THE SENSORS:
Walk-Bot has 3 different distance sensors placed at an angle of 45 degrees to each other:
Ultrasonic Sensors: There are 2 ultrasonic sensors present on the device: one in the front and one at an angle of 45 degrees upwards. They work on the principle of SONAR(i.e. the reflection of sound waves) to measure the distance of the obstacle in front of them.
Infrared Sensor: This is the third sensor which is placed at an angle of 45 degrees towards the bottom. This sensor has been used at the bottom instead of the ultrasonic sensor because the ultrasonic waves have a tendency to get reflected by flat surfaces at particular angles resulting in inaccurate measurements.
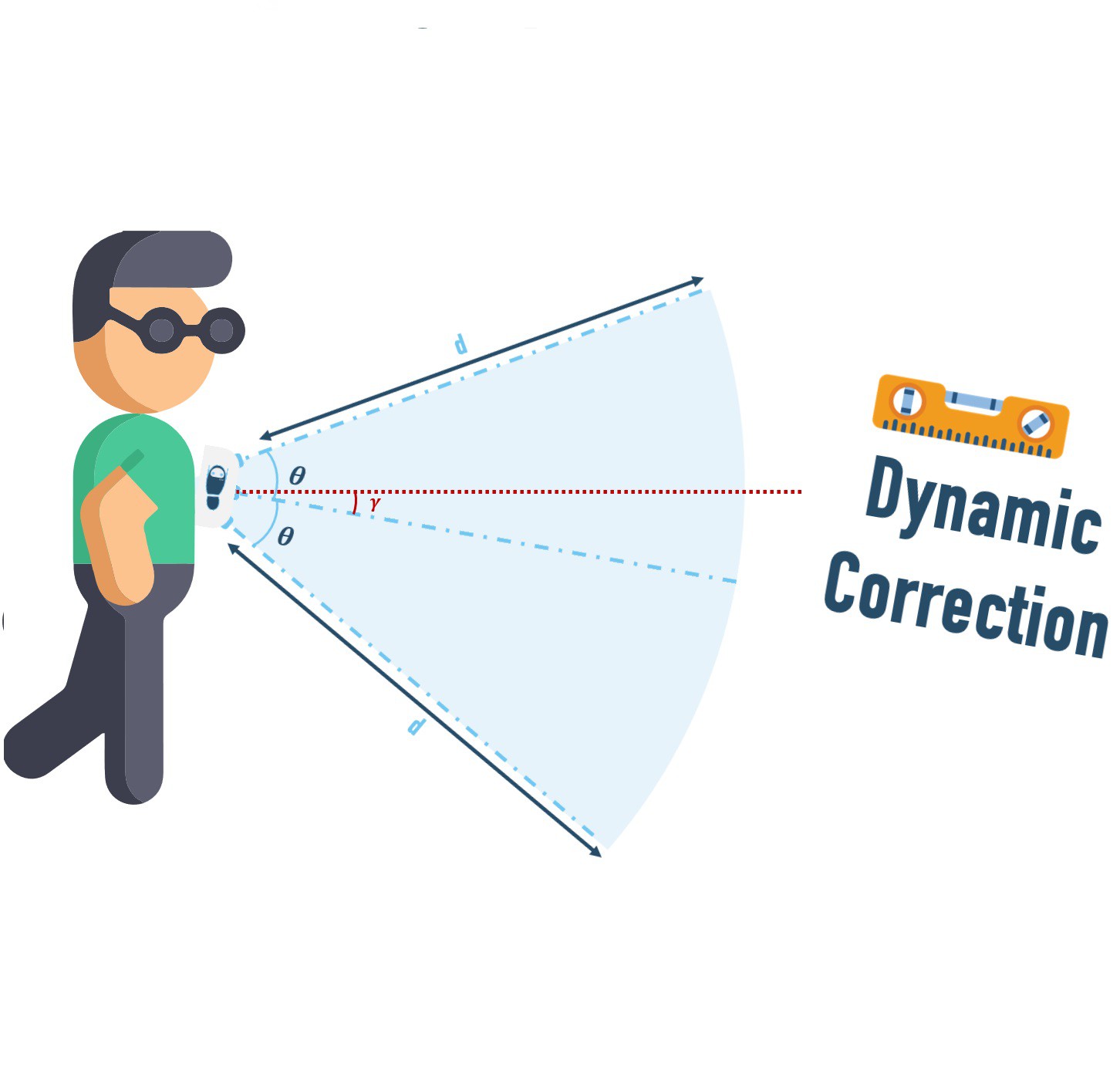
PROCESSING THE DATA: The raw input from these sensors is then processed by the microprocessor using trigonometry to obtain much more refined and usable data. THIS IS THE MOST IMPORTANT FEATURE OF WALK-BOT AS IT ENABLES US TO FIND THE DISTANCE OF THE OBSTACLE FROM THE USER 29.3% MORE ACCURATELY THAN THE DISTANCE OF THE OBSTACLE FROM THE SENSOR ITSELF.
