory is 3.6 GB, with 155 MB currently in use. Background processes and the Mali GPU likely consume some memory.
We have eight I²C buses available, with one connected to the display connector for Display Data Channel (DDC) management.
The eMMC storage has multiple partitions. The board features seven...
Read more -
Implementation of Forlinx RK3568 SoM Automatic Screen-off Configuration Program
05/24/2024 at 09:01 • 0 commentsSoftware version: Linux 4.19
Design Idea: Detect screen touch events to determine whether the screen is being used or not in an auto-break application. If the screen detects input events, it will remain on. If no touch events are received for a period of time, the screen will transition from on to a dimmed state, reminding the user that it is about to enter the screen-off mode. If no touch events occur after dimming, the screen will enter the screen-off mode. When a touch event occurs again, the screen will transition from screen-off mode to the on state.
Currently, the approach to implement automatic screen-off is to treat touch events as a fixed path that can be applied to familiar boards. To enhance convenience in application, two additional alternative approaches are provided below:
▊ The first implementation method
You can apply the evtest command to get the path to/dev/input/event1 (event1 is the name of the touch event on my board). You can then pass the path to your program as a parameter.
For example, you can modify your program to accept command-line arguments to specify the path of the device file to open
int argc, char *argv[];
Opens a file with the passed in parameters as the device file path
int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
You can compile and run the program, passing it/dev/input/event1 as a command-line argument, like this:
./your_program /dev/input/event1
▊ The second implementation method is to fix the screen touch node in the device tree.
Look for the screen touch node in the device tree and note its address.
On the I2C bus, the address of the touch node is simply 2-0038
So we can use grep to filter out touch nodes based on their addresses.
ls -l /sys/class/input | grep "0038" | awk -F ' ' '{print $9}' | grep "event"
The following command is used in the application to find the touch event based on the touch address.
char *command_output = exec("ls -l /sys/class/input | grep '0038' | awk -F ' ' '{print $9}' | grep 'event'"); Use the sprintf function to splice the path containing the event, and then read the event. Examples of using Sprintf: int main() { char str[100]; int num = 123; float f = 3.14; //Write the formatted data to the string sprintf(str, "%d%.2f", num, f); //print the generated string printf("The output is. %s\n", str); return 0; } -
Application of Automatic Screen-off Function and Power Management Technology Based on T507
05/22/2024 at 06:23 • 0 commentsSome customers rely on battery power for their products and have limited battery capacity. If a screen is used in the product, the screen will be one of the main sources of energy consumption. Therefore, turning off the screen in time can effectively extend the battery life and improve the user experience. In addition, the auto-screen-off function not only extends the life of the screen but also effectively prevents the risk of information leakage and privacy exposure. Generally speaking, the automatic screen-off function plays an important role in improving the performance of the device, saving energy and protecting privacy.
Knowledge points involved:
1. Struct input _ event: a data structure used to represent Linux input event
This structure usually contains various information of the input event, such as event type, event code, value, etc. When dealing with input devices such as keyboards and mice, you can use this structure to store and pass information about input events.
Specifically, the struct input _ event structure typically contains the following fields:
- Struct timeval time: The timestamp of the event occurrence.
- Unsigned short type: The type of event (e.g., key press, release, etc.)
- Unsigned short code: Code of the event (such as which key was pressed).
- Int value: The value of the event (key press/release, etc.)
By defining such a structure, it is easy to package together the various attributes of an input event for processing and passing in the program. When reading the events of the input device, this structure can be used to store the specific information of each event, which is convenient for subsequent analysis and response to the input events.
2. Functions and differences of read function and select function
The read () function and the select () function are both functions used in Linux systems to handle I/O operations, but there are some differences in what they do and how they are used.
(1)Read () function:
The read () function is used to read data from a file descriptor, such as a file, socket, and so on.It is a blocking system call, that is, when there is no data to read, the program will be blocked until there is data to read or an error. The read () function reads data from the file descriptor into the specified buffer and returns the actual number of bytes read, or -1 if an error occurs.
(2)Select () function:
The select () function monitors multiple file descriptors to determine whether they are in a readable, writable, or abnormal state.
Through the select () function, multiplexing can be achieved, that is, one of multiple file descriptors is selected for I/O operation without blocking and waiting. The select () function blocks the process until at least one of the specified file descriptors is in a readable, writable, or exception state, or the specified timeout has passed. The select () function is usually used to listen to multiple file descriptors at the same time, so that when any file descriptor is ready, the corresponding read and write operations can be performed to improve the efficiency of the program.
In summary, the read () function is a blocking operation to read data from a single file descriptor, while the select () function is a function to multiplex the state of multiple file descriptors to help the program manage multiple I/O operations more efficiently. The select () function is typically used in situations where you need to listen to multiple file descriptors at the same time.
In the program, events are read from the input device through the read () function. If no event is reported, the read () function blocks the program and does not return until an event occurs or an error occurs. Therefore, if there is no event reported, the program will stay at the read () function and will not perform subsequent printing operations. If an event is reported, the read() function reads the event data and returns the number of bytes of the event. In this case, the program...
Read more -
Unveil Power | Let's Explore Forlinx Embedded Development Lab
05/17/2024 at 06:47 • 0 commentsThe research and development laboratory serves as the technological backbone and innovation engine of a high-tech enterprise, equipped with complete facilities, standardised processes, and strict standards. This guarantees the advanced functionality, stable operation, and reliable quality of products in the face of intense market competition, enabling them to stand out. Over the past eighteen years, the R&D laboratory has played a vital role in helping tens of thousands of companies get their products to market quickly, and in providing thousands of companies with a stable batch supply of boards and other products. Behind these impressive achievements is the robust support provided by the R&D laboratory.
Self-built multi-million labs, testing in line with stringent national standards
Folinx Embedded Three R&D laboratories: a Physical Environment Laboratory, an Electromagnetic Compatibility Laboratory, and a Stability Laboratory. There are total 10 major items, each designed to simulate the extreme conditions that may be encountered in real-world applications. This ensures that the product is able to perform in a wide range of complex environments.
1. Physical environment laboratory
(1) High and low temperature/temperature change/humidity test
High and low temperature test: The operating environment temperature of the equipment (product) can have a certain impact on the normal operating performance of the equipment, and in severe cases, it can lead to equipment failure or damage. High and low temperature test is to examine the adaptability of electronic and electrical products to such environmental temperatures—by simulating extreme high temperatures (up to +125°C) and low temperatures (down to -55°C), testing the product's performance under extreme temperatures.
Temperature variation test: It requires the high and low temperature test chamber. It assesses the product's ability to withstand such environmental temperature changes through one or multiple rapid temperature change tests.
Humidity Test: Changes in environmental temperature or humidity can have a certain impact on the normal operating performance of equipment. In severe cases, this can lead to equipment failure or damage. Humidity test: It examines the adaptability of electronic and electrical products to such environmental temperature and humidity changes. Humidity range is 20% ~ 98% RH.
High and Low Temperature and Humidity Test Chamber
(2) Vibration test/shock/impact test
Vibration Test is conducted to simulate the various vibration environmental impacts that the product may encounter during transportation, installation and use. The test is used to determine whether the product can withstand the vibration of various environments. The frequency range is 2-2000 Hz, with a maximum vibration acceleration of up to 981 m/s².
Shock/Impact Test is a standard method used to assess the safety, reliability and effectiveness of a product when subjected to external impact or action. This test simulates the impacts and collisions that the product may be subjected to in use. It covers half-sine, front-peak sawtooth, back-peak sawtooth, triangular, rectangular, trapezoidal, and bell-shaped waves, with a rated thrust of 10kN(1000kgf).
Vibration Test System
(3) Salt Spray Test
Some customers will use the product in a salty and humid environment, so the salt spray test is needed. The salt spray test simulates the climate environment of the ocean or salty and humid areas, and is used to examine the salt spray corrosion resistance of products, materials and their protective layers.
Salt Spray Corrosion Chamber
(4) Drop Test
To assess the resilience of a product to a fall due to careless handling during moving, Forlinx Embedded employs a drop tester to simulate the accidental dropping of a product. This verifies the structural integrity and functional retention of the product or determines the minimum level of robustness required for safety...
Read more -
Forlinx FCU2303 5G Smart Gateway for Smart Ambulances
05/15/2024 at 02:30 • 0 commentsIn modern cities, the medical rescue system is crucial for urban safety. Emergency centers command rescue operations, essential for saving lives. With the advancement of IoT technology, many cutting-edge technologies are gradually integrated into the medical emergency system, enabling ambulances to be networked, digitized, and intelligent. Thus, 5G smart ambulances emerge. 5G-enhanced ambulances look similar to regular ones in appearance. However, by integrating 5G networks into the vehicle, developers instantly endowed it with additional "superpowers".
For instance, 5G-enhanced ambulances can achieve synchronized transmission of multiple high-definition live videos, leveraging 5G's high bandwidth, low latency, and reliability. Based on this, it can synchronously return the medical images, patient signs, illness records and other information of emergency patients to the hospital emergency center without damage, which is convenient for the emergency center to grasp the patient's condition in advance and give professional guidance to the rescuers on the bus.
Forlinx's 5G Smart Gateway FCU2303 provides reliable support for medical ambulance.
Rapid transmission of information
Bridge the gap for medical device information transmission.
Modern ambulances are equipped with advanced medical equipment such as electrocardiogram monitors, ventilators, and defibrillators to enhance rescue efficiency. Various types of diagnostic and therapeutic equipment can efficiently transmit physiological data to the Hospital Information System (HIS) through the multiple Ethernet ports, serial ports, and DI/DO of the FCU2303 industrial-grade smart gateway. This meets the data collection and transmission requirements of ambulances.
Enabling high-definition audio and video consultations
Medical imaging equipment such as cameras, microphones, displays, and ultrasound machines are deployed on the ambulance. Through the FCU2303 industrial-grade smart gateway, information is transmitted, providing real-time, lossless transmission of audio-visual images from the ambulance to the hospital emergency center. This setup offers a high-bandwidth, low-latency, and highly connected secure network, meeting the remote video consultation needs of the ambulance. It aims to secure more time for patients by implementing a rapid rescue and treatment mode where patients essentially “Be in the hospital” upon boarding the ambulance.
Enabling reliable integration of multiple technologies
- FCU2303 Smart Gateway, designed based on the NXP LS1046A processor, features a quad-core CPU with a high clock frequency of 1.8GHz. With a fanless design, it ensures stable operation of medical rescue systems for extended periods in environments ranging from -40°C to +85°C;
- It supports 5G and 4G modules, which can be easily switched with a single DIP switch. It provides users with high bandwidth, low latency, and large connectivity services. It also supports dual-band Wi-Fi, enabling both STA and AP modes;
- FCU2303 supports expandable device storage with PCIe 3.0 high-speed interface, enabling support for solid-state drives (SSDs) using the NVMe protocol (M.2 interface). This meets the requirements for small size, large capacity, and fast speed;
- It comes standard with 8 x Gigabit Ethernet ports (flexible configuration of 2/4/6/8 ports, all with independent MAC addresses), 4 RS485 ports, 4 RS485/RS232 multiplexing interfaces, 2 DI (Digital Input), 2 DO (Digital Output), and 1 USB HOST 3.0 port. This ensures the connectivity of various medical devices, enabling full vehicle networking for ambulances;
- The software integrates a variety of third-party components including Samba, Lighttpd, Docker, IPSEC, OpenSSL, and Python 3 or higher versions. It supports protocols such as TCP/IP, UDP, DHCP, TFTP, FTP, Telnet, SSH, Web, HTTP, IPtables, and provides an open system API for easy user customization and development.
In the future, smart ambulances...
