-
Reading from a US-100 Ultrasonic Sensor
11/09/2014 at 19:03 • 0 commentsReading the US-100 ultrasonic distance sensor is easy:
- Make sure the jumper is not in place
- Power from 3.3V or 5V to match your logic levels
- Pull trigger pin high for 10uS then low
- Watch echo pin to go high, measure time before it goes low. This correlates to distance
It would be better to use a hardware timer but this does work. This code example is for the Tiva C Launchpad board./*################################################ # Reading US-100 Ultrasonic Sensor using # the Tiva C Launchpad # # # This example reads from a US-100 ultrasonic sensor # * Jumper should not be in place # * VCC to 3.3V # * GND to GND # * Trigger to PF2 # * Echo to PF4 # # It would be much better to use a hardware time # instead of incrementing "counter" as I've done here # # The blue LED is on the same pin as trigger so it # will flash like crazy # # When working correctly the red LED will light up # when an obstacle is close to the sensor # #################################################*/ #include "driverlib/pin_map.h" #include <stdint.h> #include <stdbool.h> #include "inc/hw_gpio.h" #include "inc/hw_types.h" #include "inc/hw_memmap.h" #include "driverlib/sysctl.h" #include "driverlib/pin_map.h" #include "driverlib/gpio.h" #include "driverlib/rom.h" //Max wait time for reading the sensor: #define MAX_TIME 7500 void delayMS(int ms) { SysCtlDelay( (SysCtlClockGet()/(3*1000))*ms ) ; } uint32_t measureD(void) { //Pull trigger high GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2, GPIO_PIN_2); //wait appropriately SysCtlDelay(SysCtlClockGet()/(3*10)) ; //Delay 10uS //Pull trigger low GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2, 0); //Monitor echo for rising edge while (ROM_GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4) == 0) { } uint32_t counter = 0; //loop counter checking for falling edge; MAX_TIME make sure we don't miss it while ((ROM_GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4) != 0) && (counter < MAX_TIME)) { counter++; } //return value return counter; } int main(void) { //Set the clock SysCtlClockSet(SYSCTL_SYSDIV_1 | SYSCTL_USE_OSC | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_XTAL_16MHZ); //Enable PortF ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOF); //LED Pins as outputs ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1 | GPIO_PIN_2 ); //LED on PF1, Trigger on PF2 (there's also an LED there) GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2, 0); ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4); ROM_GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4, GPIO_STRENGTH_2MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD_WPD); while(1) { if (measureD() < 750) { GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_1); } //LED ON else { GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1, 0); } //LED OFF delayMS(20); } } -
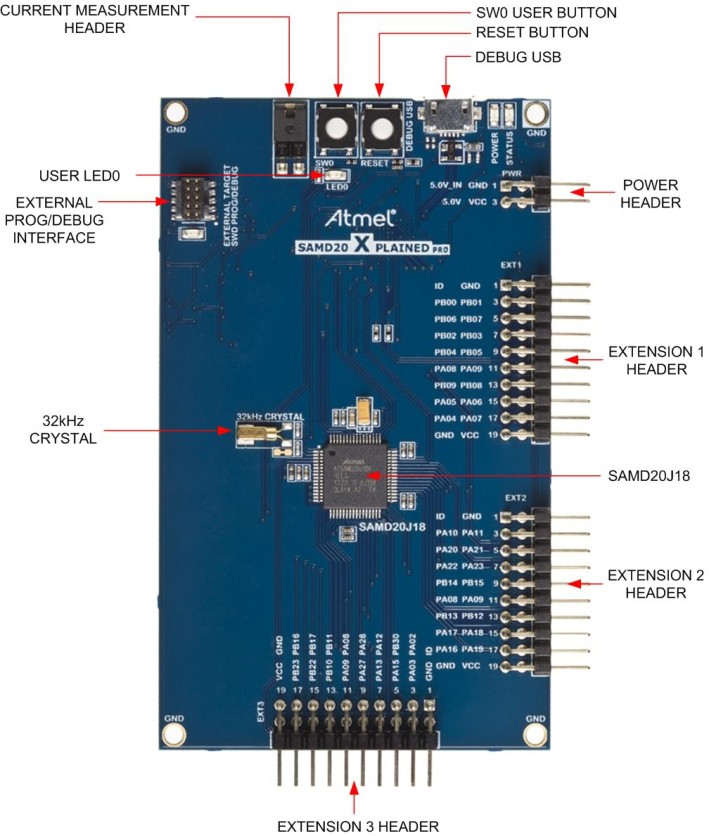
Atmel SAMD20 Xplained Pro
11/08/2014 at 03:53 • 0 comments![]()
This one's a bit of a kludge but it does work. There's a bit of drift (or something) but I didn't have time to scope the output and fix it. Sorry.
