-
8/31/2017: Design
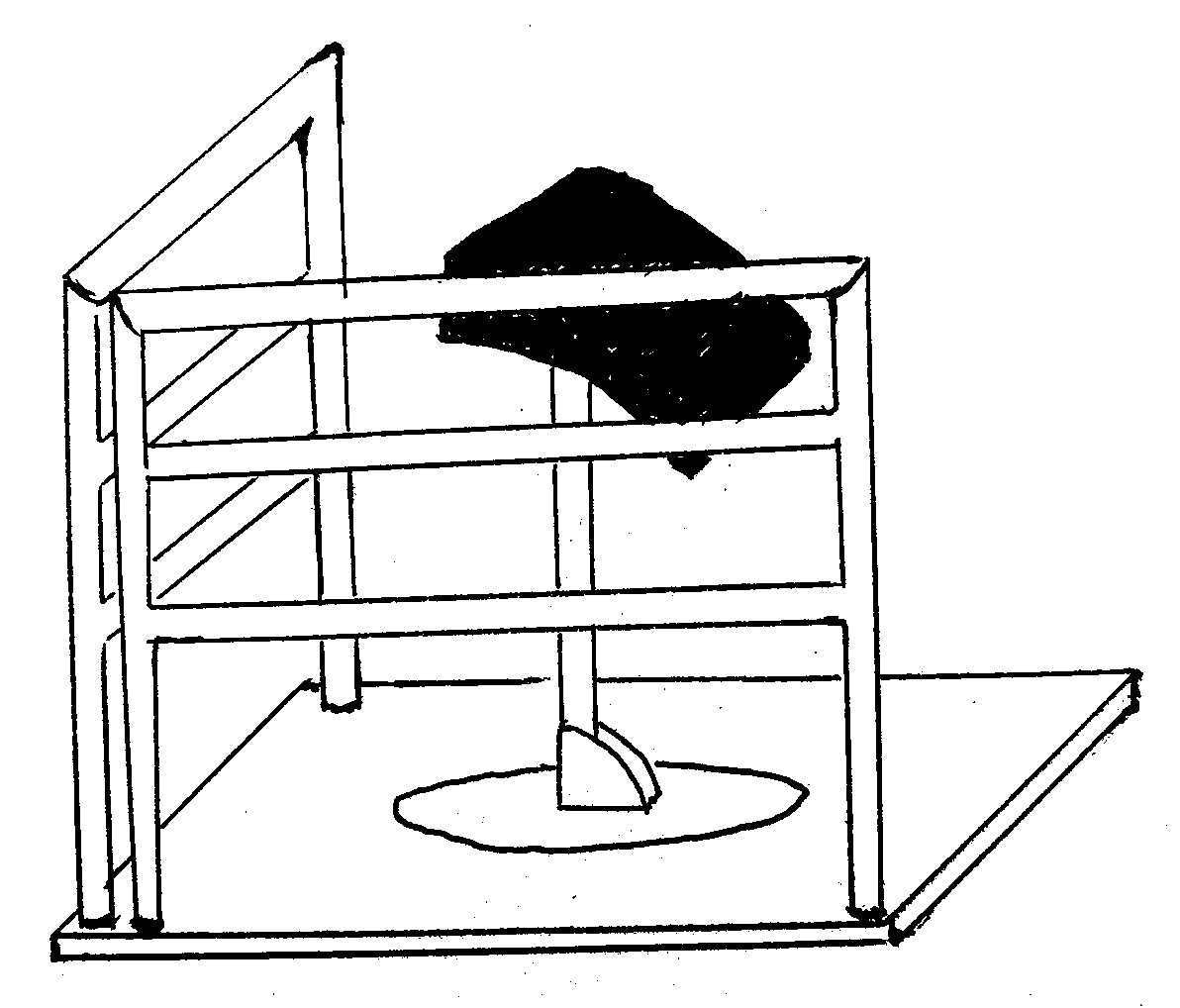
09/01/2017 at 17:45 • 0 commentsToday we met with all the team members and decided on a practical design. Considering:
- Fall risk
- Ease of use
- Simple mechanics
- Cost efficiency
This is our final design:
![]()
-
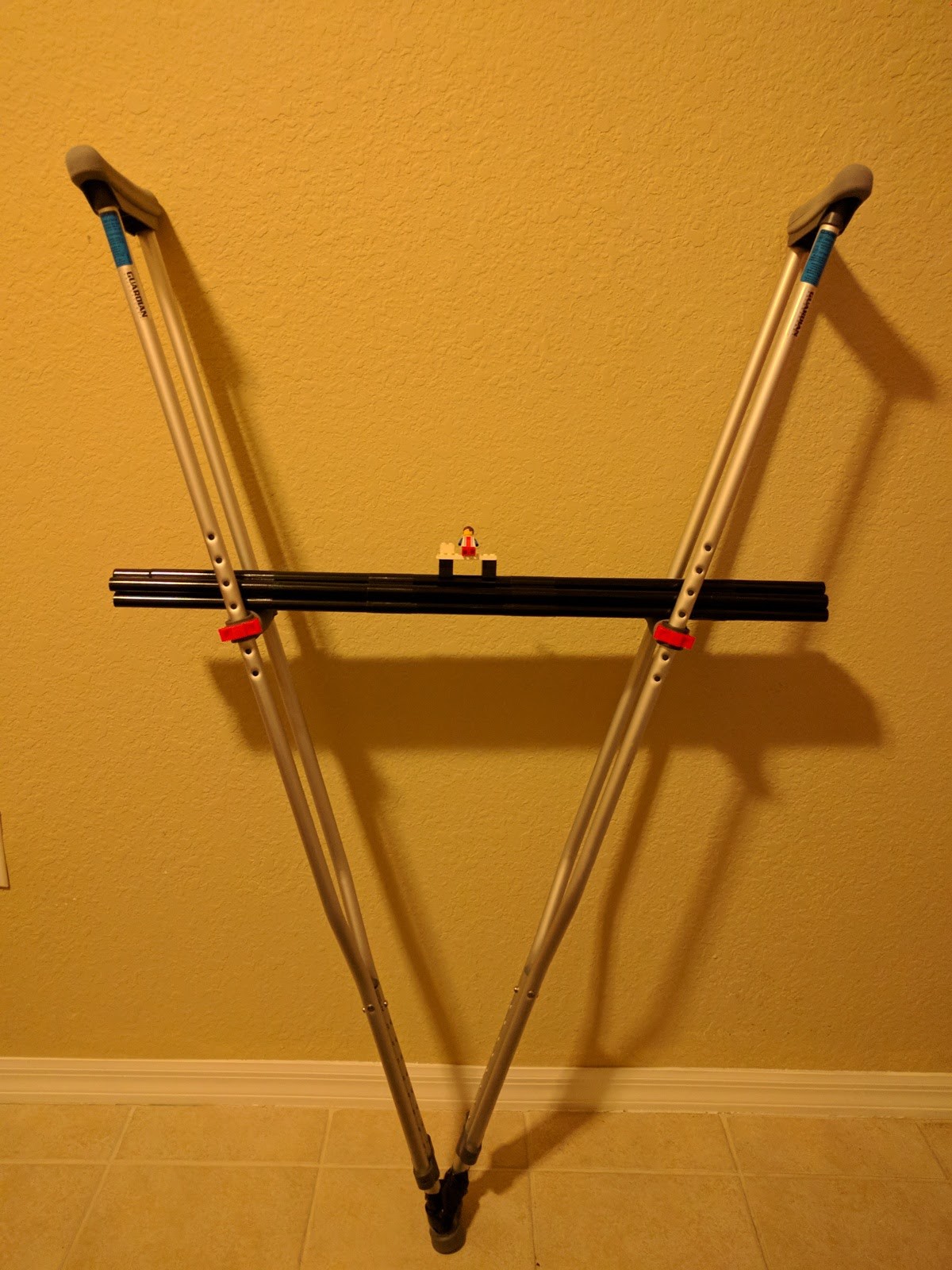
8/26/2017: First Prototype
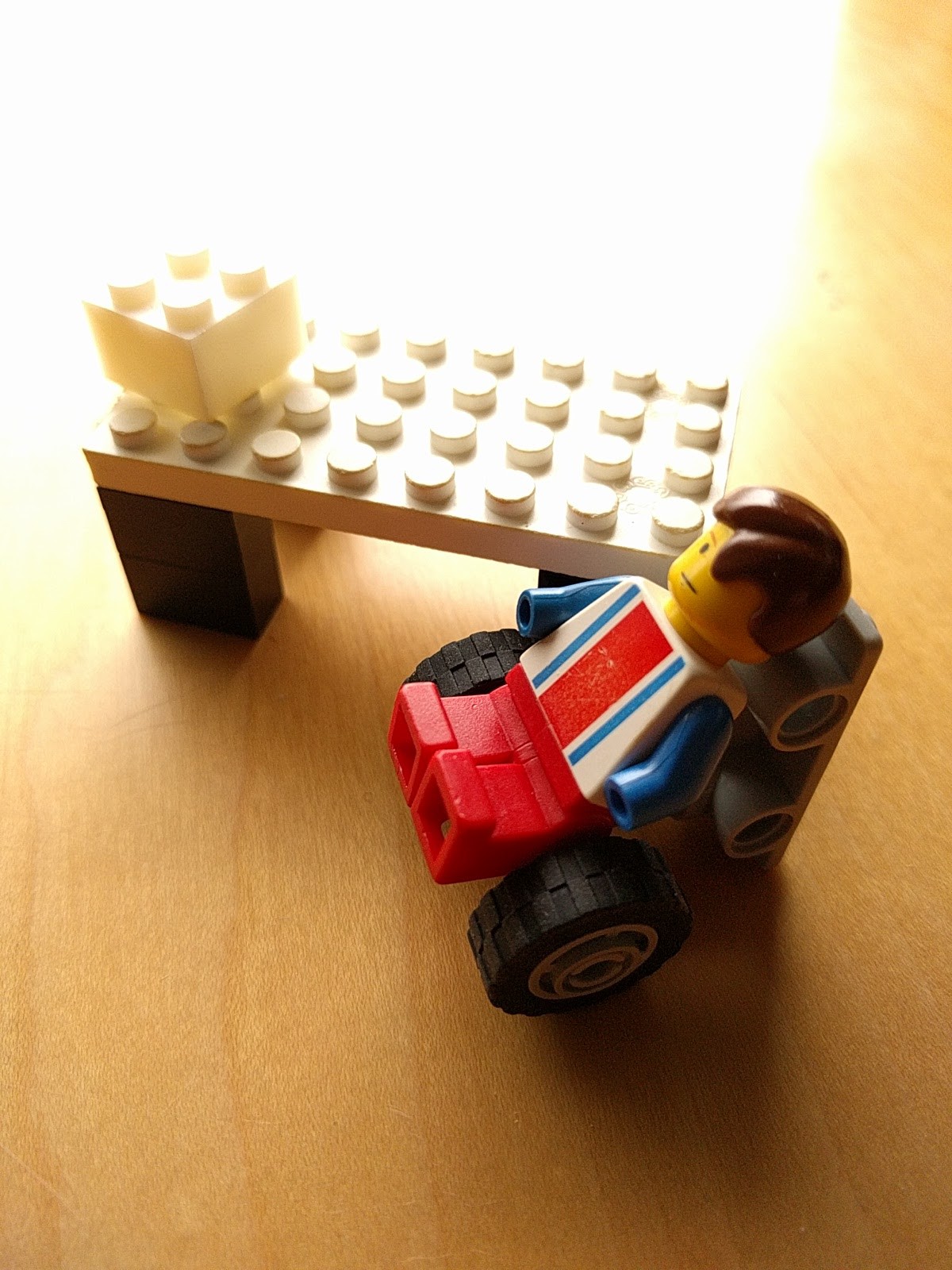
08/31/2017 at 22:40 • 0 commentsThis is our first prototype:
![]()
(You can see our legoman sitting on it!)
This is a leaning pivot system where people can lean in to the device, transfer their weight, pivot, then sit down. Here is a video on how it works:
-
8/22/2017: Design Brainstorming and Concept
08/26/2017 at 18:32 • 0 commentsWinner concept: A transfer board that allows one side to be elevated while the person is seated.
Other ideas:
- Hoyer
- Pump-able
- Automatic
- Pushes a button and automatically transfers
- Board with wheels
- Start sliding once you’re on
- A conveyor belt
- Platform for chair to become higher than the bed
- Something to lower the bed
- Air inflator in seat that deflates on one end so the patient slides
- Like a wedge
- A wheelchair that flattens to the height of bed
- The patient does a roll
- Wheelchair is part of the bed
- Hoyer lift with magnet
- A vest that assists with lifting oneself
- Like the pull up machine with weights
- Using the momentum to fall on top of the bed
- Using mini-steps to go backwards on to the bed
- A wheelchair where you can take off the back so that you can go backwards
- Go backwards
- Escalator to the bed
- A conveyor belt that will let you slide into your chair
- Monkey bar to move yourself into the bed
- Something hanging that they can grab on to
- Maybe there’s a counter weight
- Make the bed into a jungle gym
- Put a little bit of C4 under the butt and poof
- Similar to spring loaded trampolines
- Electromagnet maglev to slide the patient
- Or air pressure
- Use long stick
- The wheelchair seat that attaches to a pole and the seat moves
- Cushion that elevates from the chair
- An arm to turn onto the chair
- Back to the bed and chair pushes up
- Air mattress cushion that will lift them
- A wench that will pulls you up to the bed
- Like a zip line that will lift them up
- A slide in the seat that slides in and out like Chinese table
-
8/19/2017: Need statement
08/26/2017 at 18:24 • 0 commentsNeed statement:
- There is a need for a way to confidently transfer from bed to wheelchair and back without assistance.