Read more -
Efficient Solution for Electrical Fire Monitoring System Based on FET6254-C SoM
05/08/2024 at 09:26 • 0 commentsAccording to global fire statistics, about 30% of fires are caused by electrical faults, with as much as 70% of these fires being preventable and avoidable through technical means. Electrical fire monitoring systems are a technical means to detect early signs of fires such as current leakage and abnormal temperature increases. By triggering alarms promptly, they significantly reduce the probability of electrical fires occurring.
The electrical fire monitoring system is specifically designed to monitor electrical equipment and circuits in real time, aimed at preventing, detecting, and promptly responding to the fire risks caused by electrical faults. By integrating diverse sensors and advanced monitoring devices, the system continuously monitors key parameters such as current, voltage, and temperature, thereby ensuring the safe and stable operation of the electrical system.
Application Scenarios
Electrical fire monitoring system is widely used in all kinds of residential, commercial buildings and industrial facilities. As the number of modern electrical equipment increases, so does the risk of electrical fires. The system can monitor the status of electrical equipment in real-time, detect potential safety hazards in time, and effectively prevent fire accidents through the alarm and automatic control functions, thus ensuring the safety of people's lives and property.
Product Features
Real-time and Accurate Monitoring: The system can continuously monitor various parameters of electrical lines and equipment around the clock, such as current, voltage, temperature, etc., to ensure that any abnormality can be found in time.
Efficient Early Warning Response: Once a potential fire risk is detected, such as overloading, short-circuiting, or temperature abnormality, the system triggers an alarm immediately and informs the relevant personnel quickly using acoustic and visual signals or remote notification.Stable and Reliable Operation: The product is manufactured with industrial-grade design standards and high-quality materials to ensure stable operation in various harsh environments and reduce the possibility of false alarms and missed alarms.
Intelligent Data Analysis: The system provides real-time monitoring functions and collects and analyses historical data to help users identify potential problems in the electrical system, providing strong support for preventive maintenance.
Combined with the product characteristics of the electrical fire monitoring system, Forlinx Embedded recommends the FET6254-C platform as the hardware design solution for the main control unit of the electrical fire monitoring system.
FET6254-C embedded board exhibits the following significant advantages:
- Performance and Reliability: Adopts a quad-core industrial-grade processor with Arm Cortex-A53 architecture to ensure high-speed and stable operation performance.
- Interface Richness: FET6254-C provides a variety of interfaces including LVDS, Gigabit Ethernet, UART, CAN-FD, etc., which comprehensively meets the demand for hardware interfaces in the monitoring system and ensures efficient and accurate data transmission and smooth connection of devices.
- Dual-core Architecture: FET6254-C has independent M-cores and A-cores, which run without interfering with each other. The M-core is used to interface with other modules (e.g. emergency lighting, emergency alarms) to guarantee the continuous execution of critical tasks, and even if the A-core system fails, the M-core can still work normally to maintain system stability.
- Flexible Scalability: The modular design of the FET6254-C enables the system to respond easily to a variety of customized requirements and achieve flexible expansion.
In summary, the hardware solution for electrical fire monitoring systems based on the FET6254-C SoM, with its rich interface resources, high-performance processing capabilities, unique dual-core architecture, and flexible scalability,...
Read more -
Kernel Trimming Ideas Based on the T507 Linux System
05/07/2024 at 03:04 • 0 commentsPurpose of Trimming
Customers sometimes have certain requirements for the boot time after power-on, so it is necessary to tailor the kernel to optimize the boot time and reduce it. Low system power consumption.
Brief Introduction to Makefiles, Kconfig and .config Files
- Makefile: A file in text form that compiles the source files
- Kconfig: A file in text for the kernel's configuration menu.
- .config: The configuration on which the kernel is compiled
- Kconfig and Makefile files are usually present in the directory structure of the Linux kernel.
- Distributed at all levels of the catalogue
- Kconfig constitutes a distributed database of kernel configurations, with each Kconfig describing the kernel associated with the source files of the directory to which it belongs.
- Configuration menu. Read out the configuration menu from Kconfig when the kernel graphically configures make menuconfig, and save it to.config after the user finishes the configuration.
- When the kernel is compiled, the main Makefile calls this.config to know how the user has configured the kernel.
Introduction to Makefile and Kconfig Syntax
● Makefile
The Makefile subdirectory is contained by the top-level Makefile. It is used to define what is compiled as a module and what is conditionally compiled.
(1) Direct compilation obj-y +=xxx.o
It means that xxx.o is compiled from xxx.c or xxx.s and compiled directly into the kernel.
(2) Conditional compilation obj-$(CONFIG_HELLO) +=xxx.o
The CONFIG_XXX of the .config file determines whether a file is compiled into the kernel or not.
(3) Module compilation obj-m +=xxx.o
It means that xxx is compiled as a module, i.e. it is compiled when make modules is executed.
● Kconfig
Each config menu item has a type definition. bool: boolean type, tristate: three states (built-in, module, remove), string: a sequence of characters, hex: hexadecimal, integer: a whole number
Function: determine the menu item displayed when make menuconfig.
1) NEW _ LEDS: The name of the configuration option. The prefix "CONFIG _" "is omitted.
2) tristate: Indicates whether the item is programmed into the kernel or into a module. The display as < >, if selected to compile as a kernel module, it will generate a configuration CONFIG_HELLO_MODULE=m in .config. Choosing Y will directly compile into the kernel, generating a configuration CONFIG_HELLO_MODULE=y in .config.
3) bool: This type can only be checked or unchecked. It is displayed as [ ] when making menuconfig, that is, it cannot be configured as a module.
4) dependon: This option depends on another option, only when the dependon is checked, the prompt message of the current configuration item will appear to set the current configuration item.
5) select: Reverse dependency, when this option is checked, the item defined after select is also checked.
6) help: help information.
tristate and bool followed by strings are the configuration item names displayed in make menuconfig.
Definitions in Kconfig like "menuconfig NEW_LEDS" or "menu "Video support for sunxi"" are typically top-level directories of a directory, where in menuconfig you can directly trim the corresponding driver by searching for that configuration item.
Catalogue Hierarchy Iteration :
In Kconfig, there are statements like "source "drivers/usb/Kconfig"" used to include (or nest) new Kconfig files, allowing each directory to manage its own configuration content without having to write all those configurations in the same file, making it easier for modification and management.
Partially Driven Tailoring
1. Tailoring Ideas
Taking the GPADC function as an example, the location of the driver in the source code kernel is:drivers/input/sensor/sunxi_gpadc.c,
So we can go to the Kconfig file in that path, and directly search for "menu” in the Kconfig file, which generally corresponds to the top-level directory of that driver.
We can see that the configuration option is named INPUT_SENSOR, corresponding...
Read more -
Forlinx RK3588 SoM Circuit Problems: MaskRom Mode Entry Causes and Solutions
04/26/2024 at 02:31 • 0 commentsProblems Description:
When using the Forlinx RK3588 SoM and a homemade carrier board, the system enters MaskRom mode as soon as it's powered on. The difference between the Forlinx carrier board and the homemade carrier board lies in the value of the ground capacitors in Figure 1, where one is 10uF and the other is 100nF.
Solutions:
The MaskRom mode of OK3588-C can only be pulled low to GND by the BOOT _ SARADC _ IN0 when the CPU starts to detect.
The OK3588-C development board enters MaskRom mode by tapping the BOOT _ SARADC _ IN0 to GND. As shown in the figure 1: This part of the circuit has a 100 nF capacitor C3 to ground. If this capacitor is replaced with a larger one, such as a 10 uF capacitor, it will cause the development board to enter MaskRom mode as soon as it is powered on.
Figure 1
This is because capacitors have the property of blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass, and they also exhibit charging and discharging characteristics. When the power is turned on, the capacitor charges instantaneously, and the voltage across the capacitor cannot change abruptly. Initially, the voltage across the capacitor is zero while it charges, and then it rises exponentially according to a certain pattern until it reaches a steady state. Entering a steady state is equivalent to an open circuit. The charging process is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2
The charging and discharging time of a capacitor increases as its capacitance value increases. A 10uF capacitor has a longer charging time, and it enters a steady state slowly. When the OK3588-C SoM starts up, if the CPU detects that the signal level of the BOOT_SARADC_IN0 pin is within the low voltage range, it assumes that this pin is pulled to GND, thus entering MaskRom mode. The solution is to remove the 10uF capacitor or replace it with a 100nF capacitor.
-
Pressure Displacement Profile Analyzer Solution Based on FETMX8MM-C SoM
04/23/2024 at 05:36 • 0 commentsPressure displacement analyzer is a professional instrument used to measure the deformation of materials under force. It can measure the pressure, strain, displacement and other mechanical parameters of the material, and analyze and process the parameters through the built-in software system and algorithm, so as to obtain the mechanical properties of the material. Pressure and displacement analyzer is widely used in material science, machinery manufacturing, construction engineering, aerospace and other fields.
With the continuous progress of science and technology and the rapid development of industrial manufacturing, the requirements for the mechanical properties of materials in industrial production are also rising, so more accurate and reliable measuring instruments are needed to meet the demand. The emergence of stress-strain displacement analyzers fills the gap in material mechanics performance testing equipment, greatly enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of material testing.
The characteristics of stress-strain displacement analyzers to be considered during use include:
- High-precision measurement: It can measure the displacement change of the object under the action of pressure with high precision to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the measurement results;
- High reliability: It can measure stably for a long time under extreme conditions, and is suitable for various complex environments and application scenarios;
- The operation is simple, and the complex measurement task can be realized through simple operation, so that the work efficiency is improved;
- Multi-functional: It can perform various functions such as automatic recording, data processing, result analysis, and report generation to meet the needs of different application scenarios;
- Intuitive display: Pressure displacement analyzers usually have LCD displays, which can intuitively display measurement results and parameters, making it easy for users to carry out real-time monitoring and data analysis;
- Convenient data processing: Measurement data can be stored in the internal memory or external devices, and support a variety of data format export, convenient for users to carry out later data processing and analysis.
Forlinx Embedded recommends using FETMX8MM-C as the product implementation solution.
In this solution, the main functions of the i.MX8MM-C SoM are:- The human-machine interaction module displays real-time data transmitted from the MCU via MIPI, and performs drawing and data display;
- Data processing and storage is achieved through USB interface conversion to ULPI LINK for communication with the MCU end. Data is received and stored in TF cards or USB drives, then processed to output in a more concise and understandable form;
- Network transmission and remote control are facilitated through a Gigabit Ethernet port, allowing for remote monitoring of screens, network backups, and system parameter restoration.
Advantages:
- Equipped with an ARM Cortex-A53 quad-core CPU running at 1.8GHz and paired with 2GB of DDR4 RAM, it offers high performance and computational power, providing a significant advantage in data processing;
- The compact size of only 56mm * 36mm meets the requirements of miniaturization and portability of equipment and reduces the size of products;
- Support 4-line mipi display, maximum 1.5g bps transmission, high-definition output image;
- Long supply cycle, join NXP product long-term supply plan, guarantee at least 10 years of supply period;
- The operating environment temperature ranges from -40°C to 85°C, meeting the requirements for industrial and general industrial applications.
The above is the pressure displacement curve analysis solution provided by Forlinx Embedded based on the FETMX8MM-C SoM. We hope it can assist you in your selection process.
-
Forlinx Embedded AM62x SoM, Empowering a New Generation of HMI
04/19/2024 at 01:23 • 0 commentsHMI (Human-Machine Interface) is a medium for interaction and information exchange between systems and users. It is essential in fields involving human-machine communication and can be seen in many industries. As technology advances, HMI continues to evolve. In addition to data collection, control, and display, future HMI will incorporate new interactive forms to enable machines to operate more intelligently and interact more efficiently with humans.
The increasing demand for more intelligent human-machine interactions also raises higher requirements for processors used in HMI applications. To assist engineers with terminal development requirements in selecting the main controller, in this article, the author will provide a detailed explanation of the three key elements that will influence the next generation of HMI.