This uses the GCC example for "delay" in the Atmel Software Framework:
http://www.atmel.com/tools/avrsoftwareframework.aspx?tab=overview
There are 3 files you need to edit:
common2/services/delay/example/
/** * \file * * \mainpage * * \section title Delay service example * * \section file File(s) * - \ref delay_example.c * * Copyright (c) 2011 - 2014 Atmel Corporation. All rights reserved. * * \asf_license_start * * \page License * * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met: * * 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, * this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. * * 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, * this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation * and/or other materials provided with the distribution. * * 3. The name of Atmel may not be used to endorse or promote products derived * from this software without specific prior written permission. * * 4. This software may only be redistributed and used in connection with an * Atmel microcontroller product. * * THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY ATMEL "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED * WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF * MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NON-INFRINGEMENT ARE * EXPRESSLY AND SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL ATMEL BE LIABLE FOR * ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL * DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS * OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) * HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, * STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN * ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE * POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. * * \asf_license_stop * */ #include <asf.h> #define PWM_MODULE EXT1_PWM_MODULE #define PWM_OUT_PIN EXT1_PWM_0_PIN //PB02 #define PWM_OUT_MUX EXT1_PWM_0_MUX struct tc_module tc_instance; void configure_tc(void) { struct tc_config config_tc; tc_get_config_defaults(&config_tc); config_tc.counter_size = TC_COUNTER_SIZE_16BIT; config_tc.wave_generation = TC_WAVE_GENERATION_NORMAL_PWM; //config_tc.counter_16_bit.compare_capture_channel[0] = (0xFFFF / 2); config_tc.counter_32_bit.compare_capture_channel[0] = (8000); config_tc.pwm_channel[0].enabled = true; config_tc.pwm_channel[0].pin_out = PWM_OUT_PIN; config_tc.pwm_channel[0].pin_mux = PWM_OUT_MUX; tc_init(&tc_instance, PWM_MODULE, &config_tc); tc_set_top_value(&tc_instance,160000); tc_enable(&tc_instance); } void setDuty(uint32_t duty) { tc_set_compare_value(&tc_instance, TC_COMPARE_CAPTURE_CHANNEL_0, duty); //Do we need to reset the counter? What if we already passed top? } int main(void) { system_init(); delay_init(); configure_tc(); struct port_config pin; port_get_config_defaults(&pin); pin.direction = PORT_PIN_DIR_OUTPUT; port_pin_set_config(LED0_PIN, &pin); port_pin_set_output_level(LED0_PIN, LED0_INACTIVE); while (true) { delay_s(2); setDuty(16000); delay_s(2); setDuty(12000); delay_s(2); setDuty(8000); } }common2/services/delay/example/samd20_xplained_pro/gcc/asf.h
Just add this before the last #endif:
#include <tc.h>common2/services/delay/example/samd20_xplained_pro/gcc/config.mk
To this file we're just adding the includes for tc.c and the tc path but I'll paste the entire file:
# # Copyright (c) 2011 Atmel Corporation. All rights reserved. # # \asf_license_start # # \page License # # Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without # modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met: # # 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, # this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. # # 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, # this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation # and/or other materials provided with the distribution. # # 3. The name of Atmel may not be used to endorse or promote products derived # from this software without specific prior written permission. # # 4. This software may only be redistributed and used in connection with an # Atmel microcontroller product. # # THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY ATMEL "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED # WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF # MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NON-INFRINGEMENT ARE # EXPRESSLY AND SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL ATMEL BE LIABLE FOR # ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL # DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS # OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) # HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, # STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN # ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE # POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. # # \asf_license_stop # # Path to top level ASF directory relative to this project directory. PRJ_PATH = ../../../../../.. # Target CPU architecture: cortex-m3, cortex-m4 ARCH = cortex-m0plus # Target part: none, sam3n4 or sam4l4aa PART = samd20j18 # Application target name. Given with suffix .a for library and .elf for a # standalone application. TARGET_FLASH = delay_example_flash.elf TARGET_SRAM = delay_example_sram.elf # List of C source files. CSRCS = \ common/utils/interrupt/interrupt_sam_nvic.c \ common2/services/delay/example/delay_example.c \ common2/services/delay/sam0/systick_counter.c \ sam0/boards/samd20_xplained_pro/board_init.c \ sam0/drivers/port/port.c \ sam0/drivers/system/clock/clock_samd20/clock.c \ sam0/drivers/system/clock/clock_samd20/gclk.c \ sam0/drivers/system/interrupt/system_interrupt.c \ sam0/drivers/system/pinmux/pinmux.c \ sam0/drivers/system/system.c \ sam0/drivers/tc/tc.c \ sam0/utils/cmsis/samd20/source/gcc/startup_samd20.c \ sam0/utils/cmsis/samd20/source/system_samd20.c \ sam0/utils/syscalls/gcc/syscalls.c # List of assembler source files. ASSRCS = # List of include paths. INC_PATH = \ common/boards \ common/utils \ common2/services/delay \ common2/services/delay/example/samd20_xplained_pro \ common2/services/delay/sam0 \ sam0/boards \ sam0/boards/samd20_xplained_pro \ sam0/drivers/port \ sam0/drivers/system \ sam0/drivers/system/clock \ sam0/drivers/system/clock/clock_samd20 \ sam0/drivers/system/interrupt \ sam0/drivers/system/interrupt/system_interrupt_samd20 \ sam0/drivers/system/pinmux \ sam0/drivers/tc \ sam0/utils \ sam0/utils/cmsis/samd20/include \ sam0/utils/cmsis/samd20/source \ sam0/utils/header_files \ sam0/utils/preprocessor \ thirdparty/CMSIS/Include \ thirdparty/CMSIS/Lib/GCC \ common2/services/delay/example/samd20_xplained_pro/gcc # Additional search paths for libraries. LIB_PATH = \ thirdparty/CMSIS/Lib/GCC # List of libraries to use during linking. LIBS = \ arm_cortexM0l_math # Path relative to top level directory pointing to a linker script. LINKER_SCRIPT_FLASH = sam0/utils/linker_scripts/samd20/gcc/samd20j18_flash.ld LINKER_SCRIPT_SRAM = sam0/utils/linker_scripts/samd20/gcc/samd20j18_sram.ld # Path relative to top level directory pointing to a linker script. DEBUG_SCRIPT_FLASH = sam0/boards/samd20_xplained_pro/debug_scripts/gcc/samd20_xplained_pro_flash.gdb DEBUG_SCRIPT_SRAM = sam0/boards/samd20_xplained_pro/debug_scripts/gcc/samd20_xplained_pro_sram.gdb # Project type parameter: all, sram or flash PROJECT_TYPE = flash # Additional options for debugging. By default the common Makefile.in will # add -g3. DBGFLAGS = # Application optimization used during compilation and linking: # -O0, -O1, -O2, -O3 or -Os OPTIMIZATION = -O1 # Extra flags to use when archiving. ARFLAGS = # Extra flags to use when assembling. ASFLAGS = # Extra flags to use when compiling. CFLAGS = # Extra flags to use when preprocessing. # # Preprocessor symbol definitions # To add a definition use the format "-D name[=definition]". # To cancel a definition use the format "-U name". # # The most relevant symbols to define for the preprocessor are: # BOARD Target board in use, see boards/board.h for a list. # EXT_BOARD Optional extension board in use, see boards/board.h for a list. CPPFLAGS = \ -D ARM_MATH_CM0=true \ -D BOARD=SAMD20_XPLAINED_PRO \ -D SYSTICK_MODE \ -D __SAMD20J18__ # Extra flags to use when linking LDFLAGS = \ # Pre- and post-build commands PREBUILD_CMD = POSTBUILD_CMD =type "make" in the GCC directory to build the .elf file. Flash it to the hardware using OpenOCD and arm-none-eabi-gdb as explained here.
