-
Structural Health Monitoring of Civil Infrastructures
03/06/2019 at 13:00 • 0 comments
The deterioration of the old building and civil Infrastructure can lead to fatal and Hazardous situation. The constant monitoring of these structures is mandatory. Structural health monitoring is an extremely important methodology in evaluating the ‘health’ of a structure by assessing the level of deterioration and the remaining service life of civil infrastructure systems.
Wireless Sensor Networks has been installed in many industrial applications like vibration analysis of wind turbines, vibration analysis of hydro turbines etc. and has done remarkably well in eradicating many of the industrial complications. Measuring the number of vibrations, temperature and other aspects can help us to prevent the damage and deterioration of the infrastructure.
In this blog we will be going through Wireless Vibration and Temperature Sensors and it's advantages in monitoring structural Health. So here we will be demonstrating the following-
- Wireless Vibration and Temperature Sensors.
- Structural monitoring using these Sensors.
- Gathering and analyzing the data using Wireless gateway device
- Publishing and Subscribing to Sensor data using Ubidots.
Hardware and Software Specifications
Software Specification
- An UbiDots account
- Arduino IDE
Hardware Specification
- ESP32
- Wireless Temperature and Vibration Sensor
- Zigmo Gateway receiver
Wireless Vibration and Temperature Sensors

This is a Long Range Industrial IoT wireless vibration and temperature sensor, boasting up to a 2 Mile range using a wireless mesh networking architecture. Incorporating a 16-bit Vibration and Temperature sensor, this sensor transmits highly accurate vibration data at user-defined intervals. It has the following features :
- Industrial Grade 3-axis Vibration Sensor with ±32g Range
- Calculates RMS, MAX, and MIN g Vibration
- Noise Removal using Low-pass Filter
- Frequency Range (Bandwidth) up to 12, 800 Hz
- Sample Rate up to 25, 600Hz
- Encrypted Communication with 2 Mile Wireless Range
- Operating Temperature Range -40 to +85 °C
- Wall-Mounted or Magnet Mounted IP65 Rated EnclosureExample Software for Visual Studio and LabVIEW
- Vibration Sensor with External Probe Option
- Up to 500, 000 Transmissions from 4 AA BatteriesMany Gateway and Modem Options Available
Guidelines to Check Vibrations
The Vibrations in motors, turbines, civil infrastructures etc. can lead to fatal error and there should be a way to analyse the vibrations before any fatal occurs. A vibrating object experiences varying velocity and varying acceleration. The vibration is expressed as the units of gravitational constant i.e. g = 9.81 m/s2. The vibration in an object depends on many factors like:
- Vibration amplitude
- Sensitivity
To measure the Vibrations accurately, we need to follow these recommended Vibration standards. Using these standards you can predict whether your device is working properly or not:
- 0.01g or Less — Excellent condition, No action required. The device is working properly
- 0.35g or less — Good Condition, No action required unless the machine is noisy or running at an abnormal temperature
- 0.5g or less — Fair Condition, No action required unless the machine is noisy or running at an abnormal temperature
- 0.75g or More— Rough Condition, possible action required if the machine is noisy and also check the bearing temperature
- 1g or More — Very Rough Conditions, further analysis and see if it's doing this continuously. Also, check for noise and temperature
- 1.5g or More — Danger Level, there is definitely a problem in the machine or installation. Also, check the temperature Log
- 2.5g or More — Shut-down the Machine immediately and look for possible causes. Call a technician for immediate repair For Heavy Machinery these readings could be 1.5 times to 2 times more than listed above.
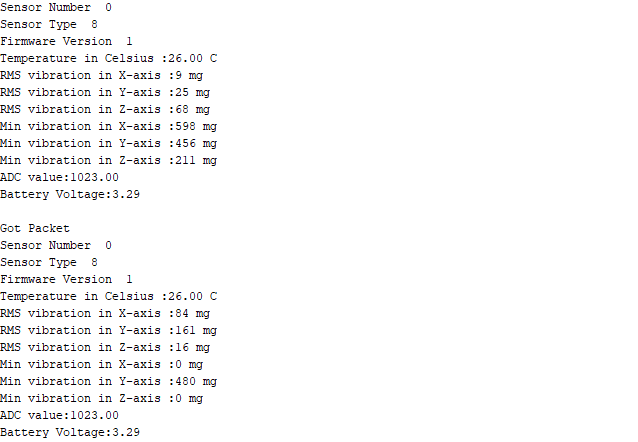
Getting the Vibration Sensor Values


The vibration values, that we are getting from the sensors are in milis. These consists of the following values
RMS vibration gives the value of Root Mean Square value along different axes...
Read more »
My Pages
Projects I Like & Follow
Share this profile
ShareBits
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.
 vaibhav sharma
vaibhav sharma


 Oskar Weigl
Oskar Weigl Tim Wilkinson
Tim Wilkinson lion mclionhead
lion mclionhead John Oliva
John Oliva Wassim
Wassim rawe
rawe Reginald Sourn
Reginald Sourn abetusk
abetusk bobricius
bobricius Szaja
Szaja Anthony Ngu
Anthony Ngu Dave
Dave Sabas
Sabas Dmitry
Dmitry CFA
CFA BB
BB