Smarter Interaction
AI support will help the new generation of HMI achieve more powerful functions. For example, AI face recognition can be used to realize human access to devices, and AI gesture recognition can also be used to realize contactless control between people and devices. At the same time, it also allows the equipment to monitor and analyze the current system status more accurately. For example, in the medical field, intelligent HMI systems can allow doctors to interact with medical devices through gestures.
Balance of Power Consumption And Performance
AI function support puts forward higher requirements for the performance of processors, and the high integration and performance improvement of chips will inevitably increase power consumption and generate more heat. In order for devices with limited size to be able to adapt to a more diverse and complex environment, it is very important to have multiple power consumption mode options - the freedom to choose between high power consumption, low power consumption, and ultra-low power consumption modes. This not only allows performance to be properly optimized but also helps to better control costs, achieving a balance between power consumption and performance.
Enhanced Communication Capabilities
The increase in real-time industrial communication protocols has also brought new challenges to the new generation of HMI applications. For example, the HMI applied in the smart factory not only needs to carry the task of exchanging information between people and equipment, but also needs to complete the function of communicating with other machines and equipments, which means that the HMI needs to have a stronger connection and control function.
FET6254-C SoM launched by Forlinx Embedded not only meets the traditional HMI's human-computer interaction needs but also can realize the three key elements mentioned above, empowering the new generation of HMI.
FET6254-C System on module is built on the TI Sitara™ AM6254 industrial-grade processor, featuring a quad-core Arm Cortex-A53 architecture with a maximum frequency of up to 1.4GHz. It enables edge AI capabilities, making the HMI smarter and more intelligent. During the development process, rigorous environmental temperature testing, pressure testing, and long-term stability testing were conducted to ensure that it can operate stably in harsh environments.
Not only the performance is guaranteed, but also the power consumption can be very low. Through a simplified power architecture design, the AM62x processor exhibits extremely low power consumption performance, with power as low as 5mW in deep sleep mode. With a core voltage of 0.75V, the operating power can be kept below 1.5W, greatly reducing system power consumption.
AM62x processor, as the next-generation MPU product in the TI Sitara™ product line, offers richer resource interfaces compared to the previous generation classic processor, the AM335x. It includes features such as 2 x Gigabit Ethernet with TSN support, 3 x CAN-FD, 9 x UART, 2 x USB 2.0 , 2 x LVDS interfaces, RGB, camera, audio, and more. This enhances the product's scalability...
Read more -
Steps for Reading and Modifying U-Boot Environment Variables at the Kernel Stage
04/17/2024 at 02:30 • 0 comments1. Compile the fw_printenv tool
Execute under the uboot source path, and then generate the executable file of the fw _ printenv under tools/env.
. /opt/fsl-imx-x11/4.1.15-2.0.0/environment-setup-cortexa7hf-neon-poky-linux-gnueabimake env
2. Configure fw_env.config file
Modify the fw_env.config file under tools/env in the uboot source directory according to the mtd partition, the location and size of the UBOOT environment variables, etc. See the instructions in the fw_env.config file and the /tools/env/README file for specific modifications.
Among them, Device offset, Env size, and Flash sector size should correspond respectively to the three macro definitions CONFIG_ENV_OFFSET, CONFIG_ENV_SIZE, and CONFIG_ENV_SECT_SIZE in the include/configs/xxxx.h file in the U-Boot source code directory.
vi include/configs/mx6ul_14x14_evk.h
Take the test 256nand as an example:
CONFIG_ENV_OFFSET = 0x600000
ONFIG_ENV_SECT_SIZE = 0x20000
Open the tools/env/fw_env.config and modify as shown in the following figures:
Take the test 1gnand as an example:
CONFIG_ENV_OFFSET = 0x1000000
ONFIG_ENV_SECT_SIZE = 0x20000
nand model number MT29F8G08ABACA
Refer to the manual to change the ENV_SECT_SIZE value to 256K.
Open the tools/env/fw_env.config and modify as shown in the following figures:
nand model number MT29F8G08ABABA
Refer to the manual to change the ENV_SECT_SIZE value to 512K.
Open the tools/env/fw_env.config and modify as shown in the following figures:
3. Copy the file
Copy tools/env/fw_env.config to the /etc path of the development board;
Copy tools/env/fw_printenv to the root file system of the development board under the path /usr/bin.
And create a soft link to fw_setenv ln -s /usr/bin/fw_printenv /usr/bin/fw_setenv
4. Read and write environment variable test
Read environment:
Write environment variable:
The uboot phase has been modified synchronously.
5. Problems and solutions
Problem: make env reports an error in the uboot source code
Solution: Comment out the CC in the top-level Makefile and use the environment variable in the CC.
-
FET-MX8MPQ-SMARC System on Module Based on NXP i.MX 8M Plus Processor
04/16/2024 at 02:21 • 0 commentsFET-MX8MP-SMARC System on Module(SoM) is developed based on the NXP i.MX 8M Plus processor, focusing on machine learning, vision, advanced multimedia, and highly reliable industrial automation. It caters to applications such as smart cities, industrial IoT, smart healthcare, and intelligent transportation.
With powerful quad-core or dual-core ARM® Cortex®-A53 reaching up to 1.6GHz and an NPU achieving 2.3 TOPS, it integrates ISP and dual camera inputs for efficient advanced vision systems. Multimedia features include video encoding (including H.265) and decoding, 3D/2D graphics acceleration, and various audio and voice functions. Real-time control is achieved through Cortex-M7, with a powerful control network using CAN-FD and dual Gigabit Ethernet, supporting Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN).
It features high-speed communication interfaces such as 2 x USB 3.0, 1x PCIe 3.0, and 1x SDIO 3.0, meeting the requirements of 5G networks, high-definition video, dual-band WiFi, high-speed industrial Ethernet, and other applications.
FET-MX8MP-SMARC SoM
High-speed Communication Interface
4K Picture Quality and HiFi Voice Experience
HDMI interface supports up to 4K display output; it also features LVDS, MIPI-DSI display interface, the latest audio technology,
Cadence® Tensilica® HiFi 4 DSP @ 800 MHz, 18x I2S TDM, DSD512, S/PDIF Tx + Rx, 8-channel PDM microphone input, eARC, ASRC.Advanced Multimedia Technology
3D/2D Graphic Acceleration
Machine Learning and Vision
Built-in NPU with 2.3 TOPS of AI computing power to meet lightweight edge computing needs
Dual Image Signal Processor (ISP)
Product Application
Carrier Board
![NXP i.MX 8M Plus SMARC Development Board]()
OK-MX8MPQ-SMARC Development Board
To minimize your development workload, we can provide starter kits that can be used as complete development platforms for evaluation and application development.
OK-MX8MPQ-SMARC Single Board Computer from Forlinx is powered by the i.MX 8M Plus processor from NXP, featuring 4x Cortex-A53@1.6GHz + 1x Cortex-M7, 2GB/4GB LPDDR4 RAM, and 16GB/32GB eMMC ROM. With a split design and 314 pins, it offers seamless functionality and ease of customization and supports Linux 6.1.36 system. Featuring open system architecture design, it can provide technical information for your secondary development.Explore more about this SoM now!
-
Display and Modification of LVDS Display Interface on AM62x Development Board
04/09/2024 at 02:55 • 0 comments1. LVDS Interface Specification
Forlinx Embedded OK6254-C development board provides 2 x 4-lane LVDS display serial interfaces supporting up to 1.19Gbps per lane; the maximum resolution supported by a single LVDS interface is WUXGA (1920 x 1200@60fps, 162MHz pixel clock).
In addition, the interface supports the following three output modes:
- (1) Single-channel LVDS output mode: at this time, only 1 x LVDS interface displays output;
- (2) 2x single-channel LVDS (copy) output mode: in this mode, 2 x LVDS display and output the same content;
- (3) Dual LVDS output mode: 8-lane data and 2-lane clock form the same display output channel.Forlinx Embedded OK6254-C development board is equipped with dual asynchronous channels (8 data, 2 clocks), supporting 1920x1200@60fps. All signals are by default compatible with Forlinx Embedded's 10.1-inch LVDS screen, with a resolution of 1280x800@60fps.
2. Output Mode Setting
(1) Single LVDS output mode:
We need a single LVDS screen cable. The black port of the cable is connected to the embedded OK6254-C development board, and the white port is connected to the embedded 10.1-inch LVDS display screen. Connection method as shown in the figure below:
Note that the red line section corresponds to the triangle position, so don't plug it in wrong.
(2) 2x single LVDS (duplicate) output mode:
This mode uses the same connections as the Single LVDS Output Mode. Two white ports link to two 10.1-inch LVDS screens from Forlinx Embedded, and a black port on the right connects to the OK6254-C board's LVDS interface for dual-screen display.
(3) Dual LVDS output mode:
The maximum resolution supported by a single LVDS interface on the OK6254-C development board is WUXGA (1920 x 1200@60fps). To achieve this high-resolution display output, dual LVDS output mode is required.
It is worth noting that the connection between the development board and the screen in this mode is the same as in [Single LVDS Output Mode], but the LVDS cable's and the screen's specifications have been improved.
3. Screen Resolution Changing Method
OK6254-C development board device tree is easy to modify, we need to open the OK6254-C-lvds.dts (single 8-way configuration) and OK6254-C-lvds-dual.dts (dual 8-way configuration) files.
Open OK6254-C-lvds.dts
Open OK6254-C-lvds-dual.dts
The above figure is the single LVDS and dual LVDS screen resolution information, the default resolution of 1024 * 600, and the maximum resolution support of 1920x1200, you can modify the corresponding parameters according to the Screen User’s Manual.
4. Compilation Configuration
Because we only modified the device tree, we don't need a full compilation. After compiling the kernel, a new Image and multiple device tree files will be generated in the images directory. Here we only need to compile the kernel separately.
- (1) Switch directory: cd OK6254-linux-sdk/
- (2) Execution environment variables:.. build.sh
- (3) Execute the instructions that compile the kernel separately: sudo./build. Sh kernel.
- (4) Pack all the device tree files to the development board /boot/ directory and replace them, then sync save and reboot scp images/OK6254-C* root@172.16.0.225:/boot/
We have modified the corresponding file. How should we select the screen after replacing it?
At present, there are three kinds of screen switching control methods: kernel device tree designation, Uboot menu dynamic control, Forlinx Desktop interface and Uboot menu application. Today, I will briefly introduce the dynamic control of Uboot menu.During Uboot, pressing the space bar will take you to the Uboot menu. There are three options in the menu:
Enter 0 to enter the Uboot command line;
Enter 1 to restart Uboot;
Enter 2 to enter the Display Configuration menu.
There are three options in the menu:
Enter 0 to return to the previous menu;
Enter 1 will toggle what option 1 displays to configure Screen 1 LVDS; Note: Screen 1 supports single LVDS, dual LVDS, and off (i.e., LVDS...
Read more -
With AMP Dual System Support, RK3568 SoM Boosts Real-Time Performance
04/02/2024 at 06:50 • 0 commentsWhat is AMP?
AMP (Asymmetric Multi-Processing) can be simply described as: Each core of a multi-core processor is isolated from the others, enabling them to run different operating systems or bare-metal (unmodified or native) programs relatively independently. This operational mode is particularly suitable for applications requiring high real-time performance.
FET3568-C SoM AMP
The RK3568 processor on Forlinx's FET3568-C SoM features a quad-core Cortex-A55 architecture, classified as a homogeneous multi-core design.
The main difference between the RK3568's AMP SDK and Linux SDK lies in the different multiprocessor modes they use. The Linux SDK adopts the SMP mode, where a single Linux operating system manages all cores; while the AMP SDK uses the AMP mode, which divides the cores into two parts, with one part running the Linux operating system and the other part running bare-metal programs.