Resources:
-
Fubarino SD
11/05/2014 at 22:46 • 0 comments![]()
I couldn't find a nice pinout image for the Fubarino SD like I did for the previous 2 boards. If you know of one please leave a comment below.
This board has a silk-screen with the tilde symbol (~) next to some of the pins. I believe these are your options if you are using the Servo library.
The board is programmed using the MPIDE. It's a fork of the Arduino IDE meaning that you can use the Arduino libraries (and code) for this. That makes PWM extremely simple. Here's a servo example:
#include <Servo.h> //Variable for a Servo object Servo hobby_servo; // variable to store the servo position int pos = 0; void setup() { // attaches the servo on pin 7 to the servo object hobby_servo.attach(7); // tell servo to go to center position hobby_servo.write(90); delay(15); } void loop() { // tell servo to go to 135 degrees hobby_servo.write(135); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position delay(15); //Do nothing for 2 seconds delay(2000); // tell servo to go to 90 degrees hobby_servo.write(90); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position delay(15); //Do nothing for 2 seconds delay(2000); } -
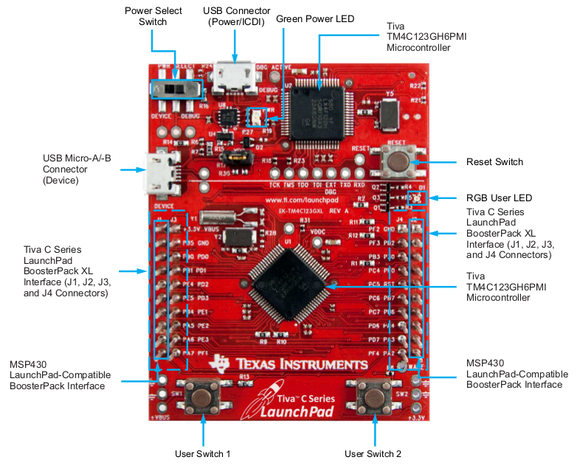
Texas Instruments Tiva C Launchpad
11/05/2014 at 16:53 • 1 comment![]()
Use the TivaWare peripheral library to get PWM working on the Tiva C launchpad: http://www.ti.com/tool/sw-tm4c
I made an example of dimming LEDs that can be complied with GCC: https://github.com/szczys/tiva-c-launchpad-hardware-pwm/blob/master/main.c
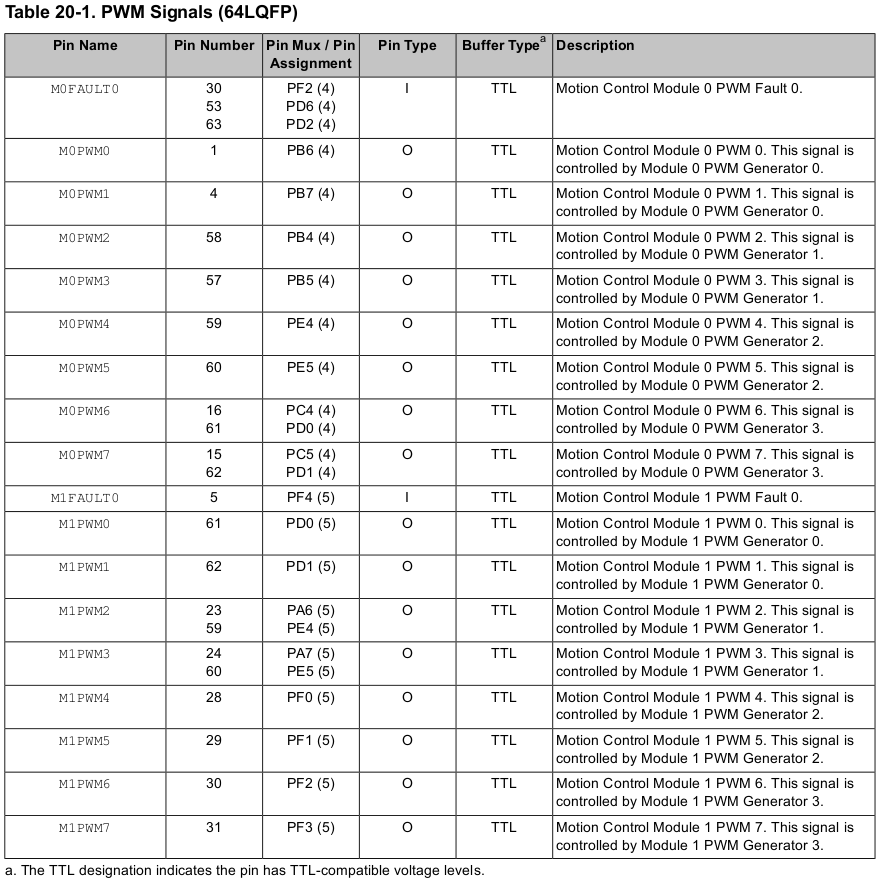
Specific code for servo timing is found below. The datasheet for the TM4C123GH6PM includes this table which can be used to find out the PWM module, generator, pin, and other values:
![]()