WARNING THE USER: Supposed to be worn on the waist, the device has two different methods of warning the user of obstructions : 1.Buzzer: The walk-bot has a buzzer which operates at varying frequencies to denote the proximity of the obstruction. In other words, it will warn the user by increasing the number of beeps as the obstacle gets closer. 2.Vibrating Motor: The walk-bot has also been equipped with a vibrating motor along with the buzzer for people who are not only visually but also audially challenged.
ERGONOMIC MAINTENANCE: Walk-Bot is equipped with a gyroscope(compass) which can detect slight changes in inclination of the device, i.e., it can sense whether the user is wearing the device in the correct manner or not and warn him/her accordingly. If the device is not perfectly parallel to the ground, the trigonometric calculations can become inaccurate. To solve this problem, information from the gyroscope can be utilized to compensate for the inclination and calculate the accurate distances.
PANIC BUTTON: In the event of the user encountering a minor accident, he/she can use the panic button for help. The walk-bot will start beeping to alert the people nearby. The user’s smartphone(connected via Bluetooth) will also send messages to selected contacts to notify them of the incident.
CASE-I
An object, like a small table or rock, which is below the level of the device can be detected through the sensor inclined at an angle of 45 degrees towards the bottom. The perpendicular distance has been calculated to be :
dcos(45)
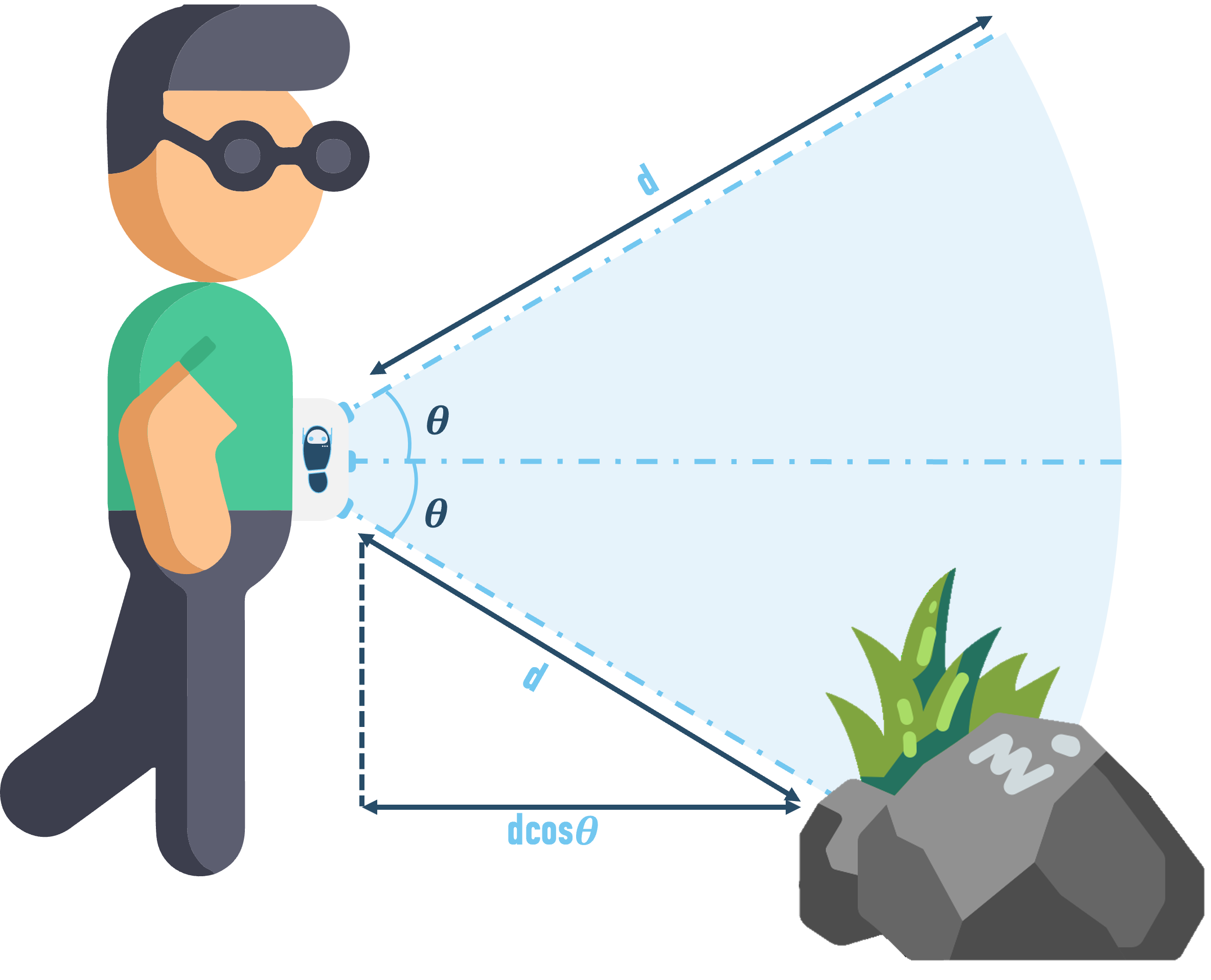
In other words, the actual distance of the person from the obstacle is lower than the distance measured by the sensor. Using trigonometry, the walk bot is able to calculate the accurate distance from the obstacle.
CASE-II
An obstacle, like stairs, which is below the level of the device and also the floor can be detected through the sensor inclined at an angle of 45 degree towards the bottom. The distance d will be much greater than the default distance from the floor.