The bare-metal program operating mode, due to its direct hardware access characteristics, can efficiently handle high real-time tasks, meeting the stringent requirements for real-time performance in areas such as smart grid, power grid protection, power system security control, and industrial automation.
Advantages
(1) Lower cost:
The traditional approach to address the insufficient real-time performance of Linux system control is to use an external microcontroller to specifically execute high real-time programs.
The AMP system on the FET3568-C SoM simplifies the hardware architecture and reduces the hardware cost by separating a core as a real-time core to perform high real-time tasks.
(2) High real-time performance:
Because of the low real-time nature of the Linux system, it cannot be used to perform tasks that require high real-time performance. The real-time performance of bare-metal program or real-time operating system is much better than that of Linux system, while the high frequency of FET3568-C SoM makes A55 core have powerful real-time performance when running real-time system.
Inter-core Communication
Like other processors with multi-core heterogeneous architectures, AMP uses shared memory to transfer data between the A-core (Linux) and the real-time cores (bare-metal or real-time operating system).
Through physical memory DDR allocation, the hardware layer is divided into two parts: the TXVring Buffer (Transmit Virtual Ring Buffer) and the RXVring Buffer (Receive Virtual Ring Buffer); where the real-time core sends data from the TXVring area and reads the received data from the RXVring area, and vice versa for the A-core.
Example of AMP Usage
Currently, the Forlinx Embedded FET568-C SoM has provided usage examples for GPIO, UART, and SPI interfaces, utilizing RPMSG for inter-core communication. Other interfaces are still being adapted and will be opened later. Bare metal programs can be debugged using JLINK emulation in the tools provided.
The following is a brief example of the use of the UART interface in a bare-metal application:
(1) Hardware connection
This example uses UART5 and uses a jumper cap to short TX5 to RX5 on the OK3568-C development board.
(2) Device tree configuration:
To prevent Linux from taking up the resources of UART5 and causing the real-time core to be unable to use UART5, it is necessary to first add resource protection for UART5, including clock and pinctrl, to the rockchip_amp node in the device tree.
(3) Configuration of bare metal program
Introduction to UART interface:
//Pin configuration: select the transceiver pin of UART5. /* uart5 tx */
Read more
HAL_PINCTRL_SetIOMUX(GPIO_BANK3, GPIO_PIN_C2, PIN_CONFIG_MUX_FUNC4);
/* uart5 rx */HAL_PINCTRL_SetIOMUX(GPIO_BANK3, GPIO_PIN_C3, PIN_CONFIG_MUX_FUNC4);
/* uart5 m1 */ HAL_PINCTRL_IOFuncSelForUART5(IOFUNC_SEL_M1);
//Communication configuration: Baud rate is 115 200, no check, data bit is 8, no flow control, stop bit is 1.
/* uart5 config */struct HAL_UART_CONFIG demo_uart_config = {
.baudRate = UART_BR_115200, // Baud rate
.dataBit... -
Introduction to SPI Communication in the TI AM62x Processor
03/29/2024 at 01:58 • 0 commentsThe Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) communication bus is widely used for its high speed, full-duplex, synchronous characteristics. With only four lines required for data transmission, it effectively saves the number of chip pins, while also bringing spatial optimization and convenience to PCB layout. Because of its simplicity and ease of use, more and more chips are now choosing to integrate the SPI communication protocol.
The TI AM62x processor, a new generation MPU product in the TI Sitara™ product line, features up to 4 x SPI interfaces and 1 x OSPI interface (also known as QSPI). This rich SPI interface configuration allows simultaneous communication with multiple devices, significantly enhancing system scalability and flexibility.
OK6254-C development board launched by Forlinx Embedded is equipped with the AM62x processor, and its NOR Flash memory is operated through the OSPI bus connection with the processor to fulfill its functionality.
SPI Workflow and Timing
We first need to look at how the SPI works – typically the SPI is connected to an external device via 4 pins:
- MISO: Master Device Input/Slave Device Output Pin
This pin sends data in slave mode and receives data in master mode; - MOSI: Master Device Output/Slave Device Input Pin
This pin sends data in master mode and receives data in slave mode; - CLK: serial port clock
As the output of the master device and the input of the slave device; - NSS: Select from Slave Device
This is an optional pin to select the slave device.
SPI Workflow:
- The host first pulls down the NSS signal to ensure that it starts to receive data;
- When the receiving end detects the edge signal of the clock, it will immediately read the signal on the data line, thus obtaining a bit of data;
- Since the clock is sent with the data, it is not important to specify the transmission speed of the data, although the device will have the highest speed at which it can operate;
- When the master sends to the slave, the master generates the corresponding clock signal, and then the data will be sent to the slave one by one from the MOSI signal line;
- When the host receives data from the slave and requires the slave to transmit data back, the host will continuously generate a predetermined clock signal, and the slave will then send data through the MISO line.
The SPI operating timing diagram is shown below:
Features of SPI Bus in AM62x Processor
TI has designed the SPI MISO and MOSI as d0 and d1 in the AM62x chip. The setting “ti,pindir-d0-out-d1-in=” in the device tree determines which one is set as input and which one is set as output.
The default attribute value is 0, i.e., d0 is the input and d1 is the output;
When the attribute value is 1, d0 is an output and d1 is an input.SPI Application of TI's AM62x
1. Menuconfig Configuration:
Check this item and the SPI driver will be compiled into the kernel.
makemenuconfiDeviceDrivers ->SPIsupport ->Usermode SPI device driver support(Note: SPI driver compilation is in the Folinx Embedded OK6254-C single board computer.)
2. Device tree Configuration:
(1) Select the SPI to be used, here we use spi0, and the node is & main _ spi0;
(2) Multiplex the pins used by this node to the appropriate function.
(3) Describe the attributes of the node. See the notes for the functions of specific configuration items.
3. Compile and Burn:
Enter the following command in the source path:
Compilation is successful if no error is reported.
Put the OK6254-C.dtb file in image under the source path into the /boot directory of the development board and reboot the board.
4. SPI Test:
Short circuit spi0 _ D0 and spi0 _ D1
After rebooting the development board, you see two more spidev devices in the /dev directory.
Use our test program
The following printing information indicates success.
spimode: 0 bitsper word: 8 maxspeed: 42000 Hz (42 KHz) FFFF FF FF FF FF 4000 00 00 00 95 FFFF FF FF FF FF FFFF FF FF FF FF FFFF FF FF FF FF ...
Read more - MISO: Master Device Input/Slave Device Output Pin
-
FETT507-C SoM for Vehicle Monitoring and 360° Surround View System Optimization and Expansion
03/27/2024 at 01:55 • 0 commentsAs engineering vehicles become smarter, onboard dashboards and 360°surround view systems are now standard configuration. The onboard dashboard monitors vehicle status in real-time, while the 360° surround view system offers a complete view of the surroundings, helping drivers better get the vehicle’s surroundings. To meet market demand and enhance the safety performance and operational efficiency of engineering vehicles, we offer the following solutions: onboard dashboard and 360° surround view system for engineering vehicles.
Function Description:
- Real-time Monitoring: Through the onboard dashboard, drivers can instantly access the operational status of engineering vehicles, such as engine speed, vehicle speed, hydraulic oil pressure, etc. Simultaneously, the 360° surround view system can instantly collect image data of the vehicle's surrounding environment, offering a comprehensive perspective to assist drivers in better understanding their surroundings.
- Data Display and Interaction: The on-board instrument panel has a clear and intuitive interface, which can display various data and information. Drivers can interact with the instrument panel through the touch screen or other input devices to achieve information inquiry, parameter setting, and other functions.
- Remote Monitoring and Diagnosis: Through the communication module, this solution can achieve communication with the remote monitoring center, upload the vehicle operation status data and image data of the 360° Around View system, and receive remote control commands. This helps the management personnel conduct remote management of vehicles and improve operation efficiency.
- Stability and Reliability: Both the hardware and software designs of this solution possess high stability and reliability, enabling them to operate stably for a long time in complex vehicle environments without being prone to malfunctions or damage.
- Easy to Operate and Maintain: This solution offers drivers seamless usage with minimal maintenance costs.
Forlinx Embedded recommends the FETT507-C SoM as a hardware solution. Here are the optimizations and extensions of the solution:
1. Support for AHD Analog High-definition Cameras: The FETT507-C SoM integrates AHD analog high-definition camera input and adopts the MIPI_CSI solution to enable signal acquisition from four AHD analog cameras. This not only provides a comprehensive view but also assists drivers in better understanding the surroundings of the vehicle, thereby enhancing driving safety.
2. Stable CAN Data Acquisition: By utilizing a stable and mature SPI-to-CAN conversion solution, real-time vehicle operational data can be collected, providing robust support for vehicle monitoring and data analysis.
3. Flexible Expansion with Multiple Interfaces: Supporting the I2C interface allows for convenient integration of audio chips for in-vehicle audio data acquisition or connection to other external sensors. Additionally, it supports four display output interfaces including RGB, LVDS, HDMI, and CVBS, with a maximum display resolution of 4K, meeting the display needs of different sizes and resolutions.
4. Communication and Positioning Capabilities: The FETT507-C SoM integrates GPS and 4G modules to enable daily vehicle communication, remote access, and positioning functions, providing support for remote vehicle monitoring.
5. Real-time Video Stream Storage: The SoM supports external SD card connection for real-time video stream storage, facilitating easy playback and data analysis.
6. GPIO Interface and Button Functionality: The provision of GPIO interfaces caters to various physical button function requirements, facilitating user operation and control.
7. Support for Multiple Operating Systems: The FETT507-C system on module supports various operating systems, including Linux 4.9 and Android 10.0, offering users greater possibilities for...
Read more -
On-line Dust Monitoring Solution Based on Forlinx FETMX6ULL-C SoM
03/22/2024 at 07:11 • 0 commentsDust is an open source of pollution due to dust on the ground, human-driven and driven to fly into the atmosphere, and is an important part of the total ambient air. Suspended particulate matter in the ambient air lasts for a long time and can be inhaled. Once the inhalable particulate enters the human body, it will accumulate in the respiratory system and cause many diseases, which is harmful to human beings.
Dust monitoring is a real-time on-line monitoring measure to prevent and control air pollution. The dust monitoring equipment can monitor the atmospheric particulate matter concentration, PM value, temperature, humidity, wind speed, wind direction and other data in real time, and the dust pollution can be prevented and rectified in time by means of real-time data monitoring and alarm.
The online monitoring system can save a lot of manpower and material resources and provide quantitative data support for on-site treatment and administrative enforcement. After the online monitoring system is installed, continuous and uninterrupted monitoring will be carried out. It mainly monitors respirable particulate matter and is complemented by a video monitoring system, a noise monitoring system, a meteorological system, a data acquisition system, and a communication system.
The online automatic monitoring system is mainly used for online dust, environmental protection, meteorological station, tunnel and other online dust monitoring, unorganized smoke and dust pollution source emissions, residential areas, commercial areas, road traffic, construction areas, etc.; online real-time automatic monitoring of ambient air quality, and can obtain evidence through the camera. The real-time data from the weather station monitoring and the tunnel subway station can be transmitted to the data platform in time through the wired or wireless network for easy management and control.
System Components
The system consists of a data collector, a sensor, a video monitoring system (optional), a wireless transmission system, a background data processing system and an information monitoring management platform. The monitoring sub-station integrates various functions such as atmospheric PM1.0, PM2.5, PM10 monitoring, ambient temperature and humidity and wind speed and direction monitoring, noise monitoring, video surveillance (optional), etc.; the data platform is a networked platform with Internet architecture, which has the monitoring function of each sub-station and various functions such as alarm processing, recording, querying, statistics, report output, etc. of the data. The system can also be linked with various pollution control devices to achieve the purpose of automatic control.
Implementation Scheme
The online dust monitoring host can be developed using the FETMX6ULL-C SoM recommended by Forlinx Embedded.