Evidence: We met with many patients in a hospital and they all needed assistance in transferring
Wheelchair:
![]()
Bed:
![]()
And back:
![]()
And so on...
-
8/19/2017: Need assessment
08/26/2017 at 18:20 • 0 commentsProblem statements:
-Urinary incontinence
--Elderly patients suffer from urinary incontinence limiting their functional and social independence-Recovering from hip fracture
--One of the leading cause of catastrophic events in elderly
--Point of entry for severe decline-Humidifier for oxygen tank
--Patients with oxygen without humidifier suffer from drying of mucous membranes leading to discomfort-Bed mobility
--Weak truncal strength limits bed mobility which leads to pressure ulcers
--What do bed-bound patients do for bowel and bladder?-Diabetes
--Finger sticks are invasive and uncomfortable
--Difficulty with self-administration of insulin
---Independent insulin management is challenging without proper finger sticks and insulin dose calculation-Hydration status
--Elderly patients are not sensitive to thirst (don't remember to drink), limited access to water, difficulty swallowing-Serious falls in the elderly
-IADLs
--Difficulty with use of smart phones due to impaired speech, dexterity, visual acuity
--Managing finances
--Transportation
--Preparing meals
--How to get elderly set up with different services as there are many out there
--Elderly patients are unable to manage medications and doctor's appointments-Social isolation
--Skype? There are services that connect people who want to learn a language
--Nutritional status. Elderly patients eat less when they are eating alone.-Eye drops
--Elderly patients have decrease manual dexterity leading to difficulties applying eye drops and managing GlaucomaPreliminary finalists:
1. Social Isolation - informal support system to support each other, to get others to remind elderly about meds/eating... etc
Why does the problem occur:
-decreased mobility, functional capacity, inability to drive, fear of fall, incontinence
-institutionalization
-memory problems
Medical implication
-depression, decreased nutrition, cognitive impairment, increased mortality
Women, older age, less education, lower wealth, marital status (single, widowed)
Evidence:
-60% have mobility impairment
-Change or loss in social network, social role, physical or mental health and resources
Effective intervention
Group activities: discussion, self-help, bereavement
Specific population: women, widow, mild cog problems
More than one method
Allows participants some level of control
Process of evaluation throughout the intervention
Aim of intervention
Reducing loneliness and or depression
Increasing the social network size
Improving the quality of supports
Increasing the frequency of social contact
Questions to ask:
-Age, marital status, family members, member of organization in community, previous occupation, level of education, sources of income, spiritual/religious, exercise, nutrition
-Ask about IADLs
-Who in your life do you interact with the most?
-How often do you get to see your family?
-Do you use your telephone to talk to them? Is it video?
-Number of new relationships, in past year?
(When did you start feeling like you losing social interactions?)
Social isolation questionnaire:
First, how often do you feel that you lack companionship: Hardly ever, some of the time, or often? 1 2 3
How often do you feel left out: Hardly ever, some of the time, or often? 1 2 3
How often do you feel isolated from others? (Is it hardly ever, some of the time, or often?) 1 2 3
2. Hydration issue - a concrete problem3. Urinary incontinence - most common problem that can lead to social isolation
-
8/4/2017: Need searching
08/26/2017 at 18:19 • 0 commentsProblem Statement: Because of either physical, cognitive or sensory deficits, elderly individuals require assistance to perform instrumental activities of daily living, which include cleaning, cooking, finances, using a telephone, taking their medications, or traveling, making them less independent.
Plan:
- Make a questionnaire about the use of smart phones and what troubles they have.
- We want to find out the most common IADL that the targeted population is having trouble -> convert to need statement
- Research online what is the most common deficits that occur in the elderly population.
TurningPoint.
An assistive device that can reliably help frail patients transfer from bed to wheelchair and back.
 Louie Cai
Louie Cai