/*################################################ # Hardware PWM proof of concept using # the Tiva C Launchpad # # Started with example code by # lawrence_jeff found here: # http://forum.stellarisiti.com/topic/707-using-hardware-pwm-on-tiva-launchpad/ # # Altered to use code found on section # 22.3 of the TivaWare Peripheral Driver # Library User's Guide found here: # http://www.ti.com/lit/ug/spmu298a/spmu298a.pdf # # # This example drives servo motors on PF1, PF2, and PF3 # #################################################*/ #include "driverlib/pin_map.h" #include <stdint.h> #include <stdbool.h> #include "inc/hw_gpio.h" #include "inc/hw_types.h" #include "inc/hw_memmap.h" #include "driverlib/sysctl.h" #include "driverlib/pin_map.h" #include "driverlib/gpio.h" #include "driverlib/pwm.h" void delayMS(int ms) { SysCtlDelay( (SysCtlClockGet()/(3*1000))*ms ) ; } int main(void) { uint32_t period = 5000; //20ms (16Mhz / 64pwm_divider / 50) uint32_t duty = 250; //1.5ms pulse width //Set the clock SysCtlClockSet(SYSCTL_SYSDIV_1 | SYSCTL_USE_OSC | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_XTAL_16MHZ); //Configure PWM Clock divide system clock by 64 SysCtlPWMClockSet(SYSCTL_PWMDIV_64); // Enable the peripherals used by this program. SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOF); SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_PWM1); //The Tiva Launchpad has two modules (0 and 1). Module 1 covers the LED pins //Configure PF1,PF2,PF3 Pins as PWM GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF1_M1PWM5); GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF2_M1PWM6); GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF3_M1PWM7); GPIOPinTypePWM(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1 | GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3); //Configure