Hardware Design: FETMX6ULL-C SoM supports 8 x RS232/RS485/TTL and multi-channel I/O interfaces, which can be connected to dust sensors and other environmental monitoring equipment. At the same time, the industrial design enables it to operate stably in harsh outdoor environment, which ensures the reliability of the monitoring system.
Network Communication: FETMX6ULL-C System on Module supports 2 x dual 100m Ethernet and standard TCP/IP and UDP protocol stacks. Monitoring data can be transmitted to the monitoring center or cloud server in real time through the network to realize remote monitoring and management.
Wireless Communication: It supports 4G and WiFi wireless communication, and after a long time of stable testing, it can ensure the stable transmission of monitoring data, and even in the absence of wired network, it can also realize the online monitoring function.
Screen Display: FETMX6ULL-C supports a variety of LCD screen designs, which enables the monitoring system to select the appropriate display screen according to actual needs, and realize the intuitive display and operation of data.
Based...
Read more -
How to Achieve Dual Camera Recording with ffmpeg?
03/20/2024 at 01:28 • 0 commentsCommand
1. The video recording was unsuccessful with the command ffmpeg -framerate 25 -f v4l2 -i /dev/video4 recording1.mp4 . According to the official ffmpeg documentation, -r and -framerate have the same function, but the actual test shows that they are different. -framerate is used to limit the input while -r is used to limit the output
2. Video can be recorded with the command ffmpeg -r 25 -f v4l2 -i /dev/video4 recording1.mp4 , but problems such as frame error and frame repetition will occur.
3. Use ffmpeg -f v4l2 -r 25 -thread_queue_size 128 -i /dev/video4 -vcodec libx264 -b:v 800k-preset ultrafast recording1.mp4 to achieve dual camera video recording at the same time.
Parameter Description:
⚫ -f Set the output format, the output format is v412 frame
(The commands found earlier all use the framework avfoundation, a full-featured framework for handling multimedia data on iOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS. The v412 framework used in this command is a framework for video device drivers in the Linux kernel, which provides a unified interface to the application layer and supports flexible expansion of various complex hardware).⚫ -r Set frame rate, set frame rate to 25fbs.
⚫ -thread_queue_size
(The thread _ queue _ size is applied to the first input specified after it. The term "thread_queue_size" can be applied to all inputs and determines at the application level. How many packets from that input can be queued while waiting for ffmpeg to receive and process them on its main thread. A few capture devices, primarily dshow, use "rtbufsize" to store incoming frames while waiting for them to be transferred to the application-level queue for that input. These two options do not adjust the value of the other, so they should be set manually. The default is 8. Common Warnings: Thread message queue blocking; consider raising the thread_queue_size option (current value: 8). To solve this problem, the official explanation: This option sets the maximum number of packets queued when reading from a file or device. (In low-latency/high-rate real-time streams, packets may be dropped if they are not read in a timely manner; increasing this value prevents this.)⚫ -i Set input stream, set input from video4
⚫ -vcodec Set the video encoder,(-vcodec and-codec:v equal in value)
Encoders are library files that implement a certain encoding format. Encoding and decoding of video/audio in a certain format can only be achieved if an encoder for that format is installed.
Here are some of FFmpeg's built-in video encoders.
- libx264: The most popular open source H.264 encoder
- NVENC: NVIDIA GPU-based H.264 encoder
- libx265: Open source HEVC encoder
- libvpx: Google's VP8 and VP9 encoders
- libaom:AV1 Encoder
⚫ -B:v Video bit rate
⚫ -preset specifies the output video quality, which will affect the file generation speed. The following values are available:
Ultrafast,superfast,veryfast,faster,fast,medium,slow,slower,veryslow,placebo from fast to slow, the ultrafast transcoding rate is the fastest, and the video is often the most blurred.
⚫ recording1.mp4 Name and file type of the output videoYou can use ffmpeg-formats to get all the file types supported by ffmpeg, where the annotation before the file is as follows:
D.=Demuxing supported(Support for video/audio encapsulation)
.E=Muxing supported(Support decapsulation of video/audio)Method:
Software:
⚫ Ubuntu:
1.Devepoment board networking
2. sudo apt-gat update upgrades apt-gat to the latest version (optional)
3. sudo apt-get install ffmpeg uses apt-gat to obtain ffmpeg
4. Enter relevant commands
Hardware:
Connect the Forlinx self-made analog camera module to support two cameras. Video4-7 are nodes generated by the TVIN, with the upper left corresponding to video7, lower left corresponding to video6, lower right corresponding to video5, and upper right corresponding to video4....
Read more -
How to Support Virtual Network on Linux 4.1.15?
03/16/2024 at 06:51 • 0 commentsTaking the FETMX6ULL-C platform as an example, if you want to use VPN, you need to open the tun configuration in the kernel in the following way:
Kernel Compilation
Choose either of the two methods below:
1. Modify the.config file directly
Locate the.config file in the kernel source path.
Find the CONFIG _ TUN in the file and modify it as follows:
Replace the kernel's config file with .config.
* Subject to actual use.
Recompile the kernel.
2. Configure the TUN using the graphical configuration interface
Make menuconfig.
Locate the following locations:
Save and exit after modification, which can be seen in.config
Replace the kernel's config file with .config.
* Subject to actual use.
Recompile the kernel.
Update kernel:
The arch/arm/boot/zImage file is generated after compilation, and the kernel can be replaced either by updating the kernel separately or by re-burning it.
Use this file to replace the file with the same name in the target path of the flashing tool.
Refer to the single-step kernel update chapter of the FETmx6ull-c User's Manual to replace the zImage file separately.
Compilation module:
In the kernel source code, some of the drivers are compiled in the form of modules, which are loaded from the specified path by the kernel version number when the system boots. When we recompile the kernel and update the kernel, the kernel version number in the system will be changed, the kernel version number can be viewed through the uname -r command. When you update the kernel, the uname -r version number changes, but the version number in the path where the module is stored (/lib/modules/) does not change. It may cause the module to fail to load, typically after updating the kernel, WiFi cannot be used.
As seen below, the name under uanme -r and the name under /lib/modules/ are not the same, so you can't load the module when you go to the/lib/modules/$(uname -r) directory when booting up, and you need to change both names to be the same.
You can solve this problem in two ways:
1. Modify the module load path and change to the version number of the kernel;
2. Repackage modules;
The first method has two disadvantages:
a. Not suitable for batch modification;
b. Not suitable for changing the module driver;
So it is possible to repackage the module when compiling the kernel:
After executing the above operation, .tmp/root/modules.tar.bz2 will be generated, which can replace the file with the same name under the target path in the flashing tool.
It is also extracted directly in the file system:
-
Solution of Edge Computing Access Control Screen Based on FET3568-C SoM
03/13/2024 at 02:30 • 0 commentsEdge Computing Access Screen is designed to provide an edge computing-based solution for access control systems. It can realize face recognition, data processing, fingerprint recognition and other functions, and improve the security and convenience of the access control system. In terms of application scenarios, intelligent monitoring and access control system is an important part of intelligent building security. The application of edge computing technology can increase the monitoring effect and response speed, avoid the security risks in the process of data transmission, and protect the privacy of users. Edge computing devices can process authentication faster and improve the response speed and security of access control systems.
Hardware requirements for edge computing access control screen
(1) Processor
Select a high-performance and low-power embedded processor, the processor itself needs to come with arithmetic power to meet the needs of edge computing.
(2) Memory
Configure appropriate memory and flash for system and application data.
(3) Interface
Provide necessary interfaces between the carrier board and other devices, such as GPIO, UART, I2C, SPI, etc.
(4) Communication module
Support Wi-Fi or 4G to facilitate data transmission with the cloud platform.
(5) Sensor
Integrate multiple sensors, such as face recognition, fingerprint recognition, and RF card reader.
Edge Computing Access Control Screen Design
The FET3568-C SoM is recommended to be used as the hardware platform of edge computing access control screen. The system on module has a quad-core ARM Cortex-A55 processor with a main frequency of 2.0 GHz, and its own NPU has a computing power of 1TOPS, which can meet the needs of lightweight edge computing tasks.
- Memory: FET3568-C SoM supports LPDDR4 and eMMC storage, and can be configured with appropriate memory and flash memory to meet the needs of the access control system.
- Interface: Native GPIO, UART, I2C, SPI, Gigabit port, etc. can communicate with other lines.
- Communication module: FET3568-C supports wireless communication technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and GPS. The appropriate communication module can be selected according to the requirements.
- Sensors: FET3568-C supports multiple sensor interfaces, such as GPIO, I2C, SPI, etc., and can easily integrate multiple sensors, including face recognition, fingerprint recognition modules, etc.
- Power supply module: According to the requirements of the access control system, the appropriate power supply chip can be selected to provide stable and reliable power supply for the entire carrier board.
- Peripheral expansion: USB and SD card slots are convenient for secondary development and function expansion.
Originally published at www.forlinx.net.
-
Smart Bus Payment Machine Core Control Platform Solution Based on Allwinner T113-i System on Module
03/07/2024 at 06:44 • 0 commentsOverview Description
In modern urban public transport, bus scanning and swiping machines are a convenient and fast payment method that allows passengers to pay their fares more conveniently and quickly, avoiding the problem of finding change as well as the time and security problems associated with cash transactions; it can automatically calculate fares and facilitate statistics and analysis of data, which largely improves the efficiency of bus operation and management; the device not only provides passengers with convenient and efficient bus payment and information services but also enhances the experience of public transportation services.
The intelligent bus card reader is equipped with a universal NFC card reader module and an embedded QR code scanner, which can be compatible with the recognition of both public transportation IC card payments and QR code scanning for payment. The system has an open interface for secondary development and docking. Passengers can use smart cards for payment, mobile NFC payment, and QR code scanning payment. It can have an embedded PSAM card slot and can be compatible with universal transit cards, UnionPay, credit cards, and other payment methods, making it a vehicle terminal that supports all payment methods and can be applied globally.
What is even more remarkable is that it comes with a high-definition facial recognition camera, which enables in-vehicle mobile facial payment functionality. In particular, with the trend towards autonomous buses in the future, multi-functional vehicle terminals can also be effectively utilized.
Features:
Two-dimensional code scanning: Support a variety of common two-dimensional code formats.Credit card payment: Support multiple payment methods such as bus card, bank card, IC card, NFC, etc.
Information display: Provide high-definition display screen, real-time display of the welcome message, ticket price, deduction status, etc.
Audio prompt: Built-in speaker supporting functions such as payment success notification.
Data statistics: Payment data can be uploaded to achieve real-time statistics and analysis of data, providing a basis for the optimisation of the public transport system.
Remote Positioning: Support remote GPS positioning.
Main Functional Interface Programme:
Integrated Barcode/IC Card Scanner for Buses Based on FET113i-S - Overall Solution Recommendation:
- FET113i-S SoM is developed based on the industrial-grade processor Allwinner T113-i, with a main frequency of 1.2GHz, equipped with a multi-core and multi-architecture design: integrating dual-core Cortex-A7 CPU, 64-bit XuanTie C906 RISC-V CPU, and DSP;
- On-board 256MB + 256MB and 512MB + 8GB configurations to meet product planning options;
- Support a variety of peripheral interfaces: USB, CAN, I2S, GPIO, UART, SPI; can connect camera module, card module, speaker, 4G/5G, GPS, etc.;
- Powerful multimedia audio and video processing capabilities support a variety of display interfaces, including RGB, MIPI-DSI, LVDS interfaces, support H.265 (4K@ 30fps), MPEG-4 (1080p @ 60fps), JPEG (1080p @ 60fps) and other full-format decoding. JPEG/MJPEG (1080p @ 60fps) format encoding; supports 8-bit parallel CSI, CVBS video input, CVBS, RGB, 2-channel LVDS, 4-channel MIPI DSI video output; also suitable for audio-related applications through DSP support.