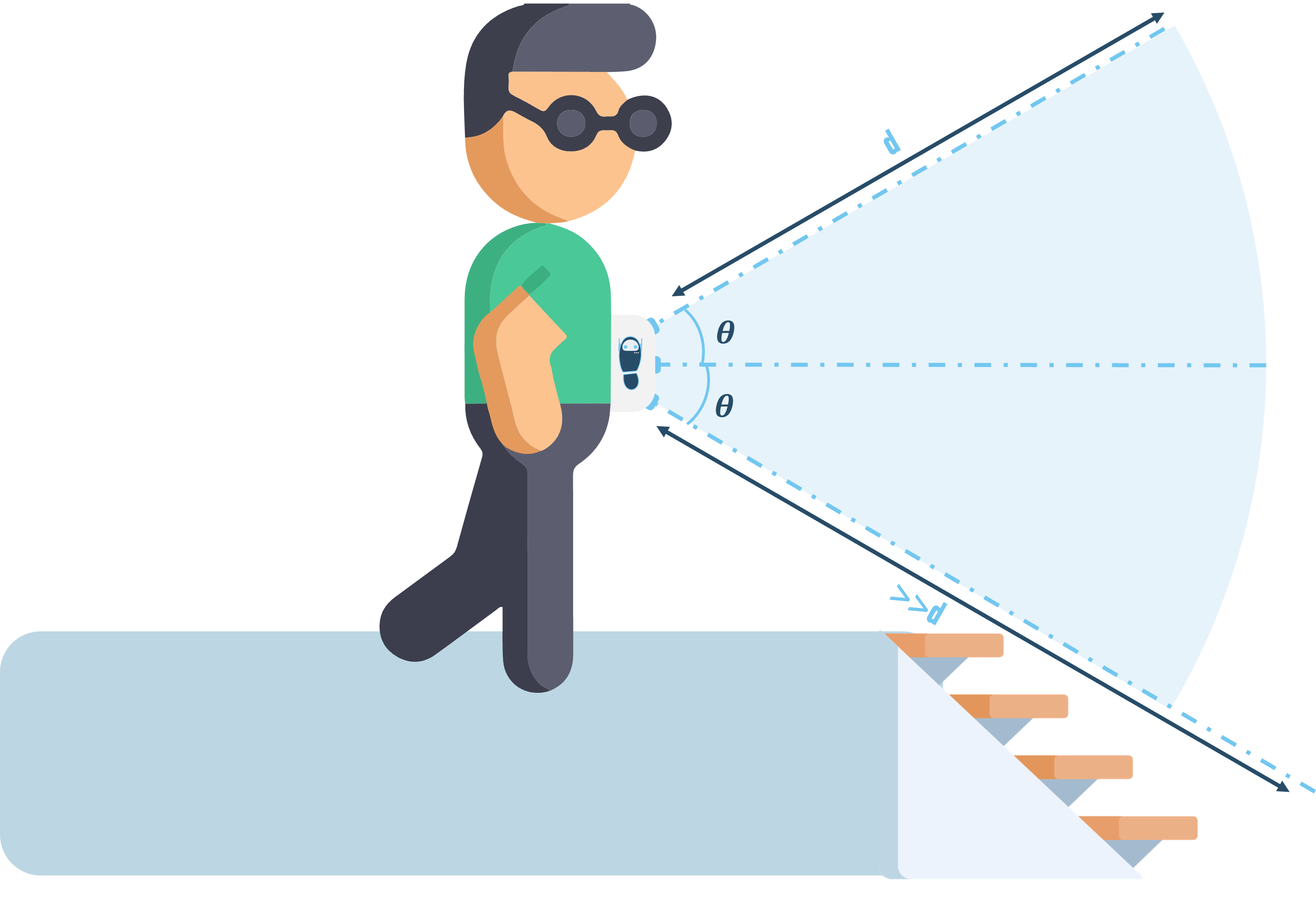
In other words, when the walk-bot comes across an obstacle like a ditch or stairs it observes an increase in the distance compared to the constant distance from the floor and notifies the user accordingly.