PWM Options //PWM_GEN_2 Covers M1PWM4 and M1PWM5 //PWM_GEN_3 Covers M1PWM6 and M1PWM7 PWMGenConfigure(PWM1_BASE, PWM_GEN_2, PWM_GEN_MODE_DOWN | PWM_GEN_MODE_NO_SYNC); PWMGenConfigure(PWM1_BASE, PWM_GEN_3, PWM_GEN_MODE_DOWN | PWM_GEN_MODE_NO_SYNC); //Set the Period (expressed in clock ticks) PWMGenPeriodSet(PWM1_BASE, PWM_GEN_2, period); PWMGenPeriodSet(PWM1_BASE, PWM_GEN_3, period); //Set PWM duty PWMPulseWidthSet(PWM1_BASE, PWM_OUT_5,duty); PWMPulseWidthSet(PWM1_BASE, PWM_OUT_6,duty); PWMPulseWidthSet(PWM1_BASE, PWM_OUT_7,duty); // Enable the PWM generator PWMGenEnable(PWM1_BASE, PWM_GEN_2); PWMGenEnable(PWM1_BASE, PWM_GEN_3); // Turn on the Output pins PWMOutputState(PWM1_BASE, PWM_OUT_5_BIT | PWM_OUT_6_BIT | PWM_OUT_7_BIT, true); while(1) { delayMS(2000); //Drive servo to 135 degrees PWMPulseWidthSet(PWM1_BASE, PWM_OUT_5,duty+(duty/2)); PWMPulseWidthSet(PWM1_BASE, PWM_OUT_6,duty+(duty/2)); PWMPulseWidthSet(PWM1_BASE, PWM_OUT_7,duty+(duty/2)); delayMS(2000); //Drive servo to 90 degrees PWMPulseWidthSet(PWM1_BASE, PWM_OUT_5,duty); PWMPulseWidthSet(PWM1_BASE, PWM_OUT_6,duty); PWMPulseWidthSet(PWM1_BASE, PWM_OUT_7,duty); } } -
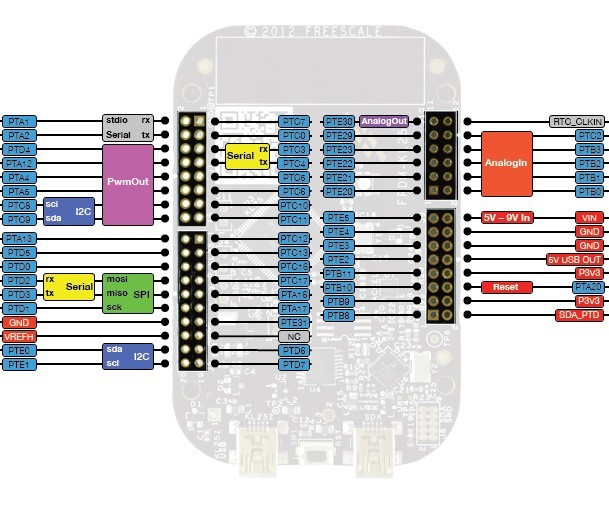
Freescale KL25z Freedom Board
11/04/2014 at 22:10 • 0 commentsI used the mbed platform to program PWM on this chip. Links to setup your board for mbed and the mbed pwm api are located here: http://hackaday.io/event/3178/log/10740
You need to use the pins that have PwmOut capability shown in this image:
![]()
#include "mbed.h" PwmOut servo(PTD4); int main() { servo.period_ms(20); servo.pulsewidth_ms(2); while(1) { wait(2); servo.pulsewidth_ms(1); wait(2); servo.pulsewidth_ms(2); } }
PWM examples with multiple architectures
This is the cheat sheet for the Embedded Hardware Workshop
 Mike Szczys
Mike Szczys