-
Implementation of Oral Dental 3D Printer Based on FET3568-C CPU Board
03/06/2024 at 07:17 • 0 commentsDue to individual differences in oral structure, some traditional oral dental films are difficult to fully adapt to the special conditions of the patient's mouth and may require multiple adjustments and break-ins, and traditional mass production methods cannot meet the demand for personalized dental films. The traditional approach relies heavily on mold production, but this makes it difficult to respond to the needs of individual patient variability.
Manufacturing methods usually require a long production cycle, with patients needing to obtain, fit, and adjust the model throughout multiple visits, which increases the time cost of the entire process, and a cumbersome fabrication process that involves multiple processes, including model acquisition, plaster model fabrication, and dental film fitting, which makes the entire fabrication process more costly, including material and labor costs.
Meeting the personalized and customized needs of dental health-care is the basis of dental film manufacturing, which happens to be a perfect match for the technical characteristics of 3D printing, thus creating a rapid growth of the dental 3D printing market, as well as fierce competition.
A good 3D printing device must have a convenient and user-friendly human-machine interface that allows doctors or technicians to easily operate and monitor the printer status.
Not only that but also a wealth of peripheral interfaces, such as USB, RS232/485, CAN, I2C, etc., can fully meet the needs of a variety of external devices and sensors, etc., to set aside enough scalability.
![Implementation of Oral Dental 3D Printer Based on FET3568-C CPU Board]()
To meet the hardware requirements of the main control board for dental and dental 3D printers, Flying Embedded has introduced the FET3568-C platform, which has a rich set of peripheral interfaces including USB, RS232/485, CAN, I2C, etc., and provides powerful connectivity for dental and dental 3D printers. At the same time, the chip platform reserves enough scalability to meet the needs of external devices and sensors, and provides flexible expansion space for the functions of dental equipment.
Details of the scheme for realizing the 3D printer in the stomatology department:
- ARM architecture processor: FET3568-C is based on Rockchip's RK3568 core processor, providing powerful computing capabilities and low power consumption design, suitable for efficient control of oral and dental 3D printers.
- Motion control and sensor interfaces: The abundant peripheral interfaces of RK3568 chip are used to connect stepper motors, temperature sensors and so on, to realize motion control and real-time monitoring of system status.
- HMI: Equipped with a 7-inch or 10.1-inch high-resolution capacitive touch screen, it provides a convenient and friendly user interaction interface. The touch screen is designed according to the current user's operating habits, making the operation more intuitive and easy to use.
- 4K display support: Additional interfaces support 4K display, such as HDMI and eDP, for external high-resolution display devices. This ensures clarity and precision of the print control operation.
- Optical connection: Integrated external optical interface for print control to ensure accuracy and efficiency of dental and dental 3D printers.
- Network connection and communication interface: The network function of FET3568-C platform is used to realize the remote monitoring and upgrading of equipment. At the same time, other devices and sensors are connected through USB, RS232/485, CAN and other interfaces.
Summary:
The FET3568-C-based dental and dental 3D printer implementation takes full advantage of the platform's powerful performance and rich peripheral interfaces. The optimization of the human-machine interface, the support of a 4K display, and the connection of multiple sensors ensure efficient, convenient, and precise operation of the equipment, providing advanced digital solutions in the field of oral dentistry.
-
Industrial Data Acquisition and Control System Solution Based on FET6254-C SoM
03/01/2024 at 02:32 • 0 commentsAgainst the backdrop of rapid development in communication and networking technologies, smart factories are gradually achieving data-driven, networked, and intelligent management. In this trend, the utilization of the Industrial IoT has become an indispensable key step in achieving industrial data collection and control.
Traditional industrial data collection and control systems typically require connection to multiple data collection devices, perform high-speed communication, handle complex data processing, and achieve high-definition multimedia display functions. The embedded system based on ARM+FPGA architecture has rich peripheral interfaces, high-definition display high-speed transmission, and other functions, which are more capable of high-speed industrial data acquisition tasks. The flexibility and performance of this embedded system make it an ideal choice to meet the needs of smart factories, which can effectively improve the efficiency and accuracy of industrial data processing.
In the industrial data acquisition and control system, high-speed data acquisition system and embedded human-computer interaction system cooperate closely to build an intelligent industrial management system. The main task of the high-speed data acquisition system is to collect the key data in the industrial production process in real time and ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the data. This involves high-speed communication with multiple data acquisition devices, as well as sophisticated data processing and multimedia display capabilities.
As the main control center, the embedded human-computer interaction system coordinates and manages each module and resource, and is responsible for receiving the data from the FPGA terminal. It not only visualizes the data to the user, but also achieves more flexible control through human-computer interaction. The system also realizes the connection with the industrial MES + ERP system through the communication module, and transmits the collected data to the cloud for storage. This design not only improves the efficiency of data processing, but also greatly reduces the risk of manual data entry, and realizes the intelligent management of industrial data.
The whole system architecture provides a more comprehensive and efficient data management solution for enterprises. This not only helps to reduce human errors in the production process, but also makes better use of human resources and improves production efficiency. With the continuous development of communication and network technology, such industrial data acquisition and control system will become an important support for industrial intelligence in the future.
The main control device of the industrial data acquisition control system can adopt Forlinx Embedded FET6254-C SoM, which is based on TI's AM62x series industrial processor design, with the main frequency up to 1.4GHz, is a multi-core heterogeneous processor, adopting the Cortex-A53+Cortex-M4F combination of processing core + control core architecture; the functional safety features can be realised by the M4F core and its dedicated peripherals, and the startup and operation of the M4F core no longer depend on the A53 core. The M4F core and its dedicated peripherals enable functional safety features, and the M4F core is no longer dependent on the A53 core for startup and operation.
It can provide excellent data processing capability and human-computer interaction experience, and can control the motor drive module in real time to meet the requirements of data processing, task scheduling and human-computer interaction of the real-time control system.
It support parallel bus support for ARM high-speed communication with the FPGA to provide access. FET6254-C supports TI processor-specific general-purpose memory controller interface GPMC, high data read and write rate of up to 100MB / s, support for multiple chip selection, the configuration is more flexible, and at the same...
Read more -
How to Adapt an LVDS Screen on the Forlinx FET113i-S System on Module?
02/27/2024 at 07:01 • 0 commentsThe FET113i-S SoM is developed and designed based on Allwinner T113-i industry processor, with a main frequency of 1.2GHz. It is equipped with multi-core and multi-architecture: integrated dual-core Cortex-A7,CPU64-bit XuanTie C906RISC-VCPU and DSP, which not only provides efficient computing power, but also has rich multimedia functions and complete interface resources; stamp hole design makes product more durable, and the development board draws out as much processor core resources as possible, which is a cost-effective choice for key areas such as industry, power, transportation and so on!
![allwinner T113 single board computer]()
This article will briefly share the process of adapting Forlinx T113i-S development board to LVDS screen display.
Development platform: Forlinx T113i-S development board
To modify the T113i screen, you need to modify the kernel and uboot respectively. Take the LVDS 1024 * 600 screen as an example.
1. Enter the following path;
2. Open OK113I-C-Linux.dts;
3. Modify the resolution parameters as shown in the figure below (for specific parameters, please refer to the screen manual of the screen you are using):
4. Save and exit after modification, and then start to modify uboot and enter the following path;
5. Open display-menu.c;
6. Modify the resolution parameters as shown in the figure below:
7. After modification, compile uboot under the initial path of the source code;
8. Complete compilation after successful compilation./build. Sh.;
9. After successful execution. /build.sh, pack image burned to the board to observe the phenomenon.
Our above parameter modification can be successfully adapted to a new display, of course, the specific operation of different master control platform boards will be different, but the overall idea is the same, specific can be based on the corresponding platform to view the relevant information to determine the specific steps.
-
Application Solutions for Intelligent Service Robots Based on the FET3588J-C Main Control Platform
02/23/2024 at 02:33 • 0 commentsAn intelligent service robot is a robot that integrates advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, perception technology, and machine learning. Its purpose is to provide a variety of services and support to meet the needs of people in daily life, business, and industrial fields. These robots can sense the environment, understand speech and images, perform tasks, and interact naturally and intelligently with human users.
Areas of Application:
Business Services: It includes services such as reception, shopping assistance, and information inquiry, and can be used in places such as shopping malls, hotels, and exhibitions.
Health Care: It provides services such as drug delivery, patient companionship and health monitoring for hospitals and nursing homes.
Educational Assistance: It is used in educational scenarios to provide auxiliary teaching, answering questions and other services.
Family Services: Provide cleaning, handling, home control and other services to improve the quality of life.
The hardware structure of the service robot includes several key components. The functions and roles of these hardware components are as follows:
Controls: As the core of the robot, the control device is responsible for receiving and processing the data provided by the sensors, executing the corresponding algorithms, and issuing instructions to the driving device to achieve the various functions of the robot. High-performance, low-power ARM chips are often chosen for the control unit, ensuring that the robot has sufficient computational and storage capacity.
Drive unit: This includes motors and drivers, which are used to execute the motion and action commands of the robot. The motor is responsible for providing power, while the driver converts electronic signals into mechanical motion. This part is the motion system of the robot, which determines the execution of actions such as walking, turning, and the mechanical arm.
Camera: As the ''eyes'' of the robot, the camera is used to capture images and facial information of the external environment. These image data can be used for tasks such as environmental perception, navigation, target recognition, allowing the robot to better understand and adapt to the surrounding environment.
Sensors: Sensors provide the robot with various perceptual abilities, including vision, touch, hearing, and distance sensing, among others. Angle sensors and current sensors reflect the robot's own state, while temperature sensors, laser sensors, ultrasonic sensors, infrared sensors, etc. are used to collect external environmental information, allowing the robot to perceive and understand the surrounding situation more comprehensively.
Display and Audio: As an important part of human-computer interaction, display and audio devices realize the presentation and interaction of user interface. The touch display provides an intuitive graphical user interface, while the voice interaction system enables the robot to understand the user's instructions and respond accordingly, thus better communicating with the human user.
Folinx Embedded has launched the FET3588J-C SoM as the main control platform for this intelligent inspection robot product to meet customers' needs for machine vision and high-speed interfaces.
FET3588J-C SoM is developed and designed based on Rockchip's RK3588 processor, integrating Cortex-A74-core-6 + 4-core Cortex-A55 architecture. The main frequency of A76 core is up to 2.4GHz, and the main frequency of A55 core is up to 1.8GHz, which can efficiently process the information collected by patrol inspection;
The built-in NPU with comprehensive computing power of up to 6 TOPS greatly improves the calculation speed and energy efficiency of neural networks, providing robots with powerful AI learning and edge computing capabilities, enabling them to intelligently adapt to different work scenarios.
RK3588J supports a 48-megapixel...
Read more -
How to Output PWM Square Waves on OK1028A-C Development Board?
02/21/2024 at 06:28 • 0 commentsAfter checking the schematic of the OK1028A-C and the "QorIQ LS1028A Reference Manual", it is found that there are 8 FlexTimers (FTM) available by defaultLS1028on the board, with each FTM having 8 pwm channels.
The default backlight uses the pwm generated by FTM1, and we use FTM7 to do the pwm test.
As shown in the figure below:
LS1028 RCWSR12 registers 12-14 are pin multiplexed for I2C4.
As shown in the figure below:
The I2C4 pin can be multiplexed into six pin functions. The OK1028A-C sets the pins to rx and tx of can2 , you can see T6_CAN2_RX, U7_CAN2_TX in the schematic "OK1028A-C_V1.1".
We can set I2C4 to the pwm pin by modifying the rcw file.
OK1028A-C supports the pwm function by default, so we do not need to transplant the driver. All we need to do is to modify the pinmux and add the corresponding device node of pwm in the device tree. Modify packages/firmware
In the /rcw/ls1028ardb/RSQPP0x85bb/rcw1500gpu600.rcw file, the setting for IIC4_PMUX is to configure the pin as a pwm output.