CASE-III
An obstacle, like a hanging lamp or signboard, which is above the level of the device can be detected through the sensor inclined at an angle of 45 degree towards the top. The perpendicular distance has been calculated to be :
dcos(45)
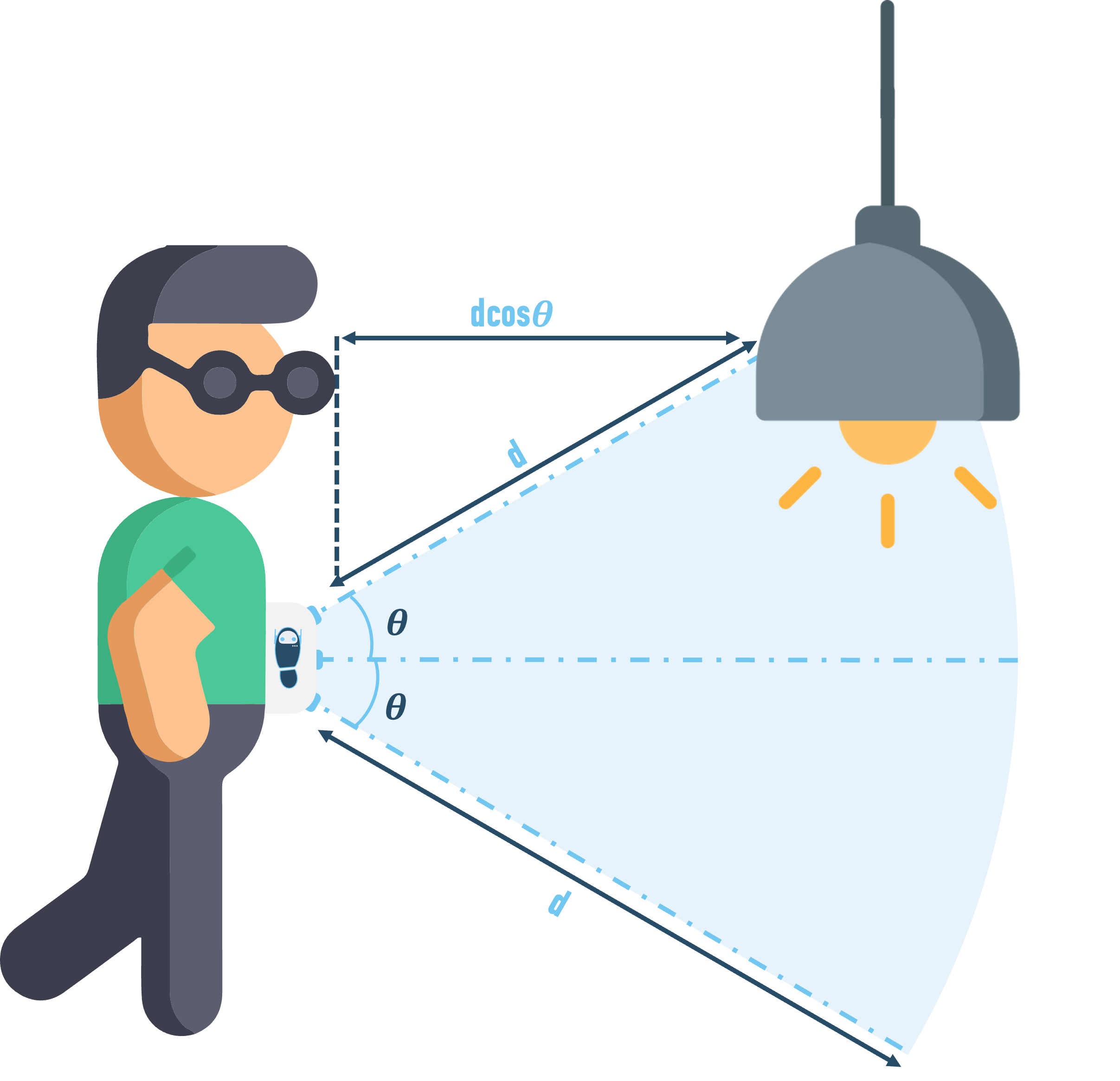
In other words, the actual distance of the person from the obstacle is lower than the distance measured by the sensor. Using trigonometry, the walk bot is able to calculate the accurate distance from the obstacle.
 Nilay Roy Choudhury
Nilay Roy Choudhury
 j
j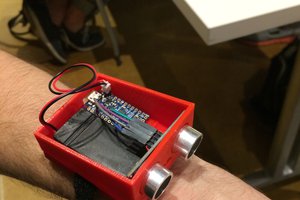
 Bill Brubaker
Bill Brubaker
 Vignesh Ravichandran
Vignesh Ravichandran
 Silas Waxter
Silas Waxter