Change IIC4 _ PMUX = 2 to IIC4 _ PMUX = 4
As shown in the figure below:
After completing the above settings, we need to modify the device tree code and add pwm configuration. The path of our modified file is as follows:
packages/linux/linux/arch/arm64/boot/dts/freescale/fsl-ls1028a.dtsi.
Then add the pwm7 device
Pwm7: pwm@2860000 { compatible = "fsl,ls1028a-ftm-pwm"; reg =; #pwm-cells =; clock-names = "ftm_sys"; clocks = <&ftm_sysclk>; };As shown in the figure below:
▐ Start the OK1028A-C system
root@forlinx:~#cat /sys/kernel/debug/pwm View our current pwm devices
As shown in the figure below:
We have now opened a pwm controller and can see that FTM1 supports 8 channels, with the backlight using pwm channel 1. Compile the modified device tree file and firmware, burn them intoFolinx EmbeddedLS1028A-CDevelopment Board, and boot up the system.
root@forlinx:~#cat /sys/kernel/debug/pwm View our current pwm devices.
As shown in the figure below:
At this time, although the pwm device we added is turned on, it is still different from the pwm0 device. Each channel of the newly added pwm device has no set period and duty cycle.
So in the next step, we do not need to add driver code, but use sys to set pwm parameters directly. Pwmchip8 is the pwm device we added.
▐ Enable pwm channel used
root@forlinx:~#echo 1 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip8/export Initialize pwm channel 1
root@forlinx:~#echo 2 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip8/export Initialize pwm channel 2
root@forlinx:~#cat /sys/kernel/debug/pwm CommandCheck out our current pwm devices:
If you want to cancel the corresponding pwm channel, you can use "echo 1 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip8/unexport".
“echo 2 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip8/unexport” command.
Since we can only enable pwm one way at a time, configure and turn on pwm1 first.
root@forlinx:~#echo 1000000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip8/pwm1/period Configure the pwm1 period to be 1000000 in ns, which is 1kHZ.
root@forlinx:~#echo 500000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip8/pwm1/duty_cycle Configure the duty_cycle to 500000, the on time in a cycle is the duty cycle,...
Read more -
How to Install WireGuard in Forlinx Desktop Image on RK3588 Platform?
02/02/2024 at 01:37 • 0 commentsInstall Wire Guard in the RK3588 Forlinx Desktop image
Solution: Mount the Forlinx Desktop image file into the development environment for installation.
(1) Download qemu-user-static in the development environment
sudo apt-get install qemu-user-static
(2) Mount the img image of Forlinx Desktop to a directory, I have mounted it to the test directory.
sudo mount focal-rootfs.img test/
(3) Use the chroot command to enter the test directory
sudo chroot test/
(4) Install WireGuard
apt-get install wireguard-dkms wireguard-tools wireguard
Solutions that cannot be used after installation:
To add the TUN and WireGuard options to the kernel, proceed as follows:
1. Modify the build. Sh in the SDK to add the $KMAKE menu config;
2. Execute. /build.sh, search for TUN and wireguard in the graphical configuration interface and check them off;
Save and Exit.
3. Overwrite OK3588-Linux _ defconfig with.config
cp kernel/.config kernel/arch/arm64/configs/OK3588-Linux_defconfig;
4. Re-flash the image;
5. Set the IP.
-
Application Solution of Forklift Driver Face Recognition and Permission Collector Based on FET3568J-C SoM
01/31/2024 at 07:36 • 0 commentsForklift is an indispensable equipment in modern industrial production and logistics transportation, but at the same time, it is also a mechanical equipment with certain risks. If operated improperly or managed poorly, it can easily lead to safety accidents, causing injuries and property losses. Therefore, improving the safety awareness and management level of forklift drivers is of great significance in ensuring the safety and smooth operation of enterprise production and logistics transportation.
In the safety protection and protective devices, it is stated that forklifts must be equipped with a driver authorization information collector. This collector is used to bind the driver's personal identity information with biometric information such as fingerprints, iris, facial features, or magnetic cards. The forklift can only be started after the driver's permission is verified.
The forklift facial recognition driver authorization collector is primarily used for driver permission management. With high-precision cameras and facial recognition algorithms, this system can accurately identify and determine the driver’s identity information. It helps ensure that only authorized individuals can operate the forklift, improving safety and security in the workplace.
Only drivers who have undergone professional training and obtained authorization will have their information entered into the system and be granted permission to operate the forklift. Once the system detects an unauthorized person attempting to operate the forklift, it immediately triggers an alarm and takes measures to prevent the forklift from starting, ensuring the safety of operations.
The forklift facial recognition driver authorization collector has the following notable features:
- Facial recognition: By using cameras to capture facial information, it can accurately identify the facial features of drivers in a short period of time with high precision, without the need for manual intervention, greatly improving management efficiency.
- Security: The system is designed with high security in mind. It effectively prevents others from impersonating drivers and provides dual protection for forklift operations.
- Integration: The system can not only operate independently but also seamlessly integrate with other security devices, access control systems, etc., forming a comprehensive security management system to further enhance safety.
- Scalability: The system supports the integration of finger print recognition and card recognition systems, allowing for the expansion of corresponding functions based on specific needs.
The overall solution for the forklift driver authorization collector based on FET3568J-C system on module is as follows:
FET3568J-C industrial-grade SoM is provided by Forlinx Embedded, which serves as the core of the forklift driver authorization collector. It features a four-core 64-bit Cortex-A55 architecture with a high frequency of up to 1.8GHz, providing powerful performance support. Additionally, it is equipped with a built-in NPU with 1TOPS computational power, meeting the requirements for lightweight edge AI computing.
The SoM has advantages such as high performance, low power consumption, and low cost.
Forlinx RK3568J industrial-grade SoM provides abundant interface resources, making it easy to connect with external modules.
- Supports DVP, MIPI-CSI, USB, and network camera interfaces.
- Supports RGB, LVDS, HDMI4, MIPI, and eDP display interfaces, making it convenient to connect external displays for facial recognition and comparison display.
- Supports 2*1000M Ethernet ports, WiFi, 4G, and 5G interfaces, enabling remote monitoring, control, and data transmission functionalities.
- Supports 3*CAN bus interfaces, allowing the collector to communicate with the forklift system through CAN bus interfaces to obtain vehicle status and driver information.
- Supports GPIO interfaces, allowing connection and control of other devices on the forklift through GPIO...
-
How to Realize Android Vertical Screen Display on the Embedded i.MX8MP Platform of Forlinx
01/25/2024 at 07:40 • 0 commentsThe default display orientation for the Android interface on the Forlinx Embedded i.MX8MP platform is landscape, but some products may require a portrait display. To address this requirement, Forlinx Embedded provides the following methods for modification:
The Android system controls the screen orientation through the persist.vendor.orientation property, which can have values of 0, 90, 180, or 270.
Configuration path: frameworks/native/services/su**ceflinger/Su**ceFlinger.cpp
Modify in processDisplayHotplugEventsLocked:
Su**ceFlinger::processDisplayHotplugEventsLocked() { continue; } + /* Rotate desktop */ + char rotationvalue[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX] = "";; + property_get("persist.vendor.orientation", rotationvalue, "-1"); + int rotation = atoi(rotationvalue); + ALOGI("Primary Display Orientation is set to rotation %2d.", rotation); + switch (rotation) { + case 0: + internalDisplayOrientation = ui::ROTATION_0; + break; + case 90: + internalDisplayOrientation = ui::ROTATION_90; + break; + case 180: + internalDisplayOrientation = ui::ROTATION_180; + break; + case 270: + internalDisplayOrientation = ui::ROTATION_270; + break; + default: + break; + } + const DisplayId displayId = info->id; const auto it = mPhysicalDisplayTokens.find(displayId);After modification, you need to add the relevant configuration in the environment variable.
Path: device/nxp/imx8m/evk_8mp/system.prop
persist.sys.timezone=Asia/Shanghai persist.sys.language=zh persist.sys.country=CN +persist.vendor.orientation=90
Rotate 90 degrees here to write 90, 180 degrees to write 180, 270 degrees to write 270.
If you encounter a failure to set the value of a property:
Add the followings in device/nxp/imx8m/sepolicy/property_contexts;
+persist.vendor.orientation u:object_r:debug_prop:s0 vendor.wc_transport. u:object_r:vendor_wc_prop:s0 ...
Read more -
Application Scheme of Blood Cell Analyzer Based on FETMX8MM-C SoM
01/24/2024 at 03:06 • 0 commentsA blood cell analyzer is one of the widely used instruments in clinical laboratory testing in hospitals. It classifies white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets in the blood using the resistance method. It can also provide data related to blood such as hemoglobin concentration and hematocrit. In clinical applications, it can be used for white blood cell counting, neutrophil counting, lymphocyte counting, red blood cell counting, and other clinical tests. It is an important reference for doctors to diagnose patients' conditions.
Function requirements
- Detection parameters: The instrument should be able to detect common blood parameters including red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, hemoglobin, and white blood cell differentials.
- Sample handling: The instrument should be capable of automated sample loading, sample distribution, cleaning, and waste disposal.
- Accuracy: The instrument should have high measurement accuracy and repeatability to meet clinical diagnostic requirements.
- Usability: The instrument should have a user-friendly interface that is easy to operate, allowing laboratory personnel to use it with ease.
- Data analysis: The instrument should have the capability to automatically generate test reports and perform basic data analysis based on the test results.
Hardware design requirements
- Controller: A high-performance microprocessor is used as the main controller of the instrument, which is responsible for realizing various control logic and data processing.
- Power supply module: Use a stable power supply module to ensure consistent instrument performance in various environmental conditions.
- Detection Module: According to the blood indexes to be detected, design the corresponding detection module, such as optical detection module, electrical detection module, etc.
- Detection Module: According to the blood indexes to be detected, design the corresponding detection module, such as optical detection module, electrical detection module, etc.
- Human-computer interaction: Use a touch screen as the operation interface, which is convenient for laboratory staff to use. At the same time, it has a printing function, which can print out the test results.
- Data storage: Data can be stored through built-in memory chip and SD card.
Design scheme
For the functional characteristics of the blood analyzer, Forlinx Embedded recommends the FETMX8MM-C system on module as the hardware development platform, which is equipped with ARM Cortex-A53*4+ARM Cortex-M4 processor with 1.8GHz main frequency. It supports LPDDR4 and eMMC storage to configure the appropriate memory and flash on demand.
i.MX8MM SoM With multiple interfaces:
- It includes display interface, supports external screens of various specifications and sizes, and is compatible with resistive capacitive touch, providing excellent human-computer interaction experience.
- USB interface is convenient to connect external devices, such as U disk, mouse, WiFi, 4G, printer, etc.
- The network interface includes 10/100/1000M Ethernet, 4G module and WiFi module to realize efficient communication with hospital HIS and laboratory information system LIS.
- The SPI bus is used to extend the FPGA to support various applications such as motor control, gate valve control, and AD sampling.
- The serial port is used to communicate and control with the bar code machine, the lower electromechanical structure and other equipment.
- For external storage, TF and SD cards are supported for storing computing data, analyzing results, and so on.
The FETMX8MM-C Core board has a wide range of applications in the medical field, providing high-performance and multi-functional processing power for medical devices, and helping to realize a smarter and more convenient medical information system.
-
Sleep and Wake-up Operation of the Embedded T113-i Development Board of Forlinx
01/19/2024 at 03:07 • 0 commentsSystem sleep and wake-up technology is the key technology in power management. It allows the system to minimize power consumption when idle, putting external devices, the chip's internal IP, and the clock into a low-power state or a completely power-off state to greatly extend battery life. Additionally, when needed by the user, the system can quickly restore the power, clock, working state of the internal IP of the chip, and external devices, ensuring that the user’s experience is not disrupted.
The embedded OK113i-S development board supports two sleep modes: freeze and mem. These two methods can be operated through the/sys/power/state file node, and the user can trigger the corresponding sleep state by writing freeze or mem to the file node.
Before hibernation, the system configures the wake up source. Once the system enters the sleep state, it can be awakened by these wake-up sources, such as keys, RTC, etc., when needed. This design allows users to choose when and how to wake up the system quickly according to their needs, achieving a balance between power consumption minimization and fast recovery. This mechanism enables the system to greatly reduce power consumption in the sleep state, while retaining the convenience of the user to use the system quickly after waking up.
This article will introduce how to put the embedded OK113i-S development board into sleep mode, and how to achieve timed wake-up through the RTC clock.
01 Two Sleep Modes
freeze
Freezing I/O devices, placing them in a low-power state, allows the processor to enter an idle state, resulting in the fastest wake-up time but higher power consumption compared to other methods. Based on the test results with the OK113i-S development board powered only through the serial port, it was found that the current is approximately 0.112A at 5V.
mem
Suspend to the memory. The computer stores the current running state and other data in the memory, closes the hard disk, peripherals and other devices, and enters the waiting state. At this time, the memory still needs power to maintain its data, but the whole machine consumes very little power. When the computer resumes from a suspended state, it reads the data stored in memory and restores itself to the exact state it was in before it was suspended.
This allows for a faster recovery time compared to a full system startup. The measured OK113i-S development board is powered by 5V when only the serial port line is connected, and the current is about 0.076 A.
1. cat /sys/power/state to see what modes are supported by the OK113i-S development board:
2. echo freeze > /sys/power/state Enter freeze mode:
3. echo mem > /sys/power/state Enter mem mode:
02 Timed wake-up via RTC
Note: Internal RTC is required here. The external RTC does not support wake-up function. We will mention this later.
Enter the kernel configuration of the development board:
root@ubuntu: /home/forlinx/work/linux/OK113i-linux-sdk# ./build.sh menuconfig
Select the function according to the box in the following figure:
After the configuration is completed, save it, and then modify the device tree file to open the internal RTC function.
Compile after saving:
After the compilation is successful, it is packaged into an image. After the programming is completed, we test it at the serial port terminal.
Enter the serial port terminal for test:
echo “+15”> /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm
You can use this 15-second timer by setting the desired time. Once the timer is set, it will begin counting down and the Real-Time Clock (RTC) will keep track of the time. If the device goes into hibernation mode within the 15-second timer window, it will not trigger the wake-up (Note that the internal RTC is required here, and the external RTC does not support wake-up)
echo mem > /sys/power/state
(The input of the two instructions here should be compact. If the interval between the two instructions is too...
Read more -
Main Control Scheme for Agricultural Picking Robots Based on i.MX8MP CPU Board
01/17/2024 at 02:22 • 0 commentsWith advantages such as modularity, high efficiency, and easy deployment, fully intelligent picking robots have been applied to agricultural fields. From pinpointing to harvesting, from cutting to collecting, it can cover the entire process of agricultural crop picking.
The operational target of agricultural robots is crops, and the characteristics of crops impose higher requirements on the movements of agricultural robots. The end effector of the agricultural robot needs to have flexible handling capabilities when in contact with the operational target. This emphasizes the importance of stability, accuracy, agility, and lightweight in the application of agricultural robots.
Agricultural Robots Main features:
Intelligent navigation: Agricultural harvesting robots are equipped with advanced navigation systems, allowing them to autonomously navigate in farmland, achieve precise positioning, and avoid colliding with obstacles.
Visual perception: Equipped with machine vision system, it can identify the maturity of fruits or vegetables, realize intelligent identification and positioning, and ensure accurate picking operation.
Flexible arm: Equipped with a mechanical arm with multiple degrees of freedom, it can flexibly adapt to fruits of different shapes and sizes to achieve efficient and accurate picking.
Data acquisition: Agricultural picking robot can collect real-time data in farmland, such as soil moisture, plant growth status, etc., which provides a scientific basis for agricultural management.
Automatic charging: Equipped with intelligent charging system, when the power is low, it can automatically return to the charging station, reduce manual intervention and improve operation efficiency.
With the rapid development of agricultural science and technology, the introduction of agricultural picking robots is pushing agricultural production towards a more intelligent and efficient direction. The FETMX8MP-C CPU board is recommended to be used as the main control scheme of the agricultural picking robot. The advantages of the platform are as follows:
- High performance, the CPU uses 1.6GHz quad-core 64-bit Cortex-A53 architecture, which provides the robot with efficient processing capability, enabling it to analyze the data collected in the farmland in real time;
- Built-in powerful neural processing unit (NPU), with a maximum running rate of 2.3 TOPS,provides powerful artificial intelligence computing power for robots;
- Abundant high-speed interface resources: It has two Gigabit Ethernet ports, two USB 3.0/2.0 interfaces, PCIe Gen 3, SDIO 3.0 interface and CAN interface (including one CAN-FD) to meet the high-speed connection needs of various sensors and communication devices, so that the robot can achieve intelligent visual perception and positioning, and improve the accuracy and efficiency of picking;
- All-weather work, the full industrial design ensures the stable operation of the robot in a variety of complex environments, and realizes the agricultural production service of the weather.
With the powerful performance of NXP i.MX8MP processor, agricultural picking robots will continue to evolve in the future to better adapt to the diversity and complexity of agricultural production. This combination will promote the development of modern agriculture in a more intelligent and digital direction, and improve the efficiency and sustainability of agricultural production.
-
OK7110-C Single Board Computer Based on RISC-V JH7110
01/15/2024 at 01:27 • 0 commentsOK7110-C RISC-V Single Board Computer(SBC) adopts a “carrier board + SoM” structural design. The SoM adopts FET7110-C of the JH7110 processor, which is designed and developed by StarFive Technology. OK7110-C development board adopts the open-source RISC-V architecture, with a frequency of 1.5GHz, and integrates the quad-core RISC-V architecture.
The JH7110 RISC-V chip has been mass-produced, featuring high performance, multi-function, and low power consumption, providing powerful GPU processing capability, supporting multi-video coding and decoding, and supporting 2xPCIe 2.0, 2xGigabit Ethernet and 2xCAN 2.0. The SoM supports Linux 5.15.0 operating system, which is suitable for the development of industrial vision-related applications.
Introducing the OK7110-C RISC-V Single Board Computer(SBC)/Development Board - Your Gateway to Enhanced Connectivity and Innovation. With versatile peripheral interfaces including HDMI, MIPI-DSI, camera, Ethernet, USB3.0, PCIe2.0, UART, RS485, CAN2.0, SPI, audio, TF card slot, 4G/5G, and more, this board empowers you to unleash the full potential of your projects. Experience seamless integration, high-speed data transfer, and reliable communication, all in one compact and powerful development board.
Equipped with High-performance RISC-V Processor JH7110
JH7110 is a high-performance RISC-V SoC launched by StarFive Technology, which has been mass-produced in 2022 and is built for the embedded industry.
It features efficient computing, high-speed connectivity, and visual processing capabilities, meeting the requirements of industrial scenarios.High-performance Quad-core 1.5 GHz MPU
JH7110 is equipped with a 64-bit high-performance quad-core RISC-V processor core.
The stable operating frequency of the CPU is 1.5 GHz, the CoreMark score is 5.09 CoreMark/MHz, and the performance is better than Cortex-A55.Powerful GPU Rendering Capabilities
JH7110 GPU uses IMG BXE-4-32 MC1 architecture to provide strong processing power.
It operates at a frequency of 600MHz and supports mainstream APIs such as OpenCL 3.0, OpenGL ES 3.2, and Vulkan 1.2.
It provides sufficient computing power support for computer vision, in-depth learning, graphics rendering, and other applications.
Dynamic Power Control Matching Different Application Scenarios
JH7110 is divided into 8 independently switchable power domains. The CPU frequency can be adjusted via software, allowing customers to dynamically adjust the frequency
based on application scenarios and achieve power consumption control.Outstanding Multimedia Processing Capabilities
JH7110 provides MIPI-CSI and DVP camera access modes, supports ISP, and supports up to 4K @ 60fps video decoding and 1080p @ 30fps video encoding.
It supports HDMI (4K @ 30fps), RGB (1080p @ 30fps) and MIPI-DSI (2K @ 30fps) display output interfaces, and can also realize dual-screen display.Rich Interfaces for Wider Applications
-
Elevator IoT: Intelligent Management and FETMX6ULL-S Industrial ARM SoM Solution
01/12/2024 at 01:13 • 0 commentsElevators, as special equipment, belong to traditional industries. But with the development of emerging technologies such as IoT, 5G, and artificial intelligence, many industries are undergoing revolutionary changes.
In addition, the digitalization and intelligent construction management needs of urbanization in recent years have also led to continuous changes in elevator manufacturing, production, and maintenance. The digitization of elevator information management, real-time monitoring, fault prediction, emergency rescue, and maintenance management have become new demands.
The development of elevator IoT technology provides a foundation for the implementation of smart elevators. Emergency rescue, diagnosis of elevator safety hazards, fault prediction, and on-demand maintenance all rely on elevator IoT. As the foundation and key component of elevator IoT, the IoT gateway is responsible for establishing a bridge between the elevator control system and remote server data exchange.
The richness of the elevator IoT gateway interfaces, efficiency and capabilities of edge computing, ease of use, universality, as well as maintenance and management convenience determine the level of data collection and transmission in elevator IoT.
The elevator IoT gateway is mainly used for real-time monitoring and displaying the elevator's operational status. It collects relevant data about elevator operation through various high-precision sensors built into it. The gateway then uses a microprocessor to analyze abnormal data and transmits the data through methods such as 3G, 4G, GPRS, Ethernet, RS232/RS485, and USB.
The comprehensive elevator management platform, hosted on the cloud platform, handles functions such as elevator fault alarms, trapped passenger rescues, daily management, quality assessment, hazard prevention, and multimedia transmission.
Elevator IoT Features:
The gateway is able to collect signals of elevator going up and down, stopping, leveling, door opening and closing, current floor, elevator speed, and single trip distance.
- It can monitor elevator fault information in real-time, such as entrapments, elevator jamming, abnormal door operations, and over-speeding or bottoming out.
- It can store various operational data, fault data, and elevator maintenance work information.
- It can transmit real-time operational data of elevators through 4G wireless network to the elevator operation real-time monitoring platform, and can also simultaneously report to the cloud platform.
FETMX6ULL-S SoM Solution Recommendation:
To achieve stability and high efficiency, Forlinx Embedded recommends using FETMX6ULL-S industrial SoM as the core solution of elevator IoT gateway. The SoM adopts NXP Cortex-A7 800MHz master, and comes standard with EMC and high and low temperature, which keeps the quality of hardware and system in all cool conditions.
FETMX6ULL-S industrial SoM Main features
- The FETMX6ULL-S SoM is based on NXP's ARM Cortex-A7 architecture i.MX6ULL low-power processor design, running at 800MHz. The SoM is designed with stamp holes, and the unique power management architecture makes the SoM consume less power.
- Rich Interfaces:
Support 8 x UART and communicate with multiple serial devices at the same time;
Support 2 x Ethernet to realize dual network redundancy;
Support 2 x USB; - Rich peripheral modules, supporting WiFi, Bluetooth, 4G and other modules.
- It adopts the 4.1.15 operating system, supports OTG, SD/TF card batch burning mode, and supports single-step kernel update, making it convenient for process development and bulk production.
- The SoM has a compact size of only 44*35mm, with an 8-layer PCB featuring immersion gold process. It is equipped with industrial-grade components and has a wide operating temperature range of -40°C to +85°C, ensuring stable operation of the product in harsh environments.
Integrating the FETMX6ULL-S industrial-grade SoM with elevator IoT technology